Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Level 1 Assessment EY Financial Analysis Prodegree
Level 1 Assessment EY Financial Analysis Prodegree
Uploaded by
Sairam GovarthananCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- SQL Project QuestionsDocument3 pagesSQL Project QuestionsSachin Singh0% (1)
- This Study Resource Was: Bank Loan Default Prediction ModelDocument9 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Bank Loan Default Prediction ModelAbdelmadjid BouamamaNo ratings yet
- Decision Making: Submitted By-Ankita MishraDocument20 pagesDecision Making: Submitted By-Ankita MishraAnkita MishraNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce Revenue Management - Python For Data Science - Great LearningDocument4 pagesE-Commerce Revenue Management - Python For Data Science - Great LearningSuchi S Bahuguna100% (1)
- Writing Test - Everest Group - Gaurav DeshpandeDocument2 pagesWriting Test - Everest Group - Gaurav DeshpandeBhadang BoysNo ratings yet
- MRA Project Milestone2 PDFDocument1 pageMRA Project Milestone2 PDFRekha Rajaram100% (1)
- Long Quiz FRA - Finance and Risk Analytics - Great LearningDocument8 pagesLong Quiz FRA - Finance and Risk Analytics - Great Learningishan upadhyay100% (1)
- Pima Indian Diabetes QuestionsDocument6 pagesPima Indian Diabetes QuestionsAMAN PRAKASHNo ratings yet
- End Term Quiz1 - Attempt ReviewDocument5 pagesEnd Term Quiz1 - Attempt ReviewAakanksha Gulabdhar MishraNo ratings yet
- SalesDocument17 pagesSalesPriyanka ManjrekarNo ratings yet
- Time Series ForecastingDocument1 pageTime Series ForecastingAshu0% (1)
- Project 4 - Predictive Modeling - Telecom Customer Churn Prediction PDFDocument22 pagesProject 4 - Predictive Modeling - Telecom Customer Churn Prediction PDFSanan OlacheryNo ratings yet
- 1) Introduction A) Defining Problem Statement:-: ST STDocument10 pages1) Introduction A) Defining Problem Statement:-: ST STRaveendra Babu GaddamNo ratings yet
- Customer Churn Prediction Using Big Data AnalyticsDocument41 pagesCustomer Churn Prediction Using Big Data AnalyticsBesty H50% (2)
- MisUse of MonteCarlo Simulation in NPV Analysis-DavisDocument5 pagesMisUse of MonteCarlo Simulation in NPV Analysis-Davisminerito2211No ratings yet
- CREATING Tourism Awareness atDocument29 pagesCREATING Tourism Awareness atMonette de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- KornFerry and Peoplescout JobsDocument994 pagesKornFerry and Peoplescout JobsDeepak PasupuletiNo ratings yet
- Data Science & Business Analytics: Post Graduate Program inDocument17 pagesData Science & Business Analytics: Post Graduate Program inValli Kowsalya AduriNo ratings yet
- Best PDFDocument16 pagesBest PDFSankarNo ratings yet
- IMC Project On Superia Soap (13,16,28,36,39,47)Document13 pagesIMC Project On Superia Soap (13,16,28,36,39,47)Doyel Ghosh0% (1)
- Answer Book - Sparkling WinesDocument10 pagesAnswer Book - Sparkling WinesAshish AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Project Report Adv Stat V1.0Document5 pagesProject Report Adv Stat V1.0Bibin VadakkekaraNo ratings yet
- Surabhi FRA PartADocument13 pagesSurabhi FRA PartAScribd SCNo ratings yet
- Code It QuestionsDocument3 pagesCode It QuestionsNimisha SharmaNo ratings yet
- SMDM Assignment 3 FinalDocument2 pagesSMDM Assignment 3 FinalHIMANSHU VARMANo ratings yet
- MIS ProjectDocument7 pagesMIS ProjectSharmila SivaramanNo ratings yet
- FRA Business ReportDocument21 pagesFRA Business ReportSurabhi Kulkarni100% (1)
- MySQL - Week 5 QuizDocument6 pagesMySQL - Week 5 QuizPratyusha Chamarti100% (1)
- Cafe Data MRADocument6,482 pagesCafe Data MRAA dNo ratings yet
- Demand Determinants of AutomobilesDocument7 pagesDemand Determinants of AutomobilesShuchi SablokNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document20 pagesBook 1Anonymous Je6oNBVNo ratings yet
- SMDM Extended ProjectDocument1 pageSMDM Extended Projectsrashti tripathiNo ratings yet
- Tushar Tukaram Bhakare: Education SkillsDocument1 pageTushar Tukaram Bhakare: Education SkillsSUMEET SARODENo ratings yet
- Business Report Project: Student's Name - ANAMIT DEB GUPTADocument12 pagesBusiness Report Project: Student's Name - ANAMIT DEB GUPTAGupta AnacoolzNo ratings yet
- FRA AssignmentDocument19 pagesFRA AssignmentAshish Tekwani100% (1)
