Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Special Education Timeline
Special Education Timeline
Uploaded by
api-483842715Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Aviation Clause Blue BookDocument128 pagesAviation Clause Blue BookSunil Kumar80% (5)
- The Spanish Tragedy LitChartDocument37 pagesThe Spanish Tragedy LitChartMODDASIR BHUIYAN MAHI100% (1)
- Dunn - Special Education For The Midly Retarded - Is Much of JustificableDocument18 pagesDunn - Special Education For The Midly Retarded - Is Much of JustificableMauricio PocasangreNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Special Education TimelineDocument5 pagesActivity 1 Special Education TimelinejaneNo ratings yet
- Organization and Administration of Special Education ProgramsDocument10 pagesOrganization and Administration of Special Education ProgramsMj Ong Pierson Garbo100% (1)
- Pre Trial Brief Petition For Declaration of Nullity of MarriageDocument5 pagesPre Trial Brief Petition For Declaration of Nullity of Marriageboniglai5100% (1)
- Historical TimelineDocument21 pagesHistorical TimelineMariell Mae GamitNo ratings yet
- Summary of ReportDocument5 pagesSummary of ReportKc Alecks V. BaliwasNo ratings yet
- On Historical Bases: A History On Educating Children With Disabilities in AmericaDocument2 pagesOn Historical Bases: A History On Educating Children With Disabilities in AmericaNnieh KhuuNo ratings yet
- Law ChartDocument2 pagesLaw Chartapi-659766270No ratings yet
- 201 History TimelineDocument2 pages201 History Timelineapi-458054294No ratings yet
- Education Timeline Edu 201Document1 pageEducation Timeline Edu 201api-548931113No ratings yet
- TimelineDocument2 pagesTimelineapi-325090049No ratings yet
- Foundation of Special and Inclusive EducationDocument11 pagesFoundation of Special and Inclusive EducationJeanlyNo ratings yet
- SNED 8 - Adapted Physical EducationDocument6 pagesSNED 8 - Adapted Physical EducationMarjorie MendozaNo ratings yet
- Education HistoryDocument1 pageEducation Historyapi-548899140No ratings yet
- What's Your IdeaDocument1 pageWhat's Your IdeadataliojhonmarkNo ratings yet
- Parts A B C and D of IdeaDocument2 pagesParts A B C and D of Ideaapi-582915098No ratings yet
- Foundation of Special & Inclusive EducationDocument10 pagesFoundation of Special & Inclusive EducationHazel GeronimoNo ratings yet
- PedaDocument12 pagesPedaJayanta BuragohainNo ratings yet
- Issue Brief - Inclusive Education in Malaysia 2014Document7 pagesIssue Brief - Inclusive Education in Malaysia 2014Fikri OthmanNo ratings yet
- UNICEF Inclusive Education MalaysiaDocument7 pagesUNICEF Inclusive Education MalaysiaZul4No ratings yet
- Education History by Von Eduardo OngDocument2 pagesEducation History by Von Eduardo Ongapi-548955489No ratings yet
- Inclusive Education Part 1 (BTVTED) FinalDocument54 pagesInclusive Education Part 1 (BTVTED) FinalChrissChan BelijionNo ratings yet
- Edu 201 Education History TimelineDocument1 pageEdu 201 Education History Timelineapi-597943088No ratings yet
- 5 Important Special Education LawsDocument2 pages5 Important Special Education LawsSheena Oro50% (2)
- Portfolio Project 5Document2 pagesPortfolio Project 5api-583146454No ratings yet
- Edu 201 Portfolio 8Document1 pageEdu 201 Portfolio 8api-450260025No ratings yet
- Special Edcation SlidesDocument19 pagesSpecial Edcation Slidesapi-534148197No ratings yet
- Historical FactsDocument8 pagesHistorical Factsapi-557330426No ratings yet
