Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Passive: Masked Thieves
The Passive: Masked Thieves
Uploaded by
Osbel Yumar RodriguezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Passive: Masked Thieves
The Passive: Masked Thieves
Uploaded by
Osbel Yumar RodriguezCopyright:
Available Formats
The passive
In an active sentence, the subject is the Use the passive:
person or thing that performs the action:
The passive Conditionals
■ when you do not know who performed
▶ Masked thieves stole a valuable painting
the action, or when this information is not
from the museum last night. important. It is common in formal writing,
When you make this into a passive sentence, for example scientific writing:
▶ The liquid is heated to 60 o and then filtered.
the object of the verb becomes the subject:
▶ A valuable painting was stolen from the
NOTE If you want to mention who
museum last night. performed the action, you use by at the end
The passive is formed with the auxiliary of the sentence:
▶ The theft is being investigated by the police.
verb be and the past participle of the verb:
▶ The painting is valued at 2 million dollars.
■ when you want to save new or important
▶ The lock had been broken and the cameras
information until the end of the sentence
had been switched off. for emphasis:
▶ Other museums have been warned to take
▶ The picture was painted by Constable.
extra care.
▶ Staff at the museum will be questioned It is possible to put a verb that has two
by police tomorrow. objects into the passive:
▶ Museum security is to be improved. ▶ ( active ) The director told the staff the
news this morning.
▶ (passive) The staff were told the news
this morning by the director.
Some verbs cannot be used in the passive,
and this is shown at the entries.
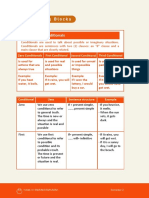
Conditionals
Sentences with if are used to express possibilities: Third conditional
if clause past perfect;
First conditional main clause conditional perfect tense
if clause present tense; used to talk about the possible consequence
main clause future tense of an action that did not happen:
▶ If I had written my essay this afternoon,
used to talk about the consequence of a
possible action: I would have had time to go out tonight.
▶ If I write my essay this afternoon, I will have ( it is now evening, and I haven’t written my
time to go out tonight. ( it is still morning, essay: it is now impossible for me to go out. )
and it is quite possible that I will do this. )
Zero conditional
Second conditional Sometimes sentences with if express certainty
if clause past simple; rather than possibility. The zero conditional
main clause conditional tense is used to talk about something that is always
true, or that was always true in the past:
used to talk about the consequences of a ▶ If you mix blue and red, you get purple.
hypothetical action: ( present simple in both parts of the sentence )
▶ If I wrote my essay this afternoon, ▶ If I asked her to come with us, she always said
I would have time to go out tonight. no. ( past simple in both parts of the sentence)
( it is still morning, but I think it is less likely
that I will do this. )
© Oxford University Press
You might also like
- Quastion in Ingles GOLDocument12 pagesQuastion in Ingles GOLAlda Ghisi FrigiNo ratings yet
- English Stage 3 Sample Paper 2 - tcm142-594873Document12 pagesEnglish Stage 3 Sample Paper 2 - tcm142-594873Givemore Murombo100% (5)
- No-Prep Worksheets: 3 - 5 GradeDocument14 pagesNo-Prep Worksheets: 3 - 5 GradeNomsa Shamu100% (1)
- Modal VerbsDocument34 pagesModal Verbsinred1230100% (6)
- The Passive: Masked ThievesDocument1 pageThe Passive: Masked ThievesMehedi Al MasudNo ratings yet
- Conditionals The Passive: First ConditionalDocument1 pageConditionals The Passive: First ConditionalGohar AliNo ratings yet
- Conditionals The Passive: First ConditionalDocument11 pagesConditionals The Passive: First ConditionalManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Conditionals The Passive: First ConditionalDocument1 pageConditionals The Passive: First Conditionalmohit009dudeNo ratings yet
- Defining Relative Clauses Non-Defining Relative ClausesDocument1 pageDefining Relative Clauses Non-Defining Relative ClausesSashidhar BaralNo ratings yet
- Grammar TensesDocument2 pagesGrammar TensesAli SharafNo ratings yet
- Talking About The PresentDocument2 pagesTalking About The PresentMuhamad arifin IlhamNo ratings yet
- 9 Grammar ReviewDocument2 pages9 Grammar ReviewFOR AKKNo ratings yet
