Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tsblet Best RG
Tsblet Best RG
Uploaded by
Mirumbi Kefa MomanyiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tsblet Best RG
Tsblet Best RG
Uploaded by
Mirumbi Kefa MomanyiCopyright:
Available Formats
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.
net/publication/344902771
A Brief Overview on Tablet and It's Types
Article · October 2020
CITATIONS READS
0 2,672
2 authors, including:
Cr Subscription
47 PUBLICATIONS 4 CITATIONS
SEE PROFILE
Some of the authors of this publication are also working on these related projects:
Journal of Pharma and Ayurved Research View project
Research Journal of Medicinal Plants in Ayurveda View project
All content following this page was uploaded by Cr Subscription on 27 October 2020.
The user has requested enhancement of the downloaded file.
Journal of Advancement in Pharmacology
Volume 1 Issue 1
A Brief Overview on Tablet and It’s Types
Tejaswi Santosh Ubhe1*, Preeti Gedam2.
1
Research Student, 2Research Guide,
Abhinav Education Society's College of Pharmacy, Pune, Maharashtra, India.
*Corresponding Author
Email Id: tejaswiubhe1234@gmail.com
ABSTRACT
Medicines are not only a science; it is also an art. It does not consist of compounding pills
and plasters; it deals with the very processes of life, which must be understood before they
may be guided. Pharmaceutical oral solid dosage forms have been used widely for decades
mainly due to their convenience of administration and their suitability for delivery for
delivery of drugs for systemic effects. The tablets can be made directly from powders or from
granules pellets, or from film-coated multiple units. Tablets are now the most popular dosage
form, accounting for some 70% of all ethical pharmaceutical preparations produced. Tablets
may be defined as solid pharmaceutical dosage forms containing drug substances with or
without suitable diluents and prepared by either compression or moulding methods. Hence,
tablets can be broadly classified as compressed tablets and moulded tablets. Compressed
tablets can be further classified as directly compressible tablets, chewable tablets and tablet
triturates etc.
Keywords: Binders, Coated Tablets, Compression, Granulation, Ingredients
.
INTRODUCTION about 70% of the total medicines are
Solid medicaments may be administered dispensed in the form of tablet. Tablets
orally as powders, pills, cachets, capsules had different shapes, sizes, as well as
or tablets. These dosage forms contain a weight depending on medicinal substances
quantity of drug which is given as a single and the intended mode of administration.
Unit and they are known collectively as In this paper the some advantages as well
solid unit dosage forms, even in the case of as some disadvantages of tablets, the basic
Sustained action preparations which, ingredients that are commonly found in
technically, contain the equivalent of tablets, methods of tablet preparation and
several Normal doses of drug .The the various types of the tablets are briefly
stringent formulation requirements of reviewed.
modern Medicaments, the many
advantages of tablet and capsule Definition
medication, coupled With expanding According to the Indian Pharmacopoeia
health services and the commitment need Pharmaceutical tablets are solid, flat or
for large‐ scale Economic manufacture, biconvex dishes, unit dosage form,
have led to a steady decline in the prepared by compressing a drugs or a
prescribing of powders And pills .Tablets mixture of drugs, with or without diluents.
and capsules, on the other hand, currently Tablet is defined as a compressed solid
account for well over Two third of the dosage form containing medicaments with
total number and cost of medicines or without excipients. They vary in shape
produced all over the world. Tablets are and differ greatly in size and weight,
solid dosage form which is the depending on amount of medicinal
conventional as well as have many substances and the intended mode of
advantages over other dosage forms. administration [1, 2].
Tablets are the most popular dosage form;
CR Journals (Page 21–31) 2020. All Rights Reserved Page 21
Journal of Advancement in Pharmacology
Volume 1 Issue 1
Properties [5] 6) Suitable for large scale production.
1) Should be elegant product having its 7) Easy to swallow with least tendency
own identity while being free of for hang-up.
defects such as chips, cracks, 8) Objectionable odour and bitter taste
discoloration and contamination. can be masked by coating technique.
2) Should have strength to withstand the 9) Sustained release product is possible
rigors of shocks encountered in its by enteric coating.
production, packaging, shipping and 10) Easy to handling.
dispensing.
3) Should have the physical stability to Disadvantages [1, 2, 5, 6]
maintain its physical attributes over 1) Difficult to swallow in case of children
time. and unconscious patients.
4) Must be able to release the 2) Some drugs resist compression into
medicament agent(s) in the body in a dense compacts, owing to amorphous
predictable and reproducible manner. nature, low density character.
5) Must have a suitable chemical stability 3) Drugs with poor wetting, slow
over time so as not to allow alteration dissolution properties, optimum
of the medicinal agent(s). absorption high in GIT may be
difficult to formulate or manufacture as
Advantages [1, 2, 5, 6] a tablet that will still provide adequate
1) Tablets are unit dosage form and offer or full drug bioavailability.
the greatest capabilities of all oral 4) Bitter testing drugs, drugs with an
dosage form for the greatest dose objectionable odor or drugs that are
precision and the least content sensitive to oxygen may require
variability. encapsulation or coating. In such cases,
2) They are easiest and cheapest to capsule may offer the best and lowest
package and strip. cost.
3) Low in cost. 5) Irritant effects on the GI mucosa by
4) Lighter and compact. some solids (e.g., aspirin).
5) Having greatest chemical and 6) Possibility of bioavailability problems
microbial stability over all oral dosage resulting from slow disintegration and
forms. dissolution.