- When Special Education and Disability Studies Intertwine: Addressing Educational Inequities Through Processes and ProgrammingDocument5 pagesWhen Special Education and Disability Studies Intertwine: Addressing Educational Inequities Through Processes and ProgrammingIrish CataNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Project 8 Education History TimelineDocument12 pagesPortfolio Project 8 Education History Timelineapi-510584254No ratings yet
- Special Education For Young Learners With Disabilities: Moving ForwardDocument12 pagesSpecial Education For Young Learners With Disabilities: Moving ForwardAliveNo ratings yet
- Assessment in The Situation of Early Childhood Special Education and Inclusive Education in The PhilippinesDocument9 pagesAssessment in The Situation of Early Childhood Special Education and Inclusive Education in The PhilippinesShailyn PorrasNo ratings yet
- Legal Basis of Sped in The Philippines and AbroadDocument28 pagesLegal Basis of Sped in The Philippines and AbroadShiela Juno100% (1)
- Task 2Document6 pagesTask 2Mariell Mae GamitNo ratings yet
- Module For RecitationDocument15 pagesModule For Recitationariannerose gonzalesNo ratings yet
- Inclusive Education Group 1 PPT - 20240425 - 091229 - 0000Document38 pagesInclusive Education Group 1 PPT - 20240425 - 091229 - 0000abesamis jaysonNo ratings yet
- Policy For Special Educators in Himachal Pradesh Drafted by Vijay HeerDocument25 pagesPolicy For Special Educators in Himachal Pradesh Drafted by Vijay HeerVIJAY KUMAR HEER100% (1)
- Historical and Legal Foundation of Special Education 1Document7 pagesHistorical and Legal Foundation of Special Education 1Ma Sherhan DolitNo ratings yet
- 1 FINAL Legal Foundations of Special Education TE PDFDocument20 pages1 FINAL Legal Foundations of Special Education TE PDFClaud HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Inclusive and Special Education Powerpoint ReportDocument21 pagesInclusive and Special Education Powerpoint ReportKe Ann Libradilla100% (1)
- What InclusiveDocument28 pagesWhat InclusiveAmusstaphaNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing The Accessibility of Education For Children With Disabilities in IndiaDocument14 pagesFactors Influencing The Accessibility of Education For Children With Disabilities in Indiayelai gutangNo ratings yet
- History Timeline of Special and Inclusive EducationDocument3 pagesHistory Timeline of Special and Inclusive EducationJonnel GadinganNo ratings yet
- Smita SarkarDocument21 pagesSmita SarkarAshutosh MishraNo ratings yet
- Foundation of Special and Inclusive Education Profed 604: Submitted By: Laika E. RamirezDocument9 pagesFoundation of Special and Inclusive Education Profed 604: Submitted By: Laika E. RamirezARCTIC FLAMENo ratings yet
- Inclusive Education Module 1 (Final Term)Document13 pagesInclusive Education Module 1 (Final Term)ChrissChan BelijionNo ratings yet
- Inclusive Education PresentationDocument26 pagesInclusive Education PresentationecahNo ratings yet
- Vision Policy Goal and ObjectivesDocument15 pagesVision Policy Goal and ObjectivesMary Jean Satorre100% (4)
- What Is Special Education?: Teacher Dodie M. de CastroDocument31 pagesWhat Is Special Education?: Teacher Dodie M. de CastroHearthy AnneNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Project 5Document1 pagePortfolio Project 5api-502037979No ratings yet
- Special Education Programs in The United States Were Made Mandatory in 1975 When TheDocument2 pagesSpecial Education Programs in The United States Were Made Mandatory in 1975 When TheBian Marie Morales ReyesNo ratings yet
