Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment No. 7 Qualitative Tests For Carbohydrates I. Data
Experiment No. 7 Qualitative Tests For Carbohydrates I. Data
Uploaded by
Kleya Parreño0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views3 pagesThis document describes the results of qualitative tests performed on various carbohydrates. Glucose, fructose, mannose, xylose, maltose, and dextrin produced positive results for the Molisch's, Benedict's, and Barfoed's tests, indicating they are reducing sugars. Sucrose was positive only for the Seliwanoff's test, identifying it as a non-reducing disaccharide. Starch and lactose were only positive for Molisch's, while lactose also tested positive for Benedict's, showing lactose is a reducing sugar but starch is not. The tests can be used to differentiate sugars like the positive fructose and negative sucrose results for Barfoed
Original Description:
QUALITATIVE TESTS FOR CARBOHYDRATES - BIOCHEMISTRY
Original Title
EXPERIMENT VII
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document describes the results of qualitative tests performed on various carbohydrates. Glucose, fructose, mannose, xylose, maltose, and dextrin produced positive results for the Molisch's, Benedict's, and Barfoed's tests, indicating they are reducing sugars. Sucrose was positive only for the Seliwanoff's test, identifying it as a non-reducing disaccharide. Starch and lactose were only positive for Molisch's, while lactose also tested positive for Benedict's, showing lactose is a reducing sugar but starch is not. The tests can be used to differentiate sugars like the positive fructose and negative sucrose results for Barfoed
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views3 pagesExperiment No. 7 Qualitative Tests For Carbohydrates I. Data
Experiment No. 7 Qualitative Tests For Carbohydrates I. Data
Uploaded by
Kleya ParreñoThis document describes the results of qualitative tests performed on various carbohydrates. Glucose, fructose, mannose, xylose, maltose, and dextrin produced positive results for the Molisch's, Benedict's, and Barfoed's tests, indicating they are reducing sugars. Sucrose was positive only for the Seliwanoff's test, identifying it as a non-reducing disaccharide. Starch and lactose were only positive for Molisch's, while lactose also tested positive for Benedict's, showing lactose is a reducing sugar but starch is not. The tests can be used to differentiate sugars like the positive fructose and negative sucrose results for Barfoed
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Name: KLEYA MONIQUE I.
PARREÑO Date Performed: November 15, 2021
Section: Lab – C Date Submitted: November 21, 2021
Experiment No. 7 QUALITATIVE TESTS FOR CARBOHYDRATES
I. Data
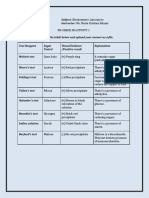
Write your observations on the space provided.
TEST
SUGAR
Molisch’s Iodine Benedict’s
(+) dark orange
Glucose (+) red ring or interface (-)
precipitate
(+) reddish violet ring or (+) dark orange
Fructose (-)
interface precipitate
(+) reddish ring or (+) moss green
Mannose (-)
interface precipitate
(+) reddish ring or (+) dark orange
Xylose (-)
interface precipitate
(+) reddish ring or (+) dark orange
Maltose (-)
interface precipitate
(+) reddish ring or
Sucrose (-) (-)
interface
(+) faint reddish ring or (+) brownish green
Lactose (-)
interface precipitate
(+) reddish ring or (+) brownish green
Dextrin (+) dark purple color
interface precipitate
(+) faint reddish ring or
Starch (+) dark blue color (-)
interface
CHEM 20 LAB EXPERIMENT 7 QUALITATIVE TESTS FOR CARBOHYDRATES 1
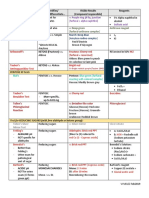
Write your observations on the space provided.
TEST
SUGAR
Barfoed’s Seliwanoff’s Osazone formation
(+) brownish yellow-
colored crystals are
Glucose (+) dark red precipitate (-)
present, close to each
other
(+) yellow and brown-
colored crystals are
Fructose (+) dark red precipitate (+) red solution
present, close to each
other
Mannose (+) dark red precipitate (-)
Xylose (+) dark red precipitate (-)
(+) yellow-colored crystals
Maltose (-) (-)
are present, scattered
Sucrose (-) (+) red solution (-)
Lactose (-) (-)
Dextrin (-) (-)
Starch (-) (-) (-)
CHEM 20 LAB EXPERIMENT 7 QUALITATIVE TESTS FOR CARBOHYDRATES 2
II. Questions
1. An unknown solution contains a single pure sugar. It gives positive results to Molisch’s and
Benedict’s tests but is negative for all others. What is the sugar? Is it sucrose, lactose, or xylose?
Explain your choice.
