Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Expirement 7 Reaction
Expirement 7 Reaction
Uploaded by
Ramos Christian0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesLaminar flow occurs at low velocities when the Reynolds number is less than 2000, with smooth parallel layers of fluid particles flowing in a calm state. Turbulent flow occurs at high velocities when the Reynolds number exceeds 4000, characterized by irregular chaotic mixing of fluid particles. In transitional flow between 2000-4000, the streamline initially flows straight but starts to change shape. Reynolds number can be determined experimentally from mean bulk flow rate or theoretically using equations involving mean velocity, pipe diameter/radius, fluid viscosity and density.
Original Description:
CASE STUDY
Original Title
Expirement-7-reaction
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLaminar flow occurs at low velocities when the Reynolds number is less than 2000, with smooth parallel layers of fluid particles flowing in a calm state. Turbulent flow occurs at high velocities when the Reynolds number exceeds 4000, characterized by irregular chaotic mixing of fluid particles. In transitional flow between 2000-4000, the streamline initially flows straight but starts to change shape. Reynolds number can be determined experimentally from mean bulk flow rate or theoretically using equations involving mean velocity, pipe diameter/radius, fluid viscosity and density.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesExpirement 7 Reaction
Expirement 7 Reaction
Uploaded by
Ramos ChristianLaminar flow occurs at low velocities when the Reynolds number is less than 2000, with smooth parallel layers of fluid particles flowing in a calm state. Turbulent flow occurs at high velocities when the Reynolds number exceeds 4000, characterized by irregular chaotic mixing of fluid particles. In transitional flow between 2000-4000, the streamline initially flows straight but starts to change shape. Reynolds number can be determined experimentally from mean bulk flow rate or theoretically using equations involving mean velocity, pipe diameter/radius, fluid viscosity and density.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
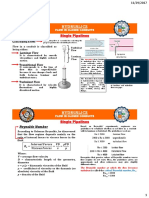
1. What is the difference between Laminar Flow and Turbulent Flow?
The differences of Laminar Flow and Turbulent Flow.
Laminar Flow Turbulent Flor
It is usually considered a calm state, This is characterized by irregular
in which layers of liquid particles flow movement and mixing of fluid
in a smooth, parallel direction and with particles, as well as a substantial
relatively low velocity. interchange of energy all across fluid,
and it occurs at high velocity
This usually occur when reynold's This is occurs when the value of
value is less than 2000 or Re <2000 Reynold's no. is less than 4000 or Re>
4000,
2. How the laminar, transitional and fully turbulent flow are demonstrated in the
video? You can make sketches or photos of the flow characteristics.
In laminar flow the pattern of fluids is not
chaotic hence the injected dye streamline is
well definition line.
In turbulent flow the dye being injected into
the head tank results in a complete mixture
of liquid throughout the tube.
In transitional flow it occurs when 2000 <Re
<4000, it is noticeable when the streamline
flows from a straight direction towards the
change of shape.
3. How are Reynolds Number are determined experimentally and theoretically?
In experimentally the (Re) is calculated by computing the mean bulk flow rate
and the value for the mean bulk speed of the fluid.
In theoretically;
For circular pipe, RE=pVD/u = VD/v = V(2ro)/v
Where:
V = mean velocity ft./s or m/s
d = diameter of pipe and ro=radius of pipe in ft or m
u = absolute viscosity in lb.-s/ft², Pa-s or N-s/m²
v = kinematic viscosity of the fluid in ft²/s or m²/s
p = mass density
For non- circular pipe, RE=V(4R)/v
Where:
V = mean velocity in ft./s or m/s
v = Kinematic viscosity of the fluid ft²/s or m²/s
You might also like
- Reynolds Experiment (Body)Document13 pagesReynolds Experiment (Body)mutencoNo ratings yet
- Internal Flow: Mehmet KanogluDocument115 pagesInternal Flow: Mehmet Kanogluizzet9696No ratings yet
- Conclusion ThermofluidDocument2 pagesConclusion ThermofluidKhairul IkhwanNo ratings yet
- Discussion Conclusion Report FluidDocument5 pagesDiscussion Conclusion Report Fluidnurlisa khaleeda100% (2)
- ObjectiveDocument22 pagesObjectiveJhecy CabangonNo ratings yet
- Handout - Reynolds Number v1Document2 pagesHandout - Reynolds Number v1kristine amerNo ratings yet
- Reynolds Number Laboratory Report - CompressDocument11 pagesReynolds Number Laboratory Report - CompressrosaleszimonNo ratings yet
- Particle SizeDocument3 pagesParticle SizeGlyra RosalemNo ratings yet
- Week 5, 6 & 7 - LecturesDocument83 pagesWeek 5, 6 & 7 - LecturesAmyHuiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 19 - Real FluidsDocument10 pagesLecture 19 - Real Fluidsيوسف عادل حسانينNo ratings yet
- Osbourne ReynoldDocument13 pagesOsbourne ReynoldN Afiqah Razak0% (1)
- Experiment No: 6: Measurement ofDocument2 pagesExperiment No: 6: Measurement ofManoj guptaNo ratings yet
- LAB REPORT-Osbourne Reynolds ApparatusDocument20 pagesLAB REPORT-Osbourne Reynolds Apparatusmizizasbonkure9055% (11)
- Discussion Osborne LabDocument2 pagesDiscussion Osborne LabLiyanna Blanda100% (3)
- Hydraulics Unit 1 Day IADocument17 pagesHydraulics Unit 1 Day IAAll DoneNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 Reynolds Number Preliminary.Document8 pagesExperiment 7 Reynolds Number Preliminary.Jasper Franz GeyrozagaNo ratings yet
- Chapter4-Flowinpipes Semakan2Document51 pagesChapter4-Flowinpipes Semakan2sufi 3393No ratings yet
- ARET 3400 - Chapter 4Document30 pagesARET 3400 - Chapter 4Harald JungkimNo ratings yet
- Act 2 Determination of Reynolds Number GP 1initialDocument8 pagesAct 2 Determination of Reynolds Number GP 1initialJunn Edgar LibotNo ratings yet
- Assignment Che 493Document3 pagesAssignment Che 493raja ariffNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics LabDocument13 pagesFluid Mechanics LabphrqdurhNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Fluid Flow Regime (Reynolds Number Apparatus) : Castro, Ethan Zachary G. Group 4Document5 pagesExperiment 1 Fluid Flow Regime (Reynolds Number Apparatus) : Castro, Ethan Zachary G. Group 4EthanNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Fluid Flow in PipesDocument14 pagesWeek 1 Fluid Flow in PipesAngelica Losares100% (1)
- TitemonamasarapDocument5 pagesTitemonamasarapAnn NavarroNo ratings yet
- Week2 Internal FlowDocument45 pagesWeek2 Internal FlowJose Carlos Obregón MartinezNo ratings yet
- 01 - 323FM - 3e - Chap08 - LectureDocument76 pages01 - 323FM - 3e - Chap08 - LectureJose LuisNo ratings yet
- 2.visualisation of The Flow PatternsDocument7 pages2.visualisation of The Flow PatternsAhmed FarazNo ratings yet
- FLUID Mechanics: Bernoullis Equation For Real Fluids and ReDocument9 pagesFLUID Mechanics: Bernoullis Equation For Real Fluids and ReDaniel TobingNo ratings yet
- MELABDocument13 pagesMELABMarvin ArnaizNo ratings yet
- Automotive Engineering Lab 2 MEC 2630) : Experiment FLUID 4: Reynold OsborneDocument6 pagesAutomotive Engineering Lab 2 MEC 2630) : Experiment FLUID 4: Reynold OsborneAhmadNafisNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Fluid Flow Regime (Reynolds Number Apparatus) : Gaspar, Rickie Mae S. Group 3Document4 pagesExperiment 1 Fluid Flow Regime (Reynolds Number Apparatus) : Gaspar, Rickie Mae S. Group 3rickiegasparNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Osborne ReynoldsDocument11 pagesLab 1 Osborne Reynoldsali mustafaNo ratings yet
- Reynolds NumberDocument1 pageReynolds NumberTimothy JonesNo ratings yet
- Internal Flow: Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd EditionDocument103 pagesInternal Flow: Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd EditionFurkan memonNo ratings yet
- Reynolds Numbers ExperimentDocument7 pagesReynolds Numbers ExperimentSufferedMuch100% (3)
- FF Exp 3Document6 pagesFF Exp 32020ch58No ratings yet
- Reynold'S Number DemonstrationDocument5 pagesReynold'S Number DemonstrationJay JackmanNo ratings yet
- هاشم عدي حاتم سيارات ثاني مخبر مقاومة التجربة الخامسةDocument13 pagesهاشم عدي حاتم سيارات ثاني مخبر مقاومة التجربة الخامسةهاشم عديNo ratings yet
- Internal Flow: DR - Syed YousufuddinDocument110 pagesInternal Flow: DR - Syed YousufuddinomarNo ratings yet
- LAB (Osbourne Reynolds Apparatus)Document13 pagesLAB (Osbourne Reynolds Apparatus)Nurul Ain50% (2)
- Fluid Mechanics: Civil Engineering Virtual LaboratoryDocument7 pagesFluid Mechanics: Civil Engineering Virtual LaboratoryCamilaAlvaradoNo ratings yet
- What Is Flow?: Turbulent Flow Laminar FlowDocument3 pagesWhat Is Flow?: Turbulent Flow Laminar FlowAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lab Exp # 4Document6 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab Exp # 4Furqan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Me 104-5Document33 pagesMe 104-5Sayed ShafeiNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 (I) : Reynolds' Experiment Objectives:: Figure 6.1 & 6.2Document2 pagesTopic 4 (I) : Reynolds' Experiment Objectives:: Figure 6.1 & 6.2daabgchiNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Apr 01, 2024Document10 pagesAdobe Scan Apr 01, 2024NimeshNo ratings yet
- Pressure DropDocument54 pagesPressure DropAbu Abdullah AlkaffNo ratings yet
- Ijet V4i3p18 PDFDocument4 pagesIjet V4i3p18 PDFInternational Journal of Engineering and TechniquesNo ratings yet
- Reynols NumberDocument4 pagesReynols Numbermariana hernandez mejiaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics and Hydrology: National Diploma in Civil Engineering TechnologyDocument29 pagesHydraulics and Hydrology: National Diploma in Civil Engineering Technologyishaq kazeemNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics (ECH3113) - Chapter 3 Flow in PipesDocument110 pagesFluid Mechanics (ECH3113) - Chapter 3 Flow in PipesTalal B. Osman100% (1)
- Introductory Laplace Transform with ApplicationsFrom EverandIntroductory Laplace Transform with ApplicationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsFrom EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNo ratings yet