Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ECON Quiz 3 Module 56 Formulas
ECON Quiz 3 Module 56 Formulas
Uploaded by
Jean MaeCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- JSA - Electrical Testing - Circuit Breaker Field TestDocument4 pagesJSA - Electrical Testing - Circuit Breaker Field TestTawfik Mohamed Abu Zaid0% (1)
- 2020 ME SESSION 12 Perfect CompetitionDocument42 pages2020 ME SESSION 12 Perfect CompetitionDr. Sakthirama VNo ratings yet
- Perfect Competition: 1. CharacteristicsDocument7 pagesPerfect Competition: 1. CharacteristicsMinh TragNo ratings yet
- Chapter-9 Imperfect CompetitionDocument23 pagesChapter-9 Imperfect Competitiongr8_amaraNo ratings yet
- HL Calculation Formulas MethodsDocument24 pagesHL Calculation Formulas MethodsMuras BaiyshevNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 ProductionDocument46 pagesChapter 5 Productionquangtm60.fbaeliteNo ratings yet
- Chap 09Document8 pagesChap 09Thabo MojavaNo ratings yet
- Session 25 - Monopoly and Market PowerDocument16 pagesSession 25 - Monopoly and Market PowerSweet tripathiNo ratings yet
- T Note 8 MonopolyDocument7 pagesT Note 8 MonopolyBella NovitasariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11-Managerial Decisions in Competitive MarketsDocument32 pagesChapter 11-Managerial Decisions in Competitive Marketsnaveen9622No ratings yet
- MONOPOLY Market Spring 2022Document50 pagesMONOPOLY Market Spring 2022Abid SunnyNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics: Lecture 10: Profit Maximization and Competitive SupplyDocument42 pagesMicroeconomics: Lecture 10: Profit Maximization and Competitive Supplyblackhawk31No ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet PMDocument2 pagesCheat Sheet PMhanifakihNo ratings yet
- Product and CostDocument49 pagesProduct and CostSahilNo ratings yet
- Definitions: Some Important Formulas in MicroeconomicsDocument3 pagesDefinitions: Some Important Formulas in MicroeconomicstrezzorNo ratings yet
- Markets Perfect CompetitionDocument47 pagesMarkets Perfect CompetitionSiddhant SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Perfect CompetitionDocument30 pagesPerfect Competitionaayush.5.parasharNo ratings yet
- Week 11 - English Muhammad Rizky RamadhanDocument44 pagesWeek 11 - English Muhammad Rizky RamadhanMuhammad Rizky RamadhanNo ratings yet
- 8 Market Structures and Profit MaximizationDocument18 pages8 Market Structures and Profit Maximizationakshat guptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Firm and IntegrationDocument10 pagesChapter 6-Firm and IntegrationUyển Nhi Lê ĐoànNo ratings yet
- SECTION 10 Need To KnowDocument2 pagesSECTION 10 Need To KnowAnisur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Definitions A-Z in Earm1Document7 pagesDefinitions A-Z in Earm1Mehul KhareNo ratings yet
- Pe Chap 14Document2 pagesPe Chap 14camlansuc09993No ratings yet
- Ions A-Z in EARM-1Document5 pagesIons A-Z in EARM-1rediah_ribbahsNo ratings yet
- ECON CH 8 & 9 NotesDocument6 pagesECON CH 8 & 9 NoteslemonaiidsNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Micro Exam III ReviewDocument6 pagesIntermediate Micro Exam III Reviewjrs55No ratings yet
- Costs and Revenues BEPDocument16 pagesCosts and Revenues BEPNguyen Thanh PhuongNo ratings yet
- Firms in Competitive MarketsDocument34 pagesFirms in Competitive MarketsRomeo DupaNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Study Sheet Microeconomics Study Sheet: More Free Study Sheet and Practice Tests atDocument3 pagesMicroeconomics Study Sheet Microeconomics Study Sheet: More Free Study Sheet and Practice Tests atanandsemails6968100% (1)
- Teori Biaya 2: Program Diploma Ekonomika Dan Bisnis Sekolah Vokasi, UGMDocument9 pagesTeori Biaya 2: Program Diploma Ekonomika Dan Bisnis Sekolah Vokasi, UGMGema Wahyu FadhilahNo ratings yet
- Principle of Economics Principle of Economics: Chapter Four Theory of Production and Theory of Production and CostDocument30 pagesPrinciple of Economics Principle of Economics: Chapter Four Theory of Production and Theory of Production and CostBiladenNo ratings yet
- CFO CH 8Document55 pagesCFO CH 8ashchua21No ratings yet
- Econ IIDocument28 pagesEcon IIworkinehamanuNo ratings yet
- Pasar Persaingan SempurnaDocument38 pagesPasar Persaingan SempurnaCandri Rahma MaharaniNo ratings yet
