Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 viewsSS Term 2 QP
SS Term 2 QP
Uploaded by
BALAJI.D MCE-AP/ECE1. The document is an exam for a Signals and Systems class, containing multiple choice and short answer questions testing concepts like linearity, causality, time invariance, and Fourier analysis.
2. Questions test the identification of periodic signals from differential equations, determining appropriate dynamic systems, properties of memoryless systems, and conditions for stability, time invariance, and periodicity.
3. Definitions and representations of Fourier series are also assessed, including Dirichlet conditions, trigonometric forms, synthesis vs. analysis equations, and pairing periodic signals with coefficient representations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- IES - Electronics Engineering - Signals and SystemsDocument70 pagesIES - Electronics Engineering - Signals and SystemsRakesh Sharma100% (2)
- London TransportDocument22 pagesLondon TransportNoelia Peirats AymerichNo ratings yet
- Yamaha XT 125 2005 Service InformationDocument32 pagesYamaha XT 125 2005 Service Informationkhargh100% (1)
- Mahendra College of Engineering: Salem-Campus, Attur Main Road, Minnampalli, Salem - 636 106Document4 pagesMahendra College of Engineering: Salem-Campus, Attur Main Road, Minnampalli, Salem - 636 106BALAJI.D MCE-AP/ECENo ratings yet
- SS Term Test 1 QPDocument3 pagesSS Term Test 1 QPBALAJI.D MCE-AP/ECENo ratings yet
- DSP QuestionsDocument2 pagesDSP Questionsveeramaniks408No ratings yet
- Btech Ee 3 Sem Basic Signals and Systems Kee303 2022Document2 pagesBtech Ee 3 Sem Basic Signals and Systems Kee303 2022Priyanshu SuryavanshiNo ratings yet
- Question Bank ECE IV S&SDocument10 pagesQuestion Bank ECE IV S&SAbhNo ratings yet
- Ese562 Lect01Document35 pagesEse562 Lect01ashralph7No ratings yet
- Parul University: Yn XN XT TDocument2 pagesParul University: Yn XN XT THarshraj MahidaNo ratings yet
- DSP MCQ With Answer-Unit IDocument9 pagesDSP MCQ With Answer-Unit IAbineshNo ratings yet
- Date: June 14, 2015: Part 1 (Multiple-Choice Questions) : For Problems in This Part, You Only Have ToDocument2 pagesDate: June 14, 2015: Part 1 (Multiple-Choice Questions) : For Problems in This Part, You Only Have ToTuấn Quốc TrịnhNo ratings yet
- Signal & Systems - EE 221 - A-1Document6 pagesSignal & Systems - EE 221 - A-1Piyush OjhaNo ratings yet
- DSP Module 1 - 2 Mark - QuestionDocument3 pagesDSP Module 1 - 2 Mark - QuestionAbhishek PandeyNo ratings yet
- Ss 2Document10 pagesSs 2Aditya PatilNo ratings yet
- Question Bank EE V S&SDocument10 pagesQuestion Bank EE V S&SAbhNo ratings yet
- S and S Examination PaperDocument3 pagesS and S Examination Paperzeeshanahmad12030No ratings yet
- HT TP: //qpa Pe R.W But .Ac .In: 2011 Signals and SystemDocument7 pagesHT TP: //qpa Pe R.W But .Ac .In: 2011 Signals and SystemSoumitra BhowmickNo ratings yet
- SspaperssDocument8 pagesSspaperssbharadwajNo ratings yet
- 1b Slides ModelingDocument61 pages1b Slides ModelingShadNo ratings yet
- Ect204 Signals and Systems, June 2022Document4 pagesEct204 Signals and Systems, June 2022instapc0210No ratings yet
- 2024 ELEC3004 Problem Set 1Document4 pages2024 ELEC3004 Problem Set 1songpengyuan123No ratings yet
- Test Booklet Series Test Booklet Electronics & Communication - Paper Topic Test - Signal & CommunicationDocument9 pagesTest Booklet Series Test Booklet Electronics & Communication - Paper Topic Test - Signal & CommunicationVishalPandeyNo ratings yet
- Mid-I - SS - Ece & Eee - 09-01-2021Document1 pageMid-I - SS - Ece & Eee - 09-01-2021v.saigeetha lakshmiNo ratings yet
- AST Exam 2021 03 19Document9 pagesAST Exam 2021 03 19Rehman SaleemNo ratings yet
- Dyt Dyt Yt XT DT DT XT Teut Dyt Dyt DXT Yt XT DT DT DTDocument4 pagesDyt Dyt Yt XT DT DT XT Teut Dyt Dyt DXT Yt XT DT DT DTPoy LinNo ratings yet
