Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Algo Arrest
Algo Arrest
Uploaded by
handris yanitraCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Burns Depression InventoryDocument2 pagesBurns Depression InventoryMarcelo de Costa83% (12)
- TMC Dosing ChartDocument6 pagesTMC Dosing ChartScott100% (1)
- Intra Aortic Ballon Pump FlowsheetDocument2 pagesIntra Aortic Ballon Pump FlowsheetYudi Aryasena Radhitya PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Endocarditis, Pericarditic, Myocarditis: TopicDocument104 pagesEndocarditis, Pericarditic, Myocarditis: TopicOM VERMANo ratings yet
- Stress TestDocument2 pagesStress TestDavid GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 - Cardiac EmergenciesDocument96 pagesChapter 20 - Cardiac EmergenciesAmit KlNo ratings yet
- NCP Nasal PolypsDocument3 pagesNCP Nasal Polypsnickanel60% (5)
- Disorders of PancreasDocument17 pagesDisorders of PancreasjonasNo ratings yet
- Care of Patient With TPM Slide PresentationDocument16 pagesCare of Patient With TPM Slide PresentationirzehronNo ratings yet
- Ivc FilterDocument15 pagesIvc FilterashishNo ratings yet
- Heart BlocksDocument6 pagesHeart BlocksMark Hammerschmidt100% (1)
- Terminology Causes of Cardiac Arrest C.P.R. For The Adult, Child & Baby Stroke & Stroke ManagementDocument28 pagesTerminology Causes of Cardiac Arrest C.P.R. For The Adult, Child & Baby Stroke & Stroke Managementbusiness911No ratings yet
- Acls TachiDocument1 pageAcls TachiratnawkNo ratings yet
- Normal Sinus RhythmDocument97 pagesNormal Sinus RhythmNatasha LiberisNo ratings yet
- 2016-TreatmentCSE Algorithm PrintReadyDocument1 page2016-TreatmentCSE Algorithm PrintReadyMauricio Rene Gutierrez CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation On CAD-DVD: Lakhinana - Srilatha Y16PHD0813 V/V Pharm DDocument19 pagesCase Presentation On CAD-DVD: Lakhinana - Srilatha Y16PHD0813 V/V Pharm DAshu AmmuNo ratings yet
- HUTTDocument25 pagesHUTTdrdj14100% (1)
- 5 Steps To Rhythm Strip InterpretationDocument2 pages5 Steps To Rhythm Strip Interpretationjosh082572No ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Analyzing A Rhythm StripDocument7 pagesChapter 5: Analyzing A Rhythm StriptellyNo ratings yet
- CPRDocument4 pagesCPRjeetNo ratings yet
- MRCP Textbook 2Document51 pagesMRCP Textbook 2cdha anphuoc100% (1)
- Cardiac AssessmentDocument48 pagesCardiac AssessmentRatheesh NathNo ratings yet
- Difficult Weaning From Cardiopulmonary Bypass Final Edit LiaDocument41 pagesDifficult Weaning From Cardiopulmonary Bypass Final Edit LiaYuri SadewoNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Artery Occlusive Disease: What To Do About Intermittent Claudication??Document46 pagesPeripheral Artery Occlusive Disease: What To Do About Intermittent Claudication??Dzariyat_Azhar_9277100% (1)
- Intra Arterial Thrombo Lys IsDocument10 pagesIntra Arterial Thrombo Lys IsIustitia Septuaginta SambenNo ratings yet
- 2010 Integrated - Updated Circulation ACLS Prehospital Fibrinolytic Checklist PDFDocument1 page2010 Integrated - Updated Circulation ACLS Prehospital Fibrinolytic Checklist PDFms_lezahNo ratings yet
- Blood Gas Analysis For Bedside DiagnosisDocument6 pagesBlood Gas Analysis For Bedside DiagnosisMuhamad Wirawan AdityoNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument124 pagesCongenital Heart DiseasemulkanmustafaNo ratings yet
- Mitral StenosisDocument50 pagesMitral Stenosissruthimeena6891No ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilation and Intracranial PressureDocument30 pagesMechanical Ventilation and Intracranial PressureFlavius AnghelNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Chest Pain PDFDocument2 pagesEvaluation of Chest Pain PDFJaredNo ratings yet
- ACLS Full LectureDocument47 pagesACLS Full LectureAdhydeva Purusanti100% (3)