- AV Project Shivakumar VangaDocument37 pagesAV Project Shivakumar VangaVanga Shiva100% (1)
- Agents Benefits 1Document87 pagesAgents Benefits 1Bharath Kumar K100% (1)
- DVT Project For PGP-BABI (2019-20) Done by Saleesh Satheeshcahandran (G6)Document3 pagesDVT Project For PGP-BABI (2019-20) Done by Saleesh Satheeshcahandran (G6)Narayana NarlaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 13: Tableau Visualizations: Visualization Tasks 1. Sales Representative and Calls PerformanceDocument3 pagesAssignment 13: Tableau Visualizations: Visualization Tasks 1. Sales Representative and Calls PerformancekeyspNo ratings yet
- Us PresidentDocument24 pagesUs PresidentAnonymous nfHBPXz178No ratings yet
- Project DVT CarInsuranceDocument10 pagesProject DVT CarInsurancecontactNo ratings yet
- Data Mining Project - PCA - Hair SalonDocument8 pagesData Mining Project - PCA - Hair SalonPriyanka SharmaNo ratings yet
- ML Assignemnt PDFDocument21 pagesML Assignemnt PDFEric NormanNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning SolutionDocument12 pagesMachine Learning Solutionprabu2125100% (1)
- Cars Project PDFDocument9 pagesCars Project PDFAshmitha ChangappaNo ratings yet
- REport Time SeriesDocument57 pagesREport Time SeriesAkshaya Kennedy100% (2)
- KADIYALA SRIBALAJI RAM - 02-Apr-2021 (Business Report)Document13 pagesKADIYALA SRIBALAJI RAM - 02-Apr-2021 (Business Report)Sri Balaji RamNo ratings yet
- Predictive Modelling Project 2Document32 pagesPredictive Modelling Project 2Purva Soni100% (3)
- Great Lakes PGPM Chennai CV TemplateDocument1 pageGreat Lakes PGPM Chennai CV Templateananth24No ratings yet
- Business Report Project SMDM - Divjyot Shah Singh - 10102021Document19 pagesBusiness Report Project SMDM - Divjyot Shah Singh - 10102021Divjyot100% (1)
- Think Pair Share Team G1 - 7Document8 pagesThink Pair Share Team G1 - 7Akash Kashyap100% (1)
- 7z1018 CW Example Predicting House Prices in King CountyDocument16 pages7z1018 CW Example Predicting House Prices in King CountyKrusty00No ratings yet
- CafeSales MRA PresentationDocument40 pagesCafeSales MRA PresentationKyotoNo ratings yet
- ML - Project - Business ReportDocument43 pagesML - Project - Business ReportROHINI ROKDENo ratings yet
- Silk Bank - Yes We Can!: Shehneez SaeedDocument22 pagesSilk Bank - Yes We Can!: Shehneez SaeedshehneezNo ratings yet
- Capstone PresentationDocument9 pagesCapstone Presentationapi-437398074No ratings yet
- Healthcare PGP - Capstone ProjectDocument32 pagesHealthcare PGP - Capstone ProjectSneh Prakhar0% (1)
- Answer Report (Preditive Modelling)Document29 pagesAnswer Report (Preditive Modelling)Shweta Lakhera100% (1)
- SMDM STATISTICS PROJECT-MARCH27th - DEEPA CHURIDocument16 pagesSMDM STATISTICS PROJECT-MARCH27th - DEEPA CHURIDeepa ChuriNo ratings yet
- DataMining Project SonaliPradhanDocument34 pagesDataMining Project SonaliPradhansonali PradhanNo ratings yet
- DADM Q7,8 and 9 ReportDocument4 pagesDADM Q7,8 and 9 ReportgreatlakesNo ratings yet
- Concept Based Practice Questions for Tableau Desktop Specialist Certification Latest Edition 2023From EverandConcept Based Practice Questions for Tableau Desktop Specialist Certification Latest Edition 2023No ratings yet
- Use The Following Information To Answer The Next Four QuestionsDocument5 pagesUse The Following Information To Answer The Next Four QuestionsAkshadaNo ratings yet
- Module - 5: Direct MarketingDocument46 pagesModule - 5: Direct Marketingwintoday01No ratings yet
- What Are The Corporations Exempt From Taxation?Document3 pagesWhat Are The Corporations Exempt From Taxation?ANGEL MAE LINABAN GONGOBNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Tushar EnterprisesDocument15 pagesCase Study On Tushar EnterprisesVivek RajNo ratings yet
- Strategic Challenges Faced by FMCG and RetailDocument53 pagesStrategic Challenges Faced by FMCG and RetailRajNo ratings yet
- PLM Nstp-Cwts Swot Analysis Training For The Community Service Project ProposalDocument26 pagesPLM Nstp-Cwts Swot Analysis Training For The Community Service Project ProposalWawit DiazNo ratings yet
- Part Ii. Competencies Core Behavioral Competencies: Self Management TeamworkDocument2 pagesPart Ii. Competencies Core Behavioral Competencies: Self Management TeamworkPaul Bryan BronNo ratings yet