- Btech Ec 3 Sem Signal and Systems Nec303 2020 PDFDocument2 pagesBtech Ec 3 Sem Signal and Systems Nec303 2020 PDFhsjjsNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems-REVISION MCQDocument47 pagesSignals and Systems-REVISION MCQrajalakshmi boopathi100% (1)
- SIGNALS and SYSTEMS PDFDocument106 pagesSIGNALS and SYSTEMS PDFShashank Tiwari100% (1)
- Ma Kai-Kuang (Tutorial+Lectures)Document157 pagesMa Kai-Kuang (Tutorial+Lectures)Ang KhengNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 SIGNALS and SYSTEMS GATE PreviDocument42 pagesCHAPTER 3 SIGNALS and SYSTEMS GATE Previa.karthik1982No ratings yet
- WEEK1 RevisionDocument21 pagesWEEK1 RevisionMOHD ENDRA SHAFIQNo ratings yet
- Ss-Model Queston PaperDocument2 pagesSs-Model Queston PapersanthoshNo ratings yet
- Signals and SystemsDocument42 pagesSignals and SystemsDeepa DhilipNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems MCQDocument85 pagesSignals and Systems MCQهاشم محمد المتوكلNo ratings yet
- Bài Tập Ôn Thi Môn Tín Hiệu - Hệ Thống Thầy Lê Vũ HàDocument25 pagesBài Tập Ôn Thi Môn Tín Hiệu - Hệ Thống Thầy Lê Vũ Hà22028026 Đàm Quang ĐạtNo ratings yet
- DSP MCQ Question BankDocument30 pagesDSP MCQ Question BankECE HoD PSNCETNo ratings yet
- Test1A SS21-22Document2 pagesTest1A SS21-22Lu LNo ratings yet
- Worksheet I 2022Document3 pagesWorksheet I 2022Wami MahammadNo ratings yet
- 17 MSE280 Assignment 1Document4 pages17 MSE280 Assignment 1ishaan28No ratings yet
- Tutorial Fourier Series and TransformDocument5 pagesTutorial Fourier Series and TransformRatish DhimanNo ratings yet
- Ch2-SS - Continuous-Time Signals and SystemsDocument55 pagesCh2-SS - Continuous-Time Signals and SystemsVõ Đình VũNo ratings yet
- ECE102 hw2Document5 pagesECE102 hw2Yi LinNo ratings yet
- Dr. TTIT, KGF WWW - Drttit.edu - in Dr. TTIT, KGF WWW - Drttit.edu - inDocument2 pagesDr. TTIT, KGF WWW - Drttit.edu - in Dr. TTIT, KGF WWW - Drttit.edu - inrama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Signal and Systems Analysis Model Exit ExamDocument6 pagesSignal and Systems Analysis Model Exit Examzelalem alemNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam: Signal and System-100 Minutes Code 0010Document16 pagesMidterm Exam: Signal and System-100 Minutes Code 0010HongThinh NguyenNo ratings yet
- 18EE54Document3 pages18EE541MV20EE017 Chaithra kmNo ratings yet
- Question Bank DSP: Preparatory Guidebook For Comprehensive ExaminationDocument6 pagesQuestion Bank DSP: Preparatory Guidebook For Comprehensive ExaminationMisbah Sajid ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Code: 13A04302Document2 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Code: 13A04302Sairam SairamNo ratings yet
- Signal and SystemDocument24 pagesSignal and SystemMagarsaa Qana'iiNo ratings yet
- II B. Tech I Semester, Regular Examinations, Nov - 2012 Signals and SystemsDocument8 pagesII B. Tech I Semester, Regular Examinations, Nov - 2012 Signals and Systemssateesh83No ratings yet
- EEE-282N - S&S Quiz, U-1,2 - SolutionsDocument2 pagesEEE-282N - S&S Quiz, U-1,2 - SolutionsMohammad Umar RehmanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - Systems & Laplace Transform (Slides)Document20 pagesLecture 7 - Systems & Laplace Transform (Slides)Buddhadev GhoshNo ratings yet
- Ss Model 2 2016 - SchemeDocument2 pagesSs Model 2 2016 - SchemeKaustubha ShahNo ratings yet
- 202 End Term Solutions 2013Document17 pages202 End Term Solutions 2013Vikash ManidharNo ratings yet
- Signals & Systems 2019-20Document2 pagesSignals & Systems 2019-20YuvRaj SinghNo ratings yet
- Signals and Networks Assignment 2Document6 pagesSignals and Networks Assignment 2Avikalp SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication Week 0Document6 pagesAnalog Communication Week 0Subhajit BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Week2 - ODL 1 - Chapter 1 - Classification of SystemsDocument18 pages3 - Week2 - ODL 1 - Chapter 1 - Classification of SystemsMuhammad MustaqimNo ratings yet