- Breast and Lung CancerDocument141 pagesBreast and Lung CancerabdurehmanNo ratings yet
- ECG InterpretationDocument82 pagesECG InterpretationIin Widya Sari Siregar100% (1)
- Acute Isolated MyocarditisDocument20 pagesAcute Isolated Myocarditismerin sunilNo ratings yet
- Heart BlockDocument20 pagesHeart BlockSumathi GopinathNo ratings yet
- Managing Psychiatric Patients in The EDDocument28 pagesManaging Psychiatric Patients in The EDfadiNo ratings yet
- Holter MonitoringDocument19 pagesHolter Monitoringomotola Ayobundle-oyewo MA206100% (1)
- Anusha Inotropes 21Document62 pagesAnusha Inotropes 21twister4No ratings yet
- ElectrocardiogramDocument52 pagesElectrocardiogramTuong HoangManhNo ratings yet
- Effect of Acupressure On Physiological and Psychological Maladies Among Peri and Post Menopausal WomenDocument6 pagesEffect of Acupressure On Physiological and Psychological Maladies Among Peri and Post Menopausal WomenInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument33 pagesCoronary Artery DiseaseAlma Rifa'Ana LiskaNo ratings yet
- Ecg Pathology 02Document95 pagesEcg Pathology 02Andi MP Manurung100% (1)
- Pacing Week PresentationsDocument54 pagesPacing Week PresentationsjoejenningsNo ratings yet
- AclsDocument4 pagesAclsAnusha Verghese100% (1)
- Assigmnt. On Cardiac RehabilitationDocument15 pagesAssigmnt. On Cardiac RehabilitationSachin Singh100% (1)
- Q: Characterize The Different Types of Pacemaker. Explain The Various Steps of PacingDocument4 pagesQ: Characterize The Different Types of Pacemaker. Explain The Various Steps of PacingKRUPALITHAKKAR100% (1)
- Atrial Fibrillation: Discussed by - DR Kunwar Sidharth SaurabhDocument45 pagesAtrial Fibrillation: Discussed by - DR Kunwar Sidharth SaurabhKunwar Sidharth SaurabhNo ratings yet
- ECG Made EasyDocument82 pagesECG Made EasyBobby SodhiNo ratings yet
- Pacemaker NotesDocument7 pagesPacemaker Notesrohit860No ratings yet
- Hemodynamic MonitoringDocument44 pagesHemodynamic Monitoringinvisigoth17No ratings yet
- Venipuncture PDFDocument6 pagesVenipuncture PDFAnna GaturianNo ratings yet
- CardiovascularDocument36 pagesCardiovascularShield Mae BalanlayNo ratings yet
- Right Heart Catheterization, NicvdDocument17 pagesRight Heart Catheterization, NicvdNavojit ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Ton Mitral Valve ReplacementDocument3 pagesTon Mitral Valve ReplacementSony TonNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary ResuscitationDocument10 pagesCardiopulmonary ResuscitationZacchariah Zeref CaraigNo ratings yet
- Sepsis Power Point Slide Presentation - The Guidelines - Implementation For The FutureDocument25 pagesSepsis Power Point Slide Presentation - The Guidelines - Implementation For The Futuremontie13No ratings yet
- Holter MonitoringDocument21 pagesHolter MonitoringAngel LeeNo ratings yet
- NIV Fs 9108147 e 1911 1 PDFDocument4 pagesNIV Fs 9108147 e 1911 1 PDFliuchenshitaoNo ratings yet
- DefibrillatorDocument17 pagesDefibrillatorsamuellivingston100% (1)
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument39 pagesMyocardial InfarctionYauffa Hanna Elt MisykahNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Unige 85299 Attachment01Document24 pagesUnige 85299 Attachment01Oky HermawanNo ratings yet
- Resume - Work Study2Document2 pagesResume - Work Study2api-91728528No ratings yet
- FilariaDocument65 pagesFilarialunaghilvin2026No ratings yet
- The Effects of Active Break and Postural Shift Interventions On Recovery FromDocument8 pagesThe Effects of Active Break and Postural Shift Interventions On Recovery FromNiko TrogerNo ratings yet
- Pioneer Nursing College Vadodara: Subject: Child Health Nursing Topic: Observation Report (Nicu)Document13 pagesPioneer Nursing College Vadodara: Subject: Child Health Nursing Topic: Observation Report (Nicu)Kinjal Vasava100% (1)
