Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.1 AC Power Generation
1.1 AC Power Generation
Uploaded by
Leojhun Palisoc0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views62 pagesThe document discusses different methods of power generation in the Philippines including hydroelectric, geothermal, oil-fired, gas-fired, solar, and wind. It then explains the basic principles of AC power generation, how an AC generator works using Faraday's Law of induction and Lenz's Law. Key aspects of AC generation such as waveforms and frequency are also covered at a high level.
Original Description:
Original Title
1.1 AC power generation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses different methods of power generation in the Philippines including hydroelectric, geothermal, oil-fired, gas-fired, solar, and wind. It then explains the basic principles of AC power generation, how an AC generator works using Faraday's Law of induction and Lenz's Law. Key aspects of AC generation such as waveforms and frequency are also covered at a high level.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views62 pages1.1 AC Power Generation
1.1 AC Power Generation
Uploaded by
Leojhun PalisocThe document discusses different methods of power generation in the Philippines including hydroelectric, geothermal, oil-fired, gas-fired, solar, and wind. It then explains the basic principles of AC power generation, how an AC generator works using Faraday's Law of induction and Lenz's Law. Key aspects of AC generation such as waveforms and frequency are also covered at a high level.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 62
ABE 150
AB Electrification & Control
Systems
AC Generation
AC Power Generation
Power Generation in the Philippines
• Hydroelectric
• Geothermal
• Oil-fired
• Gas-fired
• Solar
• Wind
Power Generation
1. Friction
2. Pressure
3. Heat
4. Light
5. Chemical Action
6. Magnetism
AC generator / Alternator Operation
AC vs. DC
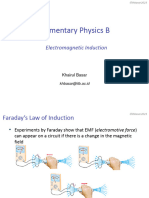
Faraday’s Law
• The voltage induced in an
electric circuit is
proportional to the time
rate of change of the flux
of the magnetic induction
linked with the circuit
• The magnitude of the
induced voltage is directly
proportional to the rate
of change of current
Lenz’s law
• The polarity of the
induced voltage must be
such that any current
resulting from it will
develop a flux that tends
to oppose any change in
the original flux
• Result of Faraday’s law of
induction
AC Generation
AC Generation
AC Generation
AC Generation
AC Generation
AC Generation
AC Generation
AC Generation
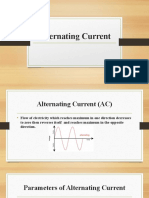
AC waveforms
• When an alternator
produces AC voltage,
the voltage switches
polarity over time in a
particular manner
• When graphed over
time, the “wave”
traced by this voltage
takes the shape of a
Frequency – number of wave cycles completed in one (1)
sine wave. second (Hertz, Hz)
Ex. RP – 60 Hz; Japan 50 Hz
You might also like
- Chapter 2 Lesson 5 - Perpetuity, Capitalized Cost, Amortization, Uniform Arithmetic GradientDocument11 pagesChapter 2 Lesson 5 - Perpetuity, Capitalized Cost, Amortization, Uniform Arithmetic GradientLeojhun PalisocNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Electromagnetic LawsDocument40 pagesLesson 7 Electromagnetic LawsMichael KaranuNo ratings yet
- ElectromagnetismDocument59 pagesElectromagnetismduhaalshwier21No ratings yet
- RT 102 Self InducDocument16 pagesRT 102 Self InducdvdmegaNo ratings yet
- "Introduction": AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsDocument14 pages"Introduction": AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsSyed HaiderNo ratings yet