- Encounter Force! v1.0gdfsgdfsDocument46 pagesEncounter Force! v1.0gdfsgdfskubala57No ratings yet
- Week 1 VirginiaDocument44 pagesWeek 1 VirginiaSandraNo ratings yet
- Unit 45-47Document6 pagesUnit 45-47Tuyết TrinhNo ratings yet
- If IWere YouDocument5 pagesIf IWere YouNick KanceNo ratings yet
- Causative Have and Get: PresentationDocument2 pagesCausative Have and Get: PresentationValeriaNo ratings yet
- Passive 1Document7 pagesPassive 1PaulaNo ratings yet
- PassivesDocument13 pagesPassivesThanh Phúc0% (1)
- Active PassiveDocument20 pagesActive PassiveKathrin WolfNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 - Mind MapDocument3 pagesUnit 6 - Mind MapRicardo SilvaNo ratings yet
- L6. Present and Past Simple PassiveDocument2 pagesL6. Present and Past Simple PassiveCristIan Ruben Pazmiño SolisNo ratings yet
- Unit 9-Things HappenDocument12 pagesUnit 9-Things HappenLeo GonellNo ratings yet
- Phrasal VerbsDocument9 pagesPhrasal VerbsJavier PachonNo ratings yet
- Literature - Relative PronounsDocument18 pagesLiterature - Relative PronounsAngelo PanseraNo ratings yet
- Note NG Pháp TA Nâng CaoDocument10 pagesNote NG Pháp TA Nâng Cao2153801011085No ratings yet
- Third Grade Model LessonDocument3 pagesThird Grade Model Lessonapi-320716438No ratings yet
- Passive 2Document6 pagesPassive 2Jose Luis Magaña PizarroNo ratings yet
- Passive 2Document6 pagesPassive 2PaulaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Articles PDFDocument1 pageGrammar Articles PDFseaNo ratings yet
- Future Tenses ExplanationDocument6 pagesFuture Tenses ExplanationYadira Pejerrey UrbinaNo ratings yet
- B Inggris XiDocument24 pagesB Inggris XiAsep SaepulNo ratings yet
- First ConditionalDocument5 pagesFirst ConditionalVraja Salazar RubioNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences, Articles, Present Perfect ContinuousDocument19 pagesConditional Sentences, Articles, Present Perfect ContinuousEster AzevedoNo ratings yet
- b2.1 - Unit 9 - GrammarDocument6 pagesb2.1 - Unit 9 - Grammarcristina.lopez.castro96No ratings yet
- Pasivul in Limba Engleza - Exercitii Si ExempleDocument7 pagesPasivul in Limba Engleza - Exercitii Si Exempleiancu_jianu_6No ratings yet
- Third Conditional British English StudentDocument3 pagesThird Conditional British English StudentAnastasia PedkoNo ratings yet
- Passives - FCEDocument10 pagesPassives - FCEChristina MoldoveanuNo ratings yet
- BẢNG THÀNH NGỮ TIẾNG ANHDocument7 pagesBẢNG THÀNH NGỮ TIẾNG ANHnguyễn Đình TuấnNo ratings yet
- Passive VoiceDocument17 pagesPassive VoiceHeba MahmoudNo ratings yet
- WHAT IF? Conditionals: Zero Conditionals First Conditional Third ConditionalDocument8 pagesWHAT IF? Conditionals: Zero Conditionals First Conditional Third ConditionalMarini JerimasNo ratings yet
- Basic Future ExercisesDocument2 pagesBasic Future ExercisesRadosław SłowińskiNo ratings yet
- TEST Cls 7ADocument3 pagesTEST Cls 7AEly CristinaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: Personality.: Universidad Politécnica Salesiana Del EcuadorDocument24 pagesUnit 4: Personality.: Universidad Politécnica Salesiana Del EcuadorLennyn SanyNo ratings yet
- Monday April 20th, 2020: Unit 9, Lesson ADocument15 pagesMonday April 20th, 2020: Unit 9, Lesson AJacqueline Hernandez HernandezNo ratings yet
- Third Conditional British English StudentDocument3 pagesThird Conditional British English StudentAnastasiya LeganNo ratings yet
- When To Use The Passive Voice: Guía Didáctica #12Document5 pagesWhen To Use The Passive Voice: Guía Didáctica #12Mariangelly CahuanaNo ratings yet
- Passives C1Document3 pagesPassives C1Aina Travé SanjuanNo ratings yet
- Idioms Meaning ExamplesDocument12 pagesIdioms Meaning ExamplesThị Bảy LêNo ratings yet
- Support Material 2Document14 pagesSupport Material 2Adriana MoralesNo ratings yet
- Conditionals GrammarDocument24 pagesConditionals GrammarJúlia LopesNo ratings yet
- Answer The Question by Choosing A, B, C or D!: The Text Is For The Questions 4 To 6Document10 pagesAnswer The Question by Choosing A, B, C or D!: The Text Is For The Questions 4 To 6Amay KrNo ratings yet
- TRUE LOVE GONE WrongDocument706 pagesTRUE LOVE GONE Wrongkegaisitsemokgomo0No ratings yet
- It Is Said That... He Is Supposed ToDocument2 pagesIt Is Said That... He Is Supposed ToJosé Manuel Henríquez GalánNo ratings yet
- Condition Result: Support MaterialDocument13 pagesCondition Result: Support MaterialTatiana NavasNo ratings yet