- Special and Inclusive EducationDocument4 pagesSpecial and Inclusive EducationLorielyn ToledoNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0738059316300888 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0738059316300888 MainMehar KahlonNo ratings yet
- USUK SEMINAR 3 EditedDocument18 pagesUSUK SEMINAR 3 Editedhoài thương nguyễnNo ratings yet
- 25 Yrs of Educating Children With Disabilities Thru IDEADocument6 pages25 Yrs of Educating Children With Disabilities Thru IDEASami HartsfieldNo ratings yet
- Mod 1Document9 pagesMod 1Loy HermosoNo ratings yet
- Edu 201 Portfolio 8Document2 pagesEdu 201 Portfolio 8api-297539374No ratings yet
- Education History by Kathleen GilmoreDocument1 pageEducation History by Kathleen Gilmoreapi-371352151No ratings yet
- Const Provisions On EducationDocument14 pagesConst Provisions On EducationAnuragKumarNo ratings yet
- EducationDocument2 pagesEducationKaylie WilsonNo ratings yet
- Educating Learners With Visual Impairment In ZambiaFrom EverandEducating Learners With Visual Impairment In ZambiaRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Final Project Outline 1Document2 pagesFinal Project Outline 1api-483842715No ratings yet
- Evidence 7 (Rubric 12) : Provide Student Feedback To Guide LearningDocument4 pagesEvidence 7 (Rubric 12) : Provide Student Feedback To Guide Learningapi-483842715No ratings yet
- Observational NotesDocument4 pagesObservational Notesapi-483842715No ratings yet
- Elements of A Lesson Plan Lesson Plan: Rhythm Tree by Kathy Neri (Grade 6)Document3 pagesElements of A Lesson Plan Lesson Plan: Rhythm Tree by Kathy Neri (Grade 6)api-483842715No ratings yet
- Strategies at A GlanceDocument13 pagesStrategies at A Glanceapi-483842715No ratings yet
- Focused Listing Study GuideDocument4 pagesFocused Listing Study Guideapi-483842715No ratings yet
- Paper To Ecdis Flyer 72dpi RGBDocument4 pagesPaper To Ecdis Flyer 72dpi RGBJoshua KinneyNo ratings yet
- OSSTETDocument1 pageOSSTETsitabehera12345678No ratings yet
- General Catechism FINALDocument16 pagesGeneral Catechism FINALRonnie EspirituNo ratings yet
- Entry Test IELTSDocument4 pagesEntry Test IELTStrangNo ratings yet
- Jenkins 071603 Conflicts EPA WTC PanelDocument207 pagesJenkins 071603 Conflicts EPA WTC PanelEnviroCatNo ratings yet
- CPA REVIEW Questions - LAMBERSDocument51 pagesCPA REVIEW Questions - LAMBERSAlellie Khay JordanNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Microfinance in IndiaDocument21 pagesEvolution of Microfinance in Indiakrnkk8812No ratings yet
- Lumify Tablet Compatibility: Screen Size Weight Approximate Continuous Scan Time Connectivity Options Internal StorageDocument1 pageLumify Tablet Compatibility: Screen Size Weight Approximate Continuous Scan Time Connectivity Options Internal StorageUmi RehanNo ratings yet
- Pengalaman Penjamin Emisi: Periode 2014 - 2018Document52 pagesPengalaman Penjamin Emisi: Periode 2014 - 2018Chim ChimmyNo ratings yet
- Copyright Case DigestsDocument15 pagesCopyright Case DigestsJethro MataNo ratings yet
- Jerry Lewis Corruption FBI Investigation - 58C-LA-244141-30 Thru 33Document7 pagesJerry Lewis Corruption FBI Investigation - 58C-LA-244141-30 Thru 33CREWNo ratings yet
- Ch10 Power PointDocument35 pagesCh10 Power PointGriechel Librado - OcampoNo ratings yet
- Chapter9 10Document5 pagesChapter9 10Nyan Lynn HtunNo ratings yet
- General HOA Property Managment LetterDocument1 pageGeneral HOA Property Managment LetterAldenilo VieiraNo ratings yet