The sugar, lactose, gives a positive result to both Molisch’s and Benedict’s tests but is negative
for all others. It gives a positive Benedict’s test because it is a reducing sugar. It is a simple
carbohydrate that contains glucose with a free aldehyde group, making it easier to react with the
Benedict’s reagent. It gives a positive Molisch’s Test because this test only detects carbohydrates in a
solution, thus the positive result in lactose. However, it gives a negative iodine test result because
lactose is not a polysaccharide. Iodine Test is specific for polysaccharides. It is also negative in the
Barfoed’s Test because lactose is not a reducing monosaccharide but a reducing disaccharide. The
Barfoed’s Test gives a red precipitate, which is positive, indicating the presence of a reducing
monosaccharide. Lastly, it is negative in Seliwanoff’s Test because lactose is an aldose. The
Seliwanoff’s Test detects keto sugars. It was not included in the Osazone Formation. The other sugars
give positive results to some of the other tests.
2. What test would allow you to differentiate fructose and sucrose? Explain your answer.
A chemical test called the Barfoed’s Test is used to distinguish fructose and sucrose from each
other. It identifies the presence of monosaccharides and detects reducing monosaccharides in the
presence of disaccharides. Since fructose is a reducing monosaccharide, it produces a positive
reaction. Sucrose, on the other hand, is a disaccharide and produces a negative reaction.
3. Explain why reducing sugars produce Osazone crystals?
The formation of a pair of hydrazone functionalities involves both oxidation and condensation
reactions. Since the reaction requires a carbonyl group, only reducing sugars participate.
phenylhydrazine reacts with the carbonyl in the sugar to create phenylhydrazone. The hydrazones
then react further with the phenylhydrazine to produce insoluble osazones that appear in crystal form.
CHEM 20 LAB EXPERIMENT 7 QUALITATIVE TESTS FOR CARBOHYDRATES 3
You might also like
- Case Presentation 1Document27 pagesCase Presentation 1Inatul Aulia67% (6)
- Biology Model Exam Grade 12Document13 pagesBiology Model Exam Grade 12All in One Tube100% (6)
- Chem 20 Lab Experiment No.7 Qualitative Tests For CarbohydratesDocument2 pagesChem 20 Lab Experiment No.7 Qualitative Tests For CarbohydratesChristine MarcellanaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5: Analysis of Carbohydrates (Post-Lab Report)Document9 pagesExperiment 5: Analysis of Carbohydrates (Post-Lab Report)Jemina SacayNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry (Laboratory) : A. Molisch TestDocument6 pagesBiochemistry (Laboratory) : A. Molisch TestDojin ParkNo ratings yet
- Chemical Examination of UrineDocument6 pagesChemical Examination of UrinehermanskyNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6 - CarbohydratesDocument4 pagesExperiment 6 - CarbohydratesShaira Dawn PlancoNo ratings yet
- Tupas, Denzel C. Module 5 Check in Activity 1 Biochem LabDocument2 pagesTupas, Denzel C. Module 5 Check in Activity 1 Biochem LabDan CasuraoNo ratings yet
- ID Test Tabular Reviewer For Philippine PLE Module 2Document3 pagesID Test Tabular Reviewer For Philippine PLE Module 2ViaNo ratings yet
- Color Reactions of Proteins and Amino AcidsDocument2 pagesColor Reactions of Proteins and Amino AcidsMhaycelle InsertapilyedohereNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument10 pagesCarbohydratesGleyr BelzaNo ratings yet
- BufferDocument2 pagesBufferKrisca DianeNo ratings yet
- AlkaloidsDocument1 pageAlkaloidsboking06No ratings yet
- EnterobacteriaceaeDocument3 pagesEnterobacteriaceaePark SunghoonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document7 pagesChapter 12J.K HomerNo ratings yet
- Activity 2A - Reactions To CarbohydratesDocument5 pagesActivity 2A - Reactions To CarbohydratesMy Roses Are RosèNo ratings yet
- LeChatelier Lab ReportDocument6 pagesLeChatelier Lab ReportSarah B - she herNo ratings yet
- FD ChongZheDian R1Document10 pagesFD ChongZheDian R1Choonbin TanNo ratings yet
- Biochem-Lab 100Document8 pagesBiochem-Lab 100AvyNo ratings yet
