Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 viewsKingswood World School Science Worksheet Grade 6, Chapter 11
Kingswood World School Science Worksheet Grade 6, Chapter 11
Uploaded by
Hardeep Singh1. The document contains a science worksheet for 6th grade students on the topic of motion and measuring time. It includes short answer and long answer questions.
2. Key concepts covered include definitions of speed, oscillation, and periodic motion. Examples of different types of motion like circular, rotational, and linear motion are provided.
3. Common devices used to measure time, distance, and speed are described, including the speedometer, odometer, stopwatch, sundial, and hourglass. Formulas to calculate speed from measurements of distance and time are also given.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Ans 1 Dkin 2Document4 pagesAns 1 Dkin 2Dolores LocañasNo ratings yet
- Report No. 1Document11 pagesReport No. 1Alex QuirimitNo ratings yet
- Ahb L544-L580Document44 pagesAhb L544-L580sanches pitaNo ratings yet
- NOTES - MOTION AND TIME CLASS VIIsahfghfjfgjhfgDocument8 pagesNOTES - MOTION AND TIME CLASS VIIsahfghfjfgjhfgForex lolNo ratings yet
- CH - 13: Motion and TimeDocument14 pagesCH - 13: Motion and TimeDeepak KansalNo ratings yet
- Asm 6193Document3 pagesAsm 6193major criticNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 7th Science Value Based Questions Chapter 13 Motion and Time PDF DownloadDocument11 pagesCBSE Class 7th Science Value Based Questions Chapter 13 Motion and Time PDF Downloadpravin161079No ratings yet
- Motion & TimeDocument2 pagesMotion & TimeRenuNo ratings yet
- 7CL L-14, ExercisesDocument6 pages7CL L-14, ExercisesArish IzaanNo ratings yet
- G 7 - Motion and TimeDocument38 pagesG 7 - Motion and Timesangeetha alurNo ratings yet
- Motion Elite 2Document4 pagesMotion Elite 2aryanyt6996No ratings yet
- Moutn Fji6914389Document15 pagesMoutn Fji6914389helo my name is 88No ratings yet
- Descriptors of MotionDocument30 pagesDescriptors of MotionCamilleNo ratings yet
- Motion and TimeDocument4 pagesMotion and TimeNIdhi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Motion and TimeDocument4 pagesMotion and TimeRenuNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 13Document6 pagesScience Chapter 13Divya SreejithNo ratings yet
- Motion and Time Class 7, 2022Document61 pagesMotion and Time Class 7, 2022Theia JacobNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Mod1 Q3Document12 pagesScience 7 Mod1 Q3Roselyn B. BitareNo ratings yet
- Kinematics 1 G10Document8 pagesKinematics 1 G10Ansh GaoneadryNo ratings yet
- Third Term Science 5 Modules 1-4Document17 pagesThird Term Science 5 Modules 1-4Kathleen FernandezNo ratings yet
- Workbook Exercise of Motion and TimeDocument7 pagesWorkbook Exercise of Motion and Timesmi_santhoshNo ratings yet
- Shraddha Children'S Academy, Kottivakkam Class: Vii Physics Motion and Time MotionDocument2 pagesShraddha Children'S Academy, Kottivakkam Class: Vii Physics Motion and Time MotionkalaiNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 7 - Chapter 13Document17 pagesExp SC 7 - Chapter 13megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Motion and TimeDocument13 pagesMotion and TimeRajeevSangam100% (1)
- 1 - Linear MotionDocument10 pages1 - Linear Motionapi-242844746No ratings yet
- Grade9 CBSE MotionDocument40 pagesGrade9 CBSE MotionSamarth KatariyaNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument31 pagesKinematicsAfrozsyed350No ratings yet
- Motion and TimeDocument4 pagesMotion and TimeSANDEEP SINGHNo ratings yet
- Motion NcertDocument16 pagesMotion NcertRanjith RajNo ratings yet
- Types of MotionDocument4 pagesTypes of MotionCeasar Epsilonian MundalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter1. Motion in A Straight Line: Speed - It Is A Scalar Quantity. - Average SpeedDocument6 pagesChapter1. Motion in A Straight Line: Speed - It Is A Scalar Quantity. - Average SpeedJonathan CasillaNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument152 pagesPhysicsanujbeniwalNo ratings yet