INGREDIENTS
In addition to active ingredients, tablet contains a number of inert materials known as
additives or excipients. Different excipients are:
S.no. Ingredients Examples
1. Diluents Calcium Phosphate; Carboxymethylcellulose Calcium; Cellulose;
Dextrin; Lactose; Microcrystalline Cellulose; PR gelatinized
Starch; Sorbitol; Starch
2. Binders Acacia; Alginic Acid; Carboxymethylcellulose; Cellulose; Dextrin;
Gelatin; Liquid Glucose; Magnesium Aluminum Silicate;
Maltodextrin; Methylcellulose; Povidone; Sodium Alginate;
Starch; Zein.
3. Lubricants Calcium Stearate; Glyceryl Palmitostearate; Magnesium Oxide;
Poloxamer; Polyvinyl Alcohol; Sodium Benzoate; Sodium Lauryl
Sulfate; Sodium Stearyl Sulfate; Stearic Acid; Talc; Zinc Stearate
4. Glidants Magnesium Trisilicate; Cellulose; Starch; Talc; Tribasic Calcium
Phosphate
CR Journals (Page 21–31) 2020. All Rights Reserved Page 22
Journal of Advancement in Pharmacology
Volume 1 Issue 1
5. Anti – Corn Starch; Metallic Stearate; Talc
adherents
6. Disintegrants Alginic Acid; Carboxymethylcellulose; Cellulose; Colloidal
Silicon Dioxide; Croscarmellose Sodium; Crospovidone;
Potassium Polacrilin; Povidone
7. Coloring FD&C or D&C Dyes or Lake Pigments
agents
8. Flavoring Ethyl Maltol; Ethyl Vanillin; Menthol; Vanillin
agents
9. Absorbents Kaolin; Magnesium Aluminum Silicate; Tricalcium Phosphate
1) Diluents: Diluents are fillers used to substance with a high affinity to water.
make required bulk of the tablet when Hygroscopic materials, if present,
the drug dosage itself is inadequate to render the blend wet and difficult to
produce the bulk. Also used to improve handle during manufacture.
cohesion, to permit use of direct
compression. PREPARATION
2) Binders: to form cohesive compacts Tablets are prepared by three methods
for directly compressed tablet. 1) Wet granulation method
3) Lubricants: Lubricants are intended to 2) Dry granulation method
prevent adhesion of the tablet materials 3) Direct compression
to the surface of dies and punches,
reduce inter particle friction and may 1) Wet Granulation Method - It is the
improve the rate of flow of the tablet most common and widely used
granulation. method. This method involves various
4) Glidants: Glidants are intended to steps like weighing of ingredients,
promote flow of granules or powder mixing, granulation, and screening of
material by reducing the friction damp pass, drying, lubrication and
between the particles. compression of tablets. The main
5) Anti–adherents: Anti-adherents are active ingredient, diluent, disintegrant
added to the tablet formulations to are blended together, and then it is
prevent the material from sticking to allowed to pass through the sieve
the walls of the tablet press. (sifting). Solutions of the binding agent
6) Disintegrates: Added to a tablet are added to the initial mixture with
formulation to facilitate its breaking or stirring. The amount of binding agent
disintegration when it contact in water added should be sufficient, in order to
in the GIT. avoid over wetting of the tablet [46-
7) Coloring Agents: The use of colors 60]. If the powder is not wetted
and dyes in a tablet has three purposes: properly, the granules will be too soft
(A) Masking of off color drugs (B) and can be broken down during
Product Identification (C) Production lubrication, which is difficult during
of more elegant product. compression of tablet. Tray drying is
8) Flavoring Agents: Flavoring oils are most common method of drying the
needed for chewable tablets. The oil is tablet granules, Tray drying was the
generally added in a dry form such as most widely used method of drying
spray-dried beadlets. tablet granulations in the past, which
9) Absorbents: The inclusion of might be replaced by fluid –bed dryers
absorbents in a tablet formulation is as a novel approach. After drying the
necessary if the product contains a granules, they are allowed to pass
CR Journals (Page 21–31) 2020. All Rights Reserved Page 23
Journal of Advancement in Pharmacology
Volume 1 Issue 1
through the screen; usually 60-100 and the remaining lubricant is added to
mesh nylon cloth is used. After dry the granulation, blended properly and
granulation, lubricant is added as fine compressed to form the tablets (Figure
powder, which is required for proper 1).
filling of the die cavity (Figure 1).
3) Direct Compression: Direct
2) Dry Granulation Method: This compression involves direct
method is used for tablet preparation, compressing the powdered material
in case tablet ingredients are highly into tablets. Direct compression is
sensitive to moisture, or unable to with adopted, if drug constitutes major
stand elevated temperatures during portion of tablet [86-90] total weight
drying, slugging may be used to form (Figure 1). Tablets containing 25% or
the granules. Dry granulation or double less of drug substances can be
compression, usually eliminates formulated, with a suitable diluent
various steps, which involves slugging which acts as a carrier or vehicle for
of the powder mass.The active the drug. Tablets prepared by above
ingredient, diluent and lubricant are method are subjected to compression
blended together, to form the slug. machine which may be single station
Thus, the compressed slug is passed or multiple stations [1, 4].
through the mesh or through the mill,
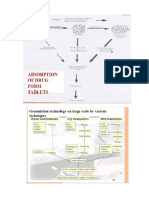
Fig. 1. Processing Steps in Wet Granulation, Dry Granulation and Direct Granulation
CR Journals (Page 21–31) 2020. All Rights Reserved Page 24
Journal of Advancement in Pharmacology
Volume 1 Issue 1
TYPES 1) Standard Compressed Tablets:
Oral Tablets for Ingestion These are standard uncoated tablets
1) Standard Compressed Tablets made by compression using wet
2) Multiple Compressed Tablets granulation, direct compression or
Compression Coated Tablets – a) sugar double compression. It provides rapid
coated, b) film coated tablets, c) disintegration and drug release. They
gelatin coated tablets, d) enteric coated are mostly intended to exert local
tablets action in GIT. It typically includes
Layered tablet water insoluble drugs such as antacid
Inlay tablet and adsorbents. In addition to
3) Targeted Tablets – a) Floating Tablet, medicinal agents compressed tables
b) Colon Targeting Tablet usually contains a number of
4) Chewable tablets pharmaceutical adjuvants such as
5) Dispersible tablets diluents, binders, disintegrants, etc.
