Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Major Development Theories Relatedto Learning and Human Development
Major Development Theories Relatedto Learning and Human Development
Uploaded by
Eazy Tip'ZOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Major Development Theories Relatedto Learning and Human Development
Major Development Theories Relatedto Learning and Human Development
Uploaded by
Eazy Tip'ZCopyright:
Available Formats
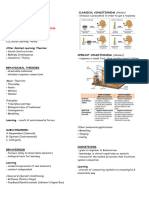
Theories Supporting
Operant Instructivist Classrooms
* Emitted *Conditioning Classical Stimulus
(Instrumental)
* Consequent or * Antecedent (Respondent) response
Contiguity
consequences Conditioning * Reflexive Conditioning
* Innate
* elicits
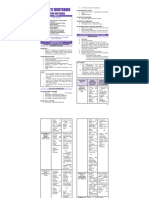
The Cognitive System
* Information Variety of * Behavioral view
Processing perspectives and * Psychoanalytic view
* Taxonomy of the * Humanistic view Cognitive Cognition
emphases within * Social cognitive psychology
Cognitive Domain
* Theory of cognitive cognitive view
development psychology
(Winn & Snyder,
1996)
Observational (Social)
Learning
* Attention
Bandura’s
* Retention
four-step
* Reproduction
pattern
* Motivation
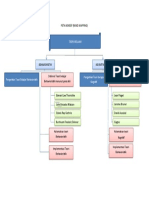
MAJOR DEVELOPMENT THEORIES RELATEDTO
LEARNING AND HUMAN DEVELOPMENT
* Skinner’s operant
conditioning theory * Secular humanism
* Piaget’s cognitive * Religious
Humanism Humanism and
development theory humanists two
* Students will learn best what theories branches Open Basic principles of the
they want and need to know. within this Education humanistic approach
* Knowing how to learn is view (Gage and Berliner 1991)
more important than
acquiring a lot of knowledge.
* Self-evaluation is the only
meaningful evaluation of a
student’s work.
* Feelings are as important as
facts
* Students learn best in a non-
threatening environment.
* Investigation five Cognitive
* Invention components of Constructivism
* Implementation an effective
* Evaluation constructivistic
* Celebration lesson
Social Constructivism
Social Cognition
Two * Cognitive-dissonance
* Self-efficacy principles of
* Self- theory (Festinger’s Theories
human 1957)
regulation functioning * Self-perception theory
(Bem’s 1972)
* Attribution theory
(Weiner’s 1985)
Connectivism
You might also like
- Sample SoP For Vigilance SystemDocument4 pagesSample SoP For Vigilance Systemsogic100% (5)
- Go To Page Word 2022Document17 pagesGo To Page Word 2022api-648417133No ratings yet
- Theories Handout With Terminology PDFDocument6 pagesTheories Handout With Terminology PDFAnonymous AFFiZnNo ratings yet
- Health Ed c1 l2b ReviewerDocument7 pagesHealth Ed c1 l2b ReviewersandeejulsestrellaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Lesson 1 Seven Philosophies of EducationDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Lesson 1 Seven Philosophies of EducationExcel Joy MarticioNo ratings yet
- Behavior TheoryDocument6 pagesBehavior Theoryapi-401555861No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word 2022Document18 pagesGo To Page Word 2022api-622214305No ratings yet
- Overview of TheoriesDocument11 pagesOverview of TheoriesArumpac, Norjanah T.No ratings yet
- Session #23 SAS - TFNDocument7 pagesSession #23 SAS - TFNKristina CassandraNo ratings yet
- Psychia MidtermsDocument30 pagesPsychia Midtermsharold smithNo ratings yet
- Go To Page EmmaDocument21 pagesGo To Page Emmaapi-677131601No ratings yet
- Theories of PersonalityDocument16 pagesTheories of PersonalityAlexándra NicoleNo ratings yet
- Constructivism Piaget Slides 1 - 17Document16 pagesConstructivism Piaget Slides 1 - 17Sabali TsofelaNo ratings yet
- Cognition Through The Lifespan Cognitive Functions: Individual-Developmental Stage - EnvironmentDocument15 pagesCognition Through The Lifespan Cognitive Functions: Individual-Developmental Stage - EnvironmentGayathri sundarajanNo ratings yet
- Go To Page Word 2022Document18 pagesGo To Page Word 2022api-677047016No ratings yet
- Psychological Foundation Sociological FoundationDocument3 pagesPsychological Foundation Sociological FoundationVallada, FebroseNo ratings yet
- Peta Konsep IDocument1 pagePeta Konsep IArifuddin ArifuddinNo ratings yet
- Berry 1967 - 1Document1 pageBerry 1967 - 1oliventeroNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Application of Learning Theories To Computer StudiesDocument16 pagesLecture 2 - Application of Learning Theories To Computer StudiesUrlsrings NdedaNo ratings yet