- 533c69bff4a152f9f6b4c88516e8a3c837d4fcfa564031f5bd7a87adabd4f3bc Transformer (3)Document12 pages533c69bff4a152f9f6b4c88516e8a3c837d4fcfa564031f5bd7a87adabd4f3bc Transformer (3)sakshamparihar2604No ratings yet
- Actavis Notes - Session6 - Elex (Compatibility Mode)Document14 pagesActavis Notes - Session6 - Elex (Compatibility Mode)Alfred GaleaNo ratings yet
- 1 Electromagnetic InductionDocument19 pages1 Electromagnetic InductiondbgareslNo ratings yet
- AC THEORY (Simplified)Document37 pagesAC THEORY (Simplified)Pseudo ?No ratings yet
- Rt10 ReviewerDocument3 pagesRt10 Reviewercorrainnejimenez.24No ratings yet
- TransformerDocument9 pagesTransformerVeankatapathy 613 Xl group BNo ratings yet
- DC FundamentalsDocument19 pagesDC FundamentalsAman TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous Instruments - FinalDocument18 pagesMiscellaneous Instruments - FinalAdityaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 PH128 Faraday Law of InductionDocument43 pagesLecture 3 PH128 Faraday Law of InductionKennedy Oswald AikaruwaNo ratings yet
- B07-Electromagnetic InductionDocument22 pagesB07-Electromagnetic InductionFikriZainNo ratings yet
- Fee 06Document29 pagesFee 06Enma AiNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current Elex 3Document34 pagesAlternating Current Elex 3Edward NoconNo ratings yet
- Lecture-5 (Electromagnetism)Document10 pagesLecture-5 (Electromagnetism)Shahriar ShamsNo ratings yet
- Harmonics Mitigation Solution & Myths PDFDocument44 pagesHarmonics Mitigation Solution & Myths PDFGauravRautNo ratings yet
- Direct Current Elex 2Document39 pagesDirect Current Elex 2Edward NoconNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 PDFDocument44 pagesChapter 7 PDFDanial JuniorNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering: (CUTM1057)Document26 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering: (CUTM1057)Yedla Santosh kumarNo ratings yet
- Tel 007 - c1 - Resistors, Capacitors, Inductance CoilDocument20 pagesTel 007 - c1 - Resistors, Capacitors, Inductance CoilMUHAMMAD DZAKIRIN HANNAN NORASHIDNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 1 - Alternating CurrentDocument39 pagesTOPIC 1 - Alternating CurrentF1038 IFFAH SYAZANA BINTI MD HASNIN HADINo ratings yet
- Chapter1 PDFDocument65 pagesChapter1 PDFAugustine JR RobertNo ratings yet
- Electrical Terms in WeldingDocument11 pagesElectrical Terms in WeldingRaviNo ratings yet
- Lecture 31 - Chapter 22 Part 4Document10 pagesLecture 31 - Chapter 22 Part 4Mircea PanteaNo ratings yet
- Alternator - and - Its - Generated - VoltageDocument8 pagesAlternator - and - Its - Generated - VoltageEpi FanioNo ratings yet
- Faraday's LawDocument12 pagesFaraday's LawsNo ratings yet
- Capacitor in ACDocument21 pagesCapacitor in ACTrex JoblinNo ratings yet
- Presentation (Autosaved)Document17 pagesPresentation (Autosaved)Muhammad Hamza Mujeeb AhmadNo ratings yet
- Resource Pack - Ac TheoryDocument12 pagesResource Pack - Ac TheoryiirshadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 ETT 05112 Magnetic InductinDocument28 pagesLecture 6 ETT 05112 Magnetic Inductinsebastian hezronNo ratings yet
- Avte 114 AcDocument17 pagesAvte 114 AcPamela Bianca PalatinoNo ratings yet
- Principles of Alternating Current: By: Rekhnor S. MagbanuaDocument10 pagesPrinciples of Alternating Current: By: Rekhnor S. Magbanuarekhnor magbanuaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction: - Emf Is Induced in A Conductor Placed in A Magnetic Field Whenever There IsDocument51 pagesElectromagnetic Induction: - Emf Is Induced in A Conductor Placed in A Magnetic Field Whenever There IseltytanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - Electromagnetic InductionDocument21 pagesChapter 14 - Electromagnetic InductionMACKENRY KEVIN ARCENONo ratings yet
- TransformersDocument9 pagesTransformersapi-3839240No ratings yet