Tablets used in the Oral Cavity 2) Multiple Compressed Tablets:
1) Lozenges and troches Multiple compressed tablets are
2) Sublingual tables prepared by more than one
3) Buccal tablet compression cycle. This process is best
4) Dental cones suited when separation of active
5) Mouth dissolved / rapidly dissolving ingredient is needed for stability
tablets purposes, or if the mixing process is
inadequate to guarantee uniform
Tablets Administered by other Routes distribution of two or more active
1. Vaginal tablet ingredients. There are three categories
2. Rectal tablet under this class: Compression coated
3. Implants tablets, Layered tablets and Inlay
tablets.[ 7 ]
Tablets used to prepare Solution
1) Effervescent tablets i Compression Coated tablets: This
2) Molded tablets tablet readily lends itself into a repeat
Hypodermic tablet action. Outer layer provides the initial
Dispensing /soluble tablet dose while the inner core releases the
3) Tablet Triturate. drug later on. Hence, it is useful for
releases of two active pharmaceutical
Structure Wise ingredients (APIs), one immediate
1) Divisible Tablets release formulation which is entrapped
2) Aperture Tablet in coat and the other sustained release
3) Concave Convex Tablets formulation entrapped in the core. It is
4) Core Tablet also possible to provide loading dose
and maintenance dose for one drug
Action Wise using this concept. Colton 232, Stock
1) Modified Release Tablet 538 and Manesty Drycota 900 are
equipment’s utilized for preparing
ORAL TABLET FOR INGESTION compression coated tablets [7].
Over 90% of tablets manufactured are
ingested orally. These are designed to a) Sugar Coated Tablets: The sugar coat
swallow intact, with exception of protect the enclosed drug from the
chewable tablets. environment and provide a barrier to
CR Journals (Page 21–31) 2020. All Rights Reserved Page 25
Journal of Advancement in Pharmacology
Volume 1 Issue 1
objectionable taste or odour. It also have the appearance of a sandwich
produces an elegant, glossy appearance. because the edges of each layer are
The patient acceptability also increases exposed. When two or more active
due to the sweet taste of tablet. Widely pharmaceutical ingredients are needed
utilized in preparing multivitamin and to be administered simultaneously and
multivitamin mineral combination. they are incompatible, the best option
for the formulation pharmacist would
b) Film Coated Tablets: It is the type of be to formulate multilayered tablet. A
coated tablets in which drug is not required single tablet composed of two or more
to coating. In case to provide more layers and usually each layer is of
strength to the tablet, film coating is used different color to produce a distinctive
as alternative to sugar coating. The looking tablet Equipment-Versa press
polymers such as HPC (Hydroxypropyl [7].
cellulose), HPMC (Hydroxypropylmethyl
cellulose), and Ethyl cellulose are used for ii Inlay Tablets: A variation of the
this technique. It is also a fast process than compression coated tablet is the inlay,
the sugar coating technique. It has the dot, or bull's-eye tablet. Instead of the
advantages over sugar coating in that it is core tablet being completely
more durable, less bulky and less time surrounded by the coating, its top
consuming to apply, but it is less attractive surface is completely exposed. This
and elegant in physical appearance than form can be useful in sustained release
sugar coating. The coating is designed to preparations to reduce the size and
rupture and expose the core tablet at the weight of the tablet. Two drugs are
desire location in the gastrointestinal tract. incorporated in tablet, one in core and
one in coat. Release of both drugs
c) Gelatin Coated Tablets: The innovator starts immediately but coating is
product, the gel cap is a capsule–shaped responsible for slow release and core is
compressed tablet that allows the coated responsible for immediate release of
product to be about one–third smaller than incorporated drugs. Inlay tablet are
a capsule filled with an equivalent amount prepared with the Stokes, Colton, or
of powder. The gelatin coating facilities Kilian machines. No alterations in
swallowing, and gelatin–coated tablets are equipment are needed only the feed
more tamper evident than unsealed frame and hopper, which normally
capsule. provide the top coating, are not
installed [7].
d) Enteric Coated Tablets: The enteric
coated tablets are coated with the material 3) Targeted Tablets: Under this category
resistant to acidic medium (stomach there are two types of tablets.
environment) and hence are not able to a. Floating tablets: These are designed
release drug in stomach. Whereas, it easily to prolong the residence time of the
releases drug in intestine (alkaline) media. dosage form within the GI tract. This
Hence, drugs have to pass through not only prolongs GI residence time
stomach and the time of release of drug is but also does so in an area of the GI
delayed and hence called delayed action tract that would maximize drug
tablet [8]. reaching its absorption site in solution
and hence, ready for absorption. These
i Layered Tablets: Layered tablets are are low density tablets. It can expand
composed of two or three layers of in gastric environment. Floating in
granulation compressed together. They diarrhoea to keep the drug in floating
CR Journals (Page 21–31) 2020. All Rights Reserved Page 26
Journal of Advancement in Pharmacology
Volume 1 Issue 1
condition in stomach to get a relatively which may or may not be coated. The
better response. Controlled delivery of core is composed of an insoluble gum
drugs. It minimizes the mucosal base like fillers, waxes, antioxidants,
irritation by releasing drug slowly. sweeteners, flavoring agents. The
Used in treatment of gastrointestinal percentage of gum base varies from
disorders such as gastro esophageal 30-60%. Mannitol is widely used as an
reflux. Ease of administration and excipient in chewable tablet for its
better patient compliance [9]. non-hygroscopic nature for moisture
sensitive drugs [11, 12 ]
b. Colon Targeting Tablets: It provides
a desired drug concentration in the 5) Dispersible Tablets: Dispersible tablets
body by delivering a therapeutic as defined in European Pharmacopoeia are
amount of drug to a target site i.e. uncoated or film coated tablets intended to
colon. It is suitable and required for the be dispersed in water before administration
drugs having instability, low solubility, giving a homogeneous dispersion.
