Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Factors: Effect On Reaction Rate If Factor Is Reduced/Decreased Effect On Reaction Rate If Factor Is Raised/Increased
Factors: Effect On Reaction Rate If Factor Is Reduced/Decreased Effect On Reaction Rate If Factor Is Raised/Increased
Uploaded by
Alfie Lyn PedregosaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Factors: Effect On Reaction Rate If Factor Is Reduced/Decreased Effect On Reaction Rate If Factor Is Raised/Increased
Factors: Effect On Reaction Rate If Factor Is Reduced/Decreased Effect On Reaction Rate If Factor Is Raised/Increased
Uploaded by
Alfie Lyn PedregosaCopyright:
Available Formats
Alfie Lyn C. Pedregosa 11- St.
Ambrose
October 8,2021
EFFECT ON REACTION EFFECT ON REACTION BRIEF EXPLANATION AS TO WHY
FACTORS THESE FACTORS AFFECT ENZYME
RATE IF FACTOR IS RATE IF FACTOR IS FUNCTION AND REACTIONS
REDUCED/DECREASED RAISED/INCREASED RATES IN THAT WAY
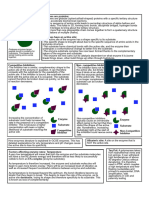
When all of the enzymes in the system As long as there is substrate to bind The concentration and activity of
bind to the substrate, the subsequent to, increasing enzyme concentration enzymes are directly proportional.
substrate molecules will have to wait will speed up the reaction. The Whether the substrate concentration
1. Enzyme Concentration until the enzyme becomes available reaction will no longer speed up is less than the enzyme
once the reaction is done. This means once all of the substrate has been concentration, hence lowering the
that the reaction rate will decrease bound, as there will be nothing for enzyme concentration has no effect
when the enzyme concentration also additional enzymes to bind to. on enzyme activity.
decreases.
If there is enough substrate, enzymes will
The enzyme becomes saturated with work optimally. As the concentration of
The enzymes have a lower chance of substrate as the concentration of substrate increases, so does the rate of
2. Substrate contacting the substrate when the substrate increases. More substrate enzyme activity. However, the rate of
enzyme activity is unlikely to increase
Concentration concentration is low and the activity or is accessible to bind and conduct
indefinitely. Because there is so much
rate of reaction is low. reaction as soon as the catalytic site
substrate, the enzymes will eventually
is empty. become saturated, and no additional
substrates will fit at the same time.
If the reaction rate factor is reduced at The inhibitor's efficacy is
low exposure levels, the inhibitor significantly reduced at high As a result, the substrate has been
3. Inhibitor Concentration significantly competes for the enzyme. substrate concentrations because unable to connect to the same active
the substrate outcompetes it due to site.
its higher concentration.
GENERAL BIOLOGY- WEEK 6
The rate of enzyme activity increases as
If this is not possible, lowering the As the temperature increases, so the temperature rises. Aside from that,
temperature can be used to reduce the does the vibrational energy, which when the enzyme is at its optimal
4. Temperature number of collisions and the kinetic strains the bonds in the enzyme temperature, it reaches the saturation
point. As the temperature rises, the active
energy available for activation energy. and substrate structures.
site of the enzyme changes shape,
resulting in a significant decrease in
activity. In fact, it’s been denatured for
quite some time.
As the size of the container
Reducing the size of the container: This increases, more particles are It has an impact on their evaluation.
places reactant closer to each other and exposed to the other reactant. With the same enzyme quality and
5. Size of Container they are more likely to encounter each There is a greater chance of substrate concentrations, the initial
other and react. particles colliding, resulting in reaction rate is the same in any size
more successful collisions per container.
second.
The structure of an enzyme's active
As pH decreases, the concentration of As the pH rises, the structure of site is affected by pH changes. Aside
hydrogen ions increases (the the enzyme's active site changes, from that, each enzyme is most
environment becomes more acidic). resulting in a significant reduction effective at a specific pH level. Truly,
6. pH in activity. the optimal pH for an enzyme is
determined by the environment in
which it operates.