- Experimentno.4 Uniform Motion I. ObjectivesDocument6 pagesExperimentno.4 Uniform Motion I. ObjectivesStephanie AzucenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document7 pagesChapter 13Pta PNo ratings yet
- Physics CapsuleDocument152 pagesPhysics CapsuledayakarNo ratings yet
- 6 ThmathsDocument3 pages6 Thmathslearn4chatgptNo ratings yet
- 1 MotionDocument39 pages1 Motiondav borlNo ratings yet
- Aees-Distant Learning Programme Class Ix - Physics Chapter - 8 MotionDocument5 pagesAees-Distant Learning Programme Class Ix - Physics Chapter - 8 Motionseenu nadarajanNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes Motion and TimeDocument9 pagesRevision Notes Motion and TimeRaman -No ratings yet
- Motion Chapter NotesDocument45 pagesMotion Chapter Notess.anoura07No ratings yet
- Workseet Chapter Part 1Document9 pagesWorkseet Chapter Part 1mohammedNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Subject Science Chapter 13 Motion and TimeDocument5 pagesClass 7 Subject Science Chapter 13 Motion and TimeSidh GargNo ratings yet
- MotionDocument5 pagesMotionvivek_theeasywaysNo ratings yet
- Rectilinear MotionDocument3 pagesRectilinear MotionGaurav JainNo ratings yet
- 9th Physics (13-04-23)Document2 pages9th Physics (13-04-23)IshitaNo ratings yet
- Class 7 NCERT CH 13Document17 pagesClass 7 NCERT CH 13rajan8286No ratings yet
- Class 7th CH 13 MOTION Very Short A-WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesClass 7th CH 13 MOTION Very Short A-WPS OfficemeghaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 10 SC Measuring MotionDocument7 pagesCHAPTER 10 SC Measuring MotionEunice Xiiao Wenn100% (2)
- Kinematics (Particles in Motion) SDocument9 pagesKinematics (Particles in Motion) SMarcusKlahnTokoeJr.No ratings yet
- Lakhmir Singh Solutions Class 9 Physics Chapter 1Document27 pagesLakhmir Singh Solutions Class 9 Physics Chapter 1Rekha PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class 7Document12 pagesCbse Class 7kalslingam100% (1)
- SPH3U - Kinematics 2: Velocity and Speed: ReviewDocument6 pagesSPH3U - Kinematics 2: Velocity and Speed: Reviewlim05abcNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Average Speed and VelocityDocument22 pagesLesson 3 Average Speed and Velocitykyoto.saeopNo ratings yet
- Motion and TimeDocument8 pagesMotion and TimeALLURI DEDEEPYA LAKSHYANo ratings yet
- Motion ByjusDocument10 pagesMotion ByjusAMIT GOYALNo ratings yet
- The Adventure of Whiz Trying to Bring His Future To Him Quicker: The Adventures of Whiz, the Whizz ScientistFrom EverandThe Adventure of Whiz Trying to Bring His Future To Him Quicker: The Adventures of Whiz, the Whizz ScientistNo ratings yet
- IPL Auction (19PT2-11)Document10 pagesIPL Auction (19PT2-11)Hardeep SinghNo ratings yet
- MCIA Project: Discover Alpas Camps and ResortsDocument18 pagesMCIA Project: Discover Alpas Camps and ResortsHardeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Emerging Market Strategy: Organization - General Electric Country - EthopiaDocument34 pagesEmerging Market Strategy: Organization - General Electric Country - EthopiaHardeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Group 6 Postponement Strategies Case Presentation SCM EMPDocument14 pagesGroup 6 Postponement Strategies Case Presentation SCM EMPHardeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Group 7 - Cadbury Case - Rev01Document12 pagesGroup 7 - Cadbury Case - Rev01Hardeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - SpriteDocument9 pagesGroup 3 - SpriteHardeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Personality: - Case On SpriteDocument8 pagesPersonality: - Case On SpriteHardeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Information Service: Electric EGR Valves (Renault, Opel)Document3 pagesInformation Service: Electric EGR Valves (Renault, Opel)Popa AurelNo ratings yet
- BS 5268-2:1996 Section 2Document2 pagesBS 5268-2:1996 Section 2Zayyan RomjonNo ratings yet
- RCC & PSC Class NotesDocument329 pagesRCC & PSC Class NotesAbhishek KandpalNo ratings yet