- ELEG 3124 Assignment # 1Document16 pagesELEG 3124 Assignment # 1Nguyễn Văn ĐứcNo ratings yet
- course file front pageDocument1 pagecourse file front pageBALAJI.D MCE-AP/ECENo ratings yet
- Government of Tamil Nadu Directorate of Technical Education Tamil Nadu Engineering Admission - 2020Document3 pagesGovernment of Tamil Nadu Directorate of Technical Education Tamil Nadu Engineering Admission - 2020BALAJI.D MCE-AP/ECENo ratings yet
- SS Term Test 1 QPDocument3 pagesSS Term Test 1 QPBALAJI.D MCE-AP/ECENo ratings yet
- Mahendra College of Engineering: Salem-Campus, Attur Main Road, Minnampalli, Salem - 636 106Document4 pagesMahendra College of Engineering: Salem-Campus, Attur Main Road, Minnampalli, Salem - 636 106BALAJI.D MCE-AP/ECENo ratings yet
- Internal Test-I SSDocument2 pagesInternal Test-I SSBALAJI.D MCE-AP/ECENo ratings yet
- Campany Profile and Document'sDocument15 pagesCampany Profile and Document'sIvan ElisioNo ratings yet
- Abeba DebruDocument90 pagesAbeba Debruabera alemayehuNo ratings yet
- NCCA Project Proposal Form 1Document4 pagesNCCA Project Proposal Form 1Ramiel Agan GuinandamNo ratings yet
- Resources Class 16 - V1 - 07 Oct Numerical Problems On Vehicle PerformanceDocument16 pagesResources Class 16 - V1 - 07 Oct Numerical Problems On Vehicle PerformancekirthikNo ratings yet
- NAT OPS Bulletin 2023 - 001 - Rev01Document7 pagesNAT OPS Bulletin 2023 - 001 - Rev01pldonnelly1No ratings yet
- V033e1-5 NT620S+NT620CDocument337 pagesV033e1-5 NT620S+NT620CMERTAL JAYA ABADINo ratings yet
- W1A W1M W1E Flyer PDFDocument2 pagesW1A W1M W1E Flyer PDFMārtiņš KubulnieksNo ratings yet
- MTM&ROBOTICS 2024 FirstCallDocument1 pageMTM&ROBOTICS 2024 FirstCallMihai TrailaNo ratings yet
- Topic Selection: Thermal Performance of Heat Sink With Modified Plate Fins Subjected To Natural ConvectionDocument11 pagesTopic Selection: Thermal Performance of Heat Sink With Modified Plate Fins Subjected To Natural ConvectionAsmNo ratings yet
- Parts 31210111 Feb-01-2015 Global English-FrenchDocument132 pagesParts 31210111 Feb-01-2015 Global English-FrenchAdam JanigaNo ratings yet
- TOEIC Reading Test 2Document18 pagesTOEIC Reading Test 2Jefferson TelanNo ratings yet
- Release ACOS 4.1.4-GR1-P10 IssuesDocument241 pagesRelease ACOS 4.1.4-GR1-P10 IssuesdanielatellaNo ratings yet
- Ni 0215Document10 pagesNi 0215renatoredeNo ratings yet
- UnknownDocument2 pagesUnknownveersingh5521No ratings yet
- Canon MP160 Maint & Error CodesDocument1 pageCanon MP160 Maint & Error CodesSyed Mokhtar Al-AttasNo ratings yet
- Raisecom RC002-16Document2 pagesRaisecom RC002-16Eka RatnaNo ratings yet
- MTS9300A V100R002C00 Telecom Power Installation GuideDocument129 pagesMTS9300A V100R002C00 Telecom Power Installation GuideVanek505100% (2)
- Special Client Onboarding TasksDocument11 pagesSpecial Client Onboarding TasksRichard Rhamil Carganillo Garcia Jr.No ratings yet
- MF5LS MH5LF InstructionDocument74 pagesMF5LS MH5LF InstructionMạh PhanNo ratings yet
- 1 16 c143 - DrawingsDocument56 pages1 16 c143 - DrawingsTorus EngenhariaNo ratings yet
- Abb 11kv Vd4 VCB CatalogueDocument10 pagesAbb 11kv Vd4 VCB CataloguePithoon UngnaparatNo ratings yet
- Malware Analysis PracticalDocument9 pagesMalware Analysis Practicalsonik sarungaleNo ratings yet
- 323-1851-201.r1.2 - OME6500 InstallationDocument254 pages323-1851-201.r1.2 - OME6500 InstallationJonatn SilvaNo ratings yet
- Applications - Red Blood Cell SeparationDocument4 pagesApplications - Red Blood Cell SeparationLy NguyenNo ratings yet
- WEG CFW300 Catalog 50066669 enDocument16 pagesWEG CFW300 Catalog 50066669 enRafael AndradeNo ratings yet