- Efn Topic 10 - Sulfi Nurafifah 1020031181Document10 pagesEfn Topic 10 - Sulfi Nurafifah 1020031181Erdin TriansyahNo ratings yet
- Applicable For Third & Fourth Year Subject Homoeopathic Materia MedicaDocument16 pagesApplicable For Third & Fourth Year Subject Homoeopathic Materia MedicaRahul MaliNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Anatomy Slides FINALDocument36 pagesPelvic Anatomy Slides FINALRajashekharNo ratings yet
- Immunotherapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer - Insights Into Tumor Immune Landscape and Therapeutic OpportunitiesDocument25 pagesImmunotherapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer - Insights Into Tumor Immune Landscape and Therapeutic OpportunitiesLee Foo WengNo ratings yet
- 39 Patient Autonomy Informed ConsentDocument3 pages39 Patient Autonomy Informed ConsentJomel BermasNo ratings yet
- PhototherapyDocument3 pagesPhototherapyNicole PageNo ratings yet
- Artikel Bu RashnahDocument7 pagesArtikel Bu RashnahSitti Rosdiana YahyaNo ratings yet
- Best Gastroenterologist in Hyderabad - Healix HospitalsDocument14 pagesBest Gastroenterologist in Hyderabad - Healix HospitalsVarsha ReddyNo ratings yet
- By Speed Post / Email / FAX R.No.115552/El /S4 /2017: AssistantDocument5 pagesBy Speed Post / Email / FAX R.No.115552/El /S4 /2017: AssistantPreethi selvanesanNo ratings yet
- Management of Obesity (Sthoulya) A Success Story-A Case StudyDocument11 pagesManagement of Obesity (Sthoulya) A Success Story-A Case StudyMr. chillNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On First AidDocument10 pagesA Presentation On First AidAshis karmakarNo ratings yet
- Anaphylaxis SOPDocument5 pagesAnaphylaxis SOPmedicshinobiNo ratings yet
- ANAESTHESIA HERZA - ArticleDocument2 pagesANAESTHESIA HERZA - ArticleRihal Adam AriestaNo ratings yet
- Food AllergensDocument49 pagesFood AllergensBareera MunirNo ratings yet
- Cobas 4800 For HPV Detection and GenotypingDocument2 pagesCobas 4800 For HPV Detection and GenotypingMolecular_Diagnostics_KKUH0% (1)
- Khanna Prachi Evidenceoflearning 2b 2 17 17Document3 pagesKhanna Prachi Evidenceoflearning 2b 2 17 17api-333768733No ratings yet
- Jaha 120 017275Document150 pagesJaha 120 017275Leonardo LiswojoNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment DaraDocument3 pagesPhysical Assessment DaraMichael Bon MargajaNo ratings yet
- V60 For Invasive VentilationDocument13 pagesV60 For Invasive Ventilationsam samiNo ratings yet
- Renal Fabs Post TestDocument3 pagesRenal Fabs Post Testlorelyn corpuzNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Artificial Intelligence in Medical JEEV AI-IJRASETDocument8 pagesResearch Paper Artificial Intelligence in Medical JEEV AI-IJRASETIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
Algo Arrest
Algo Arrest
Uploaded by
handris yanitraCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Algo Arrest
Algo Arrest
Uploaded by
handris yanitraCopyright:
Available Formats
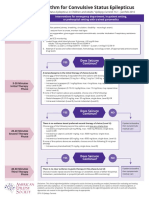
Cardiac Arrest
Circular Algorithm*
Shout for Help/Activate Emergency Response
Start CPR
Give Oxygen Attach Monitor/Defibrillator
2 minutes Return of Spontaneous
Circulation (ROSC)
Check Post-Cardiac
Rhythm Arrest Care
If VF/VT
Shock
Drug Therapy
IV/IO access
Epinephrine every 3–5 minutes
uous CPR
Amiodarone OR Lidocaine for refractory VT/VF
Continuous CPR
Consider Advanced Airway
Quantitative waveform capnography
Contin
Treat Reversible Causes
Mo
nitor y
CPR Qualit
Doses/Details for the Cardiac Arrest Algorithms
CPR Quality Indication of Spontaneous Circulation (ROSC)
Push at least 2” (100–120/min) and allow complete chest recoil Pulse and blood pressure
Minimize interruptions in compressions** Abrupt sustained increase of PETCO2 of > 25 mm Hg check perfusion status.
