Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 9
Lecture 9
Uploaded by
Keabetswe Monei0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views5 pagesPorphyrins are heterocyclic organic molecules composed of four pyrrolic units linked by methene bridges to form a planar macrocyclic structure with an 18 π-electron conjugated system. This extensive conjugation gives porphyrins their aromatic behavior and distinctive UV-VIS absorption spectra. Metalloporphyrins form when metal ions fit into the porphyrin core, and can be either in-plane or out-of-plane depending on the size of the coordinating metal cation. Important natural metalloporphyrins include heme, chlorophyll, vitamin B12, and the nickel-containing cofactor F430.
Original Description:
Bioinorganic chemistry
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPorphyrins are heterocyclic organic molecules composed of four pyrrolic units linked by methene bridges to form a planar macrocyclic structure with an 18 π-electron conjugated system. This extensive conjugation gives porphyrins their aromatic behavior and distinctive UV-VIS absorption spectra. Metalloporphyrins form when metal ions fit into the porphyrin core, and can be either in-plane or out-of-plane depending on the size of the coordinating metal cation. Important natural metalloporphyrins include heme, chlorophyll, vitamin B12, and the nickel-containing cofactor F430.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views5 pagesLecture 9
Lecture 9
Uploaded by
Keabetswe MoneiPorphyrins are heterocyclic organic molecules composed of four pyrrolic units linked by methene bridges to form a planar macrocyclic structure with an 18 π-electron conjugated system. This extensive conjugation gives porphyrins their aromatic behavior and distinctive UV-VIS absorption spectra. Metalloporphyrins form when metal ions fit into the porphyrin core, and can be either in-plane or out-of-plane depending on the size of the coordinating metal cation. Important natural metalloporphyrins include heme, chlorophyll, vitamin B12, and the nickel-containing cofactor F430.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
Porphyrins
• Heterocyclic tetrapyrrolic organic molecules
• Composed of four pyrrolic units linked in a coplanar fashion by four
methene bridges that give a planar macrocyclic structure to the
porphyrin molecule
• Extended conjugated 18 π-electron system - responsible
for its aromatic behavior,
• Limited size cavity - accommodation of large metal
cations
• Due to the conjugation of π-electrons on the frontier
orbitals, porphyrins possess distinctive UV–VIS spectra
Explain
• Extensive conjugation of 18 electrons in porphyrins gives
rise to facile π→π* transitions that give rise to two
distinct bands within the visible region of electromagnetic
radiations.
• Insertion of a metal ion into the porphyrin cavity or the
protonation of the nitrogen atoms or variation of the
peripheral substituents may result in a change in the
wavelength and intensity of the absorption spectrum.
Metalloporphyrins
• Formed when the metal ions fit into the
porphyrin core
Two types (size of coordinating metal cations).
• Cationic metal size of coordinating metal is 55–80
pm - in-plane metalloporphyrins
The metal centers are situated in the plane of
porphyrin rings.
• Cationic radius is greater than 80– 90 pm - out-of-
plane or sitting-atop (SAT) metalloporphyrins
Metal atoms are located out of the porphyrin plane
Give an example of a metalloporphyrin
Metalloporphyrins in Nature
Metalloporphyrins in Nature
• The Fe2+ containing heme group , is not just the oxygen carrier
found in hemoglobin; it is a cofactor of hemeproteins including
cytochromes and peroxidases that carry out diverse biological
reactions.
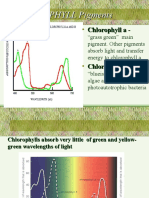
• Chlorophyll, a family of green pigments that absorb sunlight, is
central to photosynthesis. It chelates a magnesium atom center.
Chlorophyll is a reduced porphyrin (chlorin) macrocycle, which
contains two π electrons less than porphyrin.
• Vitamin B12, a crucial vitamin for nervous system function. It
contains a cobalt atom in the center of the aromatic tetrapyrrole.