- Golden Ocean Group CaseDocument31 pagesGolden Ocean Group CaseDigital GenesisNo ratings yet
- Bodiongan v. CADocument2 pagesBodiongan v. CAWhere Did Macky GallegoNo ratings yet
- ST Francis de SalesDocument4 pagesST Francis de SalesMichael TemperanteNo ratings yet
- Uthman Bin Muhammad Bin Uthman Bin Salih Ibn FodioDocument3 pagesUthman Bin Muhammad Bin Uthman Bin Salih Ibn FodiotoolzNo ratings yet
- AR AR FinancingDocument34 pagesAR AR FinancingDannis Anne RegajalNo ratings yet
- Ethnic Cleansing - War CrimeDocument13 pagesEthnic Cleansing - War Crimemike johnsonNo ratings yet
- Thailand Day 2Document51 pagesThailand Day 2Edsel BuletinNo ratings yet
- 2208238392Document1 page2208238392NEW GENERATIONSNo ratings yet
- Ebm2024 - 757download Textbook Ebook Hacking Multifactor Authentication 1St Edition Roger A Grimes All Chapter PDFDocument43 pagesEbm2024 - 757download Textbook Ebook Hacking Multifactor Authentication 1St Edition Roger A Grimes All Chapter PDFjeff.thomas460100% (6)
- 5) Weblist of F.E. (Sem-Ii) (CBCS) (C-Scheme) - 18.03.24Document6 pages5) Weblist of F.E. (Sem-Ii) (CBCS) (C-Scheme) - 18.03.24Abhiraj AutiNo ratings yet
- Schneider PLC and Unity Pro XLDocument18 pagesSchneider PLC and Unity Pro XLSrinivas VenkatramanNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Legislation (B)Document6 pagesAircraft Legislation (B)Ade Yahya100% (1)
- UNESCO Form HR 5-1Document4 pagesUNESCO Form HR 5-1Junfei QianNo ratings yet
Special Education Timeline
Special Education Timeline
Uploaded by
api-483842715Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Special Education Timeline
Special Education Timeline
Uploaded by
api-483842715Copyright:
Available Formats
pecial Educatio
S n
Robin Ayers
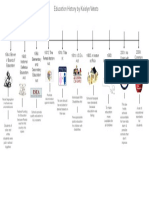
1954
BROWN V. BOARD
OF EDUCATION
Education starts to
become equal, due to
desegregating schools.
1970
EDUCATION OF THE
HANDICAPPED ACT
State grants expanded
the program for students
with disabilities. The
federal government
helped train special
education teachers by
providing money.
1972
PARC v. Commonwelath of PA
A Free and Appropriate Education
(FAPE) is required in schools.
1972
Mills v. Board of Education
It is unconstitutional to
deny students with disabilities
education.
1973
Section 504 of the
Rehabilitation Act
Students in federally funded special
education programs cannot be
discriminated against.
1975
Education for all Handicapped
Children Act
Money is provided by the federal
government for promised special education
programs. Individualized Education Plans (IEPs)
are required.
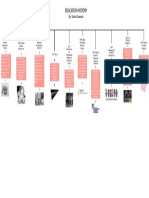
pecial Educatio
S n
Robin Ayers
1982
Henry Hudson School v. Rowley
It created a new interpretation of FAPE.
Students do not have to have maximum
support, but must have enough to
receive educational benefits.
1986
The Education of All
Handicapped Children Act
It lowered the age of eligibility of special
education programs to 3 years old. It
created early intervention methods for
ages birth-2.
1989
Timothy W v. Rochester
School District
Zero-Rejection Policy:
A child cannot be denied
special education services, no
matter how severe their
disabilities are.
1990
Individuals with Disabilities Act
Traumatic Brain Injuries and Autism
were added as to disabilities. Special
Education Programs range from 3-16
years old now. The "people first"
language is used now.
2002
No Child Left Behind Act
The government was held responsible for
the students low academic achievement.
Standardized testing began.