- MMMMMMMMMMMMMMMHHHDocument30 pagesMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMHHHAdina82No ratings yet
- 2SK1167, 2SK1168: Silicon N-Channel MOS FETDocument10 pages2SK1167, 2SK1168: Silicon N-Channel MOS FETAkramNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Vector Data Analysis: Box 11.1 Riparian Buffer WidthDocument21 pagesChapter 11 Vector Data Analysis: Box 11.1 Riparian Buffer WidthMohammad ShahnurNo ratings yet
SS Term 2 QP
SS Term 2 QP
Uploaded by
BALAJI.D MCE-AP/ECE0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pages1. The document is an exam for a Signals and Systems class, containing multiple choice and short answer questions testing concepts like linearity, causality, time invariance, and Fourier analysis.
2. Questions test the identification of periodic signals from differential equations, determining appropriate dynamic systems, properties of memoryless systems, and conditions for stability, time invariance, and periodicity.
3. Definitions and representations of Fourier series are also assessed, including Dirichlet conditions, trigonometric forms, synthesis vs. analysis equations, and pairing periodic signals with coefficient representations.
Original Description:
asfsafafafa
Original Title
SS TERM 2 QP
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document is an exam for a Signals and Systems class, containing multiple choice and short answer questions testing concepts like linearity, causality, time invariance, and Fourier analysis.
2. Questions test the identification of periodic signals from differential equations, determining appropriate dynamic systems, properties of memoryless systems, and conditions for stability, time invariance, and periodicity.
3. Definitions and representations of Fourier series are also assessed, including Dirichlet conditions, trigonometric forms, synthesis vs. analysis equations, and pairing periodic signals with coefficient representations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesSS Term 2 QP
SS Term 2 QP
Uploaded by
BALAJI.D MCE-AP/ECE1. The document is an exam for a Signals and Systems class, containing multiple choice and short answer questions testing concepts like linearity, causality, time invariance, and Fourier analysis.
2. Questions test the identification of periodic signals from differential equations, determining appropriate dynamic systems, properties of memoryless systems, and conditions for stability, time invariance, and periodicity.
3. Definitions and representations of Fourier series are also assessed, including Dirichlet conditions, trigonometric forms, synthesis vs. analysis equations, and pairing periodic signals with coefficient representations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
MAHENDRA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
Salem-Campus, Attur Main Road, Minnampalli, Salem -636 106.
Internal Test – II
Class: II YEAR/ECE 30
Date: 19.10.2020 Minutes
Time :
+30
Minutes
Semester: III
Subject Code EC8352 Signals and Systems Marks : 50
and Name :
Blooms
Course
S. No Questions Taxonomy
Outcomes
Level
Answer All Questions
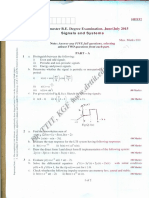
Part A— (30 X 1=30)
Which property of periodic signal in DTFS gets completely clarified / BTL 2 CO 2
identified by the equation x (n – n0)?
1 a. Conjugation b. Time Shifting
c. Frequency Shifting d. Time Reversal
Which one most appropriate dynamic system? BTL 1 CO 2
A. y(n)
+ y(n -
1)
2 + y(n
+ 1)
a. B.y(n) + y(n - 1)C.y(n) = x(n)D.y(n) + y(n - 1) + y(n + 3) = 0y(n)
+ y(n - 1) + y(n + 1) c. y(n) + y(n - 1)
b. y(n) = x(n) d. y(n) + y(n - 1) + y(n + 3) = 0
3Is the system y(t) = Rx(t), where R is a arbitrary constant, a memoryless system?
a) Yes b) NoBTL 1CO 24Does the following discrete system have the parameter of
memory, y[n] = x[n-1] + x[n] ?
a) Yes b) NoBTL 1CO 25Which of the following systems is linear?
