Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Questions - Homework - 10th - Science - 2021-11-24T05 - 39
Questions - Homework - 10th - Science - 2021-11-24T05 - 39
Uploaded by
Saurabh BhattacharyaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Questions - Homework - 10th - Science - 2021-11-24T05 - 39
Questions - Homework - 10th - Science - 2021-11-24T05 - 39
Uploaded by
Saurabh BhattacharyaCopyright:
Available Formats
Homework
Science - 10th
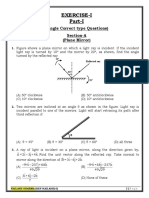
Q (1): A spherical mirror, whose reflecting surface is curved inwards, that is, faces
towards the centre of the sphere, is called a___.
(a) Concave mirror
(b) Convex mirror
(c) Plane mirror
(d) None of the above
Q (2): Assertion: The centre of curvature is not a part of the mirror. It lies outside its
reflecting surface.
Reason: The reflecting surface of a spherical mirror forms a part of a sphere. This sphere
has a centre.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Q (3): A spherical mirror whose reflecting surface is curved outwards, is called a___.
(a) Convex mirror
(b) Plane mirror
(c) Concave mirror
(d) None of the above
Q (4): A ray of light which is incident normally on a mirror is reflected back __________.
(a) in different path
(b) along its own path
(c) In a zigzag manner
(d) Can't determine
Q (5): A beam of light generally _________ after reflection from concave surfaces.
(a) Diverges (b) Converges
(c) Both of these (d) None of these
Q (6): Explain why, though both a plane mirror and a sheet of paper reflect light but we
can see the image of our face in a plane mirror but not in a sheet of paper.
(a) Because images are formed by regular reflection of light and in case of a plane mirror,
regular reflection does not takes place; while in case of a sheet of paper, diffuse
reflection takes place.
(b) Because images are formed by regular reflection of light and in case of a plane mirror,
regular reflection takes place; while in case of a sheet of paper, diffuse reflection
takes place.
(c) All of the avbove
(d) None of the above
Q (7): What are the laws of reflection of light ?
(a) The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
(b) The incident ray, the normal to the mirror at the point of incidence and the reflected ray,
all lie in the same plane.
(c) All the options
(d) None of the above
Q (8): The process of bouncing back of the light rays which fall on the surface of an
object is called as ____.
Want to access 7 lac+ questions?
powered by Get MCQs based on latest CBSE pattern & auto-check the
homework
the homework app
Homework
(a) Reflection of light
(b) Refraction of light
(c) Dispersion of light
(d) None of the above
Q (9): The laws of reflection of light applies to:
(a) Only Plane Mirror
(b) Only Spherical Mirror
(c) Both Plane and Spherical Mirror
(d) None of the above
Q (10): When a spherical mirror is held towards the sun and its sharp image is formed on
a piece of carbon paper for some time, a hole is burnt in the carbon paper. What is the
nature of spherical mirror ?
(a) Convex
(b) Concave
(c) Plane
(d) All of the above
Q (11): The nature of image formed by a plane mirror is:
(a) Real
(b) Virtual
(c) Erect
(d) Both virtual and erect
Q (12): What would be the position of image formed by concave mirror when the object is
placed at the centre of curvature?
(a) At centre of curvature C
(b) Behind the mirror
(c) Beyond centre of curvature C
(d) At the focus F
Q (13): What would be the nature of image formed by concave mirror when the object is
placed at focus?
(a) Real and inverted
(b) Virtual and erect
(c) Real and erect
(d) Virtual and inverted
Q (14): What would be the size of image formed by concave mirror when the object is
placed between principal axis and focus?
(a) Enlarged
(b) Same size
(c) Diminished
(d) Highly diminished (point-sized)
Q (15): In real image, light rays _____ after reflection.
(a) meet (b) do not meet
(c) Both of these (d) None of these
Q (16): Which of the following forms real image?
(a) Concave mirror (b) Convex mirror
(c) Plane mirror (d) None of these
Want to access 7 lac+ questions?
powered by Get MCQs based on latest CBSE pattern & auto-check the
homework
the homework app
Homework
Q (17): Assertion: Concave mirrors are used as make-up mirrors.
Reason: When the face is held within the focus of a concave mirror, then a diminished
image of the face is seen in the concave mirror.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Q (18): What would be the position of image formed by convex mirror when the object is
placed at infinity?
(a) At infinity
(b) At focus, behind the mirror
(c) At centre of curvature
(d) Between principal axis and focus, behind the mirror
Q (19): What would be the position of image formed by convex mirror when the object is
placed between infinity and the pole of the mirror?