- Type Method Determination Of: Condition Titrant Primary STD Indicator Observable Change and ReactionsDocument3 pagesType Method Determination Of: Condition Titrant Primary STD Indicator Observable Change and ReactionsbiotechNo ratings yet
- AcidicradicalsDocument1 pageAcidicradicalsDevyanshi SinghNo ratings yet
- Tests Principle Klebsiella Pneumoniae My UnknownDocument2 pagesTests Principle Klebsiella Pneumoniae My UnknownArnulfo PagudNo ratings yet
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: T C F PDocument11 pages© Ncert Not To Be Republished: T C F PAKSHAY JNo ratings yet
- Colours of Inorganic Ions and Complexes Poster PDFDocument1 pageColours of Inorganic Ions and Complexes Poster PDFSophie PriorNo ratings yet
- Results Group II Oral ReportingDocument2 pagesResults Group II Oral ReportingKervy SanjeNo ratings yet
- Data For Exercise 4Document4 pagesData For Exercise 4Louiegi AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Activity 6 - Color Test For SaccharidesDocument4 pagesActivity 6 - Color Test For SaccharidesChris Turff0% (1)
- Halogens-Recording Observations and Processing SkillsDocument3 pagesHalogens-Recording Observations and Processing SkillsEMAN ANWARNo ratings yet
- 18 - Qualitative Analysis (Cation) - 1Document4 pages18 - Qualitative Analysis (Cation) - 1Aditya SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- The Memory Part in C8 2Document2 pagesThe Memory Part in C8 2zdozddabNo ratings yet
- General Color Test For CarbohydratesDocument2 pagesGeneral Color Test For CarbohydratesDennis ValdezNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates ResultsDocument4 pagesCarbohydrates ResultsVincent ManganaanNo ratings yet
- Expt 6Document10 pagesExpt 6beatriz balingit0% (1)
- Qualitative Tests For Carbohydrates: 1) Molisch TestDocument20 pagesQualitative Tests For Carbohydrates: 1) Molisch TestFRANCEEN LEANNA KATIGBAKNo ratings yet
- CSEC Qualitative Analysis CATIONSDocument7 pagesCSEC Qualitative Analysis CATIONS-Sabiraaa -No ratings yet
- Dinosaur Island Dinosaur Island: Deluxe EditionDocument39 pagesDinosaur Island Dinosaur Island: Deluxe EditionMario Medina MontesNo ratings yet
- Dinosaur Island Dinosaur Island: Deluxe EditionDocument39 pagesDinosaur Island Dinosaur Island: Deluxe EditionMario Medina MontesNo ratings yet
- Lab Expts 3 To 4 ReviewDocument4 pagesLab Expts 3 To 4 ReviewKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Bio462 Exp6 Result (Ashiya)Document3 pagesBio462 Exp6 Result (Ashiya)NurmazillaZainalNo ratings yet
- Expt 2. Isolation of Polysaccharide and Analysis of CarbohydratesDocument18 pagesExpt 2. Isolation of Polysaccharide and Analysis of CarbohydratesLESLIE JANE BALUYOS JALANo ratings yet
- Experiment 5:: Determination of Cations and AnionsDocument18 pagesExperiment 5:: Determination of Cations and AnionsBianca VirtudasoNo ratings yet
- E05 Identification of Inorganic CompoundsDocument22 pagesE05 Identification of Inorganic CompoundsNicolás Rodríguez RubianoNo ratings yet
- Test Tube Reactions For Topic 6 1) Halogen Displacement ReactionsDocument2 pagesTest Tube Reactions For Topic 6 1) Halogen Displacement ReactionsXiandan AyjNo ratings yet
- TEST Results For Aldehydes and Ketones Carboxylic Acids and EstersDocument2 pagesTEST Results For Aldehydes and Ketones Carboxylic Acids and Estersbrent.trasmonteNo ratings yet
- Escalus SlidesCarnivalDocument48 pagesEscalus SlidesCarnivalbagusNo ratings yet
- Lab Expts 5-7 ReviewDocument6 pagesLab Expts 5-7 ReviewKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Hydrolysis of CarbohydratesDocument15 pagesHydrolysis of CarbohydratesAlhaisa BejemilNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 5 The Solubility of Common Salts in WaterDocument8 pagesExperiment No. 5 The Solubility of Common Salts in WaterJoyce Bensig CastilNo ratings yet
- Vii. Procedure 1. A) Reaction With Naoh: Greyish Blue PrecipitateDocument11 pagesVii. Procedure 1. A) Reaction With Naoh: Greyish Blue PrecipitateAnggraini Nugroho PNo ratings yet
- 4A. Preliminary Tests Objectives - To Conduct A Qualitative Tests Specific For Carbohydrates and Proteins - To Determine The Chemical Reaction of Carbohydrates To The Different TestsDocument1 page4A. Preliminary Tests Objectives - To Conduct A Qualitative Tests Specific For Carbohydrates and Proteins - To Determine The Chemical Reaction of Carbohydrates To The Different TestsAllona ReasolNo ratings yet
