Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Legend:: The Element Beryllium (Be)
Legend:: The Element Beryllium (Be)
Uploaded by
Deo Ramses BanzonCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Worksheet: Atoms, Isotopes, and Ions AtomsDocument2 pagesWorksheet: Atoms, Isotopes, and Ions AtomsLeo Torres GarcíaNo ratings yet
- 1-2 Atoms (Part 1)Document3 pages1-2 Atoms (Part 1)api-3734333No ratings yet
- AQA Physics Topic 4 Atomic Structure Knowledge OrganiserDocument2 pagesAQA Physics Topic 4 Atomic Structure Knowledge Organisergundavannessa27No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Knowledge Organiser - Foundation and HigherDocument2 pagesAtomic Structure Knowledge Organiser - Foundation and HigheranqelineeNo ratings yet
- AQA Physics Topic 4 Atomic Structure Knowledge OrganiserDocument3 pagesAQA Physics Topic 4 Atomic Structure Knowledge OrganiserGabriel HoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Exam Review Grade 11Document28 pagesChemistry Exam Review Grade 11markjohnmagcalengNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Chemistry Excursion WorkbookDocument15 pagesYear 11 Chemistry Excursion Workbookbobjess198No ratings yet
- Radioactivity 1Document2 pagesRadioactivity 1Aryan HossainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (Notes and Activities)Document10 pagesChapter 3 (Notes and Activities)Ahmed MutwakilNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Atom N RadioactivityDocument91 pagesNuclear Atom N RadioactivityLinaNo ratings yet
- Atomic PhysicsDocument130 pagesAtomic PhysicsAfnan CheemaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter No.4 Atomic Structure Notes: What Is An Atom?Document7 pagesChemistry Chapter No.4 Atomic Structure Notes: What Is An Atom?IlafNo ratings yet
- Apostila de An 2S11Document56 pagesApostila de An 2S11yebaho2182No ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument162 pagesAtomic StructurevaughanNo ratings yet
- Activities Unit 2 Physics and Chemistry. "The Composition of Matter" KEYSDocument4 pagesActivities Unit 2 Physics and Chemistry. "The Composition of Matter" KEYSgenusxyzNo ratings yet
- Emilia Sirbu - 01 BNSG AtomsDocument2 pagesEmilia Sirbu - 01 BNSG AtomsEmilia SirbuNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Elements and CompoundsDocument20 pagesAtoms, Elements and CompoundsMenaga Ilangkovan100% (1)
- Matter: Various S, Suc Objec S A Ound Yo Ased On CoDocument84 pagesMatter: Various S, Suc Objec S A Ound Yo Ased On Comaniramghimiresn23No ratings yet
- Prot ActiniumDocument13 pagesProt ActiniummikkasNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Key Concepts in Chemistry Revision 1Document1 pageTopic 1 Key Concepts in Chemistry Revision 1trishthamaheshwari01No ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument19 pagesAtomic StructureDarionNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Atomic Structure WorksheetDocument13 pagesUnit 6 Atomic Structure WorksheetMoiz BhattiNo ratings yet
- Form 4 25 RadioactivityDocument31 pagesForm 4 25 Radioactivityaegis4167No ratings yet
- 1 18 Atomic Physics The Nuclear AtomDocument18 pages1 18 Atomic Physics The Nuclear AtomRaheem Abdul ManyambaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Lecture 1234 PDFDocument58 pagesAtomic Structure Lecture 1234 PDFLokendra Shahi100% (1)
- Topic: Structure of AtomDocument27 pagesTopic: Structure of AtomKirsten De LeonNo ratings yet
- IARP Lecture Notes RSO-RA 2021Document125 pagesIARP Lecture Notes RSO-RA 2021DHARMENDRA SINGHNo ratings yet
- 2024 - Chapter3 - Atomic StructureDocument15 pages2024 - Chapter3 - Atomic Structurekaylamok3No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Nuclear RadiationDocument164 pagesChapter 3 Nuclear RadiationJoseph MabajenNo ratings yet
- Engineering ChemistryDocument272 pagesEngineering ChemistryPrem Kumar.DNo ratings yet