You might also like
- Aviation Clause Blue BookDocument128 pagesAviation Clause Blue BookSunil Kumar80% (5)
- The Spanish Tragedy LitChartDocument37 pagesThe Spanish Tragedy LitChartMODDASIR BHUIYAN MAHI100% (1)
- Dunn - Special Education For The Midly Retarded - Is Much of JustificableDocument18 pagesDunn - Special Education For The Midly Retarded - Is Much of JustificableMauricio PocasangreNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Special Education TimelineDocument5 pagesActivity 1 Special Education TimelinejaneNo ratings yet
- Organization and Administration of Special Education ProgramsDocument10 pagesOrganization and Administration of Special Education ProgramsMj Ong Pierson Garbo100% (1)
- Pre Trial Brief Petition For Declaration of Nullity of MarriageDocument5 pagesPre Trial Brief Petition For Declaration of Nullity of Marriageboniglai5100% (1)
- Historical TimelineDocument21 pagesHistorical TimelineMariell Mae GamitNo ratings yet
- Summary of ReportDocument5 pagesSummary of ReportKc Alecks V. BaliwasNo ratings yet
- On Historical Bases: A History On Educating Children With Disabilities in AmericaDocument2 pagesOn Historical Bases: A History On Educating Children With Disabilities in AmericaNnieh KhuuNo ratings yet
- Law ChartDocument2 pagesLaw Chartapi-659766270No ratings yet
- 201 History TimelineDocument2 pages201 History Timelineapi-458054294No ratings yet
- Education Timeline Edu 201Document1 pageEducation Timeline Edu 201api-548931113No ratings yet
- TimelineDocument2 pagesTimelineapi-325090049No ratings yet
- Foundation of Special and Inclusive EducationDocument11 pagesFoundation of Special and Inclusive EducationJeanlyNo ratings yet
- SNED 8 - Adapted Physical EducationDocument6 pagesSNED 8 - Adapted Physical EducationMarjorie MendozaNo ratings yet
- Education HistoryDocument1 pageEducation Historyapi-548899140No ratings yet
- What's Your IdeaDocument1 pageWhat's Your IdeadataliojhonmarkNo ratings yet
- Parts A B C and D of IdeaDocument2 pagesParts A B C and D of Ideaapi-582915098No ratings yet
- Foundation of Special & Inclusive EducationDocument10 pagesFoundation of Special & Inclusive EducationHazel GeronimoNo ratings yet
- PedaDocument12 pagesPedaJayanta BuragohainNo ratings yet
- Issue Brief - Inclusive Education in Malaysia 2014Document7 pagesIssue Brief - Inclusive Education in Malaysia 2014Fikri OthmanNo ratings yet
- UNICEF Inclusive Education MalaysiaDocument7 pagesUNICEF Inclusive Education MalaysiaZul4No ratings yet
- Education History by Von Eduardo OngDocument2 pagesEducation History by Von Eduardo Ongapi-548955489No ratings yet
- Inclusive Education Part 1 (BTVTED) FinalDocument54 pagesInclusive Education Part 1 (BTVTED) FinalChrissChan BelijionNo ratings yet
- Edu 201 Education History TimelineDocument1 pageEdu 201 Education History Timelineapi-597943088No ratings yet
- 5 Important Special Education LawsDocument2 pages5 Important Special Education LawsSheena Oro50% (2)
- Portfolio Project 5Document2 pagesPortfolio Project 5api-583146454No ratings yet
- Edu 201 Portfolio 8Document1 pageEdu 201 Portfolio 8api-450260025No ratings yet
- Special Edcation SlidesDocument19 pagesSpecial Edcation Slidesapi-534148197No ratings yet
- Historical FactsDocument8 pagesHistorical Factsapi-557330426No ratings yet
- When Special Education and Disability Studies Intertwine: Addressing Educational Inequities Through Processes and ProgrammingDocument5 pagesWhen Special Education and Disability Studies Intertwine: Addressing Educational Inequities Through Processes and ProgrammingIrish CataNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Project 8 Education History TimelineDocument12 pagesPortfolio Project 8 Education History Timelineapi-510584254No ratings yet
- Special Education For Young Learners With Disabilities: Moving ForwardDocument12 pagesSpecial Education For Young Learners With Disabilities: Moving ForwardAliveNo ratings yet