- Imperfect CompetitionDocument18 pagesImperfect CompetitionhishamsaukNo ratings yet
- CH 08Document36 pagesCH 08Xiaojie CaiNo ratings yet
- Formulaes Econ111: Average Total CostDocument1 pageFormulaes Econ111: Average Total CostjulieNo ratings yet
- CH 14 Firms in Competitive MarketsDocument31 pagesCH 14 Firms in Competitive MarketsSakibNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 MarketsDocument39 pagesLesson 5 MarketsiitNo ratings yet
- Module 8 Managing Competitive, Monopolistic, and Monopolistically Competitive Markets NotesDocument9 pagesModule 8 Managing Competitive, Monopolistic, and Monopolistically Competitive Markets NotesHazel PabloNo ratings yet
- Profit MaximizationDocument2 pagesProfit Maximizationpatelshivani033No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Production, Costs, and Organization of FirmDocument89 pagesChapter 3 - Production, Costs, and Organization of FirmHieu HoangNo ratings yet
- Q F (K, L) : Capital Is Fixed in The Short Run, Labor Is VariableDocument3 pagesQ F (K, L) : Capital Is Fixed in The Short Run, Labor Is VariableNicholas CasianoNo ratings yet
- Production Analysis PPT at BEC DOMSDocument26 pagesProduction Analysis PPT at BEC DOMSBabasab Patil (Karrisatte)No ratings yet
- CH 24 MonopolyDocument33 pagesCH 24 MonopolyNailed GownNo ratings yet
- Block 7 Monopoly Lecture TutorialDocument24 pagesBlock 7 Monopoly Lecture Tutorialshakti preeyaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 8 - To StudentsDocument54 pagesTutorial 8 - To StudentsVasif ŞahkeremNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - MonpolyDocument17 pagesChapter 6 - MonpolyEthio PNo ratings yet
- Economics Perfectly Competitive MarketDocument25 pagesEconomics Perfectly Competitive MarketEsha DivNo ratings yet
- Economics FormulasDocument2 pagesEconomics FormulasNelaNo ratings yet
- L10 W4L2 165s10 MarginalanalysisDocument35 pagesL10 W4L2 165s10 Marginalanalysismeetanshi01No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Managing in Competitive, Monopolistic, and Monopolistically Competitive MarketsDocument26 pagesChapter 8 Managing in Competitive, Monopolistic, and Monopolistically Competitive Marketsdimitri foxNo ratings yet
- REVIEW 01 - Microeconomics - Chapter 6 PDFDocument8 pagesREVIEW 01 - Microeconomics - Chapter 6 PDFKiệt NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Cost and RevenueDocument15 pagesCost and RevenueWaleed Wasti100% (1)
- Msci 607: Applied Economics For ManagementDocument4 pagesMsci 607: Applied Economics For ManagementRonak PatelNo ratings yet
- ECON Quiz 3 Module 6 Notes From HazelDocument9 pagesECON Quiz 3 Module 6 Notes From HazelJean MaeNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics and Business Strategy: PrincipleDocument4 pagesManagerial Economics and Business Strategy: PrincipleTiểu Ngân ĐồngNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Costs of Production Spring 2023Document52 pagesCH 7 Costs of Production Spring 2023sayidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document39 pagesChapter 14anchal11102003No ratings yet
- Mathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandMathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Readings in Philippine History: Pigafetta AccountDocument14 pagesReadings in Philippine History: Pigafetta AccountJean MaeNo ratings yet
- 1 - Page Chapter 2: Christian Call and Thomasian ResponseDocument12 pages1 - Page Chapter 2: Christian Call and Thomasian ResponseJean MaeNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts Revenue Cycle: List Price, Trade Discount, Prepaid Freight, Cash DiscountDocument50 pagesBasic Concepts Revenue Cycle: List Price, Trade Discount, Prepaid Freight, Cash DiscountJean MaeNo ratings yet
- Statement of Owners Equity Excel TemplateDocument1 pageStatement of Owners Equity Excel TemplateJean MaeNo ratings yet
- BSAMERCHANDISING2021Document5 pagesBSAMERCHANDISING2021Jean MaeNo ratings yet
- CA5102 Course-Plan Managerial-EconomicsDocument12 pagesCA5102 Course-Plan Managerial-EconomicsJean MaeNo ratings yet
- Module 6B - Managing in Monopolistic MarketsDocument33 pagesModule 6B - Managing in Monopolistic MarketsJean MaeNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: RequiredDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: RequiredJean MaeNo ratings yet