- Considerations For Entrepreneurs Entering The Recreational Marijuana IndustryDocument15 pagesConsiderations For Entrepreneurs Entering The Recreational Marijuana IndustryRay RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Government of Bermuda FDS Fixed Assets v3Document28 pagesGovernment of Bermuda FDS Fixed Assets v3MitchNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Contemporary Financial Management 10th Edition Moyer Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Contemporary Financial Management 10th Edition Moyer Solutions Manual PDFquachhaitpit100% (19)
- BM 1.5 External EnvironmentDocument12 pagesBM 1.5 External EnvironmentTita RachmawatiNo ratings yet
- Cost ProblemsDocument4 pagesCost ProblemsMeteor MeteorNo ratings yet
- Hse MS SlidesDocument32 pagesHse MS SlidesEneyo Victor100% (1)
- Morningstar Economic Moats II - ExcellentDocument42 pagesMorningstar Economic Moats II - Excellentee1993100% (1)
- Chap 008Document30 pagesChap 008M. Zainal AbidinNo ratings yet
- Islamic vs. Conventional BankingDocument32 pagesIslamic vs. Conventional BankingNuwan Tharanga LiyanageNo ratings yet
- Vinex Ias Academy®: About Us VINEX Is Promoted by Best Most Trusted IAS FacultyDocument19 pagesVinex Ias Academy®: About Us VINEX Is Promoted by Best Most Trusted IAS FacultyDhoorjati VommiNo ratings yet
- Cie LKPDocument9 pagesCie LKPRajiv HandaNo ratings yet
- Facility Management DefinitionDocument8 pagesFacility Management DefinitionShabin ShabiNo ratings yet
- Weygandt, Kieso, & Kimmel: Managerial AccountingDocument41 pagesWeygandt, Kieso, & Kimmel: Managerial AccountingTika GusmawarniNo ratings yet
- Transit: Problems and ProspectsDocument9 pagesTransit: Problems and ProspectsSumon Kumar DasNo ratings yet
- Setting Up of A New Quantitative Finance Firm: Business Plan, Market Driver, Capital Raising and EthicsDocument48 pagesSetting Up of A New Quantitative Finance Firm: Business Plan, Market Driver, Capital Raising and EthicsDanielNo ratings yet
- Secondary Data CollectionDocument18 pagesSecondary Data CollectionShriya ParateNo ratings yet
- 2B MismatchDocument65 pages2B Mismatchshubhamburnwal213No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Inventory ControlDocument61 pagesChapter 5 Inventory ControlJanak KarkiNo ratings yet
- Executive SummaryDocument23 pagesExecutive SummaryLois RazonNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Term 3 Business SchemesDocument4 pagesGrade 7 Term 3 Business Schemeswesley kipkoechNo ratings yet
- Objectives:: Tourism Industry in BangladeshDocument39 pagesObjectives:: Tourism Industry in BangladeshAshiqur RahmanNo ratings yet
Level 1 Assessment EY Financial Analysis Prodegree
Level 1 Assessment EY Financial Analysis Prodegree
Uploaded by
Sairam GovarthananOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Level 1 Assessment EY Financial Analysis Prodegree
Level 1 Assessment EY Financial Analysis Prodegree
Uploaded by
Sairam GovarthananCopyright:
Available Formats
Level 1 Assessment
EY Financial Analysis Prodegree
NAME:________________________________________________________________________________ DATE:__________________
Marking Scheme:
Questions 1- 17 and 26 – 31 will carry 1 mark each for correct attempt.
Questions 18 – 24 carry 3 marks each for correct attempt. Partial credit will be given if answers are
partially correct
Question 25 carries 9 marks
Questions 26 – 31 use closing nos. to calculate ratios instead of average balance sheet nos. wherever
applicable. For other questions, specific comments have been made if closing nos. are to be taken instead
of average. Wherever such comment is not made, you need to calculate ratios using average balance sheet
nos.
1. A brand new company has a building costing $10,000, machinery costing $5,000, cash of $700, and a
bank loan of $7,850. What is the owner’s equity?
A. $8,850
B. $15,700
C. $7,750
D. Cannot be Determined
E. $7,850
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
$10,000 + $5,000 + $700 = $7850 + Equity
2. If a company has owner’s equity of $100, 000, _______________.
A. Assets Minus Liabilities Equal $100,000
B. Total Assets Must Equal $100,000
C. Net Income for the Past Year Was $100,000
D. A Total of $100,000 was Invested by the Owner
E. None of the Above
Use the following information to answer the next four questions.