a) y(t) = sin(x(t)) b) y(t) = log(x(t)) c) y(t) = cos(x(t)) d) y(t) = dx(t)/dtBTL 1CO26 Which of
the following systems is stable?
a) y(t) = log(x(t)) b) y(t) = exp(x(t))
c) y(t) = sin(x(t)) d) y(t) = tx(t) + 1BTL 1CO 27Which of the following systems is
time invariant?
a) y(t) = x(2t) + x(t) b) y(t) = x(t) + x(1-t)
c) y(t) = -x(t) + x(1-t) d) y(t) = x(t) + x(t-1)BTL 1CO 28State whether the
differentiator system is causal or not.
a) True b) FalseBTL 2CO 29For what value of k, will the following system be time
invariant?
y(t) = x(t) + x(kt) – x(2t) + x(t-1)
a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 2.5BTL 3CO 210State whether the
following system is periodic or not.
y(t) = log(sin(x(t)).
a) Yes b) NoBTL 1CO 211What is Fourier series?
a) The representation of periodic signals in a mathematical manner is called a Fourier series
b) The representation of non periodic signals in a mathematical manner is called a Fourier series
c) The representation of non periodic signals in terms of complex exponentials or sinusoids is called a
Fourier series
d) The representation of periodic signals in terms of complex exponentials or sinusoids is called a Fourier
seriesBTL 1CO 212Fourier series representation can be used in case of Non-periodic signals too. True
or false?
a) True b) FalseBTL 1CO 213What are the conditions called which are required for a
signal to fulfil to be represented as Fourier series?
a) Dirichlet’s conditions b) Gibbs phenomenon
c) Fourier conditions d) Fourier phenomenonBTL 3CO 214Choose the
condition from below that is not a part of Dirichlet’s conditions?
a) If it is continuous then there are a finite number of discontinuities in the period T1
b) It has a finite average value over the period T
c) It has a finite number of positive and negative maxima in the period T
d) It is a periodic signalBTL 3CO 215What are the two types of Fourier series?
a) Trigonometric and exponential b) Trigonometric and logarithmic
c) Exponential and logarithmic d) Trigonometric onlyBTL 1CO216How is a
trigonometric Fourier series represented?
a) A0 +∑[ancos(w0t)+ ansin(w0t)] b) ∑[ancos(w0t)+ ansin(w0t)]
c) A0 *∑[ancos(w0t)+ ansin(w0t)] d) A0 +∑[ancos(w0t)+ ansin(w0t)] + sinwtBTL 1CO 217What
is the equation – X(t) = ∑Xn ejnwt called?
a) Synthesis equation b) Analysis equation
c) Frequency domain equation d) Discrete equationBTL 2CO 218What are the
Dirichlet’s conditions?
a) Conditions required for fourier series to diverge
b) Conditions required for fourier series to converge if continuous
c) Conditions required for fourier series to converge
d) Conditions required for fourier series to diverge if continuous BTL 1CO 219How do
we represent a pairing of a periodic signal with its fourier series coefficients in case of
continuous time fourier series?
a) x(t) ↔ Xn b) x(t) ↔ Xn+1 c) x(t) ↔ X d) x(n) ↔ XnBTL 2CO 220 What
are the properties of continuous time fourier series?
a) Linearity, time shifting
b) Linearity, time shifting, frequency shifting
c) Linearity, time shifting, frequency shifting, time reversal, time scaling,
periodic convolution
d) Linearity, time shifting, frequency shifting, time reversal, time scaling,
periodic convolution, multiplication, differentiationBTL 1CO 2Part B — (02 X
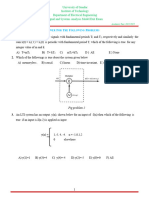
15=30)1Check whether the given system is linearity, causality, time invariance
and dynamicity of the given systems.
a. y(n)= x(n)- x(n-1)
y(t) = dx(t)/dtBTL 1CO22Check whether the given system is linearity, causality,
time invariance and dynamicity of the given systems.