- ECON Quiz 3 Module 6 Notes From HazelDocument9 pagesECON Quiz 3 Module 6 Notes From HazelJean MaeNo ratings yet
- ST ST: Jasmine Kayla G. PangilinanDocument16 pagesST ST: Jasmine Kayla G. PangilinanJean MaeNo ratings yet
- Profitability and Marketability of The Top 55 U.S. Commercial BanksDocument19 pagesProfitability and Marketability of The Top 55 U.S. Commercial BanksSasa LuNo ratings yet
- Umbilical Catheterization in ServiceDocument11 pagesUmbilical Catheterization in ServiceLucian CaelumNo ratings yet
- Ra 9288 Basis For Questionnaire PDFDocument22 pagesRa 9288 Basis For Questionnaire PDFHolden Mandapat ValdezNo ratings yet
- Gs This That Those - ExercisesDocument2 pagesGs This That Those - ExercisesWilvertein C ChambiNo ratings yet
- Overseas Manpower SuppliersDocument10 pagesOverseas Manpower SuppliersAshwini Nair0% (1)
- Introduction To Computational Finance and Financial EconometricsDocument54 pagesIntroduction To Computational Finance and Financial EconometricsMR 2No ratings yet
- CA & Sports Grade 7 Jss Simplified NotesDocument8 pagesCA & Sports Grade 7 Jss Simplified NotesHoseaNo ratings yet
- Multithreaded Airport Simulation SystemsDocument6 pagesMultithreaded Airport Simulation Systemsphanikrishnajagadesh666No ratings yet
- Letter From Harvard Leaders To EPA's Andrew Wheeler On Proposed Science PolicyDocument60 pagesLetter From Harvard Leaders To EPA's Andrew Wheeler On Proposed Science PolicyEmily AtkinNo ratings yet
- Ourlog 9089Document4 pagesOurlog 9089Prin PinkyNo ratings yet
- Vascular and Non-Vascular PlantsDocument3 pagesVascular and Non-Vascular PlantsLeonardo PigaNo ratings yet
- Sop For H3i Nefpa Simo To Mimo 251 - V1.0-JabotabekDocument14 pagesSop For H3i Nefpa Simo To Mimo 251 - V1.0-JabotabekAril GozaliNo ratings yet
- SUMMATIVE TEST 1 (Quarter 3 Science 7) A4 SIZEDocument6 pagesSUMMATIVE TEST 1 (Quarter 3 Science 7) A4 SIZEZayn Daniel World of GamesNo ratings yet
- Dealroom Embedded Finance v2Document32 pagesDealroom Embedded Finance v2Sushma KazaNo ratings yet
- NOTH Menu Aug 22Document10 pagesNOTH Menu Aug 22Devin SwanepoelNo ratings yet
- LEFORT, Claude. Thinking With and Against Hannah ArendtDocument14 pagesLEFORT, Claude. Thinking With and Against Hannah ArendtGabriel VecchiettiNo ratings yet
- Introduction SlidesDocument23 pagesIntroduction SlidesMathiselvan GopalNo ratings yet
- Responsibility AccountingDocument14 pagesResponsibility AccountingJignesh TogadiyaNo ratings yet
- Final Work 18-Arid-5983 R Internship ReportDocument34 pagesFinal Work 18-Arid-5983 R Internship ReportRaja Muhammad NomanNo ratings yet
- THE LAW PERTAINING TO PRIVATE PERSONAL & COMML RELATIONS - AdDU Bar NotesDocument54 pagesTHE LAW PERTAINING TO PRIVATE PERSONAL & COMML RELATIONS - AdDU Bar NotesDevilleres Eliza DenNo ratings yet
- Nursing Skills To Put On ResumeDocument6 pagesNursing Skills To Put On Resumeaflkubfrv100% (1)
- Environmental Systems and Societies Paper 3 SLDocument15 pagesEnvironmental Systems and Societies Paper 3 SLAfra LamisaNo ratings yet
- Whattolookforinacodereview PDFDocument53 pagesWhattolookforinacodereview PDFvamosraghavaNo ratings yet
- Cost Effective Housing PDFDocument16 pagesCost Effective Housing PDFSaurav ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Nature of Research (FIRST)Document18 pagesNature of Research (FIRST)JEMNA PITOGONo ratings yet
- BM 2 Operations Management and TQM NewDocument9 pagesBM 2 Operations Management and TQM NewEly GragasinNo ratings yet
- Implementation of HIRARC in A Small Sized Organization: September 2015Document7 pagesImplementation of HIRARC in A Small Sized Organization: September 2015faizNo ratings yet
- Mistibushi Servo Drive PDFDocument350 pagesMistibushi Servo Drive PDFnitin hadkeNo ratings yet
- Africa Asserts Its Identity Part I: The Frankfurt Book FairDocument17 pagesAfrica Asserts Its Identity Part I: The Frankfurt Book FairKhalil DialloNo ratings yet
ECON Quiz 3 Module 56 Formulas
ECON Quiz 3 Module 56 Formulas
Uploaded by
Jean MaeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ECON Quiz 3 Module 56 Formulas
ECON Quiz 3 Module 56 Formulas
Uploaded by
Jean MaeCopyright:
Available Formats
4 TYPES OF MARKET STRUCTURES
Perfect Competition
Monopoly
Monopolistic Competition
Oligopoly
How does a purely competitive seller sets the price?