- Laser Ultrasonics Techniques and Applications Drain, L E Z LibraryDocument465 pagesLaser Ultrasonics Techniques and Applications Drain, L E Z LibraryRêmulo FariasNo ratings yet
- Typical gc66 ManualDocument56 pagesTypical gc66 ManualPabloLinuxNo ratings yet
- Construction EquipmentDocument98 pagesConstruction EquipmentBejil ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Interaction DiagramDocument4 pagesInteraction Diagramjavier glzNo ratings yet
- JICA, Manual For Micro-Hydro Power DevelopmentDocument28 pagesJICA, Manual For Micro-Hydro Power DevelopmentRiza RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Bianchi 952Document87 pagesBianchi 952Abdenour KeraghelNo ratings yet
- Micromechatronics - K. Uchino, J. Giniewicz (Marcel Dekker, 2003) WW PDFDocument508 pagesMicromechatronics - K. Uchino, J. Giniewicz (Marcel Dekker, 2003) WW PDFMario Ramone100% (1)
- Pigging Slug TrickDocument38 pagesPigging Slug TrickLorena DávilaNo ratings yet
- Smaw PDFDocument10 pagesSmaw PDFArizapatazoNo ratings yet
- Din Vde 0210 - 1985-Ocr PDFDocument103 pagesDin Vde 0210 - 1985-Ocr PDFFleancuCatalinNo ratings yet
- AWS100 Appendix 12 FatigueDocument72 pagesAWS100 Appendix 12 FatiguecarlosnovoanNo ratings yet
- Helix ZC01-FD001 24092020Document9 pagesHelix ZC01-FD001 24092020achmatNo ratings yet
- Tube Expansion ProcedureDocument3 pagesTube Expansion Procedurerudi 01100% (1)
- Rolling Contact Bearings: Bearing TypesDocument6 pagesRolling Contact Bearings: Bearing Typessofyan samNo ratings yet
- Presentation Acoustic To Electric ConversionDocument16 pagesPresentation Acoustic To Electric ConversionHarsh PatelNo ratings yet
- Design Guide Joist Girder Rev4 Final 11sep06Document60 pagesDesign Guide Joist Girder Rev4 Final 11sep06Тодор ИлиескиNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials Beer 7th Edition Solutions ManualDocument5 pagesMechanics of Materials Beer 7th Edition Solutions ManualPatrick Stephens100% (38)
- FIP Corrosion Protection of Prestressing SteelsDocument79 pagesFIP Corrosion Protection of Prestressing SteelsRizwanNo ratings yet
- 02 MAA - SiDocument138 pages02 MAA - Sinowruzi8460% (5)
- 2102 - Vol - 2BDocument7 pages2102 - Vol - 2BSoumen KarNo ratings yet
- Boiler Thermal CalculationDocument83 pagesBoiler Thermal Calculation9913489806100% (1)
- Design 09b 2Document4 pagesDesign 09b 2Jim BennyNo ratings yet
- BHGE TrainingDocument6 pagesBHGE TrainingchdiNo ratings yet
- Assembly Detail Welding Details: Part No. 1Document1 pageAssembly Detail Welding Details: Part No. 1Ranjit Kumar ShahNo ratings yet
- Goldfish 4 Parts Catalogue '01 PDFDocument26 pagesGoldfish 4 Parts Catalogue '01 PDFZeeNo ratings yet
- 161115-00-S-DCL-4-241 Rev 0Document149 pages161115-00-S-DCL-4-241 Rev 0Amresh KumarNo ratings yet
Kingswood World School Science Worksheet Grade 6, Chapter 11
Kingswood World School Science Worksheet Grade 6, Chapter 11
Uploaded by
Hardeep Singh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views4 pages1. The document contains a science worksheet for 6th grade students on the topic of motion and measuring time. It includes short answer and long answer questions.
2. Key concepts covered include definitions of speed, oscillation, and periodic motion. Examples of different types of motion like circular, rotational, and linear motion are provided.
3. Common devices used to measure time, distance, and speed are described, including the speedometer, odometer, stopwatch, sundial, and hourglass. Formulas to calculate speed from measurements of distance and time are also given.
Original Description:
Original Title
Q&A - Grade 6 Ch11
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document contains a science worksheet for 6th grade students on the topic of motion and measuring time. It includes short answer and long answer questions.
2. Key concepts covered include definitions of speed, oscillation, and periodic motion. Examples of different types of motion like circular, rotational, and linear motion are provided.