• Cofactor F430, a nickel-containing tetrapyrrole (Fig. 2D), is found
in methyl-coenzyme M reductase (MCR) and catalyzes the
terminal step of methanogenesis. The successful biosynthesis of
F430 was achieved recently and holds potential for industrial
metabolic bioenergetic engineering
You might also like
- Chapter - 1: Synthesis of Symmetrical & Unsymmetrical Porphyrins & MetalloporphyrinsDocument36 pagesChapter - 1: Synthesis of Symmetrical & Unsymmetrical Porphyrins & MetalloporphyrinsHimanshu BariaNo ratings yet
- Feritin SplinDocument15 pagesFeritin SplinDorina GhermanNo ratings yet
- Bioinorganic Chemistry 1Document44 pagesBioinorganic Chemistry 1Abu S. M. GulamaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesi S: V. Madhuri Reddy BSC Fsccs Ii 562051434Document33 pagesPhotosynthesi S: V. Madhuri Reddy BSC Fsccs Ii 562051434GRAMMARNo ratings yet
- Presentation 4 Fe-S Protein, Cytochrome, NitrogenaseDocument18 pagesPresentation 4 Fe-S Protein, Cytochrome, NitrogenaseRuby AhmedNo ratings yet
- Inorg Chap 333 by MekeDocument34 pagesInorg Chap 333 by MekeAbraham AsefaNo ratings yet
- Formation, Photophysics, Photochemistry and Quantum Chemistry of The Out-Of-Plane MetalloporphyrinsDocument8 pagesFormation, Photophysics, Photochemistry and Quantum Chemistry of The Out-Of-Plane MetalloporphyrinsZsolt ValicsekNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis NotesDocument5 pagesPhotosynthesis NotesBae SeujiNo ratings yet
- Bioinorganic ChemistryDocument46 pagesBioinorganic ChemistryRojo John100% (1)
- Hemerythin: Structure, Function, and Spectroscopy: RC PresentationDocument11 pagesHemerythin: Structure, Function, and Spectroscopy: RC PresentationAnusha SinghNo ratings yet
- BIO1 Lesson-12 PhotosynthesisDocument36 pagesBIO1 Lesson-12 PhotosynthesisCath Detoperez100% (1)
- Plants, Energy, and Carbon: Plant BiochemistryDocument49 pagesPlants, Energy, and Carbon: Plant BiochemistryNathaly Kate BohulanoNo ratings yet
- L7 MetalloproitensDocument32 pagesL7 MetalloproitensChisama SichoneNo ratings yet
- Applications of Organometallic CompoundsDocument9 pagesApplications of Organometallic CompoundsUsama Talib100% (2)
- BBT 301 Unit 3a: by Dr. Sharad Agrawal Asst. Prof., SBSR Sharda UniversityDocument18 pagesBBT 301 Unit 3a: by Dr. Sharad Agrawal Asst. Prof., SBSR Sharda UniversityDristi Namchoom GohainNo ratings yet
- DissertationDocument29 pagesDissertationShobha GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Structure of ChlorophyllDocument94 pagesStructure of ChlorophyllSunil Kumar SahuNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument86 pagesPhotosynthesisDanessa Mina BalboaNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument83 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESISBea BascugNo ratings yet
- Organo - Met.chem: PDF Generated At: Tue, 28 Dec 2010 12:28:45 UTCDocument35 pagesOrgano - Met.chem: PDF Generated At: Tue, 28 Dec 2010 12:28:45 UTCdandinystNo ratings yet
- Org A No Metallic CompoundsDocument17 pagesOrg A No Metallic Compoundsthestar55100% (2)
- Animesh Kumar - 17POL202Document4 pagesAnimesh Kumar - 17POL202Animesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry in Biology: Advanced ArticleDocument9 pagesInorganic Chemistry in Biology: Advanced ArticleazzaassNo ratings yet
- Porphyrins in Analytical ChemistryDocument16 pagesPorphyrins in Analytical ChemistryEsteban ArayaNo ratings yet
- InTech-The Use of Spectrophotometry Uv Vis For The Study of PorphyrinsDocument23 pagesInTech-The Use of Spectrophotometry Uv Vis For The Study of PorphyrinsDijumoni NeogNo ratings yet
- Biology Lessons 9.2 and 9.3Document70 pagesBiology Lessons 9.2 and 9.3hayahasibnawazNo ratings yet
- Bio Inorganic Chemistry One Shot Revision by MadCh 230604 100239Document51 pagesBio Inorganic Chemistry One Shot Revision by MadCh 230604 100239sharmaashwani.iitgnNo ratings yet