(a) At focus, behind the mirror
(b) At infinity
(c) Between principal axis and focus, behind the mirror
(d) At centre of curvature
Q (20): What would be the size of image formed by convex mirror when the object is
placed at infinity?
(a) Highly diminished (point-sized)
(b) Enlarged
(c) Diminished
(d) Highly enlarged
Q (21): What would be the nature of image formed by convex mirror when the object is
placed between infinity and the pole of the mirror?
(a) Real and inverted
(b) Virtual and erect
(c) All the options
(d) None of the above
Q (22): The distance between the pole and the principal focus of a spherical mirror is
called the___.
(a) Focal length
(b) Principal distance
(c) Radius of curvature
(d) None of the above
Q (23): In case of concave mirror, the centre of curvature lies ________ it.
(a) in
front
(b) behind
(c) Inside
(d) None of the above
Q (24): For a convex mirror, the focus is ______ the mirror.
(a) in front of
(b) behind
(c) Inside
Want to access 7 lac+ questions?
powered by Get MCQs based on latest CBSE pattern & auto-check the
homework
the homework app
Homework
(d) None of the above
Q (25): The central point of the reflecting spherical surface of a spherical mirror is called:
(a) Pole (b) Aperture
(c) Focus (d) None of these
Q (26): In New Cartesian Sign Convention, all distances parallel to the principal axis are
measured from the ___.
(a) Pole of the mirror
(b) Centre of curvature
(c) Focus
(d) Aperture
Q (27): Assertion : Concave mirror has a real focus.
Reason : Concave mirror always forms real image.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Q (28): Name the spherical mirror which has virtual principal focus.
(a) Concave Mirror
(b) Convex Mirror
(c) Plane Mirror
(d) None of the above
Q (29): Find the focal length of a concave mirror whose radius of curvature is 32 cm.
(a) 64 cm (b) 16 cm
(c) 32 cm (d) 4 cm
Q (30): Fill in the following blanks with suitable words : Parallel rays of light are reflected
by a concave mirror to a point called the _____.
(a) Principal Focus
(b) Pole
(c) Centre Of Curvature
(d) None of the above
Q (31): Fill in the following blanks with suitable words : For a convex mirror, parallel rays
of light appear to diverge from a point called the_____.
(a) Principal Focus
(b) Pole
(c) Centre Of Curvature
(d) None of the above
Q (32): What is the relationship between distance of object (u), distance of image (v) and
focal length (f) for spherical mirror?
(a) (b)
(c) (d)
Q (33): A convex mirror used for rear-view on an automobile has a radius of curvature of
3.00 m. If a bus is located at 5.00 m from this mirror, find the position of image.
(a) 0.23 m in front of mirror
(b) 1.15 m behind the mirror
Want to access 7 lac+ questions?
powered by Get MCQs based on latest CBSE pattern & auto-check the
homework
the homework app
Homework
(c) 3.21 m behind the mirror
(d) 2.5 m in front of mirror
Q (34): An object, 4.0 cm in size, is placed at 25.0 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal
length 15.0 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed in
order to obtain a sharp image?
(a) 32.1 m behind the mirror
(b) 2.5 m in front of mirror
(c) 37.5 cm in front of the mirror
(d) 1.5 m behind the mirror
Q (35): Assertion: Mirror formula can be applied to a plane mirror.
Reason: A plane mirror is a spherical mirror of infinite focal length.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Q (36): A concave mirror produces three times magnified (enlarged) real image of an
object placed at 10 cm in front of it. Where is the image located?
(a) 20 cm behind the mirror
(b) 30 cm in front of mirror
(c) 45 cm in front of mirror
(d) 25.5 cm behind the mirror
Q (37): A 10 mm long alpin is placed vertically in front of a concave mirror. A 5 mm long
image of the alpin is formed at 30 cm in front of the mirror. The focal length of this
mirror is
(a) -30 cm (b) -20cm
(c) -40 cm (d) -60 cm
Q (38): A boy with a mouth 5 cm wide stands 2 m away from a plane mirror. How wide is
the image of his mouth ?
(a) 15 cm (b) 10 cm
(c) 5 cm (d) 20 cm
Q (39): A boy walks towards the plane mirror at a speed of 1 meter per second. At what
speed does his image approach him ?
(a) 1 meter per second
(b) 2 meter per second
(c) 0.5 meter per second
(d) 4 meter per second
Q (40): If the angle of reflection is
, what will be the angle of incidence ?