- The same way as other firms set
What is the Profit Maximizing output role under Perfect competition?
- Price = Marginal Cost
What is the competitive output role under Monopoly?
- Marginal Revenue = Marginal Cost (MR = MC)
What is the competitive output role under Monopolistic Competition?
- Marginal Revenue = Marginal Cost (MR = MC)
Same ba ng output role ang Monopoly at Monopolistic Competition?
- Same output role and same structure, different products offered in the market
When can we say that a purely competitive seller earns at a loss?
- Average Total Cost / Cost is higher than the Price
In this situation (loss), should the firm continue operating in the short run?
- They should still continue if they are covering their fixed cost.
- Also, since the Price is still higher that the Average Variable Cost.
When is the right time to shut down the plant to minimize losses in the short run?
- If the Average Variable Cost is higher than the Price.
What is the market power of Meralco (monopoly)?
- They have more power such as setting higher prices but they don’t have unlimited market
power because there is ‘deadweight loss of monopoly’ (inefficiency: produce less and
charge more) therefore, in order to solve this, the government can intervene.
- Monopolist’s power is constrained by the demand curve. (higher demand, lower price;
lower demand, higher price)
In relation to economies of scope, what is commissary?
- In the monopolistic competition, McDo and Jollibee, almost all of the products offered in
this 2 outlets are not produce in their respective outlets, pinoproduce siya under respective
COMMISSARIES.
- Place where all products of a particular fast food chain are produce in order to economize.
How patents and other legal barriers do generates as a market power in a monopoly?
- It is the exclusive right of the industry to produce the product, no one can copy it.
Is there an expiration date for patents?
- Yes. It needs to be renewed.
Bakit may supply curve ang Perfect Competition pero ang Monopoly wala?
- PC: P = MC kaya may supply curve
- Monopoly: PC > MR=MC
- M for our firm
- C for Competitor’s
SOLUTIONS
*derivative dapat ng cost function yung marginal cost
CAPITAL LABOR
MEASURES OF PRODUCTIVITY
AVERAGE PRODUCT OF
MARGINAL PRODUCT OF
PROFIT-MAXIMIZATION INPUT USAGE
TO MAXIMIZE PROFITS
WHEN LABOR OR CAPITAL
VARY IN THE SHORT RUN,
THE MANAGER WILL HIRE:
ALGEBRAIC FORMS OF PRODUCTION FUNCTIONS
LINEAR
AVERAGE PRODUCTS OF
MARGINAL PRODUCTS OF
LEONTIEF
COBB-DOUGLAS
AVERAGE PRODUCTS OF
MARGINAL PRODUCTS OF
MARGINAL RATE OF TECHNICAL SUBSTITUTION
ABSOLUTE VALUE OF THE SLOPE OF THE ISOQUANT
HIGHER = MORE
LOWER = LESS
THE COST FUNCTION
FIXED COST VARIABLE COST TOTAL COST
AVERAGE COSTS
MARGINAL COST
CUBIC COST FUNCTION
MARGINAL COST
FUNCTION
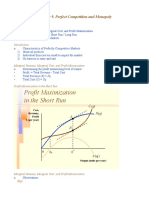
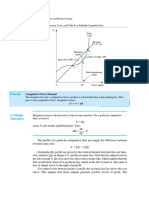
PERFECT COMPETITION
COST, REVENUES, AND PROFITS UNDER MONOPOLY
R = P*Q Revenue = Price * Unit of Output
Slope of R = MR = P = Df = Slope of Revenue = Marginal Revenue = Price = Demand
Pe Curve = Price Equilibrium
Slope of C (Q) = MC Slope of Cost = Marginal Cost
PROFIT MAXIMIZATION
Profits = ATC(Q) – Pe Profits = Average Total Cost – Price
Profit = P*Q – C(Q) Profits = Price * Quantity – (Cost Function)
COMPETITIVE OUTPUT RULE
P = MC (Q) = C (Q) Price = Marginal Cost (increasing marginal cost) = Cost
Function / Slope of Cost
SHORT RUN OUTPUT DECISION
CONTINUE if P ≥ AVC Continue if Price is above Average Variable Cost
CLOSE if P < AVC Close if Price is below Average Variable Cost
SHORT RUN SUPPLY CURVE
Short Run Supply Curve = Short Run Supply Curve = Marginal Cost above Average
MC above AVC Variable Cost
LONG RUN COMPETITIVE EQUILIBRIUM DECISION
