Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Examples of Process Hazards
Examples of Process Hazards
Uploaded by
ashumishra007Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Examples of Process Hazards
Examples of Process Hazards
Uploaded by
ashumishra007Copyright:
Available Formats
EXAMPLES OF PROCESS HAZARDS
FORM OF ENERGY ASSOCIATED HAZARD(S) TYPICAL ACCIDENTAL EVENT(S)
CHEMICAL ENERGY Ability to self-polymerize Uncontrolled polymerization
Shock-sensitivity Detonation of solid or liquid explosive or explosive mixture
Thermal instability Thermal explosion following bulk self-heating and runaway reaction
Rearranging ability Uncontrolled rearrangement reaction (e.g., ethylene oxide)
Pyrophoricity Fire upon atmospheric contact (e.g., triethylaluminum)
Flammability Vessel rupture following ignition of contained vapors + air
Vapor cloud explosion
Flash fire
Pool fire
Combustibility Bulk material fire
Dust explosion
Aerosol ignition and fast fire
Flash fire of vapors from heated combustible solid or liquid
Peroxidizing ability Energetic peroxide decomposition from contact with oxygen over time
Water-reactivity Release of water-reactive material and energetic reaction with water or humidity
Oxidizing or reducing ability Bulk material fire from contact of oxidizer with organic material
Uncontrolled redox reaction
Acidity or causticity Acid gas release (e.g., anhydrous HCl)
Corrosive liquid or solid spill
Uncontrolled acid/base reaction
Toxicity Toxic vapor release
Toxic liquid or solid spill
Heat, pressure, or toxic gas generation from inadvertent mixing or contact with
Other increased reactivity
incompatible material
Reduced chemical reactivity
Personnel entry into confined space with reduced oxygen level
(inert material, e.g., nitrogen)
THERMAL ENERGY Elevated temperature Hot material release
Contact with hot surface
Steam explosion or equivalent
Containment rupture from thermal expansion of blocked-in fluid
Reduced temperature Cryogenic material release
Fracture of embrittled containment
PRESSURE-VOLUME Volume of compressible fluid held
Tank or enclosure rupture
ENERGY at elevated pressure
High-velocity leak or spray
Liquefied material stored under
Rapid phase transition (Boiling Liquid Expanding Vapor Explosion or BLEVE)
pressure
Volume of compressible fluid
Tank or enclosure collapse
held under vacuum
Elevation of process material
POTENTIAL ENERGY Toppling over of stacked drums
above a reference level
Shifting of granular storage piles
Fluid surge from failed container
Falling material from spill/overflow
KINETIC ENERGY Moving process material Overpressure or overtemperature by deadheaded pumping
Impingement by process material
Water hammer damage
Elevated electromagnetic
ELECTROMAGNETIC Unshielded laser or microwave radiation associated with process
radiation levels
ELECTRICAL ENERGY Elevated voltage Electrical shock from process using electricity (e.g., electrolysis of brine)
You might also like
- BKM-Z24B (III) Maintenance ManualDocument36 pagesBKM-Z24B (III) Maintenance ManualJosselyn Stephanie Ayala Solís100% (1)
- Grade 10 Terms and DefinitionsDocument11 pagesGrade 10 Terms and Definitionskhotso86% (7)
- Electrocution, Lightning Thermal Injuries: Low Voltage DeathDocument5 pagesElectrocution, Lightning Thermal Injuries: Low Voltage DeathJameh RomancapNo ratings yet
- Engineering Glossary: Page 1 of 7Document7 pagesEngineering Glossary: Page 1 of 7Loukas PsarrasNo ratings yet
- Chemical Process Safety Lec6Document118 pagesChemical Process Safety Lec6asamad54100% (2)
- Lec6 PDFDocument118 pagesLec6 PDFJohn Harvey Siriban LozanoNo ratings yet
- Crowl - Understanding ExplosionsDocument6 pagesCrowl - Understanding ExplosionsJosé De Jesús Ibarra SánchezNo ratings yet
- Cdi 6Document3 pagesCdi 6Rosie DeocarezaNo ratings yet
- Explosives and Booby TrapsDocument118 pagesExplosives and Booby TrapsJesse Robert0% (1)
- Fire HazardsDocument102 pagesFire HazardsVarsha Praburam50% (2)
- HIRA HazardsDocument2 pagesHIRA HazardsRaeedi PullaraoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Hazard Analysis ProcedureDocument20 pagesChemical Hazard Analysis ProcedureDrishtiNo ratings yet
- Glossary: Accelerating Rate Calorimetry (ARC)Document9 pagesGlossary: Accelerating Rate Calorimetry (ARC)José LuísNo ratings yet
- Fire Technology and Arson InvestigationDocument14 pagesFire Technology and Arson InvestigationAzores Jerson Sabales100% (4)
- Causes of FireDocument2 pagesCauses of FiregraciaNo ratings yet
- Erdmp VulnerabilityDocument53 pagesErdmp VulnerabilityvisutsiNo ratings yet
- BFP Reviewer in ArsonDocument68 pagesBFP Reviewer in ArsonYuGenNo ratings yet
- BFP Reviewer-In-ArsonDocument67 pagesBFP Reviewer-In-ArsonMa. Genesa DingdingNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in ArsonDocument14 pagesReviewer in ArsonMichelle Anne Zapata TuazonNo ratings yet
- WMSU Lec2Document51 pagesWMSU Lec2Kaiser CarloNo ratings yet
- Fuel & Oxygen (Oxidation Reaction) : Heat/ignition SourceDocument7 pagesFuel & Oxygen (Oxidation Reaction) : Heat/ignition SourceTheødřøš ÄbNo ratings yet
- Controlling Electrostatic Hazards Combustible Dusts and Flammable LiquidsDocument46 pagesControlling Electrostatic Hazards Combustible Dusts and Flammable LiquidsSteve WanNo ratings yet
- Table 10 3 Using A Hotplate With Flammable Liquid ExampleDocument2 pagesTable 10 3 Using A Hotplate With Flammable Liquid ExampleErnesto AscenciosNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties of Matter (Grade 9)Document2 pagesThermal Properties of Matter (Grade 9)MN2022022 CHAVA VISHRUTHNo ratings yet
- Explosion, RunawayDocument24 pagesExplosion, RunawayKAUSTAV ROYNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 1 PadletDocument32 pagesLecture 5 1 Padletmuhammad izzulNo ratings yet
- Direct Vs Indirect DryersDocument2 pagesDirect Vs Indirect DryersPriyank kanjariyaNo ratings yet
- Payr $Document21 pagesPayr $Arjay MartinezNo ratings yet
- EnthalpyDocument1 pageEnthalpyRendyAlfNo ratings yet
- Fire - Hazard+explosion Hazard AssessmentDocument56 pagesFire - Hazard+explosion Hazard AssessmentSarla ShendeNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Fire and Fire Suppression: January 2019Document43 pagesThe Chemistry of Fire and Fire Suppression: January 2019MARUFNo ratings yet
- Prepared: Ms Alma C. Tesoro.,Rcim., MSCJDocument14 pagesPrepared: Ms Alma C. Tesoro.,Rcim., MSCJbalaoromichael10No ratings yet
- Explosive Terms Glossary 1Document3 pagesExplosive Terms Glossary 1werdna67No ratings yet
- Fire InvestigationDocument126 pagesFire InvestigationAbcede IloiloNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Reaction Rate: Chemistry 2Document26 pagesFactors Affecting Reaction Rate: Chemistry 2Angelica Rose Aliac CadienteNo ratings yet
- List of Materials Properties: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument4 pagesList of Materials Properties: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaThakur Manoj BharolNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 1.5.2 Sources of Fire HazardsDocument11 pagesInformation Sheet 1.5.2 Sources of Fire HazardsJerryson CabriasNo ratings yet
- Student Handout Science F1Document20 pagesStudent Handout Science F1AMILIA BT ARIFIN -No ratings yet
- Laminar Flame1Document11 pagesLaminar Flame1Kamel EsaNo ratings yet
- Week 5Document25 pagesWeek 5jujupascuaNo ratings yet
- HAZARDSDocument2 pagesHAZARDSMuhammad IshaqNo ratings yet