- Transformers: Los: Know What An Alternating Current Is. See A Transformer in Operation. Use The Transformer EquationDocument9 pagesTransformers: Los: Know What An Alternating Current Is. See A Transformer in Operation. Use The Transformer EquationterryhoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20Document59 pagesChapter 20Wahifol Wazri A WahabNo ratings yet
- CH 20 InductanceDocument42 pagesCH 20 Inductancerobomango0625No ratings yet
- Faraday's Electeomagnetic Induction.Document5 pagesFaraday's Electeomagnetic Induction.Rajesh JagadeesanNo ratings yet
- 5.2.C GenBasicsDocument8 pages5.2.C GenBasicsmaherNo ratings yet
- Induction and TransformerDocument32 pagesInduction and TransformerthomasaquinasrevannoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 Magnetic Induction - Lecture 12Document28 pagesChapter 21 Magnetic Induction - Lecture 12marcoserasmoNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of AC CircuitDocument19 pagesFundamental of AC CircuitAflatun KawserNo ratings yet
- Basic of Sine Wave 001Document8 pagesBasic of Sine Wave 001Mohammad Abdul MannanNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction: Chap 28Document28 pagesElectromagnetic Induction: Chap 28vibhakar4uNo ratings yet
- Generation of Alternating Voltages and Currents: AC FundamentalsDocument56 pagesGeneration of Alternating Voltages and Currents: AC FundamentalsLovelly ViniNo ratings yet
- Intro To EC - LVL IIDocument133 pagesIntro To EC - LVL IINDT GMFNo ratings yet
- Handout 3 Electrochemical MeasurementsDocument21 pagesHandout 3 Electrochemical MeasurementsJayaganthan IITMNo ratings yet
- PQ Lecture Chapter 1Document15 pagesPQ Lecture Chapter 1Sameep KhanalNo ratings yet
- Electronics Question BankDocument79 pagesElectronics Question BankElman CabacangNo ratings yet
- Theory of Operation of Single Phase Transformer - Custom Coils - CLIENTDocument8 pagesTheory of Operation of Single Phase Transformer - Custom Coils - CLIENTcustomcoilsNo ratings yet
- Bloch OscillationsDocument16 pagesBloch OscillationsrkluftingerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electronics Instrument: Digital Multimeter DMMDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Electronics Instrument: Digital Multimeter DMMUzair AzziNo ratings yet
- I. Electrical Systems: Ar. Harvin Julius Lasquero, Uap Ar. Earl Quinn Varilla, UapDocument70 pagesI. Electrical Systems: Ar. Harvin Julius Lasquero, Uap Ar. Earl Quinn Varilla, Uapjomarie apolinarioNo ratings yet
- $Module4Lecture4A UploadedDocument41 pages$Module4Lecture4A Uploadedchaitanya kumarNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of ElectricityDocument31 pagesFundamentals of ElectricityGeley EysNo ratings yet
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- 1.5 Electric MotorsDocument64 pages1.5 Electric MotorsLeojhun PalisocNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Power GenerationDocument31 pages1.2 Power GenerationLeojhun PalisocNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Service SystemDocument17 pages1.4 Service SystemLeojhun PalisocNo ratings yet
- Exercise No 2-Areal Mean PrecipitationDocument4 pagesExercise No 2-Areal Mean PrecipitationLeojhun PalisocNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Circuit Safe Load GuidelinesDocument9 pages3.2 Circuit Safe Load GuidelinesLeojhun PalisocNo ratings yet
- The Black CatDocument9 pagesThe Black CatLeojhun PalisocNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Lesson 1 - DepreciationDocument13 pagesChapter 3 Lesson 1 - DepreciationLeojhun PalisocNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Lesson 2 - Economic Study MethodsDocument14 pagesChapter 3 Lesson 2 - Economic Study MethodsLeojhun PalisocNo ratings yet