and short half-life, a large volume of Typically a dispersible tablet is dispersed
distribution, poor absorption, low in about 5 to 15 ml of water (e.g. in a
specificity, and therapeutic index. The tablespoonful or a glass of water) and the
pH in this region (colon) varies from resulting dispersion is administered to the
6.4-7 and presence of microbial flora patient. Dispersible tablets are required to
plays an important role in drug release. disintegrate within 3 min in water at 15 to
Various mechanisms adopted for drug 25. Also the dispersion produced from a
release in this area are: Coating with dispersible tablet should pass through a
pH sensitive polymer e.g., Eudragit sieve screen with a nominal mesh aperture
S100 and L100; Biodegradable of 710 µm [13].
polymer which are sensitive to colonic
bacteria; Bio- adhesive polymer e.g., B) TABLETS USED IN ORAL
poly carbophils. Redox sensitive CAVITY
polymers. It provides delivery of drugs 1) Lozenges and Torches: Lozenges are
accurately into the lower GI tract (by flavored medicated dosage forms
avoiding the drug release in upper intended to be sucked and held in
GIT), which occurs primarily in the mouth or pharynx. Two lozenge forms
large intestine (i.e. colon) [10]. include hard (or boiled) candy
lozenges and compressed tablet
5) Chewable Tablets: Chewable tablets lozenges (TROUCHES). Lozenges
which are required to be broken and may be used for; Local medications in
chewed in between the teeth before the mouth or throat, Systemic drug
ingestion. These tablets are given to uptake. Soft variety of lozenge, called
the children who have difficulty in a pastille, consists of medicament in a
swallowing and to the adults who gelatin or glycero- gelatin or in a base
dislike swallowing. These tablets are of acacia, sucrose and water. No
intended to disintegrate smoothly in disintegrant is included in compressed
mouth at a moderate rate either with or lozenges composition. Other additives
without actual chewing. Chewable (binder and filler) must have pleasant
tablet are often employed when the taste or feeling during dissolution.
active ingredient is intended to act in a Common binder used in compressed
localized manner rather than lozenges is gelatin; common fillers are
systemically the composition of (Sorbitol, mannitol and glucose) [1].
chewable tablet consists of gum core,
CR Journals (Page 21–31) 2020. All Rights Reserved Page 27
Journal of Advancement in Pharmacology
Volume 1 Issue 1
2) Sublingual Tablets: They are to be a small volume of serum or fluid over
placed under the tongue and produce 20-40 minutes period. Usually used
immediate systemic effect by enabling vehicles are sodium chloride, sodium
the drug absorbed directly through bicarbonate or amino acid. [1,2 ]
mucosal lining of the mouth beneath
the tongue. The tablets are usually 5) Mouth Dissolved or Rapid
small and flat, compressed lightly to Dissolving Tablets: Mouth dissolving
keep them soft. The tablet must tablets can define as "A solid dosage
dissolve quickly allowing the drugs to form containing medicinal substances,
be absorbed quickly It is designed to which disintegrates rapidly, usually
dissolve in small quantity of saliva. within a matter of seconds, when
Sublingual, meaning literally 'under placed under the tongue. Mouth
the tongue' refers to a method of Dissolving Tablet has a pleasing mouth
administering substances via the mouth feel, and it not required water to
in such a way that the substances are swallow. MDT easily dissolved or
rapidly absorbed via the blood vessels disintegrates in saliva within a few
under the tongue rather than via the seconds (15 s to 3 min). .Some MDT
digestive tract [16]. tablets are designed to dissolve in
saliva remarkably fast, within a few
3) Buccal Tablets: These drugs are seconds, and are called true fast-
intended to be dissolved in buccal dissolving tablets. Others contain
pouch. Tablets are designed not to agents to enhance the rate of tablet
disintegrate. It is placed near the disintegration in the oral cavity and are
opening of parotid duct to provide the more appropriately termed as fast-
medium to dissolve the tablet. Buccal disintegrating tablets, as they may take
tablets are most often used when about one minute to disintegrate
replacement hormonal therapy is the completely. Having good hardness,
goal. Long–Acting Buccal Tablets dose uniformity, easy administration
include use of viscous natural or and serves as the first choice of dosage
synthetic gums or mixtures of gums form for pediatrics, geriatrics and
can be compressed to form a hydrated travelling patients [14].
surface layer from which the
medicament slowly diffuses and is C) Tablets Administered by Other
available for absorption through buccal Routes
mucosa. Mucoadhesive polymers like 1) Vaginal Tablets: Designed for vaginal
PANA and carbopol 934 are used [1, administration in treatment of local vaginal
2]. infections, for systemic absorption and
absorption into vaginal tissue can be
4) Dental Cones: These tables are inserted with aid of an applicator. In the
designed to be loosely packed in the treatment of localized vaginal infections
empty socket remaining following a such as, Candida albicans, yeast and
tooth extraction. Main purpose behind Haemophilus vaginalis.
the use of this tablet is either to prevent
multiplication of bacteria in the socket These are uncoated bullet shape or ovoid
by employing a slow releasing tablets. Designed to under go slow
antibacterial compound or to reduce dissolution and drug release in vaginal
bleeding by an astringent or coagulant cavity. Pleased in an upper region of
containing tablet. It’s formulated to vaginal tract by plastic tube inserter. It
dissolve or erode slowly in presence of
CR Journals (Page 21–31) 2020. All Rights Reserved Page 28
Journal of Advancement in Pharmacology
Volume 1 Issue 1
may contain antibacterial, antiseptic, or mixture comes into contact with water.
astringents [1, 2]. They have good stomach and intestinal
tolerance [15].