Avoid excessive ventilation An increase to greater than 40 mm Hg is confirmation of ROSC.
Rotate compressor every 2 minutes Spontaneous arterial pressure waves with intra-arterial
If no advanced airway, 30:2 compression-ventilation ratio monitoring
Quantitative waveform capnography
If PETCO2<10 mm Hg, attempt to improve CPR quality
Shock Energy
Biphasic: Manufacturer recommendation (eg. initial dose of
Drug Therapy 120–200 J): if unknown, use maximum available
Second and subsequent doses should be equivalent, and
Epinephrine IV/IO Dose: 1 mg every 3–5 minutes higher doses may be considered
Amiodarone IV/IO Dose***: First dose: 300 mg bolus
Second dose: 150 mg
Lidocaine: First dose: 1–1.5 mg/kg
Second dose: 0.5–0.75 mg/kg
Reversible Causes
Hypovolemia Tension pneumothorax
Advanced Airway**** Hypoxia Tamponade, cardiac
Hydrogen ion (acidosis) Toxins
Supraglottic advanced airway or endotracheal intubation Hypo-/Hyperkalemia Thrombosis, pulmonary
10 breaths per minute with continuous chest compressions Hypothermia Thrombosis, coronary
* Link MS, Berkow LC, Kudenchuk PJ, Halperin HR, Hess EP, Moitra VK, Neumar RW, O’Neil BJ, Paxton JH, Silvers SM, White RD, Yannopoulos D, Donnino MW. Part 7: adult advanced cardiac life support. 2015 American
Heart Association Guidelines Update for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care. Circulation 2015 132 (suppl 2):S444-S464
** Bobrow BJ, Clark LL, Ewy GA, Chikani V, Sanders AB, Berg RA, Richman PB Minimally Interrupted cardiac resuscitation by emergency medical services for out of hospital cardiac arrest. JAMA 2008;299:1158-1165
*** Dorian P, Cass D, Schwartz B, Cooper R. Gelaznikas R, Barr A. Amiodarone as compared with Lidocaine for shock resistant ventricular fibrillation N Engl J Med 2002;346:884-890.
**** Dorges V, Wenzel V, Knacke P, Gerlach K, Comparison of different airway management strategies to ventilate apneic, nonpreoxygenated patients. Crit Care Med. 2003;31:800-804
Version control: This document follows 2020 American Heart Association® guidelines for CPR and ECC. American Heart Association® guidelines are updated every five years.
If you are reading this page after December 2025, please contact support@acls.net for an update. Version 2021.06.a
© ACLS Training Center +1 877-560-2940 support@acls.net
Complete your ACLS recertification online with the highest quality course at http://www.acls.net
Cardiac Arrest
Algorithm
Shout for Help/Activate Emergency Response
Start CPR
1 Give Oxygen
Attach Monitor/Defibrillator
2 VF/VT Rhythm Shockable? Asystole/PEA 9
3 Shock*
CPR 2 min
IV/IO access
4
CPR 2 min 10 Epinephrine every 3–5 min
IV/IO access Consider advanced airway,
capnography
Rhythm Shockable?
12
Rhythm Shockable?
5 Shock
If no signs of return of
spontaneous circulation
(ROSC), go to 10 or 11.
CPR 2 min
Epinephrine every 3-5 min CPR 2 min
6 Consider advanced airway, Treat reversible causes 11
capnography
If ROSC, go to Post-
Cardiac Arrest Care.
Rhythm Shockable? Rhythm Shockable?