(a) (b)
(c) (d)
Q (41): When a plane mirror is placed horizontally on a levelled ground at a distance of
40 m from the foot of a tower, the top of the tower and its image in the mirror subtend
Want to access 7 lac+ questions?
powered by Get MCQs based on latest CBSE pattern & auto-check the
homework
the homework app
Homework
an angle of 90 degrees at the eye. What is the height of the tower?
(a) 40 m (b) 20 m
(c) 35 m (d) 30 m
Q (42): Magnification of plane mirror is always
(a) (b) 0
(c) -1 (d) None
Q (43): Find the power of a concave lens of focal length 2 m.
(a) (b)
(c) (d)
Q (44): Magnification produced by a rear view mirror fitted in vehicles
(a) is more than one
(b) is equal to one
(c) is less than one
(d) can be more than or less than one depending upon the position of the object in front
of it
Q (45): Magnification is expressed _______________.
(a) As the ratio of the height of the image to the height of the object
(b) Spherical mirror
(c) Plain mirror
(d) None of the above
Q (46): Magnification produced by a _________ gives the relative extent to which the
image of an object is magnified with respect to the object size.
(a) Spherical mirror
(b) Plain mirror
(c) All of these
(d) None of the above
Q (47): Two lenses of power -2.5D and +1.5D are placed in contact. Find the total power
of the combination of the lens.
(a) 1D (b) -1D
(c) 2D (d) -2D
Q (48): An object, 4.0 cm in size, is placed at 25.0 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal
length 15.0 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed in
order to obtain a sharp image? Find the nature and the size of the image.
(a) The image is small and enlarged
(b) Plain mirror
(c) The image is inverted and enlarged
(d) None of the above
Q (49): Assersation: The magnification m is also related to the object distance (u) and
image distance (v).
Reason: You may note that the height of the object is taken to be positive as the object is
usually placed above the principal axis.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Want to access 7 lac+ questions?
powered by Get MCQs based on latest CBSE pattern & auto-check the
homework
the homework app
Homework
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Q (50): A thin converging lens forms a real magnified image of an object in front of it in
front of it. Write the position of object.
(a) Between F and 2F
(b) Between optical centre and F
(c) At F
(d) None of the above
Q (51): Find the power of convex lens which forms a real and inverted image of
magnification -1 of an object placed at a distance of 20cm from its optical
centre.
(a) 10D (b) 9D
(c) 11D (d) 12D
Q (52): The ray of light which bends when passed through second medium is known as
___.
(a) Normal ray
(b) Incident ray
(c) Refracted ray
(d) None of the above
Q (53): The ray of light which falls on the surface is called ___.
(a) Normal ray
(b) Incident ray
(c) Refracted ray
(d) None of the above
Q (54): Which of the following is not a law of refraction of light?
(a)
(b)
(c) The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal at the point of incidence lie on the
same plane.
(d) None of these
Q (55): A group of light rays originating from a source and travelling in a definite direction
is known as _______.
(a) Beam of rays
(b) beam of light
(c) beam of message
(d) None
Q (56): Assertion: A ray of light travelling from a rarer medium to a denser medium slows
down and bends away from the normal. When it travels fromma denser medium to
a rarer medium, it speeds up and bends towards the normal.
Reason: The speed of light is higher in a rarer medium than a denser medium.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Q (57): State true or false: The incident ray, the reflected ray, the normal, all lie in the
Want to access 7 lac+ questions?
powered by Get MCQs based on latest CBSE pattern & auto-check the
homework
the homework app
Homework
same plane at the point of incidence.
(a) TRUE (b) FALSE
Q (58): Refraction of light takes place when it travels from one medium to another
because the ____ is different in the two media.
(a) speed of medium
(b) speed of air
(c) speed of light
(d) none
Q (59): Name the phenomena on which the working of a lens is based.
(a) Refraction of air
(b) Reflection of air
(c) Reflection of light
(d) Refraction of light
Q (60): What are examples of phenomenon of refraction of light in everyday life
situations?
(a) A stick partly immersed in water appears to be bent at the water surface.
(b) A pool of water appears less deep than it actually is.
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Q (61): When a ray of light falls normally on the surface of a medium, then no bending of
light ray occurs. It means the light ray goes straight from one medium to another.
True or False.
(a) TRUE
(b) FALSE
(c) Maybe true maybe false
(d) None of these
Q (62): State True/False: Refractive index
can also be written as a ratio of speeds of light in the two media.
(a) TRUE (b) FALSE
Q (63): Refractive index of medium 2 with respect to medium 1 is equal to the ratio of
______
(a) Speed of light in medium 2 to the speed of light in medium 1.
(b) Speed of light in medium 1 to the speed of light in medium 2.
(c) All of the above
(d) None of the above
Q (64):
means:
(a) Refractive index of medium 1 with respect to medium 2.