3. Common devices used to measure time, distance, and speed are described, including the speedometer, odometer, stopwatch, sundial, and hourglass. Formulas to calculate speed from measurements of distance and time are also given.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views4 pagesKingswood World School Science Worksheet Grade 6, Chapter 11
Kingswood World School Science Worksheet Grade 6, Chapter 11
Uploaded by
Hardeep Singh1. The document contains a science worksheet for 6th grade students on the topic of motion and measuring time. It includes short answer and long answer questions.
2. Key concepts covered include definitions of speed, oscillation, and periodic motion. Examples of different types of motion like circular, rotational, and linear motion are provided.
3. Common devices used to measure time, distance, and speed are described, including the speedometer, odometer, stopwatch, sundial, and hourglass. Formulas to calculate speed from measurements of distance and time are also given.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
KINGSWOOD WORLD SCHOOL
SCIENCE WORKSHEET
GRADE 6, CHAPTER 11
A. Short answer type questions.
1. a. Oscillation is the back and forth (to and fro) movement of a body in
a regular rhythm.
b. A pendulum is a weight suspended from a pivot so that it can swing
freely.
c. Speed is defined as the distance covered by a body in a unit time.
d. On the body of speedometer there is another device known
as odometer which records the total distance covered by
the vehicle.
2. The base unit for time is the ‘second’ abbreviated as ‘s’.
3. The answer is ‘d’. This time is taken as a unit to determine a
day of 24 hours with the change in date. “A day of 24 hours (a
unit) is taken as time from one midnight to another midnight
with the change in date.”
4. Speed is determined in the unit in which we measure the
distance covered and the unit in which time is noted.
Mathematically, speed is:
Distance travelled by an object/Time
taken to travel that distance Or s = d/t,
where s stands for speed; d for distance
and t for time.
5. a. Earth revolving around the Sun is an example of circular motion.
b. Earth rotating on its axis is an example of rotational motion.
c. The motion which repeats itself all the time at regular
interval is called periodic motion for example see-saw.
d. Motion of a pendulum also repeats at regular intervals so it is
periodic motion.
e. Train moving on a railway track is an example of linear motion.
6. a. The speedometer indicates the speed of the vehicle in motion.
b. On the body of speedometer there is another device known
as odometer which records the total distance covered by
the vehicle.
c. Stopwatch is a device used to measure time taken for an event.
d. The sundial has a triangular rod or pin (called gnomon) fixed
vertically on a dial. In early days, people used it to tell the
time of the day, ascertained by the location and size of the
shadow of the rod on ground.
e. In early days people used hourglass to measure short time interval.
All the sand in upper bowl is so
fixed that it takes an hour to flow down into the lower bowl.
7. A second is a shorter and basic unit of time.
8. Pendulum clock is based on the principle that the time taken by a
pendulum to complete one oscillation is always the same.
9. All our activities depend on time. So we just need to measure time
B. Long answer type questions.
1. Once we measure the distance travelled by an object and the
time taken by it to travel that distance, it is easy to know how
slow or fast the object is moving. Slow motion or fast motion
of an object is termed as its speed.
The speed of an object is the distance travelled by it in a unit
time. Speed is determined in the unit in which we measure the
distance covered and the unit in which time is noted.
In a race, a boy runs to cover a distance of 100 m in 8 seconds. His
speed is 100m/8sec = 12.5m per
second.
2. a. A body is said to be in uniform motion if it travels equal
distances in equal intervals of time. The earth which is
moving around the sun is said to be in uniform motion. A
body is said to be in non- uniform motion if it covers
unequal distances in equal interval of time. A moving
vehicle covering a distance of 5 km in the first hour, 15 km
in the second hour and 10 km in the third hour, the motion
of the vehicle is said to be non-uniform.
b. There is an instrument fitted in vehicles like cars, buses,
trucks, motor cycles and trains called speedometer is fitted.
The speedometer indicates the speed of the vehicle in
motion. On the body of speedometer there is another
device known as odometer which records the total distance
covered by the vehicle.
3. A body is said to be in uniform motion if it travels equal
distances in equal intervals of time. The hands of a clock move
in a uniform circular motion as they travel equal distance in
equal interval of time.
4. The odometer of the school bus reads 0325 at home and it
reads 0345 on reaching the school. So, the distance travelled
is 345 – 325 = 20 km
Time taken to travel 20 kilometres was 45 minutes.
