Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 14
Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 14
Uploaded by
Pierre-Cécil KönigCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Great Mysteries of Our World (Reading and Training)Document5 pagesGreat Mysteries of Our World (Reading and Training)Alexander Rodriguez100% (4)
- P2132000 eDocument7 pagesP2132000 eJohn Escobar100% (1)
- Aw tf80scDocument5 pagesAw tf80scÁlvaro MéndezNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 13Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 13Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 11Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 11Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Sasw 1Document4 pagesSasw 1زوبير شطيNo ratings yet
- Kichael Carley Acoustics-40-43Document4 pagesKichael Carley Acoustics-40-43eki7777No ratings yet
- Non-Newtonian Flow in Annuli: of ofDocument6 pagesNon-Newtonian Flow in Annuli: of ofLaura NathaliaNo ratings yet
- R Zero-Offset P-P Reflection Coefficient, R Zero-Offset S-Wave Reflection CoefficientDocument14 pagesR Zero-Offset P-P Reflection Coefficient, R Zero-Offset S-Wave Reflection CoefficientYannick Ange Karmel THIERONo ratings yet
- Jamieson 1969Document2 pagesJamieson 1969Iraqi stormNo ratings yet
- BGR Bipolar JSSC 1976 IntegratedDocument4 pagesBGR Bipolar JSSC 1976 Integratedgupt_82No ratings yet
- Prediction of Wave Reflection From Rock Structures: An Integration of Field & Laboratory DataDocument10 pagesPrediction of Wave Reflection From Rock Structures: An Integration of Field & Laboratory Datamarufuddin0No ratings yet
- A Review of AVO Analysis PDFDocument24 pagesA Review of AVO Analysis PDFMohamed Abdel-FattahNo ratings yet
- A Review of AVO AnalysisDocument10 pagesA Review of AVO AnalysisYves Emmanuel KouadioNo ratings yet
- Ambraseys - Simpson - Prediction of Vertical Response Spectra in Europe PDFDocument12 pagesAmbraseys - Simpson - Prediction of Vertical Response Spectra in Europe PDFMartin Dario Mazo QuingrejoNo ratings yet
- Stability of Bodewadt FlowDocument8 pagesStability of Bodewadt FlowAmmara RaoNo ratings yet
- Erratum: "Habitable Zones Around Main-Sequence Stars: New Estimates"Document3 pagesErratum: "Habitable Zones Around Main-Sequence Stars: New Estimates"Leonidas ValenciaNo ratings yet
- PanelDocument3 pagesPanelPavan KishoreNo ratings yet
- Online 603Document5 pagesOnline 603renatogeo14No ratings yet
- AtmosphereDocument48 pagesAtmosphereVikram C KNo ratings yet
- On The Property (Z) : E H. ZariouhDocument11 pagesOn The Property (Z) : E H. Zariouhaznay zakariaeNo ratings yet
- ELE302 - PreLab 3Document21 pagesELE302 - PreLab 3hughjass39.99No ratings yet
- BBAAV Abs2Document4 pagesBBAAV Abs2Tps TaquillaNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 16Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 16Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Fabry-Perot Resonator For Hard X-Rays: Shih-Lin ChangDocument53 pagesFabry-Perot Resonator For Hard X-Rays: Shih-Lin ChangAshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Direct Numerical Simulations of Vortex Rings at Re: Michaelbergdorf, Petroskoumoutsakos AnthonyleonardDocument11 pagesDirect Numerical Simulations of Vortex Rings at Re: Michaelbergdorf, Petroskoumoutsakos AnthonyleonardShakib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Morsi 1972Document17 pagesMorsi 1972Julio HerreraNo ratings yet
- Qwitt Diode AnalysisDocument19 pagesQwitt Diode AnalysisAghna Tiyas MandalNo ratings yet
- Steven Miller Et Al - Infrared Emissions of H3 + in The Atmosphere of Jupiter in The 2.1 and 4.0 Micron RegionDocument20 pagesSteven Miller Et Al - Infrared Emissions of H3 + in The Atmosphere of Jupiter in The 2.1 and 4.0 Micron RegionPassammNo ratings yet
- Galaxies: Gamma-Ray Astrophysics in The Time DomainDocument17 pagesGalaxies: Gamma-Ray Astrophysics in The Time DomainRyu- MikaNo ratings yet
- Extended Elastic Impedance-TheoryDocument18 pagesExtended Elastic Impedance-TheorykodogsaktiNo ratings yet
- EMT 2 Marks and 16 Marks-Question BankDocument30 pagesEMT 2 Marks and 16 Marks-Question BankBright Tendai ChingwenaNo ratings yet
- Analisis - Angulo de Dominio de La Amplitud - AVODocument18 pagesAnalisis - Angulo de Dominio de La Amplitud - AVOfiebritosNo ratings yet
- EMF (Khaled Elbeltagy - 201605178)Document6 pagesEMF (Khaled Elbeltagy - 201605178)alaa AlsabehNo ratings yet