You might also like
- Lab Report: EnzymesDocument6 pagesLab Report: EnzymesJim Goetz80% (25)
- HL Biology IA 20/24Document14 pagesHL Biology IA 20/24dev0% (1)
- Topic 2.5 Enzymes: U.1. Enzymes Have An Active Site To Which Specific Substrates BindDocument7 pagesTopic 2.5 Enzymes: U.1. Enzymes Have An Active Site To Which Specific Substrates BindMajo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument13 pagesEnzymesMaria adeelNo ratings yet
- Q2 WEEK 7 Factors Affecting Enzyme ActivityDocument2 pagesQ2 WEEK 7 Factors Affecting Enzyme ActivityFlorene GumapacNo ratings yet
- Maam ButronDocument2 pagesMaam ButronSlime slimeyNo ratings yet
- Module 9Document12 pagesModule 9Danielle Raven GarciaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Another Example of Proteins in Action Showing The Relationship Between Structure and FunctionDocument27 pagesEnzymes: Another Example of Proteins in Action Showing The Relationship Between Structure and FunctionAlan TaylorNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Enzymology (Bravo)Document11 pages1.1 Enzymology (Bravo)Arman Carl DulayNo ratings yet
- Module 9Document12 pagesModule 9Danielle Raven GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Enzymes: SummaryDocument3 pagesChapter 3: Enzymes: SummaryMerimaNo ratings yet
- Group-2 EnzymesDocument10 pagesGroup-2 EnzymesSophia BiacoNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Are Always: Compressed Notes Chapter 4: Biocatalysis Sb025Document7 pagesEnzymes Are Always: Compressed Notes Chapter 4: Biocatalysis Sb025LIM ZHI SHUENNo ratings yet
- Dwadwadwad MogmahdDocument5 pagesDwadwadwad Mogmahdyahia suhaibNo ratings yet
- 1.7 1.8 1.9 Enzyme Action and InhibitionDocument2 pages1.7 1.8 1.9 Enzyme Action and InhibitionHroaldrNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Enzymes ActivityDocument11 pagesFactors Affecting Enzymes ActivityZubair AslamNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Enzyme Skeleton NotesDocument8 pages2.5 Enzyme Skeleton Notesadri baigorriNo ratings yet
- Activities On Biological MoleculesDocument4 pagesActivities On Biological MoleculesgabrielquilarioNo ratings yet
- 1.2 EnzymesDocument4 pages1.2 EnzymesMohammed RagabNo ratings yet
- Enzyme: Mode of Action of EnzymeDocument5 pagesEnzyme: Mode of Action of EnzymeAliza KhanNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Reading in ScienceDocument3 pagesEnzymes Reading in SciencecinsssNo ratings yet
- Enzymes ReviewerDocument2 pagesEnzymes ReviewerAshley MalolotNo ratings yet
- Enzyme ActivityDocument3 pagesEnzyme ActivityNabindra Ruwali100% (2)
- Factors Affecting Enzyme ActivityDocument3 pagesFactors Affecting Enzyme ActivitySemwezi EnockNo ratings yet
- 3 EnzymesDocument3 pages3 EnzymesTala AlkhawajaNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Enzyme ActivityDocument2 pagesFactors Affecting Enzyme ActivityRebekka BermudezNo ratings yet
- AQA A-Level Biology EnzymesDocument6 pagesAQA A-Level Biology EnzymesMina BeeNo ratings yet
- 2.5 EnzymesDocument5 pages2.5 EnzymeslhabNo ratings yet
- Biorevise Notes MAINDocument34 pagesBiorevise Notes MAINRS JNo ratings yet
- 20 Sayed-Modinur-Rahaman MicrobiologyDocument14 pages20 Sayed-Modinur-Rahaman Microbiologymuruganunofficial00No ratings yet
- Enzymatic Test Reaction Biochem Report Group 12Document7 pagesEnzymatic Test Reaction Biochem Report Group 12almira garciaNo ratings yet
- Essential Idea: Enzymes Control The Metabolism of The Cell.: Sigma-Nicholson Metabolic Pathways ChartDocument21 pagesEssential Idea: Enzymes Control The Metabolism of The Cell.: Sigma-Nicholson Metabolic Pathways ChartMike BevanNo ratings yet
- Enzyme KineticsDocument3 pagesEnzyme KineticsJay GaleNo ratings yet
- EnzymeDocument4 pagesEnzymeLaurence PriscillaNo ratings yet
- EnzymeDocument16 pagesEnzymeZEE zee100% (2)
- Module 1 - Enzymes PDFDocument5 pagesModule 1 - Enzymes PDFJenny GoNo ratings yet