P = MC Price (Value to Society) = Marginal Cost (Cost to Society)
P = min AC Price = Minimum of Average Cost
PRICING RULE
P = P of other firms Price = Price of other firms
ADDTL NOTES
Economic Profit = 0 If EP>0 then there’s Entry, until Df is tangent to AC curve
If EP<0 then there’s Exit, until Df is tangent to AC curve
MONOPOLY
SOURCES OF MONOPOLY POWER
Economies of Scale vAC Decline of Long Run Average Costs, Increase of Output
^Q
Diseconomies of Scale ^Q Increase of Long Run Average Costs, Increase of Output
vAC
Economies of Scope 2TC > Total Cost of producing 2 products > Cost of producing 2
1C + 1C separate products
Cost Complementarity ^ Marginal Cost of Output A is reduced when Marginal
MC of B, v MC of A Cost of Output B is increased.
MARGINAL REVENUE AND ELASTICITY / PROFIT MAXIMIZING OUTPUT
Marginal Revenue MR- Marginal Revenue
Function P- Price Charge
MR = P 𝐸
1+𝐸 E- Elasticity of Demand for the Monopolist’s Product
For P > 0 MR > 0 when E < -1 ELASTIC
MR = 0 when E = -1 UNITARY
MR < 0 when -1 < E < 0 INELASTIC
Inverse Demand Function Price = a +b (output)
P(Q) = a + b Q a > 0 and b < 0
MR (Q) = a + 2bQ Marginal Revenue = a + 2b (output)
OUTPUT RULE
MR (QM) = MC (QM) Profit Maximizing Output:
Marginal Revenue = Marginal Cost
[P > MR/MC]
PROFIT MAXIMIZATION
Profits = PM - ATC (QM)) x Profits = (Price – Average Total Cost) x Output
QM Profits = (Price x Output) – Cost
PRICING RULE
PM = P(QM) Price = Price x Output
MULTIPLANT DECISIONS
P(Q) where Q = Q1+Q2 The per-unit price consumers are willing to pay for the
total output produced at the two plants is Price *
Quantity
Where Q = Q1+Q2
PROFIT MAXIMIZING Marginal Revenue = Marginal Cost for Plant 1
RULE: Marginal Revenue = Marginal Cost for Plant 2
MR(Q) = MC1(Q1)
MR(Q) = MC2(Q2)
A MONOPOLIST EARNING ZERO PROFITS
M M
P = ATC (Q ) Optimal Price exactly equals the Average Total Cost of
Production
ADDTL NOTES
Economic Profit = Positive However, it does not guarantee positive profits
MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION
PROFIT MAXIMIZATION
MC = MR Marginal Revenue = Marginal Cost
Q*: MR(Q*) = MC(Q*) Marginal Revenue*Output = Marginal Cost*Output
P* = P(Q*) Price = Price * Output
LONG-RUN
P > MC Price > Marginal Cost
P = ATC > minimum of Price equals Average Total Cost that is greater than the
average costs minimum average cost
OPTIMAL ADVERTISING DECISIONS
𝐴
=
𝐸 𝑄,𝐴 A- Advertising
𝑅 − 𝐸 𝑄,𝑃
R- Revenue / Sales (Price*Output)
E- E Own Price Elasticity of Demand
ADDTL NOTES
Economic Profit = 0 No economic profit in the long run
You might also like
- JSA - Electrical Testing - Circuit Breaker Field TestDocument4 pagesJSA - Electrical Testing - Circuit Breaker Field TestTawfik Mohamed Abu Zaid0% (1)
- 2020 ME SESSION 12 Perfect CompetitionDocument42 pages2020 ME SESSION 12 Perfect CompetitionDr. Sakthirama VNo ratings yet
- Perfect Competition: 1. CharacteristicsDocument7 pagesPerfect Competition: 1. CharacteristicsMinh TragNo ratings yet
- Chapter-9 Imperfect CompetitionDocument23 pagesChapter-9 Imperfect Competitiongr8_amaraNo ratings yet
- HL Calculation Formulas MethodsDocument24 pagesHL Calculation Formulas MethodsMuras BaiyshevNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 ProductionDocument46 pagesChapter 5 Productionquangtm60.fbaeliteNo ratings yet
- Chap 09Document8 pagesChap 09Thabo MojavaNo ratings yet
- Session 25 - Monopoly and Market PowerDocument16 pagesSession 25 - Monopoly and Market PowerSweet tripathiNo ratings yet
- T Note 8 MonopolyDocument7 pagesT Note 8 MonopolyBella NovitasariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11-Managerial Decisions in Competitive MarketsDocument32 pagesChapter 11-Managerial Decisions in Competitive Marketsnaveen9622No ratings yet