- Go To Page Riley Skains FinalDocument17 pagesGo To Page Riley Skains Finalapi-734710904No ratings yet
- Go To Page 10 13Document18 pagesGo To Page 10 13api-723881020No ratings yet
- Foundations of Curriculum Development PART 2Document15 pagesFoundations of Curriculum Development PART 2Anne MoralesNo ratings yet
- BehaviorismDocument7 pagesBehaviorismKharrel YballeNo ratings yet
- Go To Page Word 2022-1-1 1Document17 pagesGo To Page Word 2022-1-1 1api-665020557No ratings yet
- Lecture 1-EDU 6205B-Special Methods For Teachcing TE - 020810Document19 pagesLecture 1-EDU 6205B-Special Methods For Teachcing TE - 020810Solomon kiplimoNo ratings yet
- Qualities of Effective EducatorDocument18 pagesQualities of Effective Educatorapi-665220631No ratings yet
- Diss CmapDocument4 pagesDiss CmapAila Mae E. OlitNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Cognitive Developmental Social-Cognitive ConstructivistDocument5 pagesBehavioral Cognitive Developmental Social-Cognitive ConstructivistAira Guerrero100% (2)
- Psychology 1 Individual Differences PersonalityDocument15 pagesPsychology 1 Individual Differences PersonalitySiyabonga MaphsaNo ratings yet
- SYLLABUS (Facilitating Learner Centered Teaching)Document3 pagesSYLLABUS (Facilitating Learner Centered Teaching)Zandro EbioNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Dev.Document4 pagesCognitive Dev.Vina Jane P LaurelNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument9 pagesPresentationapi-367885529No ratings yet
- Values Integration ExamDocument4 pagesValues Integration ExamJohn Ray EnajeNo ratings yet
- Pengembangan Rancangan Pembelajaran EkonomiDocument31 pagesPengembangan Rancangan Pembelajaran EkonomiAhmed C. A. LouieNo ratings yet
- Go To Page Word 0617022Document18 pagesGo To Page Word 0617022api-618483692No ratings yet
- Ismmm IsmmDocument1 pageIsmmm IsmmIrish ReponteNo ratings yet
- Go To Page Word 2022-3Document17 pagesGo To Page Word 2022-3api-708331135No ratings yet
- GRR LP TemplateDocument1 pageGRR LP TemplateRub BingNo ratings yet
- JHDocument114 pagesJHAntonio PanesoNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Learner Part 1Document29 pagesUnderstanding The Learner Part 1andrew.mooreNo ratings yet
- Bandura 1977Document2 pagesBandura 1977Dithya Malar SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Philosophies of EducationImplication To Teachinglearning Process Short NewDocument8 pagesLesson 3 Philosophies of EducationImplication To Teachinglearning Process Short NewMae Therese TaguriganNo ratings yet
- DLL 1stq - W2-W3Document4 pagesDLL 1stq - W2-W3Naneth AlavarenNo ratings yet
- Go To Page Word 2022 PDFDocument18 pagesGo To Page Word 2022 PDFapi-675422615No ratings yet
- BS605 - Congnitive Analytics and Social Skill For ProfessionDocument174 pagesBS605 - Congnitive Analytics and Social Skill For ProfessionsyrusNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Q2 DissDocument6 pagesWeek 3 Q2 DissmaytwosonNo ratings yet
- Educational Philosophies and Their ProponentsDocument2 pagesEducational Philosophies and Their ProponentsLordced SimanganNo ratings yet
- IB Psychology ERQsDocument15 pagesIB Psychology ERQsMichelle Karam LondoñoNo ratings yet
- Najeela ShihabDocument18 pagesNajeela ShihabspsmutiarahatirabbaniNo ratings yet
- Go ToDocument17 pagesGo Toapi-705875093No ratings yet
- Educational Psychology-English SyllabusDocument17 pagesEducational Psychology-English Syllabusangelearth230No ratings yet
- Cognitive Approach To LearningDocument1 pageCognitive Approach To LearningJohana Pinagayao AngkadNo ratings yet
- 3-1: Structure of The Human Brain (Figure 3-6) : Teresa M. Mcdevitt, Jeanne Ellis OrmrodDocument38 pages3-1: Structure of The Human Brain (Figure 3-6) : Teresa M. Mcdevitt, Jeanne Ellis OrmrodVijay ShanthiNo ratings yet
- Educ 1 Chapter 4 PresentationDocument42 pagesEduc 1 Chapter 4 PresentationKlarisse CruzadoNo ratings yet
- PIAGETDocument8 pagesPIAGETKay JayNo ratings yet
- A Go To Page 050423 1Document18 pagesA Go To Page 050423 1api-667375796No ratings yet
- Topic 1 IntroductionDocument9 pagesTopic 1 IntroductionNeo Derrick Adrian MartinezNo ratings yet
- Positive Social Behavior and Morality: Socialization and DevelopmentFrom EverandPositive Social Behavior and Morality: Socialization and DevelopmentNo ratings yet
- Lipon Glomira Research Action ProposalDocument4 pagesLipon Glomira Research Action ProposalEazy Tip'ZNo ratings yet
