Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
311 viewsReflex Facilitation: Vol Control of Micturition (Corticol Areas) Control EUS & Abd M
Reflex Facilitation: Vol Control of Micturition (Corticol Areas) Control EUS & Abd M
Uploaded by
Tharani KumaraThe document discusses the neural control of micturition (urination). It describes the facilitatory and inhibitory areas in the brainstem that regulate bladder filling and emptying. The sacral spinal cord centers receive input from these brain areas to influence the micturition reflex threshold. Abnormalities can result in incontinence if the inhibitory input is damaged or denervation if the afferent or efferent nerves are destroyed. Spinal shock after transection initially causes an unresponsive bladder but micturition reflex may recover without voluntary control.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Anatomy & Physiology - Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy & Physiology - Nervous SystemChristine Marylou PalomoNo ratings yet
- Pseudobulbar Palsy Bulbar PalsyDocument5 pagesPseudobulbar Palsy Bulbar PalsyFajar Rudy QimindraNo ratings yet
- A&P - 2. Blood Vessels of The Brain (9p)Document9 pagesA&P - 2. Blood Vessels of The Brain (9p)Gabriel Stratulat100% (1)
- MicturitionDocument7 pagesMicturitionOsama MohamedNo ratings yet
- 1-Indroduction To EmbryologyDocument25 pages1-Indroduction To Embryologyselman P k100% (1)
- Assessing Neurologic System - FinalDocument66 pagesAssessing Neurologic System - FinalAngelo EstanislaoNo ratings yet
- HELLP!!!: A Case Study PresentationDocument32 pagesHELLP!!!: A Case Study PresentationMaria Nena BalagtasNo ratings yet
- Review Literature Journal: Institute of Nursing EducationDocument12 pagesReview Literature Journal: Institute of Nursing EducationEr Shah Rukh QadriNo ratings yet
- Neurological Health AssessmentDocument63 pagesNeurological Health AssessmentAhmed ElryahNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Nerve Fibers: Dr. Zara BatoolDocument30 pagesPhysiology of Nerve Fibers: Dr. Zara BatoolZuhaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular TransmissionDocument45 pagesNeuromuscular TransmissionparuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Human EyeDocument41 pagesAnatomy of Human EyeCarly MelachioNo ratings yet
- New Vertin CME Slides FinalDocument98 pagesNew Vertin CME Slides FinalGaurav KatariaNo ratings yet
- Mannitol: Half-Life Onset Peak DurationDocument3 pagesMannitol: Half-Life Onset Peak DurationAmit MartinNo ratings yet
- 4 - The Temporal LobesDocument37 pages4 - The Temporal LobesYasmeen Egbaria100% (1)
- NEURON ACTION POTENTIAL - PPT - ReadyDocument83 pagesNEURON ACTION POTENTIAL - PPT - Readyelle lee100% (1)
- Unit Plan B.Sc. (Nursing) I Year Nutrition (Proteins)Document5 pagesUnit Plan B.Sc. (Nursing) I Year Nutrition (Proteins)Abhilasha SolomonNo ratings yet
- Anatomo-Physiological Peculiarities of The Respiratory System. Percussion of The Lungs.Document40 pagesAnatomo-Physiological Peculiarities of The Respiratory System. Percussion of The Lungs.Hetvi PatelNo ratings yet
- Slides For SeizureDocument15 pagesSlides For SeizureBryan Mae H. Degorio100% (3)
- 300307814sherlin SapthicaDocument100 pages300307814sherlin SapthicaTitin PrihartiniNo ratings yet
- Chemo ReceptorDocument8 pagesChemo ReceptorCheryl Lyn SanchezNo ratings yet
- UNIT PLAN (1) ResearchDocument32 pagesUNIT PLAN (1) ResearchAshish GuptaNo ratings yet
- MyelographyDocument22 pagesMyelographyKarylleNo ratings yet
- Physiology of PainDocument43 pagesPhysiology of PainNashwan ANo ratings yet
- Ring Enhancing LesionsDocument50 pagesRing Enhancing LesionsVivek GuptaNo ratings yet
- Annotated Bibliography JayitaDocument5 pagesAnnotated Bibliography JayitaJayita Gayen DuttaNo ratings yet
- Basic Overview of NeurologyDocument45 pagesBasic Overview of NeurologyDith Rivelta CallahanthNo ratings yet