7 Shock
CPR 2 min
Amiodarone or Lidocaine 8 Go to 5 or 7
Treat reversible causes
* Link MS, Atkins DL, Plassman RS, Halperin HR, Samson RA, White RD, Cudnik MT, Berg MD, Kudenchuk PJ, Kerber RE. “Part 6: electrical therapies: automated external defibrillators, defibrillation, cardioversion, and pacing:
2010 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care”. Circulation. 2010;122(suppl 3): S706-S719.
http://circ. ahajournals.org/content/122/18_suppl_3/S706
Version control: This document follows 2020 American Heart Association® guidelines for CPR and ECC. American Heart Association® guidelines are updated every five years.
If you are reading this page after December 2025, please contact support@acls.net for an update. Version 2021.06.a
© ACLS Training Center +1 877-560-2940 support@acls.net
Complete your ACLS recertification online with the highest quality course at http://www.acls.net
You might also like
- Burns Depression InventoryDocument2 pagesBurns Depression InventoryMarcelo de Costa83% (12)
- TMC Dosing ChartDocument6 pagesTMC Dosing ChartScott100% (1)
- Intra Aortic Ballon Pump FlowsheetDocument2 pagesIntra Aortic Ballon Pump FlowsheetYudi Aryasena Radhitya PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Endocarditis, Pericarditic, Myocarditis: TopicDocument104 pagesEndocarditis, Pericarditic, Myocarditis: TopicOM VERMANo ratings yet
- Stress TestDocument2 pagesStress TestDavid GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 - Cardiac EmergenciesDocument96 pagesChapter 20 - Cardiac EmergenciesAmit KlNo ratings yet
- NCP Nasal PolypsDocument3 pagesNCP Nasal Polypsnickanel60% (5)
- Disorders of PancreasDocument17 pagesDisorders of PancreasjonasNo ratings yet
- Care of Patient With TPM Slide PresentationDocument16 pagesCare of Patient With TPM Slide PresentationirzehronNo ratings yet
- Ivc FilterDocument15 pagesIvc FilterashishNo ratings yet
- Heart BlocksDocument6 pagesHeart BlocksMark Hammerschmidt100% (1)
- Terminology Causes of Cardiac Arrest C.P.R. For The Adult, Child & Baby Stroke & Stroke ManagementDocument28 pagesTerminology Causes of Cardiac Arrest C.P.R. For The Adult, Child & Baby Stroke & Stroke Managementbusiness911No ratings yet
- Acls TachiDocument1 pageAcls TachiratnawkNo ratings yet
- Normal Sinus RhythmDocument97 pagesNormal Sinus RhythmNatasha LiberisNo ratings yet
- 2016-TreatmentCSE Algorithm PrintReadyDocument1 page2016-TreatmentCSE Algorithm PrintReadyMauricio Rene Gutierrez CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation On CAD-DVD: Lakhinana - Srilatha Y16PHD0813 V/V Pharm DDocument19 pagesCase Presentation On CAD-DVD: Lakhinana - Srilatha Y16PHD0813 V/V Pharm DAshu AmmuNo ratings yet
- HUTTDocument25 pagesHUTTdrdj14100% (1)
- 5 Steps To Rhythm Strip InterpretationDocument2 pages5 Steps To Rhythm Strip Interpretationjosh082572No ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Analyzing A Rhythm StripDocument7 pagesChapter 5: Analyzing A Rhythm StriptellyNo ratings yet
- CPRDocument4 pagesCPRjeetNo ratings yet
- MRCP Textbook 2Document51 pagesMRCP Textbook 2cdha anphuoc100% (1)
- Cardiac AssessmentDocument48 pagesCardiac AssessmentRatheesh NathNo ratings yet
- Difficult Weaning From Cardiopulmonary Bypass Final Edit LiaDocument41 pagesDifficult Weaning From Cardiopulmonary Bypass Final Edit LiaYuri SadewoNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Artery Occlusive Disease: What To Do About Intermittent Claudication??Document46 pagesPeripheral Artery Occlusive Disease: What To Do About Intermittent Claudication??Dzariyat_Azhar_9277100% (1)
- Intra Arterial Thrombo Lys IsDocument10 pagesIntra Arterial Thrombo Lys IsIustitia Septuaginta SambenNo ratings yet