- 9 Ions-SDocument5 pages9 Ions-S776pmsfq2fNo ratings yet
- 0 DemoDocument22 pages0 DemoVasimNo ratings yet
- Subatomic Electric Charge Elementary Charge Nucleus Atom Neutrons Nucleons Atomic Number Element Ernest RutherfordDocument1 pageSubatomic Electric Charge Elementary Charge Nucleus Atom Neutrons Nucleons Atomic Number Element Ernest Rutherforddenerys2507986No ratings yet
- BMAT CHEMISTRY-c1-atomic structureDocument18 pagesBMAT CHEMISTRY-c1-atomic structureNapassorn WongduangpaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure WorksheetDocument12 pagesAtomic Structure WorksheetG TeenaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Radiation LeafletDocument2 pagesBasics of Radiation LeafletAhmed shabanNo ratings yet
- Welding ScienceDocument64 pagesWelding ScienceAthmane ManouNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Structure of AtomsDocument4 pagesChapter 5 - Structure of AtomsAdil Yaqub - 74665/TCHR/CNTBNo ratings yet
- 4 CO1 Waonl MQK Xy Shye HVDocument20 pages4 CO1 Waonl MQK Xy Shye HVRoshni BhaliyaNo ratings yet
- Topic 24. RadioactivityDocument25 pagesTopic 24. Radioactivitynotphoenix972No ratings yet
- Categories or Electric Materials P1 PDFDocument24 pagesCategories or Electric Materials P1 PDFZach VittoriNo ratings yet
- Topic:: STPM Term 1 ChemistryDocument47 pagesTopic:: STPM Term 1 ChemistryMenaga A/P IlangkovanNo ratings yet
- Radioactive Decay and Half LifeDocument30 pagesRadioactive Decay and Half LifeM Imran SheikhNo ratings yet
- Chemistry AssignmentDocument4 pagesChemistry AssignmentIqbal HaziqNo ratings yet
- All Notes ChemistryDocument205 pagesAll Notes ChemistrySeif MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Physics Knowledge Organiser Isotopes and Nuclear Radiation PDFDocument1 pageYear 10 Physics Knowledge Organiser Isotopes and Nuclear Radiation PDFmien namNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Module 1 3rd QuarterDocument4 pagesScience 8 Module 1 3rd QuarterSittie Ainah B. Macaumbao100% (1)
- Structure of An Atom NotesDocument7 pagesStructure of An Atom NotesRajesh Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Teng, Kin Weng - Chapter 10 - RadioactivityDocument25 pagesTeng, Kin Weng - Chapter 10 - RadioactivityFranciscaMesquitaNo ratings yet
- AtomicDocument41 pagesAtomicHassanKMNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Nuclear ChemistryDocument58 pagesLecture On Nuclear Chemistrysadia SultanaNo ratings yet
- 01. Atomic Models.pdfDocument6 pages01. Atomic Models.pdfkaranlodhi0552No ratings yet
- Atomic PhysicsDocument41 pagesAtomic PhysicsFaiq IrfanNo ratings yet
- Detection & Measurement of RadioactivityDocument7 pagesDetection & Measurement of RadioactivityChetan GandhiNo ratings yet
- ADDITIONAL RadioactivityDocument16 pagesADDITIONAL RadioactivityashensfaithNo ratings yet
- Updated - Physics 10Document28 pagesUpdated - Physics 10Ali Hussnain RazaNo ratings yet
- The Nuclear Atom: Created by Aadya and VivaanDocument7 pagesThe Nuclear Atom: Created by Aadya and VivaanvivaanNo ratings yet
- A. Where Is The Ion Charge Located in The Isotope Symbol?Document5 pagesA. Where Is The Ion Charge Located in The Isotope Symbol?rjainNo ratings yet
Legend:: The Element Beryllium (Be)
Legend:: The Element Beryllium (Be)
Uploaded by
Deo Ramses BanzonOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Legend:: The Element Beryllium (Be)
Legend:: The Element Beryllium (Be)
Uploaded by
Deo Ramses BanzonCopyright:
Available Formats
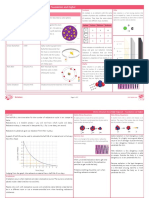
The Element Beryllium (Be)
Beryllium is a chemical element in the periodic table that has the symbol Be and atomic number 4. A toxic bivalent element,
beryllium is a steel grey, strong, light-weight yet brittle, alkaline earth metal, that is primarily used as a hardening agent in alloys
(most notably, beryllium copper).