2) Rectal tables: It is old and acceptable
means of treatment. The volume and 2) Molded Tablets
nature of rectal fluid, its buffer capacity, a. Hypodermic Tablets: These are one
pH and surface tension play a large part in type of sterile preparations. In these,
this but are subject to wide variation, even tablets are dissolved in the WFI or
within single subject, resulting in sterile water to inject before the actual
variability of absorption by this route. injection in the hypodermic cavity.
Rectal tables not required refrigeration. They are intended to be added in WFI
Better product stability even at room of sterile water to form a clear solution
temperature. which is to be injected parentally. They
are widely used by rural physician due
3) Implants: These tablets are implanted to its portability. It can be used for
in the body cavities for a prolonged effect medicaments whose stability in water
from several days to months up to year. is very poor. Their use in this manner
These tablets are small in size and cylinder should be discouraged, since the
like in shape. They are designed for resulting solutions are not sterile [1,8].
subcutaneous implantation by surgical
procedure where they are slowly absorbed b. Dispensing or Soluble Tablets: They
over a period of month or a year. Special are to be added to water or other
injector with a hollow needle and plunger solvents to make a solution containing
is used to administer the rod shaped tablet. a fixed concentration of API. Should
For other shapes surgery is used. They are contain no insoluble materials
sterile formulations without excipients. (including Glidants, binders etc.), since
Mainly these tablets are prepared to they will be made into clear solution.
deliver growth hormones to food A material incorporated in dispensing
producing animals. Ear is preferred site for tablets includes mild silver proteinate,
administration of drug [1,8]. bichloride of mercury and quaternary
ammonium compounds. These tablets
D) TABLETS USED TO PREAPER are highly toxic if taken orally by
SOLUTION mistake. These tablets provide a
1) Effervescent Tablets: Effervescent convenient quantity of potent drug [1].
tablets are designed to break in contact
with liquid such as water or juice, often 3) Tablet Triturate: Tablet triturates are
causing the tablet to dissolve into a small, usually cylindrical, Molded or
solution the benefit of effervescent tablets compressed tablets. The drugs employed
is that they dissolve completely and evenly in such products were usually quite potent
meaning that localized concentrations of and were mixed with lactose and possibly
the ingredients cannot occur. a bonder, such as powder acacia. Tablet
triturates are usually soft and friable. Many
This means not only a better taste but also of the drugs employed in these tables were
less chance of irritation and a more highly potent and drug migration could
efficient means of ingesting the occur as the alcohol evaporated. Only a
ingredients. Effervescence consists of a minimal pressure is applied during their
soluble organic acid and an alkali metal manufacturing, since they must be readily
carbonate salt, one of which is often the and completely soluble in water [1].
API. Carbon dioxide is formed if this
CR Journals (Page 21–31) 2020. All Rights Reserved Page 29
Journal of Advancement in Pharmacology
Volume 1 Issue 1
Structure Wise contains, in addition to the API, various
1) Divisible Tablet: It is sometimes substances to assure proper delivery of the
necessary to administer one-half or API to the patient. With advancement in
one-fourth of a tablet and under such technology and increase in awareness
circumstances tablets are generally towards modification in standard tablet to
scored once in the middle or twice with achieve better acceptability as well as
lines perpendicular to one another. V- bioavailability, newer and more efficient
shaped double layer tablets with tablet dosage forms are being developed.
scoring in the center have been The main reasons behind formulation of
designed. different types of tablets are to create a
2) Aperture Tablets: Designed with a delivery system that is relatively simple
view to achieve constancy in the and inexpensive to manufacture. Provide
surface area during disintegration & the dosage form that is convenient from
dissolution. patient’s perspective and utilize an
3) Concave-convex Tablets: These approach that is unlikely to add
tablets have been designed with a view complexity during regulatory approval
to keep surface area of the structure process. To understand each dosage form,
relatively constant during the tablets here are classified by their route of
dissolution process. Area is lost on the administration and by the type of drug
convex surfaces and gained at the delivery system they represent within that
concavities. route.
4) Core Tablets: These tablets have a
central core over which another layer REFERENCES
of material is compressed and are 1) Leon Lachman, Herbert A. Lieberman,
generally made by two successive Joseph L. Kanig: The theory and
compressions. Separate incompatible Practice of Industrial Pharmacy,
ingredients. Varghese publication house, 3rd
edition, 1990, 293-373.
ACTION WISE 2) Herbert A. Liberman, Martin M.
1) Modified Release Tablet: Release the Rieger and Gilbert S. Banker,
medicament slowly for long time pharmaceutical dosage forms: Tablets;
duration after administration of a volume-I.
single tablet. Used to target the site 3) Al-Achi A (2019) Tablets: A Brief
specific releases. Comparison of blood Overview. Journal of Pharm Practice
concentration vs. time any adjuvant and Pharmaceutical Science. 2019(1):
that can alter water uptake rate, 49-52.
swelling, and gelling characteristics 4) Nagashree K. Solid dosage forms:
can alter the release rate of API.The Tablets. Research and Reviews:
drug release can be modified by Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis.
providing suitable micro environment 2015.
pH in the tablet .Inclusion of alkaline 5) Kaur Harbir. International Research
polymers results in desirable drug Journal of Pharmacy. 2012, 3 (7).
release of acidic drugs. 6) G. Hymavathi, J. Adilakshmi, K.
Dwarathi, M. Kavya, G. Pravallika.