- 5 - EnzymesDocument3 pages5 - EnzymesAvyay TopraniNo ratings yet
- Jessica Lee Enzyme LabDocument15 pagesJessica Lee Enzyme LabAshalee JonesNo ratings yet
- Complete Figure Factors Affecting The Rate of Enzymatic ReactionDocument3 pagesComplete Figure Factors Affecting The Rate of Enzymatic ReactionKim NamjoonNo ratings yet
- EnzymeDocument31 pagesEnzymemiriam harriottNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Lab Theory DiscussionDocument4 pagesEnzyme Lab Theory DiscussionQuade FrancesNo ratings yet
- 5.2 - Effects of Substrate and Enzyme ConcentrationDocument2 pages5.2 - Effects of Substrate and Enzyme ConcentrationyessirrrrNo ratings yet
- 5 - EnzymesDocument5 pages5 - EnzymesIce CoffeeNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument16 pagesEnzymesRand HusseinNo ratings yet
- BioA4 04. Enzymes and MetabolismDocument8 pagesBioA4 04. Enzymes and Metabolismthanks btNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Reading and AssignmentDocument4 pagesEnzyme Reading and AssignmentJessica AminiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 A EnzymesDocument3 pagesUnit 3 A EnzymesseecatpNo ratings yet
- Enzymes IGCSE 2023Document11 pagesEnzymes IGCSE 2023chiwooutlook.com.jNo ratings yet
- As Unit 1 Jan 2024Document45 pagesAs Unit 1 Jan 2024Omar AlnaggarNo ratings yet
- Factors That Affect Enzyme Activity 101Document1 pageFactors That Affect Enzyme Activity 101Funtilar Mary FransNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument4 pagesEnzymesii15021No ratings yet
- Rev Notes ch04 eDocument5 pagesRev Notes ch04 ekathk2016No ratings yet
- Enzymes UpdatedDocument34 pagesEnzymes UpdatedLena WęglarzNo ratings yet
- Enzyme and Its Substrate and The Formation of A ProductDocument4 pagesEnzyme and Its Substrate and The Formation of A ProductMehul GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-Enzymes Part IDocument4 pagesLesson 1-Enzymes Part IAbbigail Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- GEN BIOLOGY 1 Deptal 2nd Quarter Exam ReviewerDocument3 pagesGEN BIOLOGY 1 Deptal 2nd Quarter Exam ReviewerVanessa JimenezNo ratings yet
- Bio NotesDocument14 pagesBio Notesreetir247No ratings yet
- Enzymatic Test ReactionDocument4 pagesEnzymatic Test Reactionalmira garciaNo ratings yet
- ENZYMESDocument18 pagesENZYMESJennifer DesRochersNo ratings yet
- Lec1 - CLINICAL ENZYMOLOGYDocument5 pagesLec1 - CLINICAL ENZYMOLOGYClaire GonoNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Kinetics and Equilibrium with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Kinetics and Equilibrium with AnswersNo ratings yet
- BIOL 202 MIDTERM Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument5 pagesBIOL 202 MIDTERM Cheat Sheet: by ViaAlfie Lyn PedregosaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Ms. Aira VertudazoDocument27 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Ms. Aira VertudazoAlfie Lyn PedregosaNo ratings yet
- EMTECH 2nd Grading 1Document6 pagesEMTECH 2nd Grading 1Alfie Lyn PedregosaNo ratings yet
- PEH Week 4: Sedentary (Inactive Lifestyle)Document4 pagesPEH Week 4: Sedentary (Inactive Lifestyle)Alfie Lyn PedregosaNo ratings yet
- 4th Unit AssessmentDocument7 pages4th Unit AssessmentAlfie Lyn PedregosaNo ratings yet
- One Mile Walk Exercise: TeacherDocument4 pagesOne Mile Walk Exercise: TeacherAlfie Lyn PedregosaNo ratings yet
- Solar SystemDocument2 pagesSolar SystemAlfie Lyn PedregosaNo ratings yet
- Peh Week 7: Safety Protocol During MVPA'sDocument7 pagesPeh Week 7: Safety Protocol During MVPA'sAlfie Lyn PedregosaNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication NotesDocument5 pagesOral Communication NotesAlfie Lyn PedregosaNo ratings yet
- GENERAL BIOLOGY 1 NotesDocument4 pagesGENERAL BIOLOGY 1 NotesAlfie Lyn PedregosaNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRYDocument10 pagesBIOCHEMISTRYShaira Kaye AlimariNo ratings yet