Joseph Forbes is the owner of his own business. On December 31, Forbes’ assets, liabilities, revenues and
expenses were:
Insurance Expenses (EXP) $3,000 Accounts Payable $4,000
Miscellaneous Expenses Accounts Receivable (CURR.
900 5,000
(EXP) ASSET)
Rent Expenses (EXP) 2,500 Cash (CURR. ASSET) 14,000
Confidential and restricted. Do not distribute. © Imarticus Learning 1
Level 1 Assessment
EY Financial Analysis Prodegree
Salaries Expense
3. On December (EXP)
31, total 19,000
assets are equal to: Equipment (ASSET) 11,000
A. Supplies
$25,700 Expense (EXP) 1,200 Notes Payable 4,600
B. $19,700
C. Services
$22,100 Performed (INC) 45,000 Supplies on hand (CURR. ASSET) 700
D. $30,700
E. None of the Above
4. On December 31, net income is equal to:
A. $18,400
B. $45,000
C. $17,400
D. None of the Above
5. On December 31, if net income equals $15,000 and the ending owner’s equity is $20,000, and Forbes
invested an additional $2,600 in his business, while withdrawing $6,000 during the year, the
beginning owner’s equity for this year was:
A. $7,100
B. $7,400
C. $8,400
D. $7,430
E. None of the Above
6. On December 31, current assets equal:
A. $9,000
B. $19,700
C. $19,000
D. $23,000
E. None of the Above
7. A truck was purchased on July 1 for $20,000. The estimated salvage value is $2,000. The estimated
useful life is 3 years. Using straight-line method of depreciation, the amount of depreciation at fiscal
year-end on December 31 is:
A. Depreciation Expense-Truck $555.56
B. Depreciation Expense- Truck $1,500
C. Depreciation Expense- Truck $500
D. Depreciation Expense- Truck $3,000
Using the following 2 tables, answer the next three questions.
Table of Inventory Purchases
Date Units Unit Cost Total cost
Beginning Inventory 10 $3 $30
Confidential and restricted. Do not distribute. © Imarticus Learning 2
Level 1 Assessment
EY Financial Analysis Prodegree
February 3 5 4 20
April 10 15 5 75
June 12 12 7 84
August 20 20 8 160
Total 62 369
Sales
Date Units Identified Units Price Total
March 5 February 5 $6 $30
May 2 April 10 6 60
July 4 June 2 10 20
September 1 June 8 10 80
25 $190
8. Determine the ending inventory using FIFO.
A. $179
B. $190
C. $269
D. $369
9. Determine the ending inventory using LIFO
A. $185
B. $174
C. $190
D. $369
10. Determine the ending inventory under weighted average method.
A. $190
B. $220
C. $249
D. $369
11. From merchandiser’s income statement you know that Sales revenue is $ 650,000 and the gross
margin is 20%. What is the cost of Goods Sold?
A. $650,000
B. $130,000
C. $26,000
D. $520,000
Confidential and restricted. Do not distribute. © Imarticus Learning 3
Level 1 Assessment
EY Financial Analysis Prodegree
12. A manufacturer has beginning and ending finished goods inventory of $70, 000 and $90,000
respectively. Also, the cost of goods manufactured is $200,000. What is the Cost of Goods Sold?
A. $20,000
B. $70,000
C. $180,000
D. $270,000
13. Smith. Corp. sold 100 shares of $50 par value common stock for $70 per share. What would be the
correct journal entry?
A. Cash $7,000
Equity Share Capital $7,000
B. Cash $7,000
Equity Share Capital $5,000
Securities Premium $2,000
C. Equity Share Capital $7,000
Cash $7,000
D. Cash $7,000
Equity Share Capital $2,000
Securities Premium $5,000
14. Park Inc. earned EBIT $10,000,000 last year. Tax rate was 40%, interest expense $2,000,000.
Number of common shares were as follows:
Beginning of year: 500,000
Issued on October 1: 1,000,000
Calculate the EPS of the company. Year ending of the company is March 31
A. $8.00
B. $6.00
C. $4.80
D. $4.00
15. Given the following balance sheets of three firms, which appears to have greater financial leverage?
Firm A Firm B Firm C
Debt $2 $40 $15
Equity $8 $60 $35
Confidential and restricted. Do not distribute. © Imarticus Learning 4
Level 1 Assessment
EY Financial Analysis Prodegree
Total Assets $10 $100 $50
A. Firm A
B. Firm B
C. Firm C
D. All the Same
16. Given the following income statements of three companies, which appears to have greater financial
leverage (i.e. greater debt) based upon the interest coverage ratio?
Firm A Firm B Firm C
EBIT $50 $100 $75
Interest 10 15 5
EBT 40 85 70
Taxes 20 45 50
EAT 20 40 20
A. Firm A
B. Firm B
C. Firm C
D. All the Same
17. A company is being sued for $100,000. What would be recorded on the balance sheet?
A. Nothing
B. $100,000 Set-aside Cash
C. $100,000 Liability
D. $100,000 Contingent Liability
18. Total Debt / EBITDA is 5x as of Mar 2014. Revenues in this period have increased by 20% and EBITDA
margins are 20%. D&A is 5% of Revenues for Mar 2014. Debt : Equity ratio as of Mar 2014 is 0.5x.