- MONOPOLY Market Spring 2022Document50 pagesMONOPOLY Market Spring 2022Abid SunnyNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics: Lecture 10: Profit Maximization and Competitive SupplyDocument42 pagesMicroeconomics: Lecture 10: Profit Maximization and Competitive Supplyblackhawk31No ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet PMDocument2 pagesCheat Sheet PMhanifakihNo ratings yet
- Product and CostDocument49 pagesProduct and CostSahilNo ratings yet
- Definitions: Some Important Formulas in MicroeconomicsDocument3 pagesDefinitions: Some Important Formulas in MicroeconomicstrezzorNo ratings yet
- Markets Perfect CompetitionDocument47 pagesMarkets Perfect CompetitionSiddhant SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Perfect CompetitionDocument30 pagesPerfect Competitionaayush.5.parasharNo ratings yet
- Week 11 - English Muhammad Rizky RamadhanDocument44 pagesWeek 11 - English Muhammad Rizky RamadhanMuhammad Rizky RamadhanNo ratings yet
- 8 Market Structures and Profit MaximizationDocument18 pages8 Market Structures and Profit Maximizationakshat guptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Firm and IntegrationDocument10 pagesChapter 6-Firm and IntegrationUyển Nhi Lê ĐoànNo ratings yet
- SECTION 10 Need To KnowDocument2 pagesSECTION 10 Need To KnowAnisur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Definitions A-Z in Earm1Document7 pagesDefinitions A-Z in Earm1Mehul KhareNo ratings yet
- Pe Chap 14Document2 pagesPe Chap 14camlansuc09993No ratings yet
- Ions A-Z in EARM-1Document5 pagesIons A-Z in EARM-1rediah_ribbahsNo ratings yet
- ECON CH 8 & 9 NotesDocument6 pagesECON CH 8 & 9 NoteslemonaiidsNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Micro Exam III ReviewDocument6 pagesIntermediate Micro Exam III Reviewjrs55No ratings yet
- Costs and Revenues BEPDocument16 pagesCosts and Revenues BEPNguyen Thanh PhuongNo ratings yet
- Firms in Competitive MarketsDocument34 pagesFirms in Competitive MarketsRomeo DupaNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Study Sheet Microeconomics Study Sheet: More Free Study Sheet and Practice Tests atDocument3 pagesMicroeconomics Study Sheet Microeconomics Study Sheet: More Free Study Sheet and Practice Tests atanandsemails6968100% (1)
- Teori Biaya 2: Program Diploma Ekonomika Dan Bisnis Sekolah Vokasi, UGMDocument9 pagesTeori Biaya 2: Program Diploma Ekonomika Dan Bisnis Sekolah Vokasi, UGMGema Wahyu FadhilahNo ratings yet
- Principle of Economics Principle of Economics: Chapter Four Theory of Production and Theory of Production and CostDocument30 pagesPrinciple of Economics Principle of Economics: Chapter Four Theory of Production and Theory of Production and CostBiladenNo ratings yet
- CFO CH 8Document55 pagesCFO CH 8ashchua21No ratings yet
- Econ IIDocument28 pagesEcon IIworkinehamanuNo ratings yet
- Pasar Persaingan SempurnaDocument38 pagesPasar Persaingan SempurnaCandri Rahma MaharaniNo ratings yet
- Imperfect CompetitionDocument18 pagesImperfect CompetitionhishamsaukNo ratings yet
- CH 08Document36 pagesCH 08Xiaojie CaiNo ratings yet
- Formulaes Econ111: Average Total CostDocument1 pageFormulaes Econ111: Average Total CostjulieNo ratings yet
- CH 14 Firms in Competitive MarketsDocument31 pagesCH 14 Firms in Competitive MarketsSakibNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 MarketsDocument39 pagesLesson 5 MarketsiitNo ratings yet
- Module 8 Managing Competitive, Monopolistic, and Monopolistically Competitive Markets NotesDocument9 pagesModule 8 Managing Competitive, Monopolistic, and Monopolistically Competitive Markets NotesHazel PabloNo ratings yet