- Fatal SkullDocument30 pagesFatal SkullParitosh PaneriNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On Age-Related-Geriatrics-ProblemDocument11 pagesLesson Plan On Age-Related-Geriatrics-Problemmohamad dildarNo ratings yet
- Log Book - 2009.chDocument59 pagesLog Book - 2009.chsujinthomasNo ratings yet
- MSC Thesis FormatDocument4 pagesMSC Thesis FormatAnonymous o4OUZfNo ratings yet
- What Is An EEGDocument4 pagesWhat Is An EEGTanvi NaraNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviourDocument21 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviourSufian Khan100% (1)
- 5 FMCH Research BiasDocument3 pages5 FMCH Research BiasMia CadizNo ratings yet
- Micro TaechingDocument11 pagesMicro Taechingupma sharmaNo ratings yet
- Pharma Module 8Document5 pagesPharma Module 8Chelsy Sky SacanNo ratings yet
- Neuron Notes NewDocument35 pagesNeuron Notes NewBiologie Profesor100% (1)
- Anatomy of The BreastDocument6 pagesAnatomy of The BreastJuliana Andres100% (1)
- Anatomy of Nose andDocument29 pagesAnatomy of Nose andMuhammad Waqar UlfatNo ratings yet
- 1 Pain Sensation Physiology DR Ambreen TauseefDocument73 pages1 Pain Sensation Physiology DR Ambreen TauseefbilalNo ratings yet
- Lumbar Puncture: Bagasin, Nester James S. Rodriguez, Lourdes Erika ADocument32 pagesLumbar Puncture: Bagasin, Nester James S. Rodriguez, Lourdes Erika ANdor BariboloNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NeurophysiologyDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Neurophysiologyvenkata ramakrishnaiahNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Neurological SystemDocument26 pagesAssessment of Neurological SystemBatiao Camille Claire100% (1)
- Procedural Sedation in EDDocument41 pagesProcedural Sedation in EDadam NoheNo ratings yet
- Case Study FormateDocument38 pagesCase Study Formatepriyanka bhavsarNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan ON AppendicitisDocument14 pagesLesson Plan ON AppendicitisrevathyNo ratings yet
- Neurological Examination - BashaDocument8 pagesNeurological Examination - Bashakhaderbasha2020No ratings yet
- Causes Obstruction Causes CSF To Build Up in The Brain. If The Cause Is Congenital, Symptoms Such As AnDocument22 pagesCauses Obstruction Causes CSF To Build Up in The Brain. If The Cause Is Congenital, Symptoms Such As Anmhelandie100% (1)
- Malformation of Female Reproductive SystemDocument170 pagesMalformation of Female Reproductive SystemKriti BanstolaNo ratings yet
- Cerebellum and Brain Stem: DR Asim Shrestha SRCC Ped Neuro Fellow MumbaiDocument71 pagesCerebellum and Brain Stem: DR Asim Shrestha SRCC Ped Neuro Fellow MumbaiAsim ShresthaNo ratings yet
- The Aim of Ear, Nose and ThroatDocument32 pagesThe Aim of Ear, Nose and ThroatabdulNo ratings yet
- M.SC Nursing RequirementsDocument3 pagesM.SC Nursing RequirementsSDx Sujay Daliya100% (1)
- 63 Shock in Obstetrics & GynecologyDocument29 pages63 Shock in Obstetrics & GynecologyGodsonYeboah-AwudziNo ratings yet
- Dopaminergic and Serotonergic Neurohumoural TransmissionDocument23 pagesDopaminergic and Serotonergic Neurohumoural TransmissionChaitanya Kiran PullelaNo ratings yet
- BSCSyllabus 2019-20 PDFDocument251 pagesBSCSyllabus 2019-20 PDFAmrita Charlotte KapoorNo ratings yet
- Final Hernioplasty Compilation RevisedDocument58 pagesFinal Hernioplasty Compilation RevisedRaidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Venipuncture PDFDocument6 pagesVenipuncture PDFAnna GaturianNo ratings yet
- Special NeurologyDocument115 pagesSpecial NeurologyUbaidillah Romadlon Alfairuzi100% (1)
- Neurology: by Dennis Jason Alcantara, RN, USRN, MAN CanDocument213 pagesNeurology: by Dennis Jason Alcantara, RN, USRN, MAN CanKristel-Mia Dimalanta RamosNo ratings yet
- Consultant in Audiology: Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandConsultant in Audiology: Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular PhysiologyDocument7 pagesCardiovascular PhysiologyHabib UllahNo ratings yet
- Basics of Skin Lesions EntranceDocument22 pagesBasics of Skin Lesions EntranceMohammed AsifNo ratings yet