CONCLUSION Review Article on In process Problems
As a solid dosage form, tablets are popular and Evaluation Tests of Tablet
among patients and practitioners alike as Manufacturing. International Journal
they provide a means of self- of Research in Pharmaceutical and
administration. The formulation of a tablet Nano Sciences. 2012, 3(7).
CR Journals (Page 21–31) 2020. All Rights Reserved Page 30
Journal of Advancement in Pharmacology
Volume 1 Issue 1
7) D. M. Jariwala, H. P. Patel, C. T. practical delivery system for drug
Desai, S. A. Shah and D. R. Shah. A administration. ENT Updates
Review on Multiple Compressed 2016;6(1):46–50.
Tablets. Journal of pharmaceutical 16) Ruchita Jaiswani, Ashutosh Prakash,
sciences and boiscientific research. Dinesh K Mishra, D.K. Jain.
2016, 6(3). 371-379. Sublingual Tablets: An Overview.
8) Purushottam R. Patil, Vaibhav D. Journal of Drug Delivery Research.
Bobade, Pankaj L. Sawant and 2014, 3(4).
Rajendra P. Marathe. Emerging Trends
In Compression Coated Tablet Dosage
Forms: A Review. International journal
of pharmaceutical sciences and
research. 2016, 7(3). 930-938.
9) Bhavjit Kaur, Shivani Sharma, Geetika
Sharma, Rupinder Saini, Sukhdev
Singh, Meenu Nagpal, Upendra K Jain,
Mandeep Sharma. A Review of
Floating Drug Delivery System. Asian
journal of biomedical and
Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2013. 3(24) ,
1-6.
10) Anita , Anil Singh and Ankit Dabral.
A Review On Colon Targeted Drug
Delivery System. International journal
of pharmaceutical sciences and
research. 2019; Vol. 10(1): 47-56.
11) Renu, Jyoti Dahiya, Pawan Jalwal,
Balvinder Singh. The Pharma
Innovation Journal 2015; 4(5): 100-
105.
12) Nilesh Lahanu Gawade, Raosaheb
Sopanrao Shendge. A Review on
Chewable Tablet. Journal of Emerging
Technologies and Innovative Research
(JETIR). March 2020, Volume 7, Issue
3.
13) J. Nandhini, A.N. Rajalakshm.
Dispersible Tablets: A review. Journal
of Pharmaceutical Advanced Research.
2018; 1(3): 148-155.
14) Daljit Masih, Rajesh Gupta. Mouth
Dissolving Tablets – A Review. UK
Journal of Pharmaceutical and
Biosciences Vol. 1(1), 18-24, 2013.
15) Leman Birdane, Niyazi Alt›ntoprak,
Nuray Bayar Muluk, Desiderio Passali,
Andrey Lopatin, Luisa Bellussi, Ranko
Mladina, Ruby Pawankar, Cemal
Cingi. Effervescent tablets: a safe and
CR Journals (Page 21–31) 2020. All Rights Reserved Page 31
View publication stats
You might also like
- Modern Pharmaceutics 4th Edition Chapter 10Document47 pagesModern Pharmaceutics 4th Edition Chapter 10Faysal MasoodNo ratings yet
- CP-563E, CS-563E, CP-573E, CS-573E, CS-583E, CP-663E, CS-663E and CS-683E Vibratory Compactor Electrical SystemDocument11 pagesCP-563E, CS-563E, CP-573E, CS-573E, CS-583E, CP-663E, CS-663E and CS-683E Vibratory Compactor Electrical SystemMohamed Mohamed100% (3)
- SU Copic ChartDocument6 pagesSU Copic ChartErin Dunegan RenfrowNo ratings yet
- Tablet by Lakhvir InsanDocument83 pagesTablet by Lakhvir InsanLakhvir InsanNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument15 pagesIntroductionAhinurNo ratings yet
- Topic 5: TabletsDocument15 pagesTopic 5: TabletsKate EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- TabletsDocument46 pagesTabletsSai SharathNo ratings yet
- SupposutoriaDocument7 pagesSupposutorialilim dzakyNo ratings yet
- Tablets: Unit IiiDocument43 pagesTablets: Unit IiiRushikesh DhapseNo ratings yet
- 3676-Article Text-10501-1-10-20191113Document5 pages3676-Article Text-10501-1-10-20191113SOUJANYA BONINo ratings yet
- Tablet Technology EditedDocument42 pagesTablet Technology EditedPramod Kc100% (1)
- Formulation and Standardization of NutraceuticalsDocument10 pagesFormulation and Standardization of Nutraceuticalssudhindra kini100% (3)
- 22A6761 - 222203.final ResarchDocument31 pages22A6761 - 222203.final Resarchrameshwar9595kNo ratings yet
- Tablets: Unit IiiDocument43 pagesTablets: Unit IiiAbdul KalimNo ratings yet
- International Research Journal of Pharmacy: Processing Technologies For Pharmaceutical Tablets: A ReviewDocument4 pagesInternational Research Journal of Pharmacy: Processing Technologies For Pharmaceutical Tablets: A ReviewBella Puspita HapsariNo ratings yet
- Jchps 6 (4) 15 Page 286-292 MsreddyDocument7 pagesJchps 6 (4) 15 Page 286-292 MsreddydwahyusafriNo ratings yet
- Tablte Lecture Note EditedDocument39 pagesTablte Lecture Note EditedSolomonNo ratings yet
- Dissolution Method Development For Soft Gelatin CapsulesDocument30 pagesDissolution Method Development For Soft Gelatin Capsulesbanapte599706No ratings yet
- TabletsDocument117 pagesTabletscontactamit_shah100% (1)
- TabletDocument14 pagesTabletIVLS AKCPNo ratings yet
- Fast Dissolving Films: A Novel Approach To Oral Drug DeliveryDocument7 pagesFast Dissolving Films: A Novel Approach To Oral Drug DeliveryEga TrikuntiantiNo ratings yet
- Review On The Superdisintigrant and There PhenomenonDocument12 pagesReview On The Superdisintigrant and There PhenomenonNepjune RxNo ratings yet