BTL 3CO2
You might also like
- IES - Electronics Engineering - Signals and SystemsDocument70 pagesIES - Electronics Engineering - Signals and SystemsRakesh Sharma100% (2)
- London TransportDocument22 pagesLondon TransportNoelia Peirats AymerichNo ratings yet
- Yamaha XT 125 2005 Service InformationDocument32 pagesYamaha XT 125 2005 Service Informationkhargh100% (1)
- Mahendra College of Engineering: Salem-Campus, Attur Main Road, Minnampalli, Salem - 636 106Document4 pagesMahendra College of Engineering: Salem-Campus, Attur Main Road, Minnampalli, Salem - 636 106BALAJI.D MCE-AP/ECENo ratings yet
- SS Term Test 1 QPDocument3 pagesSS Term Test 1 QPBALAJI.D MCE-AP/ECENo ratings yet
- DSP QuestionsDocument2 pagesDSP Questionsveeramaniks408No ratings yet
- Btech Ee 3 Sem Basic Signals and Systems Kee303 2022Document2 pagesBtech Ee 3 Sem Basic Signals and Systems Kee303 2022Priyanshu SuryavanshiNo ratings yet
- Question Bank ECE IV S&SDocument10 pagesQuestion Bank ECE IV S&SAbhNo ratings yet
- Ese562 Lect01Document35 pagesEse562 Lect01ashralph7No ratings yet
- Parul University: Yn XN XT TDocument2 pagesParul University: Yn XN XT THarshraj MahidaNo ratings yet
- DSP MCQ With Answer-Unit IDocument9 pagesDSP MCQ With Answer-Unit IAbineshNo ratings yet
- Date: June 14, 2015: Part 1 (Multiple-Choice Questions) : For Problems in This Part, You Only Have ToDocument2 pagesDate: June 14, 2015: Part 1 (Multiple-Choice Questions) : For Problems in This Part, You Only Have ToTuấn Quốc TrịnhNo ratings yet
- Signal & Systems - EE 221 - A-1Document6 pagesSignal & Systems - EE 221 - A-1Piyush OjhaNo ratings yet
- DSP Module 1 - 2 Mark - QuestionDocument3 pagesDSP Module 1 - 2 Mark - QuestionAbhishek PandeyNo ratings yet
- Ss 2Document10 pagesSs 2Aditya PatilNo ratings yet
- Question Bank EE V S&SDocument10 pagesQuestion Bank EE V S&SAbhNo ratings yet
- S and S Examination PaperDocument3 pagesS and S Examination Paperzeeshanahmad12030No ratings yet
- HT TP: //qpa Pe R.W But .Ac .In: 2011 Signals and SystemDocument7 pagesHT TP: //qpa Pe R.W But .Ac .In: 2011 Signals and SystemSoumitra BhowmickNo ratings yet
- SspaperssDocument8 pagesSspaperssbharadwajNo ratings yet
- 1b Slides ModelingDocument61 pages1b Slides ModelingShadNo ratings yet
- Ect204 Signals and Systems, June 2022Document4 pagesEct204 Signals and Systems, June 2022instapc0210No ratings yet
- 2024 ELEC3004 Problem Set 1Document4 pages2024 ELEC3004 Problem Set 1songpengyuan123No ratings yet
- Test Booklet Series Test Booklet Electronics & Communication - Paper Topic Test - Signal & CommunicationDocument9 pagesTest Booklet Series Test Booklet Electronics & Communication - Paper Topic Test - Signal & CommunicationVishalPandeyNo ratings yet
- Mid-I - SS - Ece & Eee - 09-01-2021Document1 pageMid-I - SS - Ece & Eee - 09-01-2021v.saigeetha lakshmiNo ratings yet
- AST Exam 2021 03 19Document9 pagesAST Exam 2021 03 19Rehman SaleemNo ratings yet
- Dyt Dyt Yt XT DT DT XT Teut Dyt Dyt DXT Yt XT DT DT DTDocument4 pagesDyt Dyt Yt XT DT DT XT Teut Dyt Dyt DXT Yt XT DT DT DTPoy LinNo ratings yet
- Btech Ec 3 Sem Signal and Systems Nec303 2020 PDFDocument2 pagesBtech Ec 3 Sem Signal and Systems Nec303 2020 PDFhsjjsNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems-REVISION MCQDocument47 pagesSignals and Systems-REVISION MCQrajalakshmi boopathi100% (1)
- SIGNALS and SYSTEMS PDFDocument106 pagesSIGNALS and SYSTEMS PDFShashank Tiwari100% (1)
- Ma Kai-Kuang (Tutorial+Lectures)Document157 pagesMa Kai-Kuang (Tutorial+Lectures)Ang KhengNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 SIGNALS and SYSTEMS GATE PreviDocument42 pagesCHAPTER 3 SIGNALS and SYSTEMS GATE Previa.karthik1982No ratings yet
- WEEK1 RevisionDocument21 pagesWEEK1 RevisionMOHD ENDRA SHAFIQNo ratings yet
- Ss-Model Queston PaperDocument2 pagesSs-Model Queston PapersanthoshNo ratings yet
- Signals and SystemsDocument42 pagesSignals and SystemsDeepa DhilipNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems MCQDocument85 pagesSignals and Systems MCQهاشم محمد المتوكلNo ratings yet
- Bài Tập Ôn Thi Môn Tín Hiệu - Hệ Thống Thầy Lê Vũ HàDocument25 pagesBài Tập Ôn Thi Môn Tín Hiệu - Hệ Thống Thầy Lê Vũ Hà22028026 Đàm Quang ĐạtNo ratings yet
- DSP MCQ Question BankDocument30 pagesDSP MCQ Question BankECE HoD PSNCETNo ratings yet
- Test1A SS21-22Document2 pagesTest1A SS21-22Lu LNo ratings yet
- Worksheet I 2022Document3 pagesWorksheet I 2022Wami MahammadNo ratings yet
- 17 MSE280 Assignment 1Document4 pages17 MSE280 Assignment 1ishaan28No ratings yet
- Tutorial Fourier Series and TransformDocument5 pagesTutorial Fourier Series and TransformRatish DhimanNo ratings yet
- Ch2-SS - Continuous-Time Signals and SystemsDocument55 pagesCh2-SS - Continuous-Time Signals and SystemsVõ Đình VũNo ratings yet
- ECE102 hw2Document5 pagesECE102 hw2Yi LinNo ratings yet
- Dr. TTIT, KGF WWW - Drttit.edu - in Dr. TTIT, KGF WWW - Drttit.edu - inDocument2 pagesDr. TTIT, KGF WWW - Drttit.edu - in Dr. TTIT, KGF WWW - Drttit.edu - inrama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Signal and Systems Analysis Model Exit ExamDocument6 pagesSignal and Systems Analysis Model Exit Examzelalem alemNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam: Signal and System-100 Minutes Code 0010Document16 pagesMidterm Exam: Signal and System-100 Minutes Code 0010HongThinh NguyenNo ratings yet
- 18EE54Document3 pages18EE541MV20EE017 Chaithra kmNo ratings yet
- Question Bank DSP: Preparatory Guidebook For Comprehensive ExaminationDocument6 pagesQuestion Bank DSP: Preparatory Guidebook For Comprehensive ExaminationMisbah Sajid ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Code: 13A04302Document2 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Code: 13A04302Sairam SairamNo ratings yet
- Signal and SystemDocument24 pagesSignal and SystemMagarsaa Qana'iiNo ratings yet
- II B. Tech I Semester, Regular Examinations, Nov - 2012 Signals and SystemsDocument8 pagesII B. Tech I Semester, Regular Examinations, Nov - 2012 Signals and Systemssateesh83No ratings yet
- EEE-282N - S&S Quiz, U-1,2 - SolutionsDocument2 pagesEEE-282N - S&S Quiz, U-1,2 - SolutionsMohammad Umar RehmanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - Systems & Laplace Transform (Slides)Document20 pagesLecture 7 - Systems & Laplace Transform (Slides)Buddhadev GhoshNo ratings yet
- Ss Model 2 2016 - SchemeDocument2 pagesSs Model 2 2016 - SchemeKaustubha ShahNo ratings yet
- 202 End Term Solutions 2013Document17 pages202 End Term Solutions 2013Vikash ManidharNo ratings yet
- Signals & Systems 2019-20Document2 pagesSignals & Systems 2019-20YuvRaj SinghNo ratings yet
- Signals and Networks Assignment 2Document6 pagesSignals and Networks Assignment 2Avikalp SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication Week 0Document6 pagesAnalog Communication Week 0Subhajit BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Week2 - ODL 1 - Chapter 1 - Classification of SystemsDocument18 pages3 - Week2 - ODL 1 - Chapter 1 - Classification of SystemsMuhammad MustaqimNo ratings yet
- ELEG 3124 Assignment # 1Document16 pagesELEG 3124 Assignment # 1Nguyễn Văn ĐứcNo ratings yet
- course file front pageDocument1 pagecourse file front pageBALAJI.D MCE-AP/ECENo ratings yet
- Government of Tamil Nadu Directorate of Technical Education Tamil Nadu Engineering Admission - 2020Document3 pagesGovernment of Tamil Nadu Directorate of Technical Education Tamil Nadu Engineering Admission - 2020BALAJI.D MCE-AP/ECENo ratings yet
- SS Term Test 1 QPDocument3 pagesSS Term Test 1 QPBALAJI.D MCE-AP/ECENo ratings yet
- Mahendra College of Engineering: Salem-Campus, Attur Main Road, Minnampalli, Salem - 636 106Document4 pagesMahendra College of Engineering: Salem-Campus, Attur Main Road, Minnampalli, Salem - 636 106BALAJI.D MCE-AP/ECENo ratings yet
- Internal Test-I SSDocument2 pagesInternal Test-I SSBALAJI.D MCE-AP/ECENo ratings yet
- Campany Profile and Document'sDocument15 pagesCampany Profile and Document'sIvan ElisioNo ratings yet
- Abeba DebruDocument90 pagesAbeba Debruabera alemayehuNo ratings yet
- NCCA Project Proposal Form 1Document4 pagesNCCA Project Proposal Form 1Ramiel Agan GuinandamNo ratings yet
- Resources Class 16 - V1 - 07 Oct Numerical Problems On Vehicle PerformanceDocument16 pagesResources Class 16 - V1 - 07 Oct Numerical Problems On Vehicle PerformancekirthikNo ratings yet
- NAT OPS Bulletin 2023 - 001 - Rev01Document7 pagesNAT OPS Bulletin 2023 - 001 - Rev01pldonnelly1No ratings yet
- V033e1-5 NT620S+NT620CDocument337 pagesV033e1-5 NT620S+NT620CMERTAL JAYA ABADINo ratings yet
- W1A W1M W1E Flyer PDFDocument2 pagesW1A W1M W1E Flyer PDFMārtiņš KubulnieksNo ratings yet
- MTM&ROBOTICS 2024 FirstCallDocument1 pageMTM&ROBOTICS 2024 FirstCallMihai TrailaNo ratings yet
- Topic Selection: Thermal Performance of Heat Sink With Modified Plate Fins Subjected To Natural ConvectionDocument11 pagesTopic Selection: Thermal Performance of Heat Sink With Modified Plate Fins Subjected To Natural ConvectionAsmNo ratings yet
- Parts 31210111 Feb-01-2015 Global English-FrenchDocument132 pagesParts 31210111 Feb-01-2015 Global English-FrenchAdam JanigaNo ratings yet
- TOEIC Reading Test 2Document18 pagesTOEIC Reading Test 2Jefferson TelanNo ratings yet
- Release ACOS 4.1.4-GR1-P10 IssuesDocument241 pagesRelease ACOS 4.1.4-GR1-P10 IssuesdanielatellaNo ratings yet
- Ni 0215Document10 pagesNi 0215renatoredeNo ratings yet
- UnknownDocument2 pagesUnknownveersingh5521No ratings yet
- Canon MP160 Maint & Error CodesDocument1 pageCanon MP160 Maint & Error CodesSyed Mokhtar Al-AttasNo ratings yet
- Raisecom RC002-16Document2 pagesRaisecom RC002-16Eka RatnaNo ratings yet
- MTS9300A V100R002C00 Telecom Power Installation GuideDocument129 pagesMTS9300A V100R002C00 Telecom Power Installation GuideVanek505100% (2)
- Special Client Onboarding TasksDocument11 pagesSpecial Client Onboarding TasksRichard Rhamil Carganillo Garcia Jr.No ratings yet
- MF5LS MH5LF InstructionDocument74 pagesMF5LS MH5LF InstructionMạh PhanNo ratings yet
- 1 16 c143 - DrawingsDocument56 pages1 16 c143 - DrawingsTorus EngenhariaNo ratings yet
- Abb 11kv Vd4 VCB CatalogueDocument10 pagesAbb 11kv Vd4 VCB CataloguePithoon UngnaparatNo ratings yet
- Malware Analysis PracticalDocument9 pagesMalware Analysis Practicalsonik sarungaleNo ratings yet
- 323-1851-201.r1.2 - OME6500 InstallationDocument254 pages323-1851-201.r1.2 - OME6500 InstallationJonatn SilvaNo ratings yet
- Applications - Red Blood Cell SeparationDocument4 pagesApplications - Red Blood Cell SeparationLy NguyenNo ratings yet
- WEG CFW300 Catalog 50066669 enDocument16 pagesWEG CFW300 Catalog 50066669 enRafael AndradeNo ratings yet
- MMMMMMMMMMMMMMMHHHDocument30 pagesMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMHHHAdina82No ratings yet
- 2SK1167, 2SK1168: Silicon N-Channel MOS FETDocument10 pages2SK1167, 2SK1168: Silicon N-Channel MOS FETAkramNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Vector Data Analysis: Box 11.1 Riparian Buffer WidthDocument21 pagesChapter 11 Vector Data Analysis: Box 11.1 Riparian Buffer WidthMohammad ShahnurNo ratings yet