Formula for average speed = Total distance
covered / Total time taken 20 km = 20000
m. covered in 45 min. = 45 × 60 = 2700 s
So, average speed= 20000/2700 = 200/27 = 7.407 m/s or simply 7.407
m/s.
Now, we have to calculate the speed per minute, so simply
multiply 7.407 × 60 = 444.42 metres per minute or 0.44442
km/minute.
Again, to calculate speed per hour, we multiply 444.42 × 60 =
26665.2 m or 26.665 km/h.
5. Students will do this on their own.
6. Average speed of the car is 45 km/h. The time taken by car to
reach Tirupati from Egmore is 8 hours. So the distance
travelled is d = s × t
D = 45 × 8 = 360 km
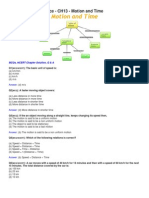
7. A graph includes two perpendicular
lines meeting at a common point
towards the left. This common point is
the initial value point. It is the origin of
the graph and is marked as ‘0’. From ‘0’
originates the perpendicular lines
which are termed as axis of the graph.
As you may notice in the figures given,
the horizontal axis is marked as X-axis
and the vertical axis as Y-axis. A graph
always represents interrelationship
between two factors. For example in
the study of motion, time and distance
are the two factors. An appropriate
scale is chosen on the graph to
represent the values of factors. On the
graph shown alongside ‘time’ is
depicted on horizontal axis, the X-axis,
and the distance is depicted on the
vertical axis, the Y-axis.
You might also like
- Ans 1 Dkin 2Document4 pagesAns 1 Dkin 2Dolores LocañasNo ratings yet
- Report No. 1Document11 pagesReport No. 1Alex QuirimitNo ratings yet
- Ahb L544-L580Document44 pagesAhb L544-L580sanches pitaNo ratings yet
- NOTES - MOTION AND TIME CLASS VIIsahfghfjfgjhfgDocument8 pagesNOTES - MOTION AND TIME CLASS VIIsahfghfjfgjhfgForex lolNo ratings yet
- CH - 13: Motion and TimeDocument14 pagesCH - 13: Motion and TimeDeepak KansalNo ratings yet
- Asm 6193Document3 pagesAsm 6193major criticNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 7th Science Value Based Questions Chapter 13 Motion and Time PDF DownloadDocument11 pagesCBSE Class 7th Science Value Based Questions Chapter 13 Motion and Time PDF Downloadpravin161079No ratings yet
- Motion & TimeDocument2 pagesMotion & TimeRenuNo ratings yet
- 7CL L-14, ExercisesDocument6 pages7CL L-14, ExercisesArish IzaanNo ratings yet
- G 7 - Motion and TimeDocument38 pagesG 7 - Motion and Timesangeetha alurNo ratings yet
- Motion Elite 2Document4 pagesMotion Elite 2aryanyt6996No ratings yet
- Moutn Fji6914389Document15 pagesMoutn Fji6914389helo my name is 88No ratings yet
- Descriptors of MotionDocument30 pagesDescriptors of MotionCamilleNo ratings yet
- Motion and TimeDocument4 pagesMotion and TimeNIdhi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Motion and TimeDocument4 pagesMotion and TimeRenuNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 13Document6 pagesScience Chapter 13Divya SreejithNo ratings yet
- Motion and Time Class 7, 2022Document61 pagesMotion and Time Class 7, 2022Theia JacobNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Mod1 Q3Document12 pagesScience 7 Mod1 Q3Roselyn B. BitareNo ratings yet
- Kinematics 1 G10Document8 pagesKinematics 1 G10Ansh GaoneadryNo ratings yet
- Third Term Science 5 Modules 1-4Document17 pagesThird Term Science 5 Modules 1-4Kathleen FernandezNo ratings yet
- Workbook Exercise of Motion and TimeDocument7 pagesWorkbook Exercise of Motion and Timesmi_santhoshNo ratings yet
- Shraddha Children'S Academy, Kottivakkam Class: Vii Physics Motion and Time MotionDocument2 pagesShraddha Children'S Academy, Kottivakkam Class: Vii Physics Motion and Time MotionkalaiNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 7 - Chapter 13Document17 pagesExp SC 7 - Chapter 13megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Motion and TimeDocument13 pagesMotion and TimeRajeevSangam100% (1)