- Profit MaximizationDocument2 pagesProfit Maximizationpatelshivani033No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Production, Costs, and Organization of FirmDocument89 pagesChapter 3 - Production, Costs, and Organization of FirmHieu HoangNo ratings yet
- Q F (K, L) : Capital Is Fixed in The Short Run, Labor Is VariableDocument3 pagesQ F (K, L) : Capital Is Fixed in The Short Run, Labor Is VariableNicholas CasianoNo ratings yet
- Production Analysis PPT at BEC DOMSDocument26 pagesProduction Analysis PPT at BEC DOMSBabasab Patil (Karrisatte)No ratings yet
- CH 24 MonopolyDocument33 pagesCH 24 MonopolyNailed GownNo ratings yet
- Block 7 Monopoly Lecture TutorialDocument24 pagesBlock 7 Monopoly Lecture Tutorialshakti preeyaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 8 - To StudentsDocument54 pagesTutorial 8 - To StudentsVasif ŞahkeremNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - MonpolyDocument17 pagesChapter 6 - MonpolyEthio PNo ratings yet
- Economics Perfectly Competitive MarketDocument25 pagesEconomics Perfectly Competitive MarketEsha DivNo ratings yet
- Economics FormulasDocument2 pagesEconomics FormulasNelaNo ratings yet
- L10 W4L2 165s10 MarginalanalysisDocument35 pagesL10 W4L2 165s10 Marginalanalysismeetanshi01No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Managing in Competitive, Monopolistic, and Monopolistically Competitive MarketsDocument26 pagesChapter 8 Managing in Competitive, Monopolistic, and Monopolistically Competitive Marketsdimitri foxNo ratings yet
- REVIEW 01 - Microeconomics - Chapter 6 PDFDocument8 pagesREVIEW 01 - Microeconomics - Chapter 6 PDFKiệt NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Cost and RevenueDocument15 pagesCost and RevenueWaleed Wasti100% (1)
- Msci 607: Applied Economics For ManagementDocument4 pagesMsci 607: Applied Economics For ManagementRonak PatelNo ratings yet
- ECON Quiz 3 Module 6 Notes From HazelDocument9 pagesECON Quiz 3 Module 6 Notes From HazelJean MaeNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics and Business Strategy: PrincipleDocument4 pagesManagerial Economics and Business Strategy: PrincipleTiểu Ngân ĐồngNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Costs of Production Spring 2023Document52 pagesCH 7 Costs of Production Spring 2023sayidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document39 pagesChapter 14anchal11102003No ratings yet
- Mathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandMathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Readings in Philippine History: Pigafetta AccountDocument14 pagesReadings in Philippine History: Pigafetta AccountJean MaeNo ratings yet
- 1 - Page Chapter 2: Christian Call and Thomasian ResponseDocument12 pages1 - Page Chapter 2: Christian Call and Thomasian ResponseJean MaeNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts Revenue Cycle: List Price, Trade Discount, Prepaid Freight, Cash DiscountDocument50 pagesBasic Concepts Revenue Cycle: List Price, Trade Discount, Prepaid Freight, Cash DiscountJean MaeNo ratings yet
- Statement of Owners Equity Excel TemplateDocument1 pageStatement of Owners Equity Excel TemplateJean MaeNo ratings yet
- BSAMERCHANDISING2021Document5 pagesBSAMERCHANDISING2021Jean MaeNo ratings yet
- CA5102 Course-Plan Managerial-EconomicsDocument12 pagesCA5102 Course-Plan Managerial-EconomicsJean MaeNo ratings yet
- Module 6B - Managing in Monopolistic MarketsDocument33 pagesModule 6B - Managing in Monopolistic MarketsJean MaeNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: RequiredDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: RequiredJean MaeNo ratings yet
- ECON Quiz 3 Module 6 Notes From HazelDocument9 pagesECON Quiz 3 Module 6 Notes From HazelJean MaeNo ratings yet
- ST ST: Jasmine Kayla G. PangilinanDocument16 pagesST ST: Jasmine Kayla G. PangilinanJean MaeNo ratings yet