The name beryllium comes from the Greek beryllos, beryl. At one time beryllium was referred to as glucinium (from
Greek glykys, sweet), due to the sweet taste of its salts. This element was discovered by Louis Vauquelin in 1798 as the oxide in beryl
and in emeralds. Friedrich Wöhler and A. A. Bussy independently isolatated the metal in 1828 by reacting potassium on beryllium
chloride.
Beryllium has one of the highest melting points of the light metals. The modulus of elasticity of beryllium is approximately 1/3
greater than that of steel. It has excellent thermal conductivity, is nonmagnetic and resists attack by concentrated nitric acid. It is
highly permeable to X-rays, and neutrons are liberated when it is hit by alpha particles, as from radium or polonium (about 30
neutrons/million alpha particles). At standard temperature and pressures beryllium resists oxidation when exposed to air (although its
ability to scratch glass is probably due to the formation of a thin layer of the oxide).
LEGEND
:
Proton
Neutron
Electon
You might also like
- Worksheet: Atoms, Isotopes, and Ions AtomsDocument2 pagesWorksheet: Atoms, Isotopes, and Ions AtomsLeo Torres GarcíaNo ratings yet
- 1-2 Atoms (Part 1)Document3 pages1-2 Atoms (Part 1)api-3734333No ratings yet
- AQA Physics Topic 4 Atomic Structure Knowledge OrganiserDocument2 pagesAQA Physics Topic 4 Atomic Structure Knowledge Organisergundavannessa27No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Knowledge Organiser - Foundation and HigherDocument2 pagesAtomic Structure Knowledge Organiser - Foundation and HigheranqelineeNo ratings yet
- AQA Physics Topic 4 Atomic Structure Knowledge OrganiserDocument3 pagesAQA Physics Topic 4 Atomic Structure Knowledge OrganiserGabriel HoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Exam Review Grade 11Document28 pagesChemistry Exam Review Grade 11markjohnmagcalengNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Chemistry Excursion WorkbookDocument15 pagesYear 11 Chemistry Excursion Workbookbobjess198No ratings yet
- Radioactivity 1Document2 pagesRadioactivity 1Aryan HossainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (Notes and Activities)Document10 pagesChapter 3 (Notes and Activities)Ahmed MutwakilNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Atom N RadioactivityDocument91 pagesNuclear Atom N RadioactivityLinaNo ratings yet
- Atomic PhysicsDocument130 pagesAtomic PhysicsAfnan CheemaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter No.4 Atomic Structure Notes: What Is An Atom?Document7 pagesChemistry Chapter No.4 Atomic Structure Notes: What Is An Atom?IlafNo ratings yet
- Apostila de An 2S11Document56 pagesApostila de An 2S11yebaho2182No ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument162 pagesAtomic StructurevaughanNo ratings yet
- Activities Unit 2 Physics and Chemistry. "The Composition of Matter" KEYSDocument4 pagesActivities Unit 2 Physics and Chemistry. "The Composition of Matter" KEYSgenusxyzNo ratings yet
- Emilia Sirbu - 01 BNSG AtomsDocument2 pagesEmilia Sirbu - 01 BNSG AtomsEmilia SirbuNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Elements and CompoundsDocument20 pagesAtoms, Elements and CompoundsMenaga Ilangkovan100% (1)
- Matter: Various S, Suc Objec S A Ound Yo Ased On CoDocument84 pagesMatter: Various S, Suc Objec S A Ound Yo Ased On Comaniramghimiresn23No ratings yet
- Prot ActiniumDocument13 pagesProt ActiniummikkasNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Key Concepts in Chemistry Revision 1Document1 pageTopic 1 Key Concepts in Chemistry Revision 1trishthamaheshwari01No ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument19 pagesAtomic StructureDarionNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Atomic Structure WorksheetDocument13 pagesUnit 6 Atomic Structure WorksheetMoiz BhattiNo ratings yet
- Form 4 25 RadioactivityDocument31 pagesForm 4 25 Radioactivityaegis4167No ratings yet
- 1 18 Atomic Physics The Nuclear AtomDocument18 pages1 18 Atomic Physics The Nuclear AtomRaheem Abdul ManyambaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Lecture 1234 PDFDocument58 pagesAtomic Structure Lecture 1234 PDFLokendra Shahi100% (1)
- Topic: Structure of AtomDocument27 pagesTopic: Structure of AtomKirsten De LeonNo ratings yet
- IARP Lecture Notes RSO-RA 2021Document125 pagesIARP Lecture Notes RSO-RA 2021DHARMENDRA SINGHNo ratings yet
- 2024 - Chapter3 - Atomic StructureDocument15 pages2024 - Chapter3 - Atomic Structurekaylamok3No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Nuclear RadiationDocument164 pagesChapter 3 Nuclear RadiationJoseph MabajenNo ratings yet
- Engineering ChemistryDocument272 pagesEngineering ChemistryPrem Kumar.DNo ratings yet
- 9 Ions-SDocument5 pages9 Ions-S776pmsfq2fNo ratings yet
- 0 DemoDocument22 pages0 DemoVasimNo ratings yet
- Subatomic Electric Charge Elementary Charge Nucleus Atom Neutrons Nucleons Atomic Number Element Ernest RutherfordDocument1 pageSubatomic Electric Charge Elementary Charge Nucleus Atom Neutrons Nucleons Atomic Number Element Ernest Rutherforddenerys2507986No ratings yet
- BMAT CHEMISTRY-c1-atomic structureDocument18 pagesBMAT CHEMISTRY-c1-atomic structureNapassorn WongduangpaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure WorksheetDocument12 pagesAtomic Structure WorksheetG TeenaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Radiation LeafletDocument2 pagesBasics of Radiation LeafletAhmed shabanNo ratings yet
- Welding ScienceDocument64 pagesWelding ScienceAthmane ManouNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Structure of AtomsDocument4 pagesChapter 5 - Structure of AtomsAdil Yaqub - 74665/TCHR/CNTBNo ratings yet
- 4 CO1 Waonl MQK Xy Shye HVDocument20 pages4 CO1 Waonl MQK Xy Shye HVRoshni BhaliyaNo ratings yet
- Topic 24. RadioactivityDocument25 pagesTopic 24. Radioactivitynotphoenix972No ratings yet
- Categories or Electric Materials P1 PDFDocument24 pagesCategories or Electric Materials P1 PDFZach VittoriNo ratings yet
- Topic:: STPM Term 1 ChemistryDocument47 pagesTopic:: STPM Term 1 ChemistryMenaga A/P IlangkovanNo ratings yet
- Radioactive Decay and Half LifeDocument30 pagesRadioactive Decay and Half LifeM Imran SheikhNo ratings yet
- Chemistry AssignmentDocument4 pagesChemistry AssignmentIqbal HaziqNo ratings yet
- All Notes ChemistryDocument205 pagesAll Notes ChemistrySeif MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Physics Knowledge Organiser Isotopes and Nuclear Radiation PDFDocument1 pageYear 10 Physics Knowledge Organiser Isotopes and Nuclear Radiation PDFmien namNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Module 1 3rd QuarterDocument4 pagesScience 8 Module 1 3rd QuarterSittie Ainah B. Macaumbao100% (1)
- Structure of An Atom NotesDocument7 pagesStructure of An Atom NotesRajesh Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Teng, Kin Weng - Chapter 10 - RadioactivityDocument25 pagesTeng, Kin Weng - Chapter 10 - RadioactivityFranciscaMesquitaNo ratings yet
- AtomicDocument41 pagesAtomicHassanKMNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Nuclear ChemistryDocument58 pagesLecture On Nuclear Chemistrysadia SultanaNo ratings yet
- 01. Atomic Models.pdfDocument6 pages01. Atomic Models.pdfkaranlodhi0552No ratings yet
- Atomic PhysicsDocument41 pagesAtomic PhysicsFaiq IrfanNo ratings yet
- Detection & Measurement of RadioactivityDocument7 pagesDetection & Measurement of RadioactivityChetan GandhiNo ratings yet
- ADDITIONAL RadioactivityDocument16 pagesADDITIONAL RadioactivityashensfaithNo ratings yet
- Updated - Physics 10Document28 pagesUpdated - Physics 10Ali Hussnain RazaNo ratings yet
- The Nuclear Atom: Created by Aadya and VivaanDocument7 pagesThe Nuclear Atom: Created by Aadya and VivaanvivaanNo ratings yet
- A. Where Is The Ion Charge Located in The Isotope Symbol?Document5 pagesA. Where Is The Ion Charge Located in The Isotope Symbol?rjainNo ratings yet