- 1 - Linear MotionDocument10 pages1 - Linear Motionapi-242844746No ratings yet
- Grade9 CBSE MotionDocument40 pagesGrade9 CBSE MotionSamarth KatariyaNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument31 pagesKinematicsAfrozsyed350No ratings yet
- Motion and TimeDocument4 pagesMotion and TimeSANDEEP SINGHNo ratings yet
- Motion NcertDocument16 pagesMotion NcertRanjith RajNo ratings yet
- Types of MotionDocument4 pagesTypes of MotionCeasar Epsilonian MundalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter1. Motion in A Straight Line: Speed - It Is A Scalar Quantity. - Average SpeedDocument6 pagesChapter1. Motion in A Straight Line: Speed - It Is A Scalar Quantity. - Average SpeedJonathan CasillaNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument152 pagesPhysicsanujbeniwalNo ratings yet
- Experimentno.4 Uniform Motion I. ObjectivesDocument6 pagesExperimentno.4 Uniform Motion I. ObjectivesStephanie AzucenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document7 pagesChapter 13Pta PNo ratings yet
- Physics CapsuleDocument152 pagesPhysics CapsuledayakarNo ratings yet
- 6 ThmathsDocument3 pages6 Thmathslearn4chatgptNo ratings yet
- 1 MotionDocument39 pages1 Motiondav borlNo ratings yet
- Aees-Distant Learning Programme Class Ix - Physics Chapter - 8 MotionDocument5 pagesAees-Distant Learning Programme Class Ix - Physics Chapter - 8 Motionseenu nadarajanNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes Motion and TimeDocument9 pagesRevision Notes Motion and TimeRaman -No ratings yet
- Motion Chapter NotesDocument45 pagesMotion Chapter Notess.anoura07No ratings yet
- Workseet Chapter Part 1Document9 pagesWorkseet Chapter Part 1mohammedNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Subject Science Chapter 13 Motion and TimeDocument5 pagesClass 7 Subject Science Chapter 13 Motion and TimeSidh GargNo ratings yet
- MotionDocument5 pagesMotionvivek_theeasywaysNo ratings yet
- Rectilinear MotionDocument3 pagesRectilinear MotionGaurav JainNo ratings yet
- 9th Physics (13-04-23)Document2 pages9th Physics (13-04-23)IshitaNo ratings yet
- Class 7 NCERT CH 13Document17 pagesClass 7 NCERT CH 13rajan8286No ratings yet
- Class 7th CH 13 MOTION Very Short A-WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesClass 7th CH 13 MOTION Very Short A-WPS OfficemeghaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 10 SC Measuring MotionDocument7 pagesCHAPTER 10 SC Measuring MotionEunice Xiiao Wenn100% (2)
- Kinematics (Particles in Motion) SDocument9 pagesKinematics (Particles in Motion) SMarcusKlahnTokoeJr.No ratings yet
- Lakhmir Singh Solutions Class 9 Physics Chapter 1Document27 pagesLakhmir Singh Solutions Class 9 Physics Chapter 1Rekha PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class 7Document12 pagesCbse Class 7kalslingam100% (1)
- SPH3U - Kinematics 2: Velocity and Speed: ReviewDocument6 pagesSPH3U - Kinematics 2: Velocity and Speed: Reviewlim05abcNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Average Speed and VelocityDocument22 pagesLesson 3 Average Speed and Velocitykyoto.saeopNo ratings yet
- Motion and TimeDocument8 pagesMotion and TimeALLURI DEDEEPYA LAKSHYANo ratings yet
- Motion ByjusDocument10 pagesMotion ByjusAMIT GOYALNo ratings yet
- The Adventure of Whiz Trying to Bring His Future To Him Quicker: The Adventures of Whiz, the Whizz ScientistFrom EverandThe Adventure of Whiz Trying to Bring His Future To Him Quicker: The Adventures of Whiz, the Whizz ScientistNo ratings yet
- IPL Auction (19PT2-11)Document10 pagesIPL Auction (19PT2-11)Hardeep SinghNo ratings yet