Calculate the Total Asset Turnover ratio for Mar 2014 (Note: Assume Total Asset Turnover ratio is
calculated on Closing Total Assets i.e. Total Assets as of Mar 2014 rather than Average Total Assets).
Please also calculate the average interest cost on debt assuming the interest coverage ratio is 3x
Confidential and restricted. Do not distribute. © Imarticus Learning 5
Level 1 Assessment
EY Financial Analysis Prodegree
19. If Net Profit Margin for 2014 is 10% and assuming that all the information in question 18 applies to
this question as well, please calculate the Return on Equity for 2014. (Note: Assume Closing nos.
instead of average nos. for all calculations)
20. Super quick ratio at the end of the year is 0.25x. Revenues are INR 120 Cr and the Gross Profit Margin
of the Company is 25%. Assuming that Opening Stock = Closing Stock and Accounts Payable Turnover
Ratio is 6x, please calculate the cash balance. Please note that Opening Accounts Payable = 1.25 times
Closing Accounts Payable and there are no other liabilities in the balance sheet [Hint: Super Quick
Ratio assumes only Cash in the Numerator]
21. The Price / Book ratio for Company A at the beginning of the year was 3.25x. At the end of the year, the
Price / Book ratio was 2.8x and the share price had increased by 25% between the years – the share
price at the end of the year was INR 125. Assuming that the P/E ratio at the beginning of the year was
10x and it had decreased to 8x at the end of the year, please calculate the Return on Equity for the
year.
22. A company has 10,000 equity shares outstanding throughout the year (there have been no share
issuances during the year). During the year, the Company clocked sales of INR 150 Cr and had an
EBITDA margin of 20%. D&A as a % of Capex was 5% and Capex for the year was INR 20 Cr. The
company also had debt in its balance sheet to the tune of INR 50 Cr – this was issued at an interest rate
of 13%. The debt is convertible into equity with a ratio of 1 equity share for every Rs. 50,000 of debt.
The effective tax rate for the Company is 30%. Calculate the Basic and Diluted Earnings per share.
[Hint: Factor interest cost in your calculations of diluted EPS]
23. In question 22, assume that all information stays the same. However, instead of debt of INR 50 Cr, the
Company has issued convertible preference shares of INR 50 Cr and the dividend on these shares is
8%. Calculate the Basic and Diluted Earnings per Share
24. Compare the Basic and Diluted EPS arrived at in questions 22 and 23. Explain with reasons as to why
one of the diluted EPS (either diluted EPS arrived at in question 22 or diluted EPS arrived at in
question 23) should be higher or lower than the other
25. On 1 April 2014, Company A recently acquired 75% of the equity shares of Company B. Company B
had total shares outstanding of 100,000 of a face value of Rs. 10. It had also issued convertible
debentures. Company B had issued 20,000 such debentures and each debenture was convertible into
2.5 equity shares of a face value of Rs. 10. The debentures were convertible into equity shares before
any company acquired a majority stake in Company B.
Further, Company B had made profits of INR 10 Crore in the financial year ended 31 March 2014,
which represented only 5% of its total reserves on the balance sheet as on April 1, 2014. Company A
on the other hand had made a profit of INR 100 Crore for the financial year ended 31 March 2014.
Confidential and restricted. Do not distribute. © Imarticus Learning 6
Level 1 Assessment
EY Financial Analysis Prodegree
Company A’s outstanding and paid up share capital was INR 200 Crores and its reserves and surplus
were INR 500 Crore.
Company A acquired Company B by paying a consideration of INR 450 Crore. Using the above
information, please calculate:
A. Goodwill on Consolidation
B. Minority Interest
C. Company A’s Share in Consolidated Profits
D. Minority Share in Consolidated Profits
26. Holding all else equal, ROE will rise with an increase in:
A. Total Assets.
B. Sales.
C. Stockholders’ Equity.
D. None of These.
Suppose a company with the following financial information:
Income Statement $ Balance Sheet $
Sales 12,500,000 Cash 550,000
Cost of Goods Sold 6,550,000 Accounts Receivable 1,450,000
Gross Profit 5,950,000 Inventory 1,040,000
Operating Expenses 2,400,000 Total Current Assets 3,040,000
Interest Expense 450,000 Total Fixed Assets 10,000,000
Taxes 750,000 Total Current Liabilities 2,500,000
Net Income 2,350,000 Long-term Liabilities 6,000,000
Paid-in Capital 2,000,000
Number of Outstanding Shares 1,000,000 Retained Earnings 2,540,000
Current Market price 37.90
27. What is the net profit margin?
A. 18.80%
B. 27.20%
C. 32.40%
D. 47.60%
28. What is the return on equity?
Confidential and restricted. Do not distribute. © Imarticus Learning 7
Level 1 Assessment
EY Financial Analysis Prodegree
A. 17.50%
B. 51.76%
C. 92.52%
D. 117.50%
29. What is the receivables turnover?
A. 2.50
B. 4.87
C. 6.30
D. 8.62
30. What is the inventory turnover?
A. 2.50
B. 4.87
C. 6.30
D. 8.62
31. All else equal, a rise in Asset Turnover will result in a rise in:
A. Depreciation.
B. Leverage.
C. Profit Margin.
D. ROE
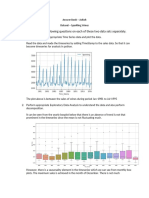
32. Prepare a Cash Flow statement for March 14 based on the excel attached. (10 Marks)
33. Calculate the following ratios based on the balance sheet, income statement and cash flow prepared in
question 33 above (for March 14): (1 Mark per Ratio)
a. ROE
b. Return on Capital Employed (post-tax)
c. Net Profit Margin
d. EBITDA Margin
e. Effective Tax Rate
f. Operating Cost Ratio
g. Gross Profit Margin
h. Total Asset Turnover Ratio
i. Fixed Asset Turnover Ratio
j. Receivables Turnover Ratio
k. Leverage Ratio [Avg. Total Assets / Avg. Total Equity]
l. FCF / EBITDA
m. Interest Coverage Ratio
n. Debt Service Coverage Ratio
o. Basic EPS (Assume Face Value of each share is INR 10)
p. Debt : Equity Ratio
Confidential and restricted. Do not distribute. © Imarticus Learning 8
Level 1 Assessment
EY Financial Analysis Prodegree
Confidential and restricted. Do not distribute. © Imarticus Learning 9
You might also like
- SQL Project QuestionsDocument3 pagesSQL Project QuestionsSachin Singh0% (1)
- This Study Resource Was: Bank Loan Default Prediction ModelDocument9 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Bank Loan Default Prediction ModelAbdelmadjid BouamamaNo ratings yet
- Decision Making: Submitted By-Ankita MishraDocument20 pagesDecision Making: Submitted By-Ankita MishraAnkita MishraNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce Revenue Management - Python For Data Science - Great LearningDocument4 pagesE-Commerce Revenue Management - Python For Data Science - Great LearningSuchi S Bahuguna100% (1)
- Writing Test - Everest Group - Gaurav DeshpandeDocument2 pagesWriting Test - Everest Group - Gaurav DeshpandeBhadang BoysNo ratings yet
- MRA Project Milestone2 PDFDocument1 pageMRA Project Milestone2 PDFRekha Rajaram100% (1)
- Long Quiz FRA - Finance and Risk Analytics - Great LearningDocument8 pagesLong Quiz FRA - Finance and Risk Analytics - Great Learningishan upadhyay100% (1)
- Pima Indian Diabetes QuestionsDocument6 pagesPima Indian Diabetes QuestionsAMAN PRAKASHNo ratings yet
- End Term Quiz1 - Attempt ReviewDocument5 pagesEnd Term Quiz1 - Attempt ReviewAakanksha Gulabdhar MishraNo ratings yet
- SalesDocument17 pagesSalesPriyanka ManjrekarNo ratings yet
- Time Series ForecastingDocument1 pageTime Series ForecastingAshu0% (1)
- Project 4 - Predictive Modeling - Telecom Customer Churn Prediction PDFDocument22 pagesProject 4 - Predictive Modeling - Telecom Customer Churn Prediction PDFSanan OlacheryNo ratings yet
- 1) Introduction A) Defining Problem Statement:-: ST STDocument10 pages1) Introduction A) Defining Problem Statement:-: ST STRaveendra Babu GaddamNo ratings yet
- Customer Churn Prediction Using Big Data AnalyticsDocument41 pagesCustomer Churn Prediction Using Big Data AnalyticsBesty H50% (2)
- MisUse of MonteCarlo Simulation in NPV Analysis-DavisDocument5 pagesMisUse of MonteCarlo Simulation in NPV Analysis-Davisminerito2211No ratings yet
- CREATING Tourism Awareness atDocument29 pagesCREATING Tourism Awareness atMonette de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- KornFerry and Peoplescout JobsDocument994 pagesKornFerry and Peoplescout JobsDeepak PasupuletiNo ratings yet