- Industrial Pharmaceutical Tecnology: (Essentials)Document44 pagesIndustrial Pharmaceutical Tecnology: (Essentials)Selvakumar MuthumanickamNo ratings yet
- 1206 PDFDocument4 pages1206 PDFHamid HamidNo ratings yet
- Paper 8678Document13 pagesPaper 8678IJARSCT JournalNo ratings yet
- Tabletmanufactureprocess Elixer PDFDocument8 pagesTabletmanufactureprocess Elixer PDFGhazanfar AyazNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Drug Dosage Forms II Lecture 1 09-10. - 2Document12 pagesMicrosoft Word - Drug Dosage Forms II Lecture 1 09-10. - 2princeamitNo ratings yet
- Tablet 1Document24 pagesTablet 1Anis Yahya100% (1)
- A Review On Pelletization Techniques: International Journal of Research in Ayurveda and Pharmacy June 2020Document6 pagesA Review On Pelletization Techniques: International Journal of Research in Ayurveda and Pharmacy June 2020ES MMNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument10 pagesReportPemal KaurNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 Industrial Pharmacy II 2023Document36 pagesLec 1 Industrial Pharmacy II 2023saifmohanad.usNo ratings yet
- TabletsDocument78 pagesTabletsLoverboy ForuNo ratings yet
- Integrated Pharmaceutics Lecture NotesDocument64 pagesIntegrated Pharmaceutics Lecture NotesSolomonNo ratings yet
- Some of The Advantages and Disadvantages of Tablets Are Given BelowDocument17 pagesSome of The Advantages and Disadvantages of Tablets Are Given BelowTasmih Rob MowNo ratings yet
- CapsulereviewarticleDocument11 pagesCapsulereviewarticleRicardo GomesNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical TabletDocument44 pagesPharmaceutical TabletMurtaza Choudhary100% (4)
- The Incredible World of TabletDocument10 pagesThe Incredible World of TabletIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Superdisintegrants in Orally Administered Products of Pharmaceuticals A ReviewDocument5 pagesSuperdisintegrants in Orally Administered Products of Pharmaceuticals A ReviewEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- IJCRT2311592Document12 pagesIJCRT2311592Alexandra CorceaNo ratings yet
- Recent Trends of Fast Dissolving Tablet - An Overview of Formulation TechnologyDocument10 pagesRecent Trends of Fast Dissolving Tablet - An Overview of Formulation TechnologyAnkush BhushanNo ratings yet
- Review On "Mouth Dissolving Tablet As Fast Dissolving Drug Delivery System"Document13 pagesReview On "Mouth Dissolving Tablet As Fast Dissolving Drug Delivery System"Editor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutics I Dosage FormsDocument20 pagesPharmaceutics I Dosage FormsShweta Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Mouth Dissolving Tablets A ReviewDocument9 pagesMouth Dissolving Tablets A ReviewEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical ExcipientsDocument5 pagesPharmaceutical Excipientsmads56091No ratings yet
- Seminar On Films and StripsDocument22 pagesSeminar On Films and StripskeyurNo ratings yet
- Herbal Drug Technology Lab Manual 1Document35 pagesHerbal Drug Technology Lab Manual 1Shiva Durga Nagaraju KannellaNo ratings yet
- Tablet (Print) PDFDocument17 pagesTablet (Print) PDFAsif Hasan NiloyNo ratings yet
- Capsules Types Manufacturing Formulation Quality CDocument13 pagesCapsules Types Manufacturing Formulation Quality CPriyanshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Tablets: Unit IiiDocument43 pagesTablets: Unit Iiilovehope100% (2)
- Diazepam Od TDocument7 pagesDiazepam Od TnurulNo ratings yet
- TABlet PDFDocument39 pagesTABlet PDFRania HamamNo ratings yet
- Compaction and Compression of PowderDocument23 pagesCompaction and Compression of Powderjabed sarkar100% (1)
- Tablets TextDocument18 pagesTablets TextarunbaskaranjNo ratings yet
- TABLETSDocument9 pagesTABLETSKeith OmwoyoNo ratings yet
- A Review On Fast Dissolving Tablets FDTsDocument10 pagesA Review On Fast Dissolving Tablets FDTsKamran AlamNo ratings yet
- Recent Advancement in Tablet Coating TechnologyDocument16 pagesRecent Advancement in Tablet Coating TechnologyAdhi WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- Recent Trends of Fast Dissolving Tablet - An Overview of Formulation TechnologyDocument11 pagesRecent Trends of Fast Dissolving Tablet - An Overview of Formulation TechnologyAisyah Al-mumtahanahNo ratings yet
- Drug Delivery Strategies for Poorly Water-Soluble DrugsFrom EverandDrug Delivery Strategies for Poorly Water-Soluble DrugsNo ratings yet
- Role of Lipid Excipients in Modifying Oral and Parenteral Drug Delivery: Basic Principles and Biological ExamplesFrom EverandRole of Lipid Excipients in Modifying Oral and Parenteral Drug Delivery: Basic Principles and Biological ExamplesKishor M. WasanNo ratings yet