- Assessment in The Situation of Early Childhood Special Education and Inclusive Education in The PhilippinesDocument9 pagesAssessment in The Situation of Early Childhood Special Education and Inclusive Education in The PhilippinesShailyn PorrasNo ratings yet
- Legal Basis of Sped in The Philippines and AbroadDocument28 pagesLegal Basis of Sped in The Philippines and AbroadShiela Juno100% (1)
- Task 2Document6 pagesTask 2Mariell Mae GamitNo ratings yet
- Module For RecitationDocument15 pagesModule For Recitationariannerose gonzalesNo ratings yet
- Inclusive Education Group 1 PPT - 20240425 - 091229 - 0000Document38 pagesInclusive Education Group 1 PPT - 20240425 - 091229 - 0000abesamis jaysonNo ratings yet
- Policy For Special Educators in Himachal Pradesh Drafted by Vijay HeerDocument25 pagesPolicy For Special Educators in Himachal Pradesh Drafted by Vijay HeerVIJAY KUMAR HEER100% (1)
- Historical and Legal Foundation of Special Education 1Document7 pagesHistorical and Legal Foundation of Special Education 1Ma Sherhan DolitNo ratings yet
- 1 FINAL Legal Foundations of Special Education TE PDFDocument20 pages1 FINAL Legal Foundations of Special Education TE PDFClaud HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Inclusive and Special Education Powerpoint ReportDocument21 pagesInclusive and Special Education Powerpoint ReportKe Ann Libradilla100% (1)
- What InclusiveDocument28 pagesWhat InclusiveAmusstaphaNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing The Accessibility of Education For Children With Disabilities in IndiaDocument14 pagesFactors Influencing The Accessibility of Education For Children With Disabilities in Indiayelai gutangNo ratings yet
- History Timeline of Special and Inclusive EducationDocument3 pagesHistory Timeline of Special and Inclusive EducationJonnel GadinganNo ratings yet
- Smita SarkarDocument21 pagesSmita SarkarAshutosh MishraNo ratings yet
- Foundation of Special and Inclusive Education Profed 604: Submitted By: Laika E. RamirezDocument9 pagesFoundation of Special and Inclusive Education Profed 604: Submitted By: Laika E. RamirezARCTIC FLAMENo ratings yet
- Inclusive Education Module 1 (Final Term)Document13 pagesInclusive Education Module 1 (Final Term)ChrissChan BelijionNo ratings yet
- Inclusive Education PresentationDocument26 pagesInclusive Education PresentationecahNo ratings yet
- Vision Policy Goal and ObjectivesDocument15 pagesVision Policy Goal and ObjectivesMary Jean Satorre100% (4)
- What Is Special Education?: Teacher Dodie M. de CastroDocument31 pagesWhat Is Special Education?: Teacher Dodie M. de CastroHearthy AnneNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Project 5Document1 pagePortfolio Project 5api-502037979No ratings yet
- Special Education Programs in The United States Were Made Mandatory in 1975 When TheDocument2 pagesSpecial Education Programs in The United States Were Made Mandatory in 1975 When TheBian Marie Morales ReyesNo ratings yet
- Special and Inclusive EducationDocument4 pagesSpecial and Inclusive EducationLorielyn ToledoNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0738059316300888 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0738059316300888 MainMehar KahlonNo ratings yet
- USUK SEMINAR 3 EditedDocument18 pagesUSUK SEMINAR 3 Editedhoài thương nguyễnNo ratings yet
- 25 Yrs of Educating Children With Disabilities Thru IDEADocument6 pages25 Yrs of Educating Children With Disabilities Thru IDEASami HartsfieldNo ratings yet
- Mod 1Document9 pagesMod 1Loy HermosoNo ratings yet
- Edu 201 Portfolio 8Document2 pagesEdu 201 Portfolio 8api-297539374No ratings yet
- Education History by Kathleen GilmoreDocument1 pageEducation History by Kathleen Gilmoreapi-371352151No ratings yet
- Const Provisions On EducationDocument14 pagesConst Provisions On EducationAnuragKumarNo ratings yet
- EducationDocument2 pagesEducationKaylie WilsonNo ratings yet