- Data Science & Business Analytics: Post Graduate Program inDocument17 pagesData Science & Business Analytics: Post Graduate Program inValli Kowsalya AduriNo ratings yet
- Best PDFDocument16 pagesBest PDFSankarNo ratings yet
- IMC Project On Superia Soap (13,16,28,36,39,47)Document13 pagesIMC Project On Superia Soap (13,16,28,36,39,47)Doyel Ghosh0% (1)
- Answer Book - Sparkling WinesDocument10 pagesAnswer Book - Sparkling WinesAshish AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Project Report Adv Stat V1.0Document5 pagesProject Report Adv Stat V1.0Bibin VadakkekaraNo ratings yet
- Surabhi FRA PartADocument13 pagesSurabhi FRA PartAScribd SCNo ratings yet
- Code It QuestionsDocument3 pagesCode It QuestionsNimisha SharmaNo ratings yet
- SMDM Assignment 3 FinalDocument2 pagesSMDM Assignment 3 FinalHIMANSHU VARMANo ratings yet
- MIS ProjectDocument7 pagesMIS ProjectSharmila SivaramanNo ratings yet
- FRA Business ReportDocument21 pagesFRA Business ReportSurabhi Kulkarni100% (1)
- MySQL - Week 5 QuizDocument6 pagesMySQL - Week 5 QuizPratyusha Chamarti100% (1)
- Cafe Data MRADocument6,482 pagesCafe Data MRAA dNo ratings yet
- Demand Determinants of AutomobilesDocument7 pagesDemand Determinants of AutomobilesShuchi SablokNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document20 pagesBook 1Anonymous Je6oNBVNo ratings yet
- SMDM Extended ProjectDocument1 pageSMDM Extended Projectsrashti tripathiNo ratings yet
- Tushar Tukaram Bhakare: Education SkillsDocument1 pageTushar Tukaram Bhakare: Education SkillsSUMEET SARODENo ratings yet
- Business Report Project: Student's Name - ANAMIT DEB GUPTADocument12 pagesBusiness Report Project: Student's Name - ANAMIT DEB GUPTAGupta AnacoolzNo ratings yet
- FRA AssignmentDocument19 pagesFRA AssignmentAshish Tekwani100% (1)
- AV Project Shivakumar VangaDocument37 pagesAV Project Shivakumar VangaVanga Shiva100% (1)
- Agents Benefits 1Document87 pagesAgents Benefits 1Bharath Kumar K100% (1)
- DVT Project For PGP-BABI (2019-20) Done by Saleesh Satheeshcahandran (G6)Document3 pagesDVT Project For PGP-BABI (2019-20) Done by Saleesh Satheeshcahandran (G6)Narayana NarlaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 13: Tableau Visualizations: Visualization Tasks 1. Sales Representative and Calls PerformanceDocument3 pagesAssignment 13: Tableau Visualizations: Visualization Tasks 1. Sales Representative and Calls PerformancekeyspNo ratings yet
- Us PresidentDocument24 pagesUs PresidentAnonymous nfHBPXz178No ratings yet
- Project DVT CarInsuranceDocument10 pagesProject DVT CarInsurancecontactNo ratings yet
- Data Mining Project - PCA - Hair SalonDocument8 pagesData Mining Project - PCA - Hair SalonPriyanka SharmaNo ratings yet
- ML Assignemnt PDFDocument21 pagesML Assignemnt PDFEric NormanNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning SolutionDocument12 pagesMachine Learning Solutionprabu2125100% (1)
- Cars Project PDFDocument9 pagesCars Project PDFAshmitha ChangappaNo ratings yet
- REport Time SeriesDocument57 pagesREport Time SeriesAkshaya Kennedy100% (2)
- KADIYALA SRIBALAJI RAM - 02-Apr-2021 (Business Report)Document13 pagesKADIYALA SRIBALAJI RAM - 02-Apr-2021 (Business Report)Sri Balaji RamNo ratings yet
- Predictive Modelling Project 2Document32 pagesPredictive Modelling Project 2Purva Soni100% (3)
- Great Lakes PGPM Chennai CV TemplateDocument1 pageGreat Lakes PGPM Chennai CV Templateananth24No ratings yet
- Business Report Project SMDM - Divjyot Shah Singh - 10102021Document19 pagesBusiness Report Project SMDM - Divjyot Shah Singh - 10102021Divjyot100% (1)
- Think Pair Share Team G1 - 7Document8 pagesThink Pair Share Team G1 - 7Akash Kashyap100% (1)
- 7z1018 CW Example Predicting House Prices in King CountyDocument16 pages7z1018 CW Example Predicting House Prices in King CountyKrusty00No ratings yet
- CafeSales MRA PresentationDocument40 pagesCafeSales MRA PresentationKyotoNo ratings yet
- ML - Project - Business ReportDocument43 pagesML - Project - Business ReportROHINI ROKDENo ratings yet
- Silk Bank - Yes We Can!: Shehneez SaeedDocument22 pagesSilk Bank - Yes We Can!: Shehneez SaeedshehneezNo ratings yet
- Capstone PresentationDocument9 pagesCapstone Presentationapi-437398074No ratings yet
- Healthcare PGP - Capstone ProjectDocument32 pagesHealthcare PGP - Capstone ProjectSneh Prakhar0% (1)