- Current Advances in Drug Delivery Through Fast Dissolving/Disintegrating Dosage FormsFrom EverandCurrent Advances in Drug Delivery Through Fast Dissolving/Disintegrating Dosage FormsNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Drugs IDocument3 pagesAdrenergic Drugs IMirumbi Kefa MomanyiNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Receptors 2Document2 pagesAdrenergic Receptors 2Mirumbi Kefa MomanyiNo ratings yet
- Suppositories As A Dosage FormDocument11 pagesSuppositories As A Dosage FormMirumbi Kefa MomanyiNo ratings yet
- Veterinary PharmaceuticsDocument15 pagesVeterinary PharmaceuticsMirumbi Kefa MomanyiNo ratings yet
- Parenteral Preparations AssignmentDocument3 pagesParenteral Preparations AssignmentMirumbi Kefa MomanyiNo ratings yet
- Parenteral PreparationsDocument11 pagesParenteral PreparationsMirumbi Kefa MomanyiNo ratings yet
- Capsu LES: Pharma Ceutics 2Document14 pagesCapsu LES: Pharma Ceutics 2Mirumbi Kefa MomanyiNo ratings yet
- Aerosols .Document19 pagesAerosols .Mirumbi Kefa MomanyiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Calculations Review: Pharmacy Tech Topics™ Volume 16 Number 3 July 2011Document24 pagesPharmacy Calculations Review: Pharmacy Tech Topics™ Volume 16 Number 3 July 2011Mirumbi Kefa Momanyi100% (1)
- Page 8Document1 pagePage 8Mirumbi Kefa MomanyiNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Hypothalamus Pituitary GlandDocument58 pagesThe Endocrine System: Hypothalamus Pituitary GlandMirumbi Kefa MomanyiNo ratings yet
- Types of Bonds in Drug Receptor InteractionDocument12 pagesTypes of Bonds in Drug Receptor InteractionMirumbi Kefa MomanyiNo ratings yet
- Pharm AnalysisDocument6 pagesPharm AnalysisMirumbi Kefa MomanyiNo ratings yet
- PM40 Risk Analysis andDocument101 pagesPM40 Risk Analysis andprincessmuneebashahNo ratings yet
- UMRAH Supplications DUADocument10 pagesUMRAH Supplications DUAsamNo ratings yet
- Module 2 UrineDocument17 pagesModule 2 UrineGiulia Nădășan-CozmaNo ratings yet
- ICH Quality Guidelines - AnuragDocument4 pagesICH Quality Guidelines - AnuragAnurag BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Note On F3 SC C2 TransportationDocument4 pagesNote On F3 SC C2 Transportationgan tong hock a.k.a ganosNo ratings yet
- 25 Duas From The Holy QuranDocument4 pages25 Duas From The Holy QuranKhan Amir Younus KamalNo ratings yet
- Chords Like Jeff BuckleyDocument5 pagesChords Like Jeff BuckleyTDROCKNo ratings yet
- MEDINA, Chandra Micole P. - Activity 6 Both A and BDocument2 pagesMEDINA, Chandra Micole P. - Activity 6 Both A and BChandra Micole MedinaNo ratings yet
- TestDocument3 pagesTestPopovska KristinaNo ratings yet
- Ivermectin TabletsDocument2 pagesIvermectin Tabletsluis diazNo ratings yet
- How To Cite A Research Paper in TextDocument8 pagesHow To Cite A Research Paper in Textafnkaufhczyvbc100% (1)
- Adebabay AbayDocument23 pagesAdebabay Abaymaheder wegayehuNo ratings yet
- ACA - Exam - Objectives - Photoshop - CC 2018Document5 pagesACA - Exam - Objectives - Photoshop - CC 2018Jeffrey FarillasNo ratings yet
- Central Bank Employees Vs BSP DigestDocument6 pagesCentral Bank Employees Vs BSP DigestEmmanuel Ortega100% (2)
- Precision LTC Pharmacy: Servicing Long Term Care Organizations Throughout The Greater New York City AreaDocument2 pagesPrecision LTC Pharmacy: Servicing Long Term Care Organizations Throughout The Greater New York City AreaPR.comNo ratings yet
- BSI BCI Horizon Scan Report 2016 PDFDocument32 pagesBSI BCI Horizon Scan Report 2016 PDFSandraNo ratings yet
- RUNET BETONexpress v21Document2 pagesRUNET BETONexpress v21Angeles Juliana MorenoNo ratings yet
- Construction Contract: Contract For Construction of Apco Hyundai Car Showroom at Uppala, Kasaragod, KeralaDocument2 pagesConstruction Contract: Contract For Construction of Apco Hyundai Car Showroom at Uppala, Kasaragod, KeralakrishnanunniNo ratings yet
- P2P Partnering Success Playbook PDFDocument48 pagesP2P Partnering Success Playbook PDFYesenia RamirezNo ratings yet
- Third Party Logistics: A Literature Review and Research AgendaDocument26 pagesThird Party Logistics: A Literature Review and Research AgendaRuxandra Radus100% (1)
- GenEd - Lumabas Jan 2022Document4 pagesGenEd - Lumabas Jan 2022angelo mabulaNo ratings yet
- World Red Cross DayDocument17 pagesWorld Red Cross DayAshwani K SharmaNo ratings yet
- (Promotion Policy of APDCL) by Debasish Choudhury: RecommendationDocument1 page(Promotion Policy of APDCL) by Debasish Choudhury: RecommendationDebasish ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Assignment 11 STM DavisDocument8 pagesAssignment 11 STM Davisrajesh laddhaNo ratings yet
- Alzheimer's - Alzheimer's Disease - Kaj Blennow, Mony J de Leon, Henrik ZeterbergDocument17 pagesAlzheimer's - Alzheimer's Disease - Kaj Blennow, Mony J de Leon, Henrik ZeterbergCatinean DanielaNo ratings yet
- Campaign For Tobacco Free KidsDocument1 pageCampaign For Tobacco Free KidsNurses For Tobacco ControlNo ratings yet
- EvalsDocument11 pagesEvalsPaul Adriel Balmes50% (2)
- Pre-Reading Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesPre-Reading Lesson Planapi-489274706No ratings yet