- Immunology and Serology Lec: Immunology - Study of The Immune System orDocument6 pagesImmunology and Serology Lec: Immunology - Study of The Immune System orAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Bibliografie: Vizitati WWW - Tocilar.ro ! Arhiva Online Cu Diplome, Cursuri Si Referate Postate de UtilizatoriDocument7 pagesBibliografie: Vizitati WWW - Tocilar.ro ! Arhiva Online Cu Diplome, Cursuri Si Referate Postate de UtilizatoriAndrutza AndraNo ratings yet
- Guide To Breast Self ExamsDocument7 pagesGuide To Breast Self Examsaamer_rasheed1571No ratings yet
- Immunology Review For FPGEEDocument8 pagesImmunology Review For FPGEEMina MinawyNo ratings yet
- 24 - Proprioception and Neuromuscular ControlDocument24 pages24 - Proprioception and Neuromuscular ControlCarlos Garcia100% (2)
- THE Excretory SystemDocument24 pagesTHE Excretory SystemZain HaiderNo ratings yet
- Notes in Science LT 10 - Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesNotes in Science LT 10 - Endocrine SystemAlven ReyNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Breast Milk ProductionDocument5 pagesPhysiology of Breast Milk ProductionIvyNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument18 pagesDigestive System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBDNo ratings yet
- M4vmvns3ua5zc1zzyn0sigr2Document2 pagesM4vmvns3ua5zc1zzyn0sigr2Sagar VashisthNo ratings yet
- Excretion and KidneysDocument39 pagesExcretion and KidneyselizabethNo ratings yet
- Nerve Cell - Cell ProjectDocument23 pagesNerve Cell - Cell Projectapi-327766139No ratings yet
- Natural World Series Science and Technology Biology.: Heart-The Heart Is A Part of The Circulatory SystemDocument8 pagesNatural World Series Science and Technology Biology.: Heart-The Heart Is A Part of The Circulatory SystemjowieNo ratings yet
- Horner'S Syndrome - : Far Eastern University - Nicanor Reyes Medical FoundationDocument3 pagesHorner'S Syndrome - : Far Eastern University - Nicanor Reyes Medical FoundationVictorija Evania Lucille DeldioNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Coronary Arteries and VeinsDocument80 pagesAnatomy of The Coronary Arteries and Veinstreelife111No ratings yet
- Q.P. Code: 801521Document15 pagesQ.P. Code: 801521CARDIAC SRINITHI DHANA DHARSHIKAA N100% (1)
- All Life Begins With A Single - .: A) Organ B) Microbe C) Tissue D) CellDocument18 pagesAll Life Begins With A Single - .: A) Organ B) Microbe C) Tissue D) CellRonalynAlonsabeBernadasNo ratings yet
- Renal PhysiologyDocument43 pagesRenal PhysiologyRabi SyedNo ratings yet
- ISAP Lecture 1 Module 1 - Studocu NotesDocument6 pagesISAP Lecture 1 Module 1 - Studocu NotesLyndonNo ratings yet
- The Clinical Significance of Subclinical Thyroid Dysfunction Bernadette Biondi and David S. Cooper PDFDocument56 pagesThe Clinical Significance of Subclinical Thyroid Dysfunction Bernadette Biondi and David S. Cooper PDFLorena IbarrolaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 ScienceDocument5 pagesGrade 8 ScienceChristian jade QuijanoNo ratings yet
- Class X LN - 6 Life Processes Work Sheet 20-21Document2 pagesClass X LN - 6 Life Processes Work Sheet 20-21Saraswathi GopalNo ratings yet
- Breast Chek Kit BookletDocument16 pagesBreast Chek Kit BookletPlexusNo ratings yet
- Feeding of Healthy Newborn BabiesDocument37 pagesFeeding of Healthy Newborn BabiesSulfie HarsNo ratings yet
- Histology of Sebaceous Glands and Nails by Dr. RoomiDocument10 pagesHistology of Sebaceous Glands and Nails by Dr. RoomiMudassar Roomi100% (1)
- Multiple-Choice Questions: Chapter 45 Hormones and The Endocrine SystemDocument15 pagesMultiple-Choice Questions: Chapter 45 Hormones and The Endocrine SystemshasagailNo ratings yet
- Basic Coronary Angiography All SlidesDocument55 pagesBasic Coronary Angiography All SlidesSaud ShirwanNo ratings yet
- Smooth Muscle Cell Molecules: © 2012 Pearson Education, IncDocument28 pagesSmooth Muscle Cell Molecules: © 2012 Pearson Education, IncNicole EncinaresNo ratings yet