- Answer Report (Preditive Modelling)Document29 pagesAnswer Report (Preditive Modelling)Shweta Lakhera100% (1)
- SMDM STATISTICS PROJECT-MARCH27th - DEEPA CHURIDocument16 pagesSMDM STATISTICS PROJECT-MARCH27th - DEEPA CHURIDeepa ChuriNo ratings yet
- DataMining Project SonaliPradhanDocument34 pagesDataMining Project SonaliPradhansonali PradhanNo ratings yet
- DADM Q7,8 and 9 ReportDocument4 pagesDADM Q7,8 and 9 ReportgreatlakesNo ratings yet
- Concept Based Practice Questions for Tableau Desktop Specialist Certification Latest Edition 2023From EverandConcept Based Practice Questions for Tableau Desktop Specialist Certification Latest Edition 2023No ratings yet
- Use The Following Information To Answer The Next Four QuestionsDocument5 pagesUse The Following Information To Answer The Next Four QuestionsAkshadaNo ratings yet
- Module - 5: Direct MarketingDocument46 pagesModule - 5: Direct Marketingwintoday01No ratings yet
- What Are The Corporations Exempt From Taxation?Document3 pagesWhat Are The Corporations Exempt From Taxation?ANGEL MAE LINABAN GONGOBNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Tushar EnterprisesDocument15 pagesCase Study On Tushar EnterprisesVivek RajNo ratings yet
- Strategic Challenges Faced by FMCG and RetailDocument53 pagesStrategic Challenges Faced by FMCG and RetailRajNo ratings yet
- PLM Nstp-Cwts Swot Analysis Training For The Community Service Project ProposalDocument26 pagesPLM Nstp-Cwts Swot Analysis Training For The Community Service Project ProposalWawit DiazNo ratings yet
- Part Ii. Competencies Core Behavioral Competencies: Self Management TeamworkDocument2 pagesPart Ii. Competencies Core Behavioral Competencies: Self Management TeamworkPaul Bryan BronNo ratings yet
- Considerations For Entrepreneurs Entering The Recreational Marijuana IndustryDocument15 pagesConsiderations For Entrepreneurs Entering The Recreational Marijuana IndustryRay RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Government of Bermuda FDS Fixed Assets v3Document28 pagesGovernment of Bermuda FDS Fixed Assets v3MitchNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Contemporary Financial Management 10th Edition Moyer Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Contemporary Financial Management 10th Edition Moyer Solutions Manual PDFquachhaitpit100% (19)
- BM 1.5 External EnvironmentDocument12 pagesBM 1.5 External EnvironmentTita RachmawatiNo ratings yet
- Cost ProblemsDocument4 pagesCost ProblemsMeteor MeteorNo ratings yet
- Hse MS SlidesDocument32 pagesHse MS SlidesEneyo Victor100% (1)
- Morningstar Economic Moats II - ExcellentDocument42 pagesMorningstar Economic Moats II - Excellentee1993100% (1)
- Chap 008Document30 pagesChap 008M. Zainal AbidinNo ratings yet
- Islamic vs. Conventional BankingDocument32 pagesIslamic vs. Conventional BankingNuwan Tharanga LiyanageNo ratings yet
- Vinex Ias Academy®: About Us VINEX Is Promoted by Best Most Trusted IAS FacultyDocument19 pagesVinex Ias Academy®: About Us VINEX Is Promoted by Best Most Trusted IAS FacultyDhoorjati VommiNo ratings yet
- Cie LKPDocument9 pagesCie LKPRajiv HandaNo ratings yet
- Facility Management DefinitionDocument8 pagesFacility Management DefinitionShabin ShabiNo ratings yet
- Weygandt, Kieso, & Kimmel: Managerial AccountingDocument41 pagesWeygandt, Kieso, & Kimmel: Managerial AccountingTika GusmawarniNo ratings yet
- Transit: Problems and ProspectsDocument9 pagesTransit: Problems and ProspectsSumon Kumar DasNo ratings yet
- Setting Up of A New Quantitative Finance Firm: Business Plan, Market Driver, Capital Raising and EthicsDocument48 pagesSetting Up of A New Quantitative Finance Firm: Business Plan, Market Driver, Capital Raising and EthicsDanielNo ratings yet
- Secondary Data CollectionDocument18 pagesSecondary Data CollectionShriya ParateNo ratings yet
- 2B MismatchDocument65 pages2B Mismatchshubhamburnwal213No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Inventory ControlDocument61 pagesChapter 5 Inventory ControlJanak KarkiNo ratings yet
- Executive SummaryDocument23 pagesExecutive SummaryLois RazonNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Term 3 Business SchemesDocument4 pagesGrade 7 Term 3 Business Schemeswesley kipkoechNo ratings yet
- Objectives:: Tourism Industry in BangladeshDocument39 pagesObjectives:: Tourism Industry in BangladeshAshiqur RahmanNo ratings yet