- Profitability and Marketability of The Top 55 U.S. Commercial BanksDocument19 pagesProfitability and Marketability of The Top 55 U.S. Commercial BanksSasa LuNo ratings yet
- Umbilical Catheterization in ServiceDocument11 pagesUmbilical Catheterization in ServiceLucian CaelumNo ratings yet
- Ra 9288 Basis For Questionnaire PDFDocument22 pagesRa 9288 Basis For Questionnaire PDFHolden Mandapat ValdezNo ratings yet
- Gs This That Those - ExercisesDocument2 pagesGs This That Those - ExercisesWilvertein C ChambiNo ratings yet
- Overseas Manpower SuppliersDocument10 pagesOverseas Manpower SuppliersAshwini Nair0% (1)
- Introduction To Computational Finance and Financial EconometricsDocument54 pagesIntroduction To Computational Finance and Financial EconometricsMR 2No ratings yet
- CA & Sports Grade 7 Jss Simplified NotesDocument8 pagesCA & Sports Grade 7 Jss Simplified NotesHoseaNo ratings yet
- Multithreaded Airport Simulation SystemsDocument6 pagesMultithreaded Airport Simulation Systemsphanikrishnajagadesh666No ratings yet
- Letter From Harvard Leaders To EPA's Andrew Wheeler On Proposed Science PolicyDocument60 pagesLetter From Harvard Leaders To EPA's Andrew Wheeler On Proposed Science PolicyEmily AtkinNo ratings yet
- Ourlog 9089Document4 pagesOurlog 9089Prin PinkyNo ratings yet
- Vascular and Non-Vascular PlantsDocument3 pagesVascular and Non-Vascular PlantsLeonardo PigaNo ratings yet
- Sop For H3i Nefpa Simo To Mimo 251 - V1.0-JabotabekDocument14 pagesSop For H3i Nefpa Simo To Mimo 251 - V1.0-JabotabekAril GozaliNo ratings yet
- SUMMATIVE TEST 1 (Quarter 3 Science 7) A4 SIZEDocument6 pagesSUMMATIVE TEST 1 (Quarter 3 Science 7) A4 SIZEZayn Daniel World of GamesNo ratings yet
- Dealroom Embedded Finance v2Document32 pagesDealroom Embedded Finance v2Sushma KazaNo ratings yet
- NOTH Menu Aug 22Document10 pagesNOTH Menu Aug 22Devin SwanepoelNo ratings yet
- LEFORT, Claude. Thinking With and Against Hannah ArendtDocument14 pagesLEFORT, Claude. Thinking With and Against Hannah ArendtGabriel VecchiettiNo ratings yet
- Introduction SlidesDocument23 pagesIntroduction SlidesMathiselvan GopalNo ratings yet
- Responsibility AccountingDocument14 pagesResponsibility AccountingJignesh TogadiyaNo ratings yet
- Final Work 18-Arid-5983 R Internship ReportDocument34 pagesFinal Work 18-Arid-5983 R Internship ReportRaja Muhammad NomanNo ratings yet
- THE LAW PERTAINING TO PRIVATE PERSONAL & COMML RELATIONS - AdDU Bar NotesDocument54 pagesTHE LAW PERTAINING TO PRIVATE PERSONAL & COMML RELATIONS - AdDU Bar NotesDevilleres Eliza DenNo ratings yet
- Nursing Skills To Put On ResumeDocument6 pagesNursing Skills To Put On Resumeaflkubfrv100% (1)
- Environmental Systems and Societies Paper 3 SLDocument15 pagesEnvironmental Systems and Societies Paper 3 SLAfra LamisaNo ratings yet
- Whattolookforinacodereview PDFDocument53 pagesWhattolookforinacodereview PDFvamosraghavaNo ratings yet
- Cost Effective Housing PDFDocument16 pagesCost Effective Housing PDFSaurav ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Nature of Research (FIRST)Document18 pagesNature of Research (FIRST)JEMNA PITOGONo ratings yet
- BM 2 Operations Management and TQM NewDocument9 pagesBM 2 Operations Management and TQM NewEly GragasinNo ratings yet
- Implementation of HIRARC in A Small Sized Organization: September 2015Document7 pagesImplementation of HIRARC in A Small Sized Organization: September 2015faizNo ratings yet
- Mistibushi Servo Drive PDFDocument350 pagesMistibushi Servo Drive PDFnitin hadkeNo ratings yet
- Africa Asserts Its Identity Part I: The Frankfurt Book FairDocument17 pagesAfrica Asserts Its Identity Part I: The Frankfurt Book FairKhalil DialloNo ratings yet