- Appendix-07-Symbols For Chemical ReactionsDocument2 pagesAppendix-07-Symbols For Chemical ReactionsGueen Bacala MalbasNo ratings yet
- Biochem CombinedDocument14 pagesBiochem CombinedAmber De la CernaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of CompoundsDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Compoundskpmhydro10No ratings yet
- Gram Negative BacilliDocument1 pageGram Negative BacilliDe Guzman E AldrinNo ratings yet
- TabelDocument4 pagesTabelayu irsalinaNo ratings yet
- Alur + Reaction Transition MetalDocument11 pagesAlur + Reaction Transition MetalKafitaNo ratings yet
- Practical Chemistry - OcDocument14 pagesPractical Chemistry - Ocdakshanatab255No ratings yet
- Soil Structure Evidence Synthesis ReportDocument35 pagesSoil Structure Evidence Synthesis ReportrezahosseinpourNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13. Insights of ToxicologyDocument3 pagesChapter 13. Insights of Toxicology5pn4x4czxnNo ratings yet
- Ecotri One - MSDS - enDocument18 pagesEcotri One - MSDS - enmutlununNo ratings yet
- Brazilian Journal of Chemical EngineeringDocument8 pagesBrazilian Journal of Chemical Engineeringcarol choquecallataNo ratings yet
- Object Med ChemDocument7 pagesObject Med ChemPrabhat UikeyNo ratings yet
- LGHH Chemical Product Catalog V1Document4 pagesLGHH Chemical Product Catalog V1Akmal CoinNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Topic: Stream EcosystemDocument20 pagesAssignment: Topic: Stream EcosystemAbhija YacobNo ratings yet
- Conditions On Early Earth Made The Origin of Life PossibleDocument8 pagesConditions On Early Earth Made The Origin of Life PossibleHikmah UmarNo ratings yet
- Microbial Biotechnology AssignmentDocument7 pagesMicrobial Biotechnology AssignmenthajraNo ratings yet
- Olechomical Ester Plant-Merged (This)Document21 pagesOlechomical Ester Plant-Merged (This)Calvin Lin Jia RongNo ratings yet
- Ad 1191551Document141 pagesAd 1191551Falesh FirakeNo ratings yet
- Alkyl Halides ÖğrenciDocument6 pagesAlkyl Halides ÖğrenciSudeNo ratings yet
- Appendix 1 Epon Resin - Curing Agent Systems: Ã Resolution Performance ProductsDocument59 pagesAppendix 1 Epon Resin - Curing Agent Systems: Ã Resolution Performance ProductsWALTER KLISSMANNo ratings yet
- BIOL BCHM 111 BiomoleculesDocument49 pagesBIOL BCHM 111 BiomoleculeshavenNo ratings yet
- Background: CH 301 NAMEDocument4 pagesBackground: CH 301 NAMEItzel NavaNo ratings yet
- Banana Peel ShampooDocument14 pagesBanana Peel ShampooMhay DingleNo ratings yet
- Meselson and Stahl Experiment DeterminedDocument1 pageMeselson and Stahl Experiment DeterminedCarolina RelvaNo ratings yet
- MSC Project Work, Anis Ahmed, SA-28.5.19Document24 pagesMSC Project Work, Anis Ahmed, SA-28.5.19mahfooz zin noorineNo ratings yet
- PFD FileDocument44 pagesPFD FilerahulkhakhriyaNo ratings yet
- H&M Group Chemical Restrictions 2020: Restricted Substances List (RSL) Chemical ProductsDocument18 pagesH&M Group Chemical Restrictions 2020: Restricted Substances List (RSL) Chemical ProductsHarianto SuhendroNo ratings yet
- AQA A Level Chem CH13 Practice Question AnswersDocument3 pagesAQA A Level Chem CH13 Practice Question AnswersMahebul MazidNo ratings yet
- Finding Main IdeaDocument8 pagesFinding Main IdeaRisyda ZannawaNo ratings yet
- Qubit 4 Fluorometer-Fast Answers For Precious Samples: Find Out If You Have Enough DNA or RNA For Your ExperimentDocument2 pagesQubit 4 Fluorometer-Fast Answers For Precious Samples: Find Out If You Have Enough DNA or RNA For Your ExperimentmisuakechiNo ratings yet
- Common Polyatomic IonsDocument1 pageCommon Polyatomic Ionsmudasser_rafiq3271No ratings yet
- Histopath TransDocument5 pagesHistopath TransRobNo ratings yet
- Boron - : The BouncerDocument3 pagesBoron - : The BouncerACU PLUNGERNo ratings yet
- Amines WorksheetDocument5 pagesAmines WorksheetMeenakshi Saji0% (1)
- II PUC Chemistry Passing PackageDocument30 pagesII PUC Chemistry Passing PackageGorpadii TechNo ratings yet
- Titrimetric Analysis of An Amino AcidDocument15 pagesTitrimetric Analysis of An Amino Acidapi-535149918No ratings yet