- Educating Learners With Visual Impairment In ZambiaFrom EverandEducating Learners With Visual Impairment In ZambiaRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Final Project Outline 1Document2 pagesFinal Project Outline 1api-483842715No ratings yet
- Evidence 7 (Rubric 12) : Provide Student Feedback To Guide LearningDocument4 pagesEvidence 7 (Rubric 12) : Provide Student Feedback To Guide Learningapi-483842715No ratings yet
- Observational NotesDocument4 pagesObservational Notesapi-483842715No ratings yet
- Elements of A Lesson Plan Lesson Plan: Rhythm Tree by Kathy Neri (Grade 6)Document3 pagesElements of A Lesson Plan Lesson Plan: Rhythm Tree by Kathy Neri (Grade 6)api-483842715No ratings yet
- Strategies at A GlanceDocument13 pagesStrategies at A Glanceapi-483842715No ratings yet
- Focused Listing Study GuideDocument4 pagesFocused Listing Study Guideapi-483842715No ratings yet
- Paper To Ecdis Flyer 72dpi RGBDocument4 pagesPaper To Ecdis Flyer 72dpi RGBJoshua KinneyNo ratings yet
- OSSTETDocument1 pageOSSTETsitabehera12345678No ratings yet
- General Catechism FINALDocument16 pagesGeneral Catechism FINALRonnie EspirituNo ratings yet
- Entry Test IELTSDocument4 pagesEntry Test IELTStrangNo ratings yet
- Jenkins 071603 Conflicts EPA WTC PanelDocument207 pagesJenkins 071603 Conflicts EPA WTC PanelEnviroCatNo ratings yet
- CPA REVIEW Questions - LAMBERSDocument51 pagesCPA REVIEW Questions - LAMBERSAlellie Khay JordanNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Microfinance in IndiaDocument21 pagesEvolution of Microfinance in Indiakrnkk8812No ratings yet
- Lumify Tablet Compatibility: Screen Size Weight Approximate Continuous Scan Time Connectivity Options Internal StorageDocument1 pageLumify Tablet Compatibility: Screen Size Weight Approximate Continuous Scan Time Connectivity Options Internal StorageUmi RehanNo ratings yet
- Pengalaman Penjamin Emisi: Periode 2014 - 2018Document52 pagesPengalaman Penjamin Emisi: Periode 2014 - 2018Chim ChimmyNo ratings yet
- Copyright Case DigestsDocument15 pagesCopyright Case DigestsJethro MataNo ratings yet
- Jerry Lewis Corruption FBI Investigation - 58C-LA-244141-30 Thru 33Document7 pagesJerry Lewis Corruption FBI Investigation - 58C-LA-244141-30 Thru 33CREWNo ratings yet
- Ch10 Power PointDocument35 pagesCh10 Power PointGriechel Librado - OcampoNo ratings yet
- Chapter9 10Document5 pagesChapter9 10Nyan Lynn HtunNo ratings yet
- General HOA Property Managment LetterDocument1 pageGeneral HOA Property Managment LetterAldenilo VieiraNo ratings yet
- Golden Ocean Group CaseDocument31 pagesGolden Ocean Group CaseDigital GenesisNo ratings yet
- Bodiongan v. CADocument2 pagesBodiongan v. CAWhere Did Macky GallegoNo ratings yet
- ST Francis de SalesDocument4 pagesST Francis de SalesMichael TemperanteNo ratings yet
- Uthman Bin Muhammad Bin Uthman Bin Salih Ibn FodioDocument3 pagesUthman Bin Muhammad Bin Uthman Bin Salih Ibn FodiotoolzNo ratings yet
- AR AR FinancingDocument34 pagesAR AR FinancingDannis Anne RegajalNo ratings yet
- Ethnic Cleansing - War CrimeDocument13 pagesEthnic Cleansing - War Crimemike johnsonNo ratings yet
- Thailand Day 2Document51 pagesThailand Day 2Edsel BuletinNo ratings yet
- 2208238392Document1 page2208238392NEW GENERATIONSNo ratings yet
- Ebm2024 - 757download Textbook Ebook Hacking Multifactor Authentication 1St Edition Roger A Grimes All Chapter PDFDocument43 pagesEbm2024 - 757download Textbook Ebook Hacking Multifactor Authentication 1St Edition Roger A Grimes All Chapter PDFjeff.thomas460100% (6)
- 5) Weblist of F.E. (Sem-Ii) (CBCS) (C-Scheme) - 18.03.24Document6 pages5) Weblist of F.E. (Sem-Ii) (CBCS) (C-Scheme) - 18.03.24Abhiraj AutiNo ratings yet
- Schneider PLC and Unity Pro XLDocument18 pagesSchneider PLC and Unity Pro XLSrinivas VenkatramanNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Legislation (B)Document6 pagesAircraft Legislation (B)Ade Yahya100% (1)
- UNESCO Form HR 5-1Document4 pagesUNESCO Form HR 5-1Junfei QianNo ratings yet