- Coordination CompoundsDocument7 pagesCoordination Compoundsfake37554No ratings yet
- Photosynthesispresentationbyme 120608123750 Phpapp01Document23 pagesPhotosynthesispresentationbyme 120608123750 Phpapp01Shaquille McdonaldNo ratings yet
- Autotrophy: Collecting Energy From The Non-Living EnvironmentDocument96 pagesAutotrophy: Collecting Energy From The Non-Living EnvironmentNathan ArthurNo ratings yet
- Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument40 pagesOxidative PhosphorylationIram AnwarNo ratings yet
- Synthesis Characteristics and PhotochemiDocument5 pagesSynthesis Characteristics and Photochemialeena.taufiq125No ratings yet
- Materi 5-Bioleaching Mineral OksidaDocument44 pagesMateri 5-Bioleaching Mineral OksidaVicky Faras Barunson PanggabeanNo ratings yet
- Non-Cyclic Photophosphorylation Notes 10-26 and 10-28Document18 pagesNon-Cyclic Photophosphorylation Notes 10-26 and 10-28kegalina100% (1)
- MetalloenzymesDocument5 pagesMetalloenzymesAzabo KennedyNo ratings yet
- Porphyrins: Chemistry and Biology: 1 March, 2012Document28 pagesPorphyrins: Chemistry and Biology: 1 March, 2012hammode88885138No ratings yet
- Bioinorganic 1Document57 pagesBioinorganic 1Abhishek tiwariNo ratings yet
- BIO C6 @notastpm04Document152 pagesBIO C6 @notastpm04Huey KaNo ratings yet
- MetalloenzymesDocument5 pagesMetalloenzymesazabokennedy09No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis COMPLETEDocument44 pagesPhotosynthesis COMPLETEsantoshnairsNo ratings yet
- Chromophore - WikipediaDocument20 pagesChromophore - WikipediaVadivelanNo ratings yet
- Microbial NutritionDocument17 pagesMicrobial Nutritionkenny100% (1)
- Bio-Inorganic ChemistryDocument66 pagesBio-Inorganic ChemistryPhalynxNo ratings yet
- Fujii - IMP Cmpd-I ReviweDocument10 pagesFujii - IMP Cmpd-I ReviweneerajNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument35 pagesPhotosynthesisYuh moddaNo ratings yet
- Research of PhthalocyaninesDocument167 pagesResearch of PhthalocyaninesKristin PittmanNo ratings yet
- Topics: 1. What Are The Key Pigments Involved in Photosynthesis? 2. Where & How Does Photosynthesis Take Place?Document42 pagesTopics: 1. What Are The Key Pigments Involved in Photosynthesis? 2. Where & How Does Photosynthesis Take Place?Elizabeth AjayiNo ratings yet
- Molecules: ROMP Synthesis of Iron-Containing Organometallic PolymersDocument16 pagesMolecules: ROMP Synthesis of Iron-Containing Organometallic PolymersBetty WangNo ratings yet
- Moser 1964Document5 pagesMoser 1964Ramona AndronesiNo ratings yet
- Electron Transfer in BiologyDocument20 pagesElectron Transfer in BiologyVani KaushikNo ratings yet
- 411 Unit 3FDocument20 pages411 Unit 3Fkiya01No ratings yet
- 4.3.1 PhotosynthesisDocument7 pages4.3.1 PhotosynthesisMariam AymanNo ratings yet
- Photochromic Organometallics, A Stimuli-Responsive System: An Approach To Smart Chemical SystemsDocument9 pagesPhotochromic Organometallics, A Stimuli-Responsive System: An Approach To Smart Chemical SystemsArfaigah GhaniNo ratings yet
- BOT HW Chapter 8Document11 pagesBOT HW Chapter 8albelqinNo ratings yet
- Copper and Iron Homeostasis in Plants: The Challenges of Oxidative StressDocument14 pagesCopper and Iron Homeostasis in Plants: The Challenges of Oxidative StressEddard StarkNo ratings yet
- Unit 7. Autotrophic NutritionDocument48 pagesUnit 7. Autotrophic Nutritionmunyanezaolivier422No ratings yet
- CH 10 PhotosynthesisDocument67 pagesCH 10 PhotosynthesisDVRaoNo ratings yet
- 17uch08 Inorganic ChemistryDocument72 pages17uch08 Inorganic ChemistryVadivelanNo ratings yet
- Organometallic Chemistry: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Eighth International Conference on Organometallic Chemistry, Kyoto, Japan, 12-16 September 1977From EverandOrganometallic Chemistry: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Eighth International Conference on Organometallic Chemistry, Kyoto, Japan, 12-16 September 1977Y. IshiiNo ratings yet