- 2010 Integrated - Updated Circulation ACLS Prehospital Fibrinolytic Checklist PDFDocument1 page2010 Integrated - Updated Circulation ACLS Prehospital Fibrinolytic Checklist PDFms_lezahNo ratings yet
- Blood Gas Analysis For Bedside DiagnosisDocument6 pagesBlood Gas Analysis For Bedside DiagnosisMuhamad Wirawan AdityoNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument124 pagesCongenital Heart DiseasemulkanmustafaNo ratings yet
- Mitral StenosisDocument50 pagesMitral Stenosissruthimeena6891No ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilation and Intracranial PressureDocument30 pagesMechanical Ventilation and Intracranial PressureFlavius AnghelNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Chest Pain PDFDocument2 pagesEvaluation of Chest Pain PDFJaredNo ratings yet
- ACLS Full LectureDocument47 pagesACLS Full LectureAdhydeva Purusanti100% (3)
- Breast and Lung CancerDocument141 pagesBreast and Lung CancerabdurehmanNo ratings yet
- ECG InterpretationDocument82 pagesECG InterpretationIin Widya Sari Siregar100% (1)
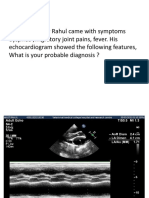
- Acute Isolated MyocarditisDocument20 pagesAcute Isolated Myocarditismerin sunilNo ratings yet
- Heart BlockDocument20 pagesHeart BlockSumathi GopinathNo ratings yet
- Managing Psychiatric Patients in The EDDocument28 pagesManaging Psychiatric Patients in The EDfadiNo ratings yet
- Holter MonitoringDocument19 pagesHolter Monitoringomotola Ayobundle-oyewo MA206100% (1)
- Anusha Inotropes 21Document62 pagesAnusha Inotropes 21twister4No ratings yet
- ElectrocardiogramDocument52 pagesElectrocardiogramTuong HoangManhNo ratings yet
- Effect of Acupressure On Physiological and Psychological Maladies Among Peri and Post Menopausal WomenDocument6 pagesEffect of Acupressure On Physiological and Psychological Maladies Among Peri and Post Menopausal WomenInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument33 pagesCoronary Artery DiseaseAlma Rifa'Ana LiskaNo ratings yet
- Ecg Pathology 02Document95 pagesEcg Pathology 02Andi MP Manurung100% (1)
- Pacing Week PresentationsDocument54 pagesPacing Week PresentationsjoejenningsNo ratings yet
- AclsDocument4 pagesAclsAnusha Verghese100% (1)
- Assigmnt. On Cardiac RehabilitationDocument15 pagesAssigmnt. On Cardiac RehabilitationSachin Singh100% (1)
- Q: Characterize The Different Types of Pacemaker. Explain The Various Steps of PacingDocument4 pagesQ: Characterize The Different Types of Pacemaker. Explain The Various Steps of PacingKRUPALITHAKKAR100% (1)
- Atrial Fibrillation: Discussed by - DR Kunwar Sidharth SaurabhDocument45 pagesAtrial Fibrillation: Discussed by - DR Kunwar Sidharth SaurabhKunwar Sidharth SaurabhNo ratings yet
- ECG Made EasyDocument82 pagesECG Made EasyBobby SodhiNo ratings yet
- Pacemaker NotesDocument7 pagesPacemaker Notesrohit860No ratings yet
- Hemodynamic MonitoringDocument44 pagesHemodynamic Monitoringinvisigoth17No ratings yet
- Venipuncture PDFDocument6 pagesVenipuncture PDFAnna GaturianNo ratings yet
- CardiovascularDocument36 pagesCardiovascularShield Mae BalanlayNo ratings yet
- Right Heart Catheterization, NicvdDocument17 pagesRight Heart Catheterization, NicvdNavojit ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Ton Mitral Valve ReplacementDocument3 pagesTon Mitral Valve ReplacementSony TonNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary ResuscitationDocument10 pagesCardiopulmonary ResuscitationZacchariah Zeref CaraigNo ratings yet
- Sepsis Power Point Slide Presentation - The Guidelines - Implementation For The FutureDocument25 pagesSepsis Power Point Slide Presentation - The Guidelines - Implementation For The Futuremontie13No ratings yet
- Holter MonitoringDocument21 pagesHolter MonitoringAngel LeeNo ratings yet