Reflex Facilitation: Vol Control of Micturition (Corticol Areas) Control EUS & Abd M
Reflex Facilitation: Vol Control of Micturition (Corticol Areas) Control EUS & Abd M
Uploaded by
Tharani Kumara0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
311 views1 pageThe document discusses the neural control of micturition (urination). It describes the facilitatory and inhibitory areas in the brainstem that regulate bladder filling and emptying. The sacral spinal cord centers receive input from these brain areas to influence the micturition reflex threshold. Abnormalities can result in incontinence if the inhibitory input is damaged or denervation if the afferent or efferent nerves are destroyed. Spinal shock after transection initially causes an unresponsive bladder but micturition reflex may recover without voluntary control.
Original Description:
Original Title
Micturition reflex
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the neural control of micturition (urination). It describes the facilitatory and inhibitory areas in the brainstem that regulate bladder filling and emptying. The sacral spinal cord centers receive input from these brain areas to influence the micturition reflex threshold. Abnormalities can result in incontinence if the inhibitory input is damaged or denervation if the afferent or efferent nerves are destroyed. Spinal shock after transection initially causes an unresponsive bladder but micturition reflex may recover without voluntary control.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
311 views1 pageReflex Facilitation: Vol Control of Micturition (Corticol Areas) Control EUS & Abd M
Reflex Facilitation: Vol Control of Micturition (Corticol Areas) Control EUS & Abd M
Uploaded by
Tharani KumaraThe document discusses the neural control of micturition (urination). It describes the facilitatory and inhibitory areas in the brainstem that regulate bladder filling and emptying. The sacral spinal cord centers receive input from these brain areas to influence the micturition reflex threshold. Abnormalities can result in incontinence if the inhibitory input is damaged or denervation if the afferent or efferent nerves are destroyed. Spinal shock after transection initially causes an unresponsive bladder but micturition reflex may recover without voluntary control.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
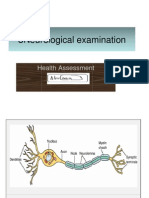
Center : Brain stem
Facilitatory area : Pontine
REFLEX FACILITATION & Post hypothalamus
FILLING THE BLADDER
Inhibitory : Midbrain
Sacral center: (+) facilitatory impulses
from pontine micturating c. & (-) by Vol control of micturition
medullary c. influcences threshold
for micturition reflex (corticol areas) control EUS & abd m.
Urine collected in renal pelvis
Pudendal n. Pelvic floor m.
Pressure in pelvis somatic fiber
Retain urine Untimely to Contrxn retain
Peristaltic contrx initiated (in pelvis) urinate → urine by tighten
signal from openings of the
Contrx spread (ureter to bladder) pons excite urethra
the nerve→
Peristaltic wave occur (1.5x / min) keep EUS to
contract
ABNORMALITY Voiding Time to Relaxing/lowering
Symp : invol
urinate (reach allows passage
Parasymp : invol control bladder wall & IUS threshold)→ of urine
Incontinence
(-) nerve
Somatic: Vol. (skeletal m) Parasym.n damaged absence of micturition r. →EUS relax
Contxn of bladder shrunk & bladder wall hypertrophied
detrusor m in contxn/relaxtn. EUS
detrusor m hyperactive expel urine
bladder walls &
involve in incontinence
micturition r.
Spinal Shock transection
Deafferentation
Bladder is flaccid & unresponsive
Urine dribbles out when overfilled: overflow incontinence Loss of sacral afferents no micturition r.
Upon recovery:- micturition r. returns, but loss of voluntary
control & no inhibition / facilitation from higher c. Denervation
Spastic neurogenic bladder AN & EN destroyed no micturition r.
CYSTOMETROGRAM
eg: tumours of cauda equine
Micturition r. becomes hyperactive, bladder capacity & wall
of bladder hypertrophied
You might also like
- Anatomy & Physiology - Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy & Physiology - Nervous SystemChristine Marylou PalomoNo ratings yet
- Pseudobulbar Palsy Bulbar PalsyDocument5 pagesPseudobulbar Palsy Bulbar PalsyFajar Rudy QimindraNo ratings yet
- A&P - 2. Blood Vessels of The Brain (9p)Document9 pagesA&P - 2. Blood Vessels of The Brain (9p)Gabriel Stratulat100% (1)
- MicturitionDocument7 pagesMicturitionOsama MohamedNo ratings yet
- 1-Indroduction To EmbryologyDocument25 pages1-Indroduction To Embryologyselman P k100% (1)
- Assessing Neurologic System - FinalDocument66 pagesAssessing Neurologic System - FinalAngelo EstanislaoNo ratings yet
- HELLP!!!: A Case Study PresentationDocument32 pagesHELLP!!!: A Case Study PresentationMaria Nena BalagtasNo ratings yet
- Review Literature Journal: Institute of Nursing EducationDocument12 pagesReview Literature Journal: Institute of Nursing EducationEr Shah Rukh QadriNo ratings yet
- Neurological Health AssessmentDocument63 pagesNeurological Health AssessmentAhmed ElryahNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Nerve Fibers: Dr. Zara BatoolDocument30 pagesPhysiology of Nerve Fibers: Dr. Zara BatoolZuhaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular TransmissionDocument45 pagesNeuromuscular TransmissionparuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Human EyeDocument41 pagesAnatomy of Human EyeCarly MelachioNo ratings yet
- New Vertin CME Slides FinalDocument98 pagesNew Vertin CME Slides FinalGaurav KatariaNo ratings yet
- Mannitol: Half-Life Onset Peak DurationDocument3 pagesMannitol: Half-Life Onset Peak DurationAmit MartinNo ratings yet
- 4 - The Temporal LobesDocument37 pages4 - The Temporal LobesYasmeen Egbaria100% (1)
- NEURON ACTION POTENTIAL - PPT - ReadyDocument83 pagesNEURON ACTION POTENTIAL - PPT - Readyelle lee100% (1)
- Unit Plan B.Sc. (Nursing) I Year Nutrition (Proteins)Document5 pagesUnit Plan B.Sc. (Nursing) I Year Nutrition (Proteins)Abhilasha SolomonNo ratings yet
- Anatomo-Physiological Peculiarities of The Respiratory System. Percussion of The Lungs.Document40 pagesAnatomo-Physiological Peculiarities of The Respiratory System. Percussion of The Lungs.Hetvi PatelNo ratings yet
- Slides For SeizureDocument15 pagesSlides For SeizureBryan Mae H. Degorio100% (3)
- 300307814sherlin SapthicaDocument100 pages300307814sherlin SapthicaTitin PrihartiniNo ratings yet
- Chemo ReceptorDocument8 pagesChemo ReceptorCheryl Lyn SanchezNo ratings yet
- UNIT PLAN (1) ResearchDocument32 pagesUNIT PLAN (1) ResearchAshish GuptaNo ratings yet
- MyelographyDocument22 pagesMyelographyKarylleNo ratings yet
- Physiology of PainDocument43 pagesPhysiology of PainNashwan ANo ratings yet
- Ring Enhancing LesionsDocument50 pagesRing Enhancing LesionsVivek GuptaNo ratings yet
- Annotated Bibliography JayitaDocument5 pagesAnnotated Bibliography JayitaJayita Gayen DuttaNo ratings yet
- Basic Overview of NeurologyDocument45 pagesBasic Overview of NeurologyDith Rivelta CallahanthNo ratings yet
- Fatal SkullDocument30 pagesFatal SkullParitosh PaneriNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On Age-Related-Geriatrics-ProblemDocument11 pagesLesson Plan On Age-Related-Geriatrics-Problemmohamad dildarNo ratings yet
- Log Book - 2009.chDocument59 pagesLog Book - 2009.chsujinthomasNo ratings yet
- MSC Thesis FormatDocument4 pagesMSC Thesis FormatAnonymous o4OUZfNo ratings yet
- What Is An EEGDocument4 pagesWhat Is An EEGTanvi NaraNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviourDocument21 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviourSufian Khan100% (1)
- 5 FMCH Research BiasDocument3 pages5 FMCH Research BiasMia CadizNo ratings yet
- Micro TaechingDocument11 pagesMicro Taechingupma sharmaNo ratings yet
- Pharma Module 8Document5 pagesPharma Module 8Chelsy Sky SacanNo ratings yet
- Neuron Notes NewDocument35 pagesNeuron Notes NewBiologie Profesor100% (1)
- Anatomy of The BreastDocument6 pagesAnatomy of The BreastJuliana Andres100% (1)
- Anatomy of Nose andDocument29 pagesAnatomy of Nose andMuhammad Waqar UlfatNo ratings yet
- 1 Pain Sensation Physiology DR Ambreen TauseefDocument73 pages1 Pain Sensation Physiology DR Ambreen TauseefbilalNo ratings yet
- Lumbar Puncture: Bagasin, Nester James S. Rodriguez, Lourdes Erika ADocument32 pagesLumbar Puncture: Bagasin, Nester James S. Rodriguez, Lourdes Erika ANdor BariboloNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NeurophysiologyDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Neurophysiologyvenkata ramakrishnaiahNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Neurological SystemDocument26 pagesAssessment of Neurological SystemBatiao Camille Claire100% (1)
- Procedural Sedation in EDDocument41 pagesProcedural Sedation in EDadam NoheNo ratings yet
- Case Study FormateDocument38 pagesCase Study Formatepriyanka bhavsarNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan ON AppendicitisDocument14 pagesLesson Plan ON AppendicitisrevathyNo ratings yet
- Neurological Examination - BashaDocument8 pagesNeurological Examination - Bashakhaderbasha2020No ratings yet
- Causes Obstruction Causes CSF To Build Up in The Brain. If The Cause Is Congenital, Symptoms Such As AnDocument22 pagesCauses Obstruction Causes CSF To Build Up in The Brain. If The Cause Is Congenital, Symptoms Such As Anmhelandie100% (1)
- Malformation of Female Reproductive SystemDocument170 pagesMalformation of Female Reproductive SystemKriti BanstolaNo ratings yet
- Cerebellum and Brain Stem: DR Asim Shrestha SRCC Ped Neuro Fellow MumbaiDocument71 pagesCerebellum and Brain Stem: DR Asim Shrestha SRCC Ped Neuro Fellow MumbaiAsim ShresthaNo ratings yet
- The Aim of Ear, Nose and ThroatDocument32 pagesThe Aim of Ear, Nose and ThroatabdulNo ratings yet
- M.SC Nursing RequirementsDocument3 pagesM.SC Nursing RequirementsSDx Sujay Daliya100% (1)
- 63 Shock in Obstetrics & GynecologyDocument29 pages63 Shock in Obstetrics & GynecologyGodsonYeboah-AwudziNo ratings yet
- Dopaminergic and Serotonergic Neurohumoural TransmissionDocument23 pagesDopaminergic and Serotonergic Neurohumoural TransmissionChaitanya Kiran PullelaNo ratings yet
- BSCSyllabus 2019-20 PDFDocument251 pagesBSCSyllabus 2019-20 PDFAmrita Charlotte KapoorNo ratings yet
- Final Hernioplasty Compilation RevisedDocument58 pagesFinal Hernioplasty Compilation RevisedRaidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Venipuncture PDFDocument6 pagesVenipuncture PDFAnna GaturianNo ratings yet
- Special NeurologyDocument115 pagesSpecial NeurologyUbaidillah Romadlon Alfairuzi100% (1)
- Neurology: by Dennis Jason Alcantara, RN, USRN, MAN CanDocument213 pagesNeurology: by Dennis Jason Alcantara, RN, USRN, MAN CanKristel-Mia Dimalanta RamosNo ratings yet
- Consultant in Audiology: Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandConsultant in Audiology: Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular PhysiologyDocument7 pagesCardiovascular PhysiologyHabib UllahNo ratings yet
- Basics of Skin Lesions EntranceDocument22 pagesBasics of Skin Lesions EntranceMohammed AsifNo ratings yet
- Immunology and Serology Lec: Immunology - Study of The Immune System orDocument6 pagesImmunology and Serology Lec: Immunology - Study of The Immune System orAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Bibliografie: Vizitati WWW - Tocilar.ro ! Arhiva Online Cu Diplome, Cursuri Si Referate Postate de UtilizatoriDocument7 pagesBibliografie: Vizitati WWW - Tocilar.ro ! Arhiva Online Cu Diplome, Cursuri Si Referate Postate de UtilizatoriAndrutza AndraNo ratings yet