- 2ND LT in English 6Document4 pages2ND LT in English 6jessica holgadoNo ratings yet
- Anggie Hernita Azzura-XII Science 8Document6 pagesAnggie Hernita Azzura-XII Science 8Anggie hernitaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - PrivilegesDocument87 pagesLesson 3 - Privilegesapi-550082451No ratings yet
- 02-Exercises To Make You See Stories - EverywhereDocument2 pages02-Exercises To Make You See Stories - Everywherehilajo1363No ratings yet
- Guia Nivel 3 ConditionalsDocument2 pagesGuia Nivel 3 ConditionalsBrayan RicardoNo ratings yet
- French Verbs: Intensive Lexical Builder with Embedded SentencesFrom EverandFrench Verbs: Intensive Lexical Builder with Embedded SentencesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Week 1 Activity Sheet-RQTDocument3 pagesWeek 1 Activity Sheet-RQTFranklyn TroncoNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Pengajaran Slot (RPS)Document3 pagesRancangan Pengajaran Slot (RPS)Azrinna BasriNo ratings yet
- Using Language - Assignment 1 Use of Language in "Blood Diamond" From A Sociolinguistic Perspective Tôn N Hoàng Anh Ho Chi Minh City Open UniversityDocument9 pagesUsing Language - Assignment 1 Use of Language in "Blood Diamond" From A Sociolinguistic Perspective Tôn N Hoàng Anh Ho Chi Minh City Open UniversityAnh Ton100% (2)
- Ethnography and Lanuage in Educational SettingsDocument381 pagesEthnography and Lanuage in Educational SettingsJudith Green100% (1)
- A Possessive Pronoun Shows Ownership. Unlike Possessive Adjectives (My, Your, His, Her, Its, Our, Their)Document3 pagesA Possessive Pronoun Shows Ownership. Unlike Possessive Adjectives (My, Your, His, Her, Its, Our, Their)Ferry AryaNo ratings yet
- 4th Learning Program 2019-2020Document22 pages4th Learning Program 2019-2020Marvin NavaNo ratings yet
- Portions For Common Assessment - Term 3 (Grade 5)Document4 pagesPortions For Common Assessment - Term 3 (Grade 5)Balloon90 90No ratings yet
- DFC Factors Influencing Legal DraftingDocument23 pagesDFC Factors Influencing Legal DraftingHardial LimbongNo ratings yet
- Yusiana Irmawati - Best PracticeDocument63 pagesYusiana Irmawati - Best PracticeYusiana IrmawatiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document8 pagesUnit 3Mayank GuptaNo ratings yet
- Possessive Adjectives Writing ActivityDocument3 pagesPossessive Adjectives Writing ActivityarsmeoNo ratings yet
- Speakout Extra: Grammar PracticeDocument2 pagesSpeakout Extra: Grammar PracticeАнгелина ПрибыльскаяNo ratings yet
- Magazine Making RubricDocument1 pageMagazine Making Rubrickathleen panuelos100% (1)
- DAIS Year 1 Term 1Document116 pagesDAIS Year 1 Term 1Sohaib AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Directed Writing Practice 1 Formal LetterDocument4 pagesDirected Writing Practice 1 Formal LetterTini Leng Loy Cushing100% (4)
- Syntax: Though), and Interjections (Oh, Phew) - Modern Linguists, Though AcceptDocument4 pagesSyntax: Though), and Interjections (Oh, Phew) - Modern Linguists, Though AcceptÁnderli PérezNo ratings yet
- Realia in Translation Course WorkDocument5 pagesRealia in Translation Course Workafaocsazx100% (2)
- Phonology Group 3Document9 pagesPhonology Group 3Diah Ayu050No ratings yet
- Oral-Communication11 Q1 Module-7 08082020Document26 pagesOral-Communication11 Q1 Module-7 08082020Mesryl AutidaNo ratings yet
- 口语考试介绍CELPIP Speaking SyllabusDocument26 pages口语考试介绍CELPIP Speaking Syllabushonglu.cheng.pubNo ratings yet
- Foreign Language Annals - 2009 - Gregersen - To Err Is Human A Reminder To Teachers of Language Anxious StudentsDocument8 pagesForeign Language Annals - 2009 - Gregersen - To Err Is Human A Reminder To Teachers of Language Anxious StudentsPetraNo ratings yet
- 7 AdjektiveDocument5 pages7 Adjektiveadinda afifahNo ratings yet
- VSC - French 3 Honors Pacing Guide - LatiniDocument10 pagesVSC - French 3 Honors Pacing Guide - LatiniIan RutledgeNo ratings yet
- ECA1 Tests Language Test 8CDocument3 pagesECA1 Tests Language Test 8Cs-malachowskaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Focus On The Learner: Part A: Learner ProfileDocument5 pagesAssignment 1: Focus On The Learner: Part A: Learner ProfileMehdi RoostapourNo ratings yet
- Caha 2009 The Nanosyntax of CaseDocument334 pagesCaha 2009 The Nanosyntax of CaseJohnsonNo ratings yet
- Christopher Columbus British English TeacherDocument8 pagesChristopher Columbus British English TeacherIrina Del Rio BarreroNo ratings yet
- Determiners NotesDocument7 pagesDeterminers NotesMankirat SinghNo ratings yet