(b) Refractive index of medium 2 with respect to medium 1
(c) All of the above
(d) None of the above
Q (65): When light is going from one medium (other than vacuum or air) to another
medium, then the value of refractive index is called ________________?
Want to access 7 lac+ questions?
powered by Get MCQs based on latest CBSE pattern & auto-check the
homework
the homework app
Homework
(a) Refractive index of medium 1 with respect to medium 2.
(b) Absolute refractive index
(c) Relative refractive index
(d) All of the above
Q (66): When light is going from vacuum to another medium, then the value of refractive
index is called ___________ ?
(a) Refractive index of medium 1 with respect to medium 2.
(b) Absolute refractive index
(c) Relative refractive index
(d) All of the above
Q (67): Assertion: Refractive index has no units.
Reason: The refractive index is a ratio of two similar quantities.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Q (68): Which of the following has highest optical density?
(a) Refractive index of diamond is 2.42
(b) Refractive index of kerosene is 1.44
(c) Refractive index of turpetine is 1.47
(d) Refractive index of air is 1.0003
Q (69): Which of the following is correct?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d) None of the above
Q (70): If the refractive index of water for light going from air to water be 1.33, what will
be the refractive index for light going from water to air ?
(a) 1.33 (b) 1.75
(c) 0.75 (d) 1.75
Q (71): You are given water, mustard oil, glycerine and kerosene. In which of these
media a ray of light incident obliquely at same angle would bend the most?
(a) Kerosene (b) Water
(c) Mustard oil (d) Glycerine
Q (72): A lens bounded by two spherical surfaces, bulging outwards. Such a lens is
called ___.
(a) Convex lens
(b) Concave lens
(c) All of the above
(d) None of the above
Q (73): Convex lens ___ light rays.
(a) Converges
(b) Diverges
(c) All of the above
Want to access 7 lac+ questions?
powered by Get MCQs based on latest CBSE pattern & auto-check the
homework
the homework app
Homework
(d) None of the above
Q (74): A lens bounded by two spherical surfaces, curved inwards. Such a lens is called
___.
(a) Convex lens
(b) Concave lens
(c) All of the above
(d) None of the above
Q (75): Concave lens ___ light rays.
(a) Converges
(b) Diverges
(c) All of the above
(d) None of the above
Q (76): Assertion: If the rays are diverging after emerging from a lens; the lens must be
concave.
Reason: The convex lens can give diverging rays.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Q (77): Fill in the blank: A ray of light which is parallel to the _____ of a convex lens,
passes through its focus after refraction through the lens.
(a) Principal axis
(b) Vertical height
(c) All of te above
(d) None of the above
Q (78): _______ of a lens is the degree of convergence or divergence of light rays
achieved by a lens.
(a) Speed (b) Power
(c) Intensity (d) Transparency
Q (79): If the distance between two lenses become equal to sum of their focal lengths,
then the parallel beam of light will emerge _____ after passing through the second
lens.
(a) parallel (b) converging
(c) diverging (d) none
Q (80): Identify the device used (a spherical mirror or lens) in following cases, when the
image formed is virtual and erect. Object is placed between infinity and device,
image formed is diminished and between focus and optical centre on the same
side as that of the object.
(a) Concave mirror (b) Convex lens
(c) Concave lens (d) Convex mirror
Q (81): You are provided with two lwnses of focal length 20 cm and 40 cm respectively.
Which lens will you use to obtain more convergent light?
(a) Focal length of 40 cm
(b) Focal length of 20 cm
(c) Both lenses
(d) None of these
Want to access 7 lac+ questions?
powered by Get MCQs based on latest CBSE pattern & auto-check the
homework
the homework app
Homework
Q (82): “A lens can form a magnified erect image as well as magnified inverted image of
an object placed in front of it.” State the nature of this lens
(a) Convex
(b) Concave
(c) Both convex and concave
(d) None of these
Q (83): Rohit claims to have obtained an image twice the size of object with a concave
lens. Is he correct? Give reason.
(a) No, concave lens does not forms magnified image.
(b) Yes. concave lens forms magnified image.
(c) Depends on the situation
(d) None of the above
Q (84): Assertion : Power of a convex lens is positive and that of a concave lens is
negative.
Reason : Convex lens forms real image and concave lens forms virtual image.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Q (85): What would be the position of image formed by convex lens when the object is
placed between $F_{1}$ and $2F_{1}$ ?
(a) At infinity
(b) Between
and
(c) Beyond
(d) On the same side of the lens as the object
Q (86): What would be the relative size of the image formed by concave lens when the
object is placed between infinity and optical centre O of the lens?
