Professional Documents
Culture Documents
02966bee-c215-4ac0-bc40-87ab713ed2c3
02966bee-c215-4ac0-bc40-87ab713ed2c3
Uploaded by
Dash Shaa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 page02966bee-c215-4ac0-bc40-87ab713ed2c3
02966bee-c215-4ac0-bc40-87ab713ed2c3
Uploaded by
Dash ShaaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
KOLEJ MATRIKULASI SELANGOR physics\akademik\1PN\SF016\ch9
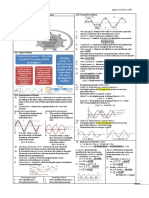
9 Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) 7. Velocity-displacement graph (v-x)
IDEA/ Examples of SHM system: simple pendulum, vertical and Information:
horizontal spring oscillations (i) Maximum
velocity, vmax =
A
(ii) Maximum
displacement/
Amplitude = A
8. Acceleration-displacement graph (a-x)
Information:
(i) Maximum acceleration,
amax = A2
SHM is about a system that (ii) Maximum
WHY? displacement/
doing a periodic motion/
oscillations Amplitude = A
•There is a force, restoring
(iii) Gradient of the graph =
WHAT? force FS which causes simple
harmonic motion to occur – 2
•This force is proportional to 9. Energy-displacement graph (E-x)
•The back & forth motion of an
object about a fixed point the displacement from
(equilibrium position) equilibrium & always directed
towards equilibrium
Oscillation/ Periodic Motion
9.1 Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)
1. A periodic motion without loss of energy in which the
acceleration of a body is directly proportional to its
displacement from the equilibrium position (fixed point) and
is directed towards the equilibrium position but in opposite
direction of the displacement 1 1 1
Potential energy, 𝑈 = k𝑥 2 = 𝑚2 𝑥 2 = 𝑚2 𝐴2 𝑠𝑖𝑛2 (𝑡 + )
𝑑2 𝑥 2 2 2
𝑎 = −2 𝑥 = 2 1 1 1
𝑑𝑡 Kinetic energy, 𝐾 = 𝑚𝑣 2 𝑚2 (𝐴2 − 𝑥 2 ) = 𝑚2 𝐴2 𝑐𝑜𝑠 2 (𝑡 + )
2. Amplitude, A = maximum magnitude of the displacement 2 2 2
1 1
from the equilibrium position 𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑒𝑛𝑒𝑟𝑔𝑦, 𝐸 = 𝐾 + 𝑈 = 𝑚 𝐴 = 𝑘𝐴2
2 2
3. Period, T = time to make one complete oscillation 2 2
4. Frequency, f = number of cycles in one second 9.4 Period of SHM
1 1 2
𝑇 = f = , = = 2𝑓
𝑓 𝑇 𝑇
9.2 Kinematics of SHM
5. Solution for SHM
𝑑2 𝑥
𝑎 = 2 = −2 𝑥
𝑑𝑡
x = A sin (t + )
𝑑𝑥
𝑣= = 𝐴 cos(𝑡 + )
𝑑𝑡
𝑑2 𝑥
𝑎 = 2 = −2 𝐴 sin(𝑡 + )
𝑑𝑡
In term of t
x = A cos (t + )
𝑑𝑥
𝑣= = −𝐴 sin(𝑡 + )
𝑑𝑡
𝑑2 𝑥
𝑎 = 2 = −2 𝐴 cos(𝑡 + )
𝑑𝑡
In term of x 𝑣 = ±√𝐴2 − 𝑥 2 , 𝑣𝑚𝑎𝑥 = 𝐴
𝑎 = −2 𝑥, 𝑎𝑚𝑎𝑥 = 𝐴
9.3 Graphs of SHM
6. Displacement-time graph (x-t), Velocity-time graph (v-t) & ,
Acceleration-time graph (a-t)
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (824)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Kubota v3800 Shop ManualDocument203 pagesKubota v3800 Shop ManualRonald Mosquera100% (6)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Major Head Losses in Pipe Flow: Major Head Loss, H Major Head Loss, HDocument4 pagesMajor Head Losses in Pipe Flow: Major Head Loss, H Major Head Loss, HLi ReNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Transport Across Membrane: Passive Transport Active TransportDocument7 pages2.4 Transport Across Membrane: Passive Transport Active TransportDash ShaaNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Animal Cells and TissueDocument13 pages2.3 Animal Cells and TissueDash ShaaNo ratings yet
- Progressive Waves - The One: in Which The Wave Profile PropagatesDocument1 pageProgressive Waves - The One: in Which The Wave Profile PropagatesDash ShaaNo ratings yet
- Bio Score: Chapter 2: Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument41 pagesBio Score: Chapter 2: Cell Structure and FunctionsDash ShaaNo ratings yet