- Internship Teacher F1Document2 pagesInternship Teacher F1Eazy Tip'ZNo ratings yet
- Bulletin Board and Room PlanDocument1 pageBulletin Board and Room PlanEazy Tip'ZNo ratings yet
- Factor TheoremDocument6 pagesFactor TheoremEazy Tip'ZNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus - Science, Technology, and SocietyDocument7 pagesCourse Syllabus - Science, Technology, and SocietyEazy Tip'ZNo ratings yet
- MATH 6 - ELEMENTARY STATISTICS AND PROBABILITY (Edited)Document16 pagesMATH 6 - ELEMENTARY STATISTICS AND PROBABILITY (Edited)Eazy Tip'ZNo ratings yet
- ContentServer PDFDocument10 pagesContentServer PDFSilvia Patricia Rodríguez Peña 2171033No ratings yet
- 2022 Liugong Overseas Warranty Administration General Version) - V2-Final Updated Oct 22Document70 pages2022 Liugong Overseas Warranty Administration General Version) - V2-Final Updated Oct 22frannnnsNo ratings yet
- Nabhasa Yogas Nabhasa Yogas Nabhasa Yogas Nabhasa Yogas: Sara "Arrow" Yoga: All Planets in All 4 Houses Commencing FromDocument1 pageNabhasa Yogas Nabhasa Yogas Nabhasa Yogas Nabhasa Yogas: Sara "Arrow" Yoga: All Planets in All 4 Houses Commencing FromNeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- Conclusion 4aDocument8 pagesConclusion 4amuhammad muiz100% (2)
- National Compassionate, Respectful and Caring Orientation: Federal Ministry of HealthDocument54 pagesNational Compassionate, Respectful and Caring Orientation: Federal Ministry of Healthtatu100% (1)
- Proyecto. CrossoverDocument15 pagesProyecto. CrossoverAppa D. LuffyNo ratings yet
- Service Manual Brother MFC9420cnDocument428 pagesService Manual Brother MFC9420cnRoschyNo ratings yet
- TANDO 700: High-Precision Measuring and Analysis System For Dissipation/power Factor and CapacitanceDocument8 pagesTANDO 700: High-Precision Measuring and Analysis System For Dissipation/power Factor and CapacitanceAndrew SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - BT MLH Lop 12 - KeyDocument6 pagesUnit 3 - BT MLH Lop 12 - KeyThao NguyenNo ratings yet
- Is Tunnel Ventilation SustainableDocument5 pagesIs Tunnel Ventilation SustainableHassan AbdoNo ratings yet
- Earthly Knowledge Is But A Shadow: Plato's Theory of Recollection in The MenoDocument17 pagesEarthly Knowledge Is But A Shadow: Plato's Theory of Recollection in The Menogeline joyNo ratings yet
- J. R. Kantor - Psychology and Logic - Vol. I. 1-Principia Press (1945)Document385 pagesJ. R. Kantor - Psychology and Logic - Vol. I. 1-Principia Press (1945)Alejandro CalocaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: Aicd-Base TitrationDocument12 pagesLab Report: Aicd-Base TitrationJeff LimNo ratings yet
- Ballistite: Military AdoptionDocument18 pagesBallistite: Military AdoptionChaeyoung SonNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesErnesto Mayo FogataNo ratings yet
- Moment Ext AnswersDocument4 pagesMoment Ext Answersapi-200073732No ratings yet
- 50 Sample Is T QB ProblemsDocument19 pages50 Sample Is T QB Problemssupermary405No ratings yet
- Makadwan Nagda Ratlam Pipeline Project (MNRPL) Daily Progress ReportDocument8 pagesMakadwan Nagda Ratlam Pipeline Project (MNRPL) Daily Progress ReportSumit SinghNo ratings yet
- PSM - Mural - AdvisedSkills 9-10052022 - PSMDocument1 pagePSM - Mural - AdvisedSkills 9-10052022 - PSMMargreta BaltgalveNo ratings yet
- ASA Firewal BackupDocument20 pagesASA Firewal BackupPrathvi R SinghNo ratings yet
- IENA 2020 Annales Concours AnglaisDocument82 pagesIENA 2020 Annales Concours AnglaisMarie MorganNo ratings yet
- SOP+ TECNAM P MentorDocument3 pagesSOP+ TECNAM P MentorjonathanaldazmNo ratings yet
- Education UcspDocument3 pagesEducation UcspzhareiNo ratings yet
- Skills Teaching in ESL Classroom Discrete Vs IntegratedDocument8 pagesSkills Teaching in ESL Classroom Discrete Vs IntegratedcalookaNo ratings yet
- Project Report: Data Analysis System For Behavioural Biometric Authentication (Keystroke Dynamics)Document46 pagesProject Report: Data Analysis System For Behavioural Biometric Authentication (Keystroke Dynamics)Evin JoyNo ratings yet
- Mixture and AlligationDocument42 pagesMixture and AlligationOliver ZadeNo ratings yet
- C++ by Dissection PDFDocument520 pagesC++ by Dissection PDFBianca ViorelaNo ratings yet
- Moisture Suppressant For Electrical FittingsDocument2 pagesMoisture Suppressant For Electrical FittingsFraz AhmadNo ratings yet
- 10 1108 - Yc 03 2016 00590Document13 pages10 1108 - Yc 03 2016 00590AreebaNo ratings yet