(a) Highly diminished (point-sized)
(b) Enlarged
(c) Diminished
(d) Infinitely large or highly enlarged
Q (87): What would be the position of image formed by concave lens when the object is
placed at infinity?
(a) At infinity
(b) At focus
(c) On the same side of the lens as the object
(d) At
Want to access 7 lac+ questions?
powered by Get MCQs based on latest CBSE pattern & auto-check the
homework
the homework app
Homework
Q (88): when an object is placed between F' and 2F' in front of a convex lens, the image
formed is :
(a) Real and erect
(b) Virtual and inverted
(c) Virtual and erect
(d) Real and inverted
Q (89): What would be the position of image formed by convex lens when the object is
placed at infinity?
(a) At
(b) At infinity
(c) At focus
(d) On the same side of the lens as the object
Q (90): What would be the relative size of the image formed by convex lens when the
object is placed at infinity?
(a) Highly diminished(point-sized)
(b) Enlarged
(c) Diminished
(d) Infinitely large or highly enlarged
Q (91): What would be the position of image formed by convex lens when the object is
placed beyond $2F_{1}$ ?
(a) At focus
(b) Between
and
(c) Beyond
(d) At infinity
Q (92): What is the relationship between distance of object (u), distance of image (v) and
focal length (f) in spherical lens?
(a) (b)
(c) (d)
Q (93): A concave lens has focal length of 15 cm. At what distance should the object
from the lens be placed so that it forms an image at 10 cm from the lens?
(a) 30 cm on left side of lens
(b) 15 cm on right side of lens
(c) 25.82 cm on left side of lens
(d) 10.32 cm on right side of lens
Want to access 7 lac+ questions?
powered by Get MCQs based on latest CBSE pattern & auto-check the
homework
the homework app
Homework
Q (94): A concave lens has focal length of 15 cm. If the object is placed at 30cm and
image is at distance of 10cm, find the magnification produced by lens.
(a) -0.33 (b) 3
(c) -3 (d) 0.33
Q (95): A spherical mirror and a thin spherical lens have each a focal length of –15 cm.
The mirror and the lens are likely to be ___.
(a) Both concave
(b) Both convex
(c) The mirror is concave and the lens is convex
(d) The mirror is convex, but the lens is concave
Q (96): The image of a candle flame formed by a lens is obtained on a screen placed on
the other side of the lens. If the image is three times the size of the flame and the
distance between lens and image is 80 cm, at what distance should the candle
be placed from the lens?
(a) 100 cm (b) cm
(c) 60 cm (d) cm
Q (97): A 6 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of
focal length 25 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 40 cm. By calculation
determine the position of the image formed.
(a) 66.67 cm (b) 56.63 cm
(c) 62.55 cm (d) 63.57 cm
Q (98): An object 1 m tall is placed on the principal axis of a convex lens and its 40 cm
tall image is formed on the screen placed at a distance of 70 cm from the object.
What is the focal length of the lens?
(a) 14.2 cm (b) 14.3 cm
(c) 14.4 cm (d) 14.5 cm
Q (99):
A student focused the image of a candle flame on a white screen by placing the
flame at various distances from a convex lens. He noted his observations in above
table. Analyse the above table and tell the focal length of the convex lens.
(a) 15 cm (b) 12 cm
(c) 14 cm (d) 11 cm
Q (100): Assersation: The lens formula given above is general and is valid in all situations
Want to access 7 lac+ questions?
powered by Get MCQs based on latest CBSE pattern & auto-check the
homework
the homework app
Homework
for any spherical lens.
Reason: For lenses, we follow sign convention.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Q (101): Ravi is given lenses with powers +5D, -5D, +10D and -20D. Considering a pair
of lenses at a time, which two lenses will he select to have a combination of focal
length of 20cm when two lenses are kept in contact in case 20cm.
(a) 10D and -20D (b) 5D and -5D
(c) 5D and -20D (d) -5D and 10D
Want to access 7 lac+ questions?
powered by Get MCQs based on latest CBSE pattern & auto-check the
homework
the homework app
You might also like
- Boeing 737 GuideDocument4 pagesBoeing 737 GuideIvo Van den Heuvel100% (7)
- Reflection of Light: Multiple Choice Questions: (MCQS)Document4 pagesReflection of Light: Multiple Choice Questions: (MCQS)Arushi100% (5)
- PVS14 - Spare - Parts - and - Options (1) - 1Document4 pagesPVS14 - Spare - Parts - and - Options (1) - 1carlos ibarraNo ratings yet
- At Pop RecordDocument84 pagesAt Pop Recordedward77100% (3)
- s5 Physics Holiday Homework WorksheetDocument1 pages5 Physics Holiday Homework WorksheetA.P.SNo ratings yet
- Weekly TEst 20th Sep 2021Document4 pagesWeekly TEst 20th Sep 2021Sarvesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Questions - Quiz - 10th - Science - 2021-11-11T17 - 15Document8 pagesQuestions - Quiz - 10th - Science - 2021-11-11T17 - 15panavjprNo ratings yet
- Light SolutionsDocument105 pagesLight SolutionsShreyas Salunkhe X ANo ratings yet
- Class 10 Holiday Hmework (Physics)Document8 pagesClass 10 Holiday Hmework (Physics)Study ZNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document12 pagesCH 10ojha.ramNo ratings yet
- Quiz - Light 1Document5 pagesQuiz - Light 1padmajasingh1junNo ratings yet
- CL 10 CH Light Obj 1Document29 pagesCL 10 CH Light Obj 1Harshavardhan RajaramNo ratings yet
- Phylight 1594463562136Document22 pagesPhylight 1594463562136akshat goyalNo ratings yet
- Physics HW Set 1Document5 pagesPhysics HW Set 1janyashetty2407No ratings yet
- X Physics PracticeDocument6 pagesX Physics PracticeJeena RajNo ratings yet
- NCERT ExemplarDocument10 pagesNCERT Exemplarrohitpatra708024No ratings yet
- Light - MCQDocument9 pagesLight - MCQMinuteBrain LearningNo ratings yet
- GZBXHHWPHYSICSWSJUNE2425pdf 202405310831 9Document3 pagesGZBXHHWPHYSICSWSJUNE2425pdf 202405310831 9vatsdakshataNo ratings yet
- 25 Reflection of Light - MirrorsDocument6 pages25 Reflection of Light - MirrorsJames SullivanNo ratings yet
- G10 - Chapter Test 5 Ans - Ch.10 - 06 NOV 23Document10 pagesG10 - Chapter Test 5 Ans - Ch.10 - 06 NOV 23Urmila GNo ratings yet
- MCQs On Refraction of Light Through LensDocument10 pagesMCQs On Refraction of Light Through LensDigant DonthyNo ratings yet
- Sara QuestionsDocument3 pagesSara QuestionsKCC UdgirNo ratings yet
- Physics Revision Worksheet Grade X ChlightDocument3 pagesPhysics Revision Worksheet Grade X ChlightKhushi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Competency-Based Questions - As Per NEP RecommendationsDocument5 pagesCompetency-Based Questions - As Per NEP RecommendationsWolf2No ratings yet
- Sainik School Goalpara: Extra Homework Subject: Science (Physics) Class: XDocument4 pagesSainik School Goalpara: Extra Homework Subject: Science (Physics) Class: XBornil Bikash BhuyanNo ratings yet
- Mcqs Light FullDocument12 pagesMcqs Light FullHariprasanthNo ratings yet
- ACP - Light With SolutionDocument21 pagesACP - Light With Solution748197054sNo ratings yet
- Class-10 Lesson-10Document5 pagesClass-10 Lesson-10lambulamb15No ratings yet
- X - Science - Physics - CH-9 Light - Assignment-1Document2 pagesX - Science - Physics - CH-9 Light - Assignment-1Shweta DuhanNo ratings yet
- Physics MCQ Worksheet3Document4 pagesPhysics MCQ Worksheet3Ponnusamy ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - QWADocument58 pagesChapter 10 - QWADr.K E Reby RoyNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection and Refraction QuestionsDocument16 pagesLight Reflection and Refraction Questionsruturajgawande21No ratings yet
- Worksheet 3 Class 10 Notes.Document9 pagesWorksheet 3 Class 10 Notes.John WickNo ratings yet
- Open Book Test - OpticsDocument9 pagesOpen Book Test - OpticsGagandeep WadhawanNo ratings yet
- Ch.10 - Light (Reflection)Document35 pagesCh.10 - Light (Reflection)Urmila GNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science HOTs Reflection and RefractionDocument20 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science HOTs Reflection and RefractionAadi PunjabiNo ratings yet
- Kssirs12thsheet01 GeometricalopticsDocument66 pagesKssirs12thsheet01 GeometricalopticsAshutosh TripathiNo ratings yet
- Geometric Optics Practice Problems: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument23 pagesGeometric Optics Practice Problems: Multiple Choice QuestionsMohamedNo ratings yet
- Light PDF of Practice QuestionsDocument24 pagesLight PDF of Practice Questionsyuvrajchourasia786No ratings yet
- Term 1 Questions - LightDocument24 pagesTerm 1 Questions - LightAmbitious StudentNo ratings yet
- Class X PhyDocument4 pagesClass X PhyNilima Aparajita SahuNo ratings yet
- Optics PacketDocument24 pagesOptics Packetjayen romaNo ratings yet
- Important Question For Class 10 Science Light Reflection and RefractionDocument1 pageImportant Question For Class 10 Science Light Reflection and RefractionAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- 0 DocumentDocument4 pages0 Documentrmvb7cbfv9No ratings yet
- Hysicsaholics: Video Solution On Website:-Video Solution On Youtube: - Written Solution On YoutubeDocument2 pagesHysicsaholics: Video Solution On Website:-Video Solution On Youtube: - Written Solution On YoutubeBottle MasterNo ratings yet
- Assign IiDocument4 pagesAssign IiSangeeta ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Light Revision Class 10Document34 pagesLight Revision Class 10karun.senthil.kumar.25No ratings yet
- Big Bro - Test 1 For 30Document5 pagesBig Bro - Test 1 For 30Elamparithi ANo ratings yet
- Sheet of Geometrical Optics Student Copy With Ans New 05-04-2022 Updated 5 1716869685357Document68 pagesSheet of Geometrical Optics Student Copy With Ans New 05-04-2022 Updated 5 1716869685357amandaksh157No ratings yet
- Revision QP Set ADocument5 pagesRevision QP Set Aimraan smNo ratings yet
- Ntse - Assignment 1 - Level 1Document9 pagesNtse - Assignment 1 - Level 1Anmol SinghNo ratings yet
- Ks Sirs 12th Sheet 01 Geometrical Optics 1664891760221 1Document65 pagesKs Sirs 12th Sheet 01 Geometrical Optics 1664891760221 1Shubham BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Geometricaloptics 2 31Document30 pagesGeometricaloptics 2 31Harshit RajNo ratings yet
- 03 Light (Reflection of Spherical Surfaces) Elevate 1Document5 pages03 Light (Reflection of Spherical Surfaces) Elevate 1akshitwalia209No ratings yet
- MCQ Questions For Class 10 Science CH - 10 Light - Reflection and RefractionDocument15 pagesMCQ Questions For Class 10 Science CH - 10 Light - Reflection and RefractionRB Technical Point100% (1)
- Classroom Practice Assignment Cbse Class-X: PhysicsDocument3 pagesClassroom Practice Assignment Cbse Class-X: PhysicsAditya MondalNo ratings yet
- MCQ Class 10 LightDocument8 pagesMCQ Class 10 LightRithika GoruNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and Salts Light-Reflection and Refraction: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS)Document12 pagesAcids, Bases and Salts Light-Reflection and Refraction: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS)Bhanu PurushothamaNo ratings yet
- Revision Lecture 2 (L.O 3.3,6)Document23 pagesRevision Lecture 2 (L.O 3.3,6)kirolosgeorge20005No ratings yet
- ACFrOgCggT71E HfapMy80vxxTqharAWqAcja6twdvl URhy6t0 ScCDOkJGyvlde6kUrDINqpSjaytLmlh-u3pLtCciXv7SpOr5fu2MqbePk9ZlRajNRfSzw3jJEjhM99W - 1GMx TyACrLQ-0CDocument5 pagesACFrOgCggT71E HfapMy80vxxTqharAWqAcja6twdvl URhy6t0 ScCDOkJGyvlde6kUrDINqpSjaytLmlh-u3pLtCciXv7SpOr5fu2MqbePk9ZlRajNRfSzw3jJEjhM99W - 1GMx TyACrLQ-0CAltaf Hussain ShaikNo ratings yet
- CH - 01 - Light - Only PDFDocument12 pagesCH - 01 - Light - Only PDFrohitdodamanib352No ratings yet
- Class 10 Light AssignmentDocument5 pagesClass 10 Light AssignmentDrawing With SoumaryaNo ratings yet