- Guide To Breast Self ExamsDocument7 pagesGuide To Breast Self Examsaamer_rasheed1571No ratings yet
- Immunology Review For FPGEEDocument8 pagesImmunology Review For FPGEEMina MinawyNo ratings yet
- 24 - Proprioception and Neuromuscular ControlDocument24 pages24 - Proprioception and Neuromuscular ControlCarlos Garcia100% (2)
- THE Excretory SystemDocument24 pagesTHE Excretory SystemZain HaiderNo ratings yet
- Notes in Science LT 10 - Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesNotes in Science LT 10 - Endocrine SystemAlven ReyNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Breast Milk ProductionDocument5 pagesPhysiology of Breast Milk ProductionIvyNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument18 pagesDigestive System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBDNo ratings yet
- M4vmvns3ua5zc1zzyn0sigr2Document2 pagesM4vmvns3ua5zc1zzyn0sigr2Sagar VashisthNo ratings yet
- Excretion and KidneysDocument39 pagesExcretion and KidneyselizabethNo ratings yet
- Nerve Cell - Cell ProjectDocument23 pagesNerve Cell - Cell Projectapi-327766139No ratings yet
- Natural World Series Science and Technology Biology.: Heart-The Heart Is A Part of The Circulatory SystemDocument8 pagesNatural World Series Science and Technology Biology.: Heart-The Heart Is A Part of The Circulatory SystemjowieNo ratings yet
- Horner'S Syndrome - : Far Eastern University - Nicanor Reyes Medical FoundationDocument3 pagesHorner'S Syndrome - : Far Eastern University - Nicanor Reyes Medical FoundationVictorija Evania Lucille DeldioNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Coronary Arteries and VeinsDocument80 pagesAnatomy of The Coronary Arteries and Veinstreelife111No ratings yet
- Q.P. Code: 801521Document15 pagesQ.P. Code: 801521CARDIAC SRINITHI DHANA DHARSHIKAA N100% (1)
- All Life Begins With A Single - .: A) Organ B) Microbe C) Tissue D) CellDocument18 pagesAll Life Begins With A Single - .: A) Organ B) Microbe C) Tissue D) CellRonalynAlonsabeBernadasNo ratings yet
- Renal PhysiologyDocument43 pagesRenal PhysiologyRabi SyedNo ratings yet
- ISAP Lecture 1 Module 1 - Studocu NotesDocument6 pagesISAP Lecture 1 Module 1 - Studocu NotesLyndonNo ratings yet
- The Clinical Significance of Subclinical Thyroid Dysfunction Bernadette Biondi and David S. Cooper PDFDocument56 pagesThe Clinical Significance of Subclinical Thyroid Dysfunction Bernadette Biondi and David S. Cooper PDFLorena IbarrolaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 ScienceDocument5 pagesGrade 8 ScienceChristian jade QuijanoNo ratings yet
- Class X LN - 6 Life Processes Work Sheet 20-21Document2 pagesClass X LN - 6 Life Processes Work Sheet 20-21Saraswathi GopalNo ratings yet
- Breast Chek Kit BookletDocument16 pagesBreast Chek Kit BookletPlexusNo ratings yet
- Feeding of Healthy Newborn BabiesDocument37 pagesFeeding of Healthy Newborn BabiesSulfie HarsNo ratings yet
- Histology of Sebaceous Glands and Nails by Dr. RoomiDocument10 pagesHistology of Sebaceous Glands and Nails by Dr. RoomiMudassar Roomi100% (1)
- Multiple-Choice Questions: Chapter 45 Hormones and The Endocrine SystemDocument15 pagesMultiple-Choice Questions: Chapter 45 Hormones and The Endocrine SystemshasagailNo ratings yet
- Basic Coronary Angiography All SlidesDocument55 pagesBasic Coronary Angiography All SlidesSaud ShirwanNo ratings yet
- Smooth Muscle Cell Molecules: © 2012 Pearson Education, IncDocument28 pagesSmooth Muscle Cell Molecules: © 2012 Pearson Education, IncNicole EncinaresNo ratings yet