- NIV Fs 9108147 e 1911 1 PDFDocument4 pagesNIV Fs 9108147 e 1911 1 PDFliuchenshitaoNo ratings yet
- DefibrillatorDocument17 pagesDefibrillatorsamuellivingston100% (1)
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument39 pagesMyocardial InfarctionYauffa Hanna Elt MisykahNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Unige 85299 Attachment01Document24 pagesUnige 85299 Attachment01Oky HermawanNo ratings yet
- Resume - Work Study2Document2 pagesResume - Work Study2api-91728528No ratings yet
- FilariaDocument65 pagesFilarialunaghilvin2026No ratings yet
- The Effects of Active Break and Postural Shift Interventions On Recovery FromDocument8 pagesThe Effects of Active Break and Postural Shift Interventions On Recovery FromNiko TrogerNo ratings yet
- Pioneer Nursing College Vadodara: Subject: Child Health Nursing Topic: Observation Report (Nicu)Document13 pagesPioneer Nursing College Vadodara: Subject: Child Health Nursing Topic: Observation Report (Nicu)Kinjal Vasava100% (1)
- Efn Topic 10 - Sulfi Nurafifah 1020031181Document10 pagesEfn Topic 10 - Sulfi Nurafifah 1020031181Erdin TriansyahNo ratings yet
- Applicable For Third & Fourth Year Subject Homoeopathic Materia MedicaDocument16 pagesApplicable For Third & Fourth Year Subject Homoeopathic Materia MedicaRahul MaliNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Anatomy Slides FINALDocument36 pagesPelvic Anatomy Slides FINALRajashekharNo ratings yet
- Immunotherapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer - Insights Into Tumor Immune Landscape and Therapeutic OpportunitiesDocument25 pagesImmunotherapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer - Insights Into Tumor Immune Landscape and Therapeutic OpportunitiesLee Foo WengNo ratings yet
- 39 Patient Autonomy Informed ConsentDocument3 pages39 Patient Autonomy Informed ConsentJomel BermasNo ratings yet
- PhototherapyDocument3 pagesPhototherapyNicole PageNo ratings yet
- Artikel Bu RashnahDocument7 pagesArtikel Bu RashnahSitti Rosdiana YahyaNo ratings yet
- Best Gastroenterologist in Hyderabad - Healix HospitalsDocument14 pagesBest Gastroenterologist in Hyderabad - Healix HospitalsVarsha ReddyNo ratings yet
- By Speed Post / Email / FAX R.No.115552/El /S4 /2017: AssistantDocument5 pagesBy Speed Post / Email / FAX R.No.115552/El /S4 /2017: AssistantPreethi selvanesanNo ratings yet
- Management of Obesity (Sthoulya) A Success Story-A Case StudyDocument11 pagesManagement of Obesity (Sthoulya) A Success Story-A Case StudyMr. chillNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On First AidDocument10 pagesA Presentation On First AidAshis karmakarNo ratings yet
- Anaphylaxis SOPDocument5 pagesAnaphylaxis SOPmedicshinobiNo ratings yet
- ANAESTHESIA HERZA - ArticleDocument2 pagesANAESTHESIA HERZA - ArticleRihal Adam AriestaNo ratings yet
- Food AllergensDocument49 pagesFood AllergensBareera MunirNo ratings yet
- Cobas 4800 For HPV Detection and GenotypingDocument2 pagesCobas 4800 For HPV Detection and GenotypingMolecular_Diagnostics_KKUH0% (1)
- Khanna Prachi Evidenceoflearning 2b 2 17 17Document3 pagesKhanna Prachi Evidenceoflearning 2b 2 17 17api-333768733No ratings yet
- Jaha 120 017275Document150 pagesJaha 120 017275Leonardo LiswojoNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment DaraDocument3 pagesPhysical Assessment DaraMichael Bon MargajaNo ratings yet
- V60 For Invasive VentilationDocument13 pagesV60 For Invasive Ventilationsam samiNo ratings yet
- Renal Fabs Post TestDocument3 pagesRenal Fabs Post Testlorelyn corpuzNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Artificial Intelligence in Medical JEEV AI-IJRASETDocument8 pagesResearch Paper Artificial Intelligence in Medical JEEV AI-IJRASETIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet