Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Q1 Grade 7
Q1 Grade 7
Uploaded by
Albec Sagrado Ballacar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesThis document contains a mathematics examination for 7th grade students with 3 sections: (1) identification questions to match terms to mathematicians and concepts, (2) measures of central tendency problems calculating mean, median, and mode for grouped and ungrouped data, (3) probability questions calculating probabilities of events occurring from samples with specified parameters. The exam tests students on key topics in statistics and probability through short answer questions ranging from matching to calculations.
Original Description:
Original Title
Q1 Grade 7 Converted
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains a mathematics examination for 7th grade students with 3 sections: (1) identification questions to match terms to mathematicians and concepts, (2) measures of central tendency problems calculating mean, median, and mode for grouped and ungrouped data, (3) probability questions calculating probabilities of events occurring from samples with specified parameters. The exam tests students on key topics in statistics and probability through short answer questions ranging from matching to calculations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesQ1 Grade 7
Q1 Grade 7
Uploaded by
Albec Sagrado BallacarThis document contains a mathematics examination for 7th grade students with 3 sections: (1) identification questions to match terms to mathematicians and concepts, (2) measures of central tendency problems calculating mean, median, and mode for grouped and ungrouped data, (3) probability questions calculating probabilities of events occurring from samples with specified parameters. The exam tests students on key topics in statistics and probability through short answer questions ranging from matching to calculations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
The Montessori Schoolhouse at Kent
First Quarter Examination
Mathematics 7
Name: Score:
Grade: Date:
GENERAL DIRECTIONS
READ THE INSTRUCTIONS/DIRECTIONS CAREFULLY. USE BLACK OR BLUE BALLPEN ONLY.
USE ANOTHER SHEET OF PAPER FOR SOLUTIONS.
I. IDENTIFICATION (1-40)
Direction: Determine what is being described. Refer to the word pool to answer the given figure. Write your
answer on the space provided.
Statistics Interpreting data Organizing data John Graunt Blaise Pascal & Pierre de Ferma
Collecting data Analyzing data Pierre Laplace Lambert Quetelet Inferential Statistics
Francis Galton Frank Wilcoxon
Karl Pearson John Tukey William Gosset Charles Spearman Carl Friedrich
Ronald Fisher
Gauss Descriptive Statis
David Kendall
1-2. He studied records of death in London in the early 1600s.
3-4. He used descriptive statistics to analyze crime and mortality data.
5-6. It refers to the determining/ascertaining of data.
7-8. It is the branch of statistics that involves the collection, organization, presentation,
summarization or analysis of data
9-10. It refers to the process of extracting from the given data relevant information from
which numerical description can be formed.
11-12. It is a branch of mathematics dealing with the collection, analysis, interpretation, and
presentation of masses of numerical data.
13-14. It refers to the task of drawing conclusions from the analyzed data.
15-16. He studied probability and is credited with putting probability on a sure
mathematical footing.
17-18. It refers to the process of obtaining information.
19-20. It is the branch of statistics that involves using a sample to interpret, and draw
conclusions based on the data or about a population.
21-22. He used regression and correlation to study genetic variation in humans.
23-24. He is a British psychologist who was one of the first to develop intelligence testing
using factor analysis.
25-26. They corresponded about basic probability problems especially those dealing with
gaming and gambling.
27-28. He studied natural selection using correlation.
29-30. He worked at Princeton and Cambridge. Was a leading authority on applied
probability and data analysis.
31-32. He studied biology and natural selection and developed ANOVA
33-34. He worked at Princeton during World War II. Introduced exploratory data
analysis techniques such as stem-and-leaf plots.
35-36. He studied process of brewing and developed t - test to correct problems connected
with small sample sizes.
37-38. A biochemist who used statistics to study plant pathology.
39-40. He studied regression and the method of least squares through astronomy.
II. MEASURE OF CENTRAL TENDENCY (41-95)
A. Direction: Solve for the MEAN, MEDIAN and MODE of the following data. (Ungrouped Data)
a. A group of students b. The number of c. The grades of five grade d. The scores of five grade
took a math exam. The cupcakes sold by a bakery 7 students in Math were 7 students in Math exam
scores were: every month were as as follows: were:
10, 23, 32, 32, 32, 35, 69, follows: 11, 12, 53, 58, 75, 85,80,78,94,92 120, 85, 75,150,66
94, 94, 95 75, 78,
Solve for: 88, 96, Solve for: Solve for:
41-42. Mean of the data Solve for: 51-52. Mean of the data 56-57. Mean of the data
43-44. Median of the data 46-47. Mean of the data 53-54. Median of the data 58-59. Median of the data
45. Mode of the data 48-49. Median of the 55. Mode of the data 60. Mode of the data
data
50. Mode of the data
B. Direction: Solve for the MEAN, MEDIAN and MODE of the following data. (Grouped Data)
Class Limits Frequency (F) Midpoint (M) FM LB CF
1–3 5 61. 66. 71. 76.
4–6 7 62. 67. 72. 77.
7–9 3 63. 68. 73. 78.
10 – 12 15 64. 69. 74. 79.
13 – 15 10 65. 70. 75. 80.
Total (n)
Solve for the following:
81-85. Mean of the data 86-90. Median of the data 91-95. Mode of the data
II. PROBABILITY (96-125)
Direction: Determine the probability of the following events to happen.
a. From numbers 1 to 40 what is the probability that:
96-98. you will choose an even number?
99-101. you will choose an odd number?
102-104. you will choose a prime number?
105-107. you will choose a composite number?
108-110. you will choose a number divisible by 3?
b. Suppose you roll a die, what is the probability that:
111-113. the result will be an odd number?
114-116. the result will be number 5?
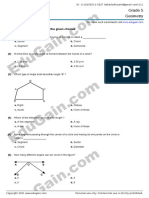
c. Refer to the figure on right side then answer the following questions.
117-119. If you spin the spinner 1 time, what is the probability
it would land on a gray piece?
120-122. If you spin the spinner 1 time, what is the probability
it would land on a black piece?
123-125. If you spin the spinner 1 time, what is the probability
it would land on a white piece?
Prepared by: Noted by:
Rochelle E. Cabison Mrs. Paz V. Alcantara
Mathematics Teacher School Directress
You might also like
- Statistics A. IntroductionDocument24 pagesStatistics A. IntroductionBianca Trish Manlangit0% (1)
- Statistics and Probability 1Document32 pagesStatistics and Probability 1Aelah Sedik100% (9)
- Formulas in Inferential StatisticsDocument4 pagesFormulas in Inferential StatisticsLlarx YuNo ratings yet
- Practice Problem - Hypothesis Testing PragatiDocument17 pagesPractice Problem - Hypothesis Testing PragatiMegha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Probability & Statistics Practice Final Exam and AnswersDocument8 pagesProbability & Statistics Practice Final Exam and Answersmisterjags0% (1)
- Topic 4A. Descripitve Statistics - ProbabilityDocument80 pagesTopic 4A. Descripitve Statistics - ProbabilityZEEL PATELNo ratings yet
- Mini Assignment - 9: X Class - MathematicsDocument2 pagesMini Assignment - 9: X Class - MathematicsbobbyNo ratings yet
- Topic 4. Statistics and ProbabilityDocument87 pagesTopic 4. Statistics and ProbabilityMuborakNo ratings yet
- Academic Contest Basic StatDocument4 pagesAcademic Contest Basic StatHannashii DiazNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics (IT302) 4 August 2020 (10:30AM-11:00AM) ClassDocument31 pagesProbability and Statistics (IT302) 4 August 2020 (10:30AM-11:00AM) Classrustom khurraNo ratings yet
- Topic 4A. Descripitve Statistics - ProbabilityDocument89 pagesTopic 4A. Descripitve Statistics - Probability3305125994No ratings yet
- Central of TendencyDocument24 pagesCentral of TendencySUNSHINE M. DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Review: Test Scores FrequencyDocument10 pagesFinal Exam Review: Test Scores FrequencyTheory SummersNo ratings yet
- Gist of The Chapters: Srimathi Sundaravalli Memorial School Chennai 2020-2021 Mathematics Class: IxDocument10 pagesGist of The Chapters: Srimathi Sundaravalli Memorial School Chennai 2020-2021 Mathematics Class: IxDhanya BalasundarrajNo ratings yet
- Summative ExamDocument2 pagesSummative ExamAndrilyn Bulanon100% (1)
- Chapter 12 - Statistics and Probability (Study Guide Review)Document13 pagesChapter 12 - Statistics and Probability (Study Guide Review)Brian ArroyoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 BFC34303 (Lyy)Document104 pagesChapter 1 BFC34303 (Lyy)shahrull1996No ratings yet
- Probability: Engr. Juicy Cordero - ValduezaDocument107 pagesProbability: Engr. Juicy Cordero - ValduezaRayan Ahmad BarodiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 BFC34303Document104 pagesChapter 1 BFC34303alipNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Data DescriptionDocument93 pagesChapter 7 Data DescriptionSIMBA The Lion KingNo ratings yet
- Contextualized Lesson Plan: Appreciates The Importance of Calculating The Mean of Grouped Data in Real Life SituationsDocument5 pagesContextualized Lesson Plan: Appreciates The Importance of Calculating The Mean of Grouped Data in Real Life SituationsRose Peñaflor DelArcuzibaNo ratings yet
- Statistics Study Material Class X (2023-24)Document9 pagesStatistics Study Material Class X (2023-24)Darsh TodiNo ratings yet
- Probability & Statistics ExercisesDocument19 pagesProbability & Statistics ExercisesjoyNo ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument21 pagesProbabilityleodogremioNo ratings yet
- Tut1 StudentsDocument4 pagesTut1 StudentsgagandeepsinghgxdNo ratings yet
- Math 114 Exam 3 ReviewDocument7 pagesMath 114 Exam 3 ReviewGenesa Buen A. PolintanNo ratings yet
- hhw10Document4 pageshhw10negikalpeswriNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument23 pagesStatisticsMohana RomanNo ratings yet
- 1 Statistics 23Document98 pages1 Statistics 23spicy MNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesLesson PlanMark John Dy Dayto100% (2)
- Act Central TendDocument2 pagesAct Central TendJessica GirardiNo ratings yet
- Submitted To: Mrs. Geetika Vashisht College of Vocational Studies University of DelhiDocument36 pagesSubmitted To: Mrs. Geetika Vashisht College of Vocational Studies University of Delhisanchit nagpalNo ratings yet
- Stat Module With AssessmentDocument11 pagesStat Module With Assessmentvillavergeraldine0No ratings yet
- JHANVI SAREEN - EDA - PracticalDocument9 pagesJHANVI SAREEN - EDA - PracticalJhanvi sareenNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 On Unit 1Document4 pagesTutorial 1 On Unit 1Sanket UkhlikarNo ratings yet
- Basic Statistics For ResearchDocument119 pagesBasic Statistics For ResearchAiko Viernes100% (1)
- Statistics and Probability Observation DDocument7 pagesStatistics and Probability Observation DMuffy FernandezNo ratings yet
- Maddogz43 - Stats Layout PracticeDocument4 pagesMaddogz43 - Stats Layout PracticeMahmoud ElsayedNo ratings yet
- Statistics 2Document74 pagesStatistics 2Free studentNo ratings yet
- Mean of Ungrouped DataDocument27 pagesMean of Ungrouped Datarock lee100% (1)
- Problems Set 2Document6 pagesProblems Set 2Hira Mohsin0% (1)
- Lesson Plan in Measures of Central Tendency of Ungrouped DataDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Measures of Central Tendency of Ungrouped DataDexter PalacaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document5 pagesTutorial 1Shanju ShanthanNo ratings yet
- Mid-Semester Test With Solution 2018Document7 pagesMid-Semester Test With Solution 2018madhavNo ratings yet
- PGL-Lesson 98-102Document26 pagesPGL-Lesson 98-102Jomabelle UbaldoNo ratings yet
- The Use Of Σ And The Formula For The Mean Of A Frequency Distribution Mean M or x = Σfx/Σf (Direct Method) Mean M or x = A + Σfd/Σf (Short-cut Method)Document16 pagesThe Use Of Σ And The Formula For The Mean Of A Frequency Distribution Mean M or x = Σfx/Σf (Direct Method) Mean M or x = A + Σfd/Σf (Short-cut Method)Parardha DharNo ratings yet
- Math2830 Chapter 08Document9 pagesMath2830 Chapter 08Sabeeh MumtazNo ratings yet
- Molecular Genetics ExamDocument3 pagesMolecular Genetics ExamJahnik KurukulasuriyaNo ratings yet
- State 301 Grand QuizDocument4 pagesState 301 Grand Quizعباس ناناNo ratings yet
- Social Work Statistics Lecture and Activity 12 (Liwagon)Document31 pagesSocial Work Statistics Lecture and Activity 12 (Liwagon)joel lacayNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Probabilty - Data Science - StatisticsDocument67 pagesIntroduction To Probabilty - Data Science - StatisticsKaushal BanthiaNo ratings yet
- Probability and StatisticsDocument51 pagesProbability and StatisticsJem Joseph MendozaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan (Incomplete)Document8 pagesLesson Plan (Incomplete)naze grace dulnuanNo ratings yet
- Statistics Finals Exam (Reviewer)Document3 pagesStatistics Finals Exam (Reviewer)Jiane ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Probability and StatisticsDocument7 pagesProbability and StatisticsDueñas Mark Anthony G.No ratings yet
- Pacheck MoDocument8 pagesPacheck MoSharmaine TuliaoNo ratings yet
- Module 3. - Measures of Central TendencyDocument21 pagesModule 3. - Measures of Central TendencyMarvin Yebes ArceNo ratings yet
- L3 Question StatementsDocument10 pagesL3 Question StatementsNimra MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- #1 Counting TechniquessDocument17 pages#1 Counting TechniquessPatricia Nicole MonderinNo ratings yet
- STATISTICSDocument48 pagesSTATISTICSSyedAsifMehdiNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Grade 11 Statistics and ProbabilityDocument7 pagesLesson Plan in Grade 11 Statistics and ProbabilityMichael P. JamisNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Methods of Statistics (PMS-9), Volume 9From EverandMathematical Methods of Statistics (PMS-9), Volume 9Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (6)
- Venture Mathematics Worksheets: Bk. S: Statistics and Extra Investigations: Blackline masters for higher ability classes aged 11-16From EverandVenture Mathematics Worksheets: Bk. S: Statistics and Extra Investigations: Blackline masters for higher ability classes aged 11-16No ratings yet
- Grades 7 and 8 (First Quarter) : Weeks Grade 7 Act/Material Feedback Grade 8 Act/Material FeedbackDocument14 pagesGrades 7 and 8 (First Quarter) : Weeks Grade 7 Act/Material Feedback Grade 8 Act/Material FeedbackAlbec Sagrado BallacarNo ratings yet
- Authorization Letter To Claim Check ExampleDocument1 pageAuthorization Letter To Claim Check ExampleAlbec Sagrado BallacarNo ratings yet
- Montessori Schoolhouse at Kent S.Y. 2021 - 2022 ScheduleDocument5 pagesMontessori Schoolhouse at Kent S.Y. 2021 - 2022 ScheduleAlbec Sagrado BallacarNo ratings yet
- I. Identification (1-40) Direction: Determine What Is Being Described. Refer To The Word Pool To Answer The Given Figure. Write YourDocument2 pagesI. Identification (1-40) Direction: Determine What Is Being Described. Refer To The Word Pool To Answer The Given Figure. Write YourAlbec Sagrado BallacarNo ratings yet
- Q2 Grade 9 MathDocument5 pagesQ2 Grade 9 MathAlbec Sagrado BallacarNo ratings yet
- The Montessori Schoolhouse at Kent Grade 6 - GeometryDocument3 pagesThe Montessori Schoolhouse at Kent Grade 6 - GeometryAlbec Sagrado BallacarNo ratings yet
- Yellowbook 2Document161 pagesYellowbook 2Albec Sagrado BallacarNo ratings yet
- Course 2Document28 pagesCourse 2Albec Sagrado BallacarNo ratings yet
- Q1 Geometry 4Document2 pagesQ1 Geometry 4Albec Sagrado BallacarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Whole Numbers Mathematics IntermediateDocument10 pagesLesson 1 Whole Numbers Mathematics IntermediateAlbec Sagrado BallacarNo ratings yet
- Qdoc - Tips - 1st Quarter Exam Grade 6Document5 pagesQdoc - Tips - 1st Quarter Exam Grade 6Albec Sagrado BallacarNo ratings yet
- Sotto, John Alexis Q1 GradesDocument1 pageSotto, John Alexis Q1 GradesAlbec Sagrado BallacarNo ratings yet
- Macrohon, Patricia D. Q1 GradesDocument1 pageMacrohon, Patricia D. Q1 GradesAlbec Sagrado BallacarNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Geometry: Choose Correct Answer(s) From The Given ChoicesDocument2 pagesGrade 5 Geometry: Choose Correct Answer(s) From The Given ChoicesAlbec Sagrado BallacarNo ratings yet
- Cristi, Rav Nathan F. Q1 GradesDocument1 pageCristi, Rav Nathan F. Q1 GradesAlbec Sagrado BallacarNo ratings yet
- Add Mixed Numbers: Mrs. Young Emc 1Document23 pagesAdd Mixed Numbers: Mrs. Young Emc 1Albec Sagrado BallacarNo ratings yet
- Linear Equation in Two VariablesDocument18 pagesLinear Equation in Two VariablesAlbec Sagrado BallacarNo ratings yet
- Promo Certification: Terms & Conditions: General DescriptionDocument3 pagesPromo Certification: Terms & Conditions: General DescriptionAlbec Sagrado BallacarNo ratings yet
- HARD RoundDocument66 pagesHARD RoundAlbec Sagrado BallacarNo ratings yet
- Linear Equation in Two VariablesDocument18 pagesLinear Equation in Two VariablesAlbec Sagrado BallacarNo ratings yet
- U Nderstanding Fractions Add & Subtract: Andrea Bonde & Ms. TaylorDocument23 pagesU Nderstanding Fractions Add & Subtract: Andrea Bonde & Ms. TaylorAlbec Sagrado BallacarNo ratings yet
- Lines, Rays and Line Segments: Observe The Figure and Answer The Questions That FollowDocument2 pagesLines, Rays and Line Segments: Observe The Figure and Answer The Questions That FollowAlbec Sagrado Ballacar100% (1)
- Compound Probability NotesDocument8 pagesCompound Probability Notesapi-310102170No ratings yet
- Question BankDocument6 pagesQuestion BankebenesarbNo ratings yet
- Probability and StatisticsDocument4 pagesProbability and StatisticsJ. KEN100% (1)
- Sta 221 Part IDocument23 pagesSta 221 Part IProf. Madya Dr. Umar Yusuf MadakiNo ratings yet
- Wilcoxon Sign TestDocument23 pagesWilcoxon Sign TestCalculus Chong Wei ChoonNo ratings yet
- Course Outline173 SDocument3 pagesCourse Outline173 Sapi-225089949No ratings yet
- Introduction To Hypothesis Testing - StatologyDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Hypothesis Testing - StatologyRuchiNo ratings yet
- 62 189 1 PBDocument8 pages62 189 1 PBDio AlifNo ratings yet
- 207 RM MbaDocument5 pages207 RM MbaGaneshNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Alpha andDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Alpha andCatherine Cheah Ming MingNo ratings yet
- BS Chap 1 MCQDocument29 pagesBS Chap 1 MCQChinmay Sirasiya (che3kuu)No ratings yet
- AMOGUIS - ULOab Week 1-3 PDFDocument8 pagesAMOGUIS - ULOab Week 1-3 PDFJennyrose AmoguisNo ratings yet
- Summative Test Q3.1 (Stat & Prob)Document2 pagesSummative Test Q3.1 (Stat & Prob)Emma Sarza100% (5)
- Sigmaxl SummaryDocument24 pagesSigmaxl Summaryleonel alejandro peña ramirezNo ratings yet
- Tribhuvan University Faculty of Management Office of The Dean 2011Document2 pagesTribhuvan University Faculty of Management Office of The Dean 2011mamannish7902No ratings yet
- Topic 3Document17 pagesTopic 3Ramli karamNo ratings yet
- SPSS Uji TabletDocument17 pagesSPSS Uji TabletAdrianNo ratings yet
- 1.62 M Height in CM - Google SearchDocument1 page1.62 M Height in CM - Google Searchlalitchoudhary0750No ratings yet
- Unit 4 StatisticsDocument33 pagesUnit 4 StatisticsNicole DeguzmanNo ratings yet
- Activity 3. Illustrating A Normal Random Variable and Its CharacteristicsDocument22 pagesActivity 3. Illustrating A Normal Random Variable and Its CharacteristicsVillasan ,Lei ashley I.No ratings yet
- Lec4 Inferential - Stats - Sampling - Distribution - CorrectDocument28 pagesLec4 Inferential - Stats - Sampling - Distribution - CorrectChrystal RhoneNo ratings yet
- Statistical Tools For Data AnalysisDocument4 pagesStatistical Tools For Data AnalysisGrace AtrazoNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5 Introduction To ProbabilityDocument15 pagesChapter-5 Introduction To ProbabilityIce KamalNo ratings yet
- University of Central Punjab Faculty of EngineeringDocument3 pagesUniversity of Central Punjab Faculty of EngineeringYasirNo ratings yet
- Statastics Blue Print I Puc 2023-24 PDFDocument1 pageStatastics Blue Print I Puc 2023-24 PDFntg386206No ratings yet
- Tutorial 9 Solutions S1 2015Document10 pagesTutorial 9 Solutions S1 2015cynthiaNo ratings yet