- Big Data Analysis For Heart Disease Detection System Using Map Reduce TechniqueDocument6 pagesBig Data Analysis For Heart Disease Detection System Using Map Reduce TechniqueSaurabh BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Data Mining Approach To Detect Heart Dieses: AuthorsDocument11 pagesData Mining Approach To Detect Heart Dieses: AuthorsSaurabh BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Questions - Homework - 10th - Science - 2021-11-24T05 - 41Document6 pagesQuestions - Homework - 10th - Science - 2021-11-24T05 - 41Saurabh BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Motwani 2016Document8 pagesMotwani 2016Saurabh BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Sciencedirect: Performance Analysis of Data Mining Classification Techniques To Predict DiabetesDocument7 pagesSciencedirect: Performance Analysis of Data Mining Classification Techniques To Predict DiabetesSaurabh BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Questions - Homework - 10th - Science - 2021-11-24T05 - 44Document12 pagesQuestions - Homework - 10th - Science - 2021-11-24T05 - 44Saurabh BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- CCS Conduct Rules MCQsDocument6 pagesCCS Conduct Rules MCQsSaurabh BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- WorldLab 9th Prototype FullDocument11 pagesWorldLab 9th Prototype FullRitvik Singh SabharwalNo ratings yet
- WHLP Q1M1, GR5Document3 pagesWHLP Q1M1, GR5Lucrecia VinluanNo ratings yet
- Powder Technology: Hamzah M. Beakawi Al-Hashemi, Omar S. Baghabra Al-AmoudiDocument21 pagesPowder Technology: Hamzah M. Beakawi Al-Hashemi, Omar S. Baghabra Al-AmoudiLaura AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Potable Water and Sewage Calculator Guide1Document16 pagesPotable Water and Sewage Calculator Guide1Roseena AdamNo ratings yet
- P.lectora Lilibeth Monserrate - Ind01Document42 pagesP.lectora Lilibeth Monserrate - Ind01Maria P. LópezNo ratings yet
- The Social Psychology of Decision MakingDocument15 pagesThe Social Psychology of Decision MakingBenjie Moronia Jr.50% (2)
- nps67 011714 01Document250 pagesnps67 011714 01Sachin ShendeNo ratings yet
- Parent Feedback FormDocument1 pageParent Feedback FormKunal Khandelwal100% (2)
- Learning Activity 2 Evidence: Blog "Pet Peeves" "A Pet Peeve Is A Particular Thing That Bugs, orDocument3 pagesLearning Activity 2 Evidence: Blog "Pet Peeves" "A Pet Peeve Is A Particular Thing That Bugs, oryoli tatiana moraNo ratings yet
- English Grade 7-10 Standards Matrix PDFDocument7 pagesEnglish Grade 7-10 Standards Matrix PDFFred Ryan Canoy DeañoNo ratings yet
- DP 1 Dr. Charles Cockell Astrobiology-A New Opportunity For Interdisciplinary ThinkingDocument4 pagesDP 1 Dr. Charles Cockell Astrobiology-A New Opportunity For Interdisciplinary ThinkingKaren Orozco RomeroNo ratings yet
- Harsha PriyaDocument3 pagesHarsha PriyaSudha Prabhakar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Compatibility List First Page of Section: Tape Drive and Library Compatibility Matrix Oracle Secure Backup 10.4.0.1Document12 pagesCompatibility List First Page of Section: Tape Drive and Library Compatibility Matrix Oracle Secure Backup 10.4.0.1kwanlok.chanNo ratings yet
- Pulse 2000 EzDocument2 pagesPulse 2000 Ezhitesh cHAUDHARINo ratings yet
- Two Marks: 40. What Are Constraints?Document3 pagesTwo Marks: 40. What Are Constraints?Victer PaulNo ratings yet
- Nebosh Igc SubDocument8 pagesNebosh Igc SubMohammad Farooquddin HSENo ratings yet
- Quiz IntegersDocument2 pagesQuiz IntegersAma AtibyNo ratings yet
- 7.3 Broadcast ReceiversDocument33 pages7.3 Broadcast Receiversdimasmaendra1213No ratings yet
- PMI 000 ClassificationsDocument5 pagesPMI 000 ClassificationsBerliandi ManikNo ratings yet
- Lab Discussion and Conclusion Report PDFDocument2 pagesLab Discussion and Conclusion Report PDFRadz Krishz100% (1)
- 1.1.4.6 CiscoDocument11 pages1.1.4.6 CiscoZeratul322100% (2)
- Supporting Children To Participate Successfully in Everyday Life Using Sensory Processing KnowledgeDocument19 pagesSupporting Children To Participate Successfully in Everyday Life Using Sensory Processing Knowledgeapi-26018051100% (1)
- Warp vs. FTL vs. HyperdriveDocument2 pagesWarp vs. FTL vs. HyperdriveKostasBaliotisNo ratings yet
- Forecasting: EM6113-Engineering Management TechniquesDocument40 pagesForecasting: EM6113-Engineering Management TechniquesasadNo ratings yet
- Theorem Environments: L TEX For Math and ScienceDocument14 pagesTheorem Environments: L TEX For Math and SciencejaxbaiadNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Seminar PaperDocument7 pagesHow To Write A Seminar Papertemujin03No ratings yet