- 1-1 Introduction To Hazard and Risk PDFDocument60 pages1-1 Introduction To Hazard and Risk PDFMira DzuNo ratings yet
- Potential Hazards in Chemical IndustriesDocument33 pagesPotential Hazards in Chemical IndustriesAMOL RASTOGI 19BCM0012No ratings yet
- Fluidization Characteristics of A Bubbling Gas-Solid Fluidized Bed at High Temperature in The Presence of Interparticle Forces PDFDocument15 pagesFluidization Characteristics of A Bubbling Gas-Solid Fluidized Bed at High Temperature in The Presence of Interparticle Forces PDFEdilberto Murrieta LunaNo ratings yet
- TemperaturrDocument8 pagesTemperaturrdanes cheeseballsNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 2 - Thermal EvaporationDocument45 pagesLecture - 2 - Thermal EvaporationSam StideNo ratings yet
- Muntinlupa City: Bureau of Fire ProtectionDocument38 pagesMuntinlupa City: Bureau of Fire ProtectionWeng MontalboNo ratings yet
- Appendix Q: Glossary: Accident Accuracy Acid Acute Effects AdulterantDocument5 pagesAppendix Q: Glossary: Accident Accuracy Acid Acute Effects AdulterantCecilio MtzNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Product IdentificationDocument4 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Product Identificationمحمد عزتNo ratings yet
- Prelim ModuleDocument13 pagesPrelim Modulek4vspvp6hdNo ratings yet
- PUIS-Fires and ExplosionsDocument63 pagesPUIS-Fires and ExplosionsHarsimran SinghNo ratings yet
- ExplosivesDocument11 pagesExplosivescrysisfear2No ratings yet
- 5.1 Endothermic and Exothermic ReactionDocument29 pages5.1 Endothermic and Exothermic ReactionLo MNo ratings yet
- Student Handout Science F1Document20 pagesStudent Handout Science F1rarmaa70% (10)
- MSDS - AluminiumDocument5 pagesMSDS - AluminiumDS ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 NotesDocument3 pagesChapter 1 NotesYi FeiNo ratings yet
- ISHMDocument49 pagesISHMmadhavNo ratings yet
- Opening Up On Control ValveDocument3 pagesOpening Up On Control Valveashumishra007No ratings yet
- Storage of Raw Materials Category Checklist ItemsDocument6 pagesStorage of Raw Materials Category Checklist Itemsashumishra007No ratings yet
- Couplings and Mechanical Soft Starts: CatalogDocument52 pagesCouplings and Mechanical Soft Starts: Catalogashumishra007No ratings yet
- Brochure UCL ENG 2018Document12 pagesBrochure UCL ENG 2018ashumishra007No ratings yet
- Vitaprime - : Self-Priming Centrifugal Pump For Sterile ApplicationsDocument2 pagesVitaprime - : Self-Priming Centrifugal Pump For Sterile Applicationsashumishra007No ratings yet
- Price List: Item Net Price Euro Water Booster Systems LineDocument11 pagesPrice List: Item Net Price Euro Water Booster Systems Lineashumishra007No ratings yet
- VFD Maintenance Tips: Restarting Your Electrical Equipment After A Long ShutdownDocument3 pagesVFD Maintenance Tips: Restarting Your Electrical Equipment After A Long Shutdownashumishra007No ratings yet
- New Cloud-Based, Remote Performance Monitoring and Alert System For AODD PumpsDocument3 pagesNew Cloud-Based, Remote Performance Monitoring and Alert System For AODD Pumpsashumishra007No ratings yet
- Understanding Suction Cavitation & Avoiding Ugly Pump Rental Repair BillsDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Suction Cavitation & Avoiding Ugly Pump Rental Repair Billsashumishra007No ratings yet
- Wear in Centrifugal PumpDocument6 pagesWear in Centrifugal Pumpashumishra007No ratings yet
- Document Details: Engine Sizing CalculationDocument3 pagesDocument Details: Engine Sizing Calculationashumishra007No ratings yet
- Secrets of Successful Hazop ScribingDocument1 pageSecrets of Successful Hazop Scribingashumishra007No ratings yet