- MCIA Project: Discover Alpas Camps and ResortsDocument18 pagesMCIA Project: Discover Alpas Camps and ResortsHardeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Emerging Market Strategy: Organization - General Electric Country - EthopiaDocument34 pagesEmerging Market Strategy: Organization - General Electric Country - EthopiaHardeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Group 6 Postponement Strategies Case Presentation SCM EMPDocument14 pagesGroup 6 Postponement Strategies Case Presentation SCM EMPHardeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Group 7 - Cadbury Case - Rev01Document12 pagesGroup 7 - Cadbury Case - Rev01Hardeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - SpriteDocument9 pagesGroup 3 - SpriteHardeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Personality: - Case On SpriteDocument8 pagesPersonality: - Case On SpriteHardeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Information Service: Electric EGR Valves (Renault, Opel)Document3 pagesInformation Service: Electric EGR Valves (Renault, Opel)Popa AurelNo ratings yet
- BS 5268-2:1996 Section 2Document2 pagesBS 5268-2:1996 Section 2Zayyan RomjonNo ratings yet
- RCC & PSC Class NotesDocument329 pagesRCC & PSC Class NotesAbhishek KandpalNo ratings yet
- Laser Ultrasonics Techniques and Applications Drain, L E Z LibraryDocument465 pagesLaser Ultrasonics Techniques and Applications Drain, L E Z LibraryRêmulo FariasNo ratings yet
- Typical gc66 ManualDocument56 pagesTypical gc66 ManualPabloLinuxNo ratings yet
- Construction EquipmentDocument98 pagesConstruction EquipmentBejil ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Interaction DiagramDocument4 pagesInteraction Diagramjavier glzNo ratings yet
- JICA, Manual For Micro-Hydro Power DevelopmentDocument28 pagesJICA, Manual For Micro-Hydro Power DevelopmentRiza RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Bianchi 952Document87 pagesBianchi 952Abdenour KeraghelNo ratings yet
- Micromechatronics - K. Uchino, J. Giniewicz (Marcel Dekker, 2003) WW PDFDocument508 pagesMicromechatronics - K. Uchino, J. Giniewicz (Marcel Dekker, 2003) WW PDFMario Ramone100% (1)
- Pigging Slug TrickDocument38 pagesPigging Slug TrickLorena DávilaNo ratings yet
- Smaw PDFDocument10 pagesSmaw PDFArizapatazoNo ratings yet
- Din Vde 0210 - 1985-Ocr PDFDocument103 pagesDin Vde 0210 - 1985-Ocr PDFFleancuCatalinNo ratings yet
- AWS100 Appendix 12 FatigueDocument72 pagesAWS100 Appendix 12 FatiguecarlosnovoanNo ratings yet
- Helix ZC01-FD001 24092020Document9 pagesHelix ZC01-FD001 24092020achmatNo ratings yet
- Tube Expansion ProcedureDocument3 pagesTube Expansion Procedurerudi 01100% (1)
- Rolling Contact Bearings: Bearing TypesDocument6 pagesRolling Contact Bearings: Bearing Typessofyan samNo ratings yet
- Presentation Acoustic To Electric ConversionDocument16 pagesPresentation Acoustic To Electric ConversionHarsh PatelNo ratings yet
- Design Guide Joist Girder Rev4 Final 11sep06Document60 pagesDesign Guide Joist Girder Rev4 Final 11sep06Тодор ИлиескиNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials Beer 7th Edition Solutions ManualDocument5 pagesMechanics of Materials Beer 7th Edition Solutions ManualPatrick Stephens100% (38)
- FIP Corrosion Protection of Prestressing SteelsDocument79 pagesFIP Corrosion Protection of Prestressing SteelsRizwanNo ratings yet
- 02 MAA - SiDocument138 pages02 MAA - Sinowruzi8460% (5)
- 2102 - Vol - 2BDocument7 pages2102 - Vol - 2BSoumen KarNo ratings yet
- Boiler Thermal CalculationDocument83 pagesBoiler Thermal Calculation9913489806100% (1)
- Design 09b 2Document4 pagesDesign 09b 2Jim BennyNo ratings yet
- BHGE TrainingDocument6 pagesBHGE TrainingchdiNo ratings yet
- Assembly Detail Welding Details: Part No. 1Document1 pageAssembly Detail Welding Details: Part No. 1Ranjit Kumar ShahNo ratings yet
- Goldfish 4 Parts Catalogue '01 PDFDocument26 pagesGoldfish 4 Parts Catalogue '01 PDFZeeNo ratings yet
- 161115-00-S-DCL-4-241 Rev 0Document149 pages161115-00-S-DCL-4-241 Rev 0Amresh KumarNo ratings yet