- Oil and The Falklands Malvinas Oil Companies Governments and IslandersDocument14 pagesOil and The Falklands Malvinas Oil Companies Governments and IslandersFrancisco Javier Rivera IbanezNo ratings yet
- AetherDocument12 pagesAetherMarygeen GrițcoNo ratings yet
- LSA42.3 CatalogueDocument12 pagesLSA42.3 CatalogueDaniel ArdilaNo ratings yet
- SSL Comparison List/ TECH - DETAILS OF SKID STEER LOADERSDocument80 pagesSSL Comparison List/ TECH - DETAILS OF SKID STEER LOADERSHuseyin TASKINNo ratings yet
- Cairo West Supercritical Power Station 1 X 650 MW 10089-Cp-118 Mechanical Equipment / Pipe InstallationDocument6 pagesCairo West Supercritical Power Station 1 X 650 MW 10089-Cp-118 Mechanical Equipment / Pipe Installationmohamed abourayaNo ratings yet
- Reflection 1Document3 pagesReflection 1edelleevangelistaNo ratings yet
- Martin Flexible Couplings CatalogDocument37 pagesMartin Flexible Couplings CatalogJean CarlosNo ratings yet
- Jeritp P 170300Document1 pageJeritp P 170300NicolaMasteNo ratings yet
- FIDIC Future Leaders Booklet 2022Document46 pagesFIDIC Future Leaders Booklet 2022BelzébuthAbscisseNo ratings yet
- Polypropylene Europe Margin Report MethodologyDocument10 pagesPolypropylene Europe Margin Report MethodologyAswin KondapallyNo ratings yet
- Emily Conover: Century of Science: Cracking The AtomDocument3 pagesEmily Conover: Century of Science: Cracking The AtomMarkAllenPascualNo ratings yet
- Module 9 - Wave Motion and SoundDocument27 pagesModule 9 - Wave Motion and SoundHanah ArzNo ratings yet
- Li# 1 - 3c X 70 + 35mm2 Swa Fr-3 BahraDocument2 pagesLi# 1 - 3c X 70 + 35mm2 Swa Fr-3 BahraMuhammad ShahidNo ratings yet
- 12V DC Linear Actuator Instructions Manual 12V DC Linear Actuator Instructions ManualDocument4 pages12V DC Linear Actuator Instructions Manual 12V DC Linear Actuator Instructions Manualdc190400841 MIAN AQIL GHAFFARNo ratings yet
- Atuador PCDocument40 pagesAtuador PCLuciano ProjetistaNo ratings yet
- CNSME. Slurry Pump CatalogDocument19 pagesCNSME. Slurry Pump CatalogJia CrystalNo ratings yet
- Control de Temperatura 9305008Document2 pagesControl de Temperatura 9305008EDUARDO GARCIA ANo ratings yet
- Integrated Annual Report 2022Document571 pagesIntegrated Annual Report 2022riddheeNo ratings yet
- Fiat Allis 545 Wheel Loader Parts CatalogDocument20 pagesFiat Allis 545 Wheel Loader Parts Catalogmartha100% (53)
- Calibracion de Valvulas Toyota 6V Hi Lux 1GRDocument19 pagesCalibracion de Valvulas Toyota 6V Hi Lux 1GRcpaolinodNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle Assessment of A Vanadium Redox Flow BatteryDocument10 pagesLife Cycle Assessment of A Vanadium Redox Flow BatteryAnastasiya Disyak QuailNo ratings yet
- Ieltsfever Listening Practice Test 5: Job HuntingDocument6 pagesIeltsfever Listening Practice Test 5: Job HuntingBARINDER RATTINo ratings yet
- Geoffrey F. Gresh - To Rule Eurasia's Waves - The New Great Power Competition at Sea-Yale University Press (2020) PDFDocument376 pagesGeoffrey F. Gresh - To Rule Eurasia's Waves - The New Great Power Competition at Sea-Yale University Press (2020) PDFKebede MichaelNo ratings yet
- Saic - K-4006Document2 pagesSaic - K-4006Bander Al–kouhlaniNo ratings yet
- Swinv2000 ManualDocument6 pagesSwinv2000 ManualventerhermanjNo ratings yet
- UHI 4 High Flow Insufflation Unit Flyer en 11020Document2 pagesUHI 4 High Flow Insufflation Unit Flyer en 11020APP SPPNo ratings yet
- Varistar Storm Trapper Secondary Class Mov Surge Arrester Catalog Ca235020enDocument8 pagesVaristar Storm Trapper Secondary Class Mov Surge Arrester Catalog Ca235020enrafeeqNo ratings yet
- March 24th Crossword CA FinalDocument31 pagesMarch 24th Crossword CA FinalVidushi pandeyNo ratings yet