- Living Organisms and The Environment PDFDocument29 pagesLiving Organisms and The Environment PDFOsmany MadrigalNo ratings yet
- B.Tech. Chemical Engineering PDFDocument70 pagesB.Tech. Chemical Engineering PDFJogi BogiNo ratings yet
- Official - ncm1004 - Harlequin Listeria Chromogenic Agar According To Ottaviani and Agosti - Technical Specifications - en UsDocument3 pagesOfficial - ncm1004 - Harlequin Listeria Chromogenic Agar According To Ottaviani and Agosti - Technical Specifications - en UsJessica ChavezNo ratings yet
- Bio LabDocument13 pagesBio LabkanishkaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology An Introduction 12Th Edition Tortora Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesMicrobiology An Introduction 12Th Edition Tortora Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFreba.alexander170100% (11)
- Chemicals of LifeDocument77 pagesChemicals of LifeHemant KumarNo ratings yet
- Katzung Trevors Pharmacology Examination and Board Review 12Th Edition Bertram G Katzung Full ChapterDocument51 pagesKatzung Trevors Pharmacology Examination and Board Review 12Th Edition Bertram G Katzung Full Chapterraymond.doyle127100% (8)
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2api-304486052No ratings yet
- Bio3110 - Biochemistry Ii-Intermediary Metabolism Enzyme and Enzyme KineticsDocument11 pagesBio3110 - Biochemistry Ii-Intermediary Metabolism Enzyme and Enzyme KineticsNaiomiNo ratings yet
- SPM 2011 English For Science and Technology 2Document14 pagesSPM 2011 English For Science and Technology 2Vixtor Ishmael HoNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 - Enzyme Kinetics-Part-4 PDFDocument20 pagesChapter-3 - Enzyme Kinetics-Part-4 PDFShivam AnandNo ratings yet
- Aktu Syllabus Bpharm 2nd Sem PDFDocument21 pagesAktu Syllabus Bpharm 2nd Sem PDFAnkit Kumar100% (1)
- 12NitbaniEtal2016OJC Vol32 No6 P 3113-3120Document9 pages12NitbaniEtal2016OJC Vol32 No6 P 3113-3120Muhammad AzkaNo ratings yet
- 7.013 Recitation 3 - Spring 2015: Summary of Lecture 4Document5 pages7.013 Recitation 3 - Spring 2015: Summary of Lecture 4CeriseNo ratings yet
- Protein Models 3Document16 pagesProtein Models 3dkisNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Module 8 Q1Document21 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Module 8 Q1Pril Gueta100% (4)
- Test-34 With KeyDocument27 pagesTest-34 With KeyIllahi Bakhsh MariNo ratings yet
- ENZYMOLOGYDocument71 pagesENZYMOLOGYJay Andrea Vea IsraelNo ratings yet
- Biological Chemistry (Concept To Remember)Document8 pagesBiological Chemistry (Concept To Remember)Kecilyn AmbrocioNo ratings yet
- The Organic Chemistry of Enzyme-Catalyzed Reactions: Revised EditionDocument63 pagesThe Organic Chemistry of Enzyme-Catalyzed Reactions: Revised EditionApocalypto StatumNo ratings yet
- How Enzymes Work - CIE IGCSE Biology Revision NotesDocument8 pagesHow Enzymes Work - CIE IGCSE Biology Revision Notesamna siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Modified Hyaluronic Acid in Terms of Rheology, Enzymatic Degradation and MucoadhesionDocument7 pagesEvaluation of Modified Hyaluronic Acid in Terms of Rheology, Enzymatic Degradation and MucoadhesionSolcan RamonaNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Metabolism PDFDocument10 pagesAn Introduction To Metabolism PDFVidanes, Earl JosephNo ratings yet
- Em Brewing Guide and ApplicationsDocument12 pagesEm Brewing Guide and ApplicationsDavidNo ratings yet
- Future Perspectives in Catalyst PDFDocument84 pagesFuture Perspectives in Catalyst PDFdie_1No ratings yet
- Indonesian Journal of Chemical ResearchDocument7 pagesIndonesian Journal of Chemical Researcho cindy glaudiaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Modeling of The Enantioselectivity in Lipase-Catalyzed Transesterification ReactionsDocument12 pagesMolecular Modeling of The Enantioselectivity in Lipase-Catalyzed Transesterification ReactionsDavid AlvarezNo ratings yet