- First Chapter Engineering TrainingDocument42 pagesFirst Chapter Engineering TrainingHaziq TarmiziNo ratings yet
- Schrodinger Game Instructions CardsDocument26 pagesSchrodinger Game Instructions CardsAnonymous xmWYLiGvzNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual En: Please Read This User Manual Carefully Before Using The Appliance!Document24 pagesInstruction Manual En: Please Read This User Manual Carefully Before Using The Appliance!marc0No ratings yet
- My Mother Are CookingDocument80 pagesMy Mother Are CookingKate FernandezNo ratings yet
- PI&DمختصراتDocument2 pagesPI&DمختصراتMohamed HassanNo ratings yet
- Imp 4Document8 pagesImp 4shradha shreyaNo ratings yet
- Review of Guidelines For PV Systems Performance and Degradations MonitoringDocument14 pagesReview of Guidelines For PV Systems Performance and Degradations Monitoringsamwel kariukiNo ratings yet
- 4.1. MOS Capacitor Deep Trench Isolation For CMOS Image SensorsDocument4 pages4.1. MOS Capacitor Deep Trench Isolation For CMOS Image SensorsLuật TrầnNo ratings yet
- Bridges Engineering Assignment: Topic: Long Span BridgesDocument9 pagesBridges Engineering Assignment: Topic: Long Span Bridgeskheiriya duskiNo ratings yet
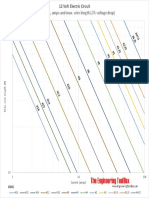
- 12 Volt Wire Loss Chart Feet AWGDocument1 page12 Volt Wire Loss Chart Feet AWGRuthNo ratings yet
- Mat435 Chapter 1 Trigonometric IntegralsDocument6 pagesMat435 Chapter 1 Trigonometric IntegralsNabil MahadzirNo ratings yet
- Astronomy: The Study of Stars, Galaxies, Planets, and MoreDocument31 pagesAstronomy: The Study of Stars, Galaxies, Planets, and MoreLunar WalkerNo ratings yet
- Smaw Stainless SteelDocument9 pagesSmaw Stainless SteelAhmad MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Cavitation of A Water Jet in WaterDocument82 pagesCavitation of A Water Jet in WaterAung KyiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Part 5Document15 pagesEngineering Drawing Part 5Joy OramaNo ratings yet
- B.Sc. PhysicsDocument72 pagesB.Sc. PhysicsDawnNo ratings yet
- # Split AC Components and Their FunctionsDocument8 pages# Split AC Components and Their FunctionsElgaham RossianantoNo ratings yet
- 2018IMTA0086 Cougoulic-FlorianDocument146 pages2018IMTA0086 Cougoulic-FlorianBenjamín Medina CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Diy Powr3Document42 pagesDiy Powr3Myhome TowenNo ratings yet
- 2.design and Analysis of Connecting RodDocument52 pages2.design and Analysis of Connecting RodNaresh DamaNo ratings yet
- Sedimentation Problems With SolutionDocument10 pagesSedimentation Problems With SolutionPappu SahNo ratings yet
- Welding Quiz 1Document2 pagesWelding Quiz 1Thanga PandiNo ratings yet
- Spin On For Return Line Amffse Technical DatasheetDocument8 pagesSpin On For Return Line Amffse Technical DatasheetHaytham Ammer MushtahaNo ratings yet
- Real & Virtual Images (3.2.7) - CIE IGCSE Physics Revision Notes 2023 - Save My ExamsDocument5 pagesReal & Virtual Images (3.2.7) - CIE IGCSE Physics Revision Notes 2023 - Save My ExamsMuzzamil AbbasiNo ratings yet
- A New Phenomenological Model To Predict Forming LiDocument18 pagesA New Phenomenological Model To Predict Forming LiAyushman kumarNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic SystemsDocument14 pagesPhotovoltaic SystemsHyma GelliNo ratings yet
- (PDF) Laser DiodeDocument16 pages(PDF) Laser DiodeSantosh SundarNo ratings yet
- Extended Life Type, Nonplowable, Raised Retroreflective Pavement MarkersDocument11 pagesExtended Life Type, Nonplowable, Raised Retroreflective Pavement MarkersROHIT0% (1)
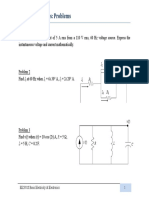
- AC Circuit Analysis: Problems: I R R IDocument13 pagesAC Circuit Analysis: Problems: I R R IWenzy BorromeoNo ratings yet