- AVO Attibute Analysis Reservoir CharacterizationDocument14 pagesAVO Attibute Analysis Reservoir CharacterizationAjendra SinghNo ratings yet
- LTTechNote1 TelescopeThroughputDocument13 pagesLTTechNote1 TelescopeThroughputJaduqueNo ratings yet
- Seismic Reservoir Characterisation: 6.1 Amplitude-Versus-Offset (AVO)Document10 pagesSeismic Reservoir Characterisation: 6.1 Amplitude-Versus-Offset (AVO)umairNo ratings yet
- Ndata 07331Document4 pagesNdata 07331niciu86No ratings yet
- 2022 SenDocument25 pages2022 SenPavan YadavNo ratings yet
- Cloud Spectral ReflectanceDocument5 pagesCloud Spectral ReflectancevmaximusNo ratings yet
- NOE0415380416 ch041Document7 pagesNOE0415380416 ch041Umed Abd-alsatarNo ratings yet
- Solvable Examples of Drift and Diffusion of Ions in Non-Uniform Electric FieldsDocument18 pagesSolvable Examples of Drift and Diffusion of Ions in Non-Uniform Electric FieldsMilan StepanovNo ratings yet
- Bond Valence Parameters Inorganic StructuresDocument4 pagesBond Valence Parameters Inorganic StructuresDavid MartinezNo ratings yet
- Test Document 9Document17 pagesTest Document 9Ufuk YazganNo ratings yet
- Localized Electrons With Wien2kDocument34 pagesLocalized Electrons With Wien2kAbu Alhabayeb HabeebNo ratings yet
- Steven Miller and Jonathan Tennyson - First Principles Calculation of The Molecular Constants of H3 +, H2D +, D2H + and D3 +Document10 pagesSteven Miller and Jonathan Tennyson - First Principles Calculation of The Molecular Constants of H3 +, H2D +, D2H + and D3 +TreaxmeANo ratings yet
- Spectral Imaging: Shock Fronts and Plasma InstabilitiesDocument5 pagesSpectral Imaging: Shock Fronts and Plasma InstabilitiesxdumpNo ratings yet
- AstroDocument20 pagesAstrosekharNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document24 pagesChapter 7Jordan A Guerra ANo ratings yet
- Analysis of Micro-Doppler SignaturesDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Micro-Doppler Signaturesnachiketakumar8882No ratings yet
- Russell 2010Document57 pagesRussell 2010a1341365100% (2)
- Exact Coherent StatesDocument12 pagesExact Coherent StatesDeborah MbaNo ratings yet
- Turbulence and Standing Waves in Oscillatory Chemical Reactions With Global CouplingDocument7 pagesTurbulence and Standing Waves in Oscillatory Chemical Reactions With Global CouplingVikram VenkatesanNo ratings yet
- The Capacity Spectrum Method As A Tool For Seismic DesignDocument8 pagesThe Capacity Spectrum Method As A Tool For Seismic DesignNIE100% (2)
- Smith 1979Document10 pagesSmith 1979urgent urgentNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0021925818648859 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0021925818648859 MainAli RazaNo ratings yet
- Bianca M. Dinelli Et Al - Bands of H3 + Up To 4-Nu-2 Rovibrational Transitions From First Principles CalculationsDocument8 pagesBianca M. Dinelli Et Al - Bands of H3 + Up To 4-Nu-2 Rovibrational Transitions From First Principles CalculationsPassammNo ratings yet
- RD Sharma Mcqs 2023-2024 Class 12 (R.D.sharMA) (Z-Library)Document547 pagesRD Sharma Mcqs 2023-2024 Class 12 (R.D.sharMA) (Z-Library)hemNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 9Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 9Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Anderson 1991Document8 pagesAnderson 1991Joel D. CruzNo ratings yet
- Crowe, 1988 - Effect of Particle Size On Modulating Turbulent IntensityDocument7 pagesCrowe, 1988 - Effect of Particle Size On Modulating Turbulent IntensityAlainIslasNo ratings yet
- Integrated Imaging of the Earth: Theory and ApplicationsFrom EverandIntegrated Imaging of the Earth: Theory and ApplicationsMax MoorkampNo ratings yet
- Physics Is SexyDocument2 pagesPhysics Is SexyPierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 49Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 49Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 53Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 53Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 45Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 45Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 51Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 51Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 46Document62 pagesZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 46Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 26Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 26Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 41Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 41Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 43Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 43Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 37Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 37Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- ! HK ! HK Log RHK RV Log RHK BIS RV BisDocument1 page! HK ! HK Log RHK RV Log RHK BIS RV BisPierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 39Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 39Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 30Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 30Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 21Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 21Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 33Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 33Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 29Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 29Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Table A.3. Offset Differences C: VLC LCDocument1 pageTable A.3. Offset Differences C: VLC LCPierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 22Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 22Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 23Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 23Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 22Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 22Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 21Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 21Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 18Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 18Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Solar SystemDocument13 pagesSolar Systemapi-286973255No ratings yet
- Cool Doody Thesis by SlidesgoDocument49 pagesCool Doody Thesis by SlidesgoLestariBonitaNo ratings yet
- Lamb'S Tales From ShakespeareDocument1 pageLamb'S Tales From ShakespearegiamegiNo ratings yet
- Legends of The SithDocument142 pagesLegends of The SithJason SturgeonNo ratings yet
- CH 04Document48 pagesCH 04Jabez Daniel GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Assignment TrigonometryDocument6 pagesAssignment TrigonometryAbdirisaq MohamedNo ratings yet
- List of Horoscope Name in Hindi and English - राशी के नामDocument1 pageList of Horoscope Name in Hindi and English - राशी के नामjoans smithNo ratings yet
- Mathabx SymbolsDocument6 pagesMathabx SymbolsGokul VijayanNo ratings yet
- LKS2 The Northern Lights Differentiated Reading Comprehension ActivityDocument15 pagesLKS2 The Northern Lights Differentiated Reading Comprehension ActivityZuhre CalisirNo ratings yet
- 11812.phedon Bilek - SibylDocument9 pages11812.phedon Bilek - SibylBuku Soul100% (5)
- Chinese and Western Combinations Aquarius (Tiger) Month Combination With Rat YearDocument2 pagesChinese and Western Combinations Aquarius (Tiger) Month Combination With Rat YearMary RoseNo ratings yet
- Comparing AdjectivesDocument2 pagesComparing AdjectivesJorge JimenezNo ratings yet
- UnkulunkuluDocument62 pagesUnkulunkuluTsegawbeztoNo ratings yet
- Sun in 1st House - Lagna - Ascendant Love, Career, MarriageDocument5 pagesSun in 1st House - Lagna - Ascendant Love, Career, MarriageSri KayNo ratings yet
- Relationships With ParentsDocument2 pagesRelationships With ParentsVaraha Mihira100% (2)
- The Void of Course MoonDocument8 pagesThe Void of Course MoonLiladhar GaurNo ratings yet
- Physicalscience12 q2 Mod1 Earthisnotthecenteroftheuniverse v4Document29 pagesPhysicalscience12 q2 Mod1 Earthisnotthecenteroftheuniverse v4Grantmars Arelacse67% (3)
- Special RelativityDocument236 pagesSpecial RelativityAndrei Avadani100% (3)
- Sankalpam and Cosmic CycleDocument4 pagesSankalpam and Cosmic Cycleraj83% (6)
- Ivo Labbé Et Al - Understanding Galaxy AssemblyDocument7 pagesIvo Labbé Et Al - Understanding Galaxy AssemblyLukoeNo ratings yet
- Astro Calculations and Impacts Based On DegreesDocument8 pagesAstro Calculations and Impacts Based On Degreesravi goyalNo ratings yet
- Anomalous Structures On The MoonDocument6 pagesAnomalous Structures On The Moondlazar_1No ratings yet
- Super Stargazer Guide BookDocument8 pagesSuper Stargazer Guide Bookarivalagan13No ratings yet
- How To Choose Binoculars: 1.choosing Binoculars For The First TimeDocument3 pagesHow To Choose Binoculars: 1.choosing Binoculars For The First TimesnclgsraoNo ratings yet
- Planisphere 45N en PDFDocument6 pagesPlanisphere 45N en PDFLiviu FerariuNo ratings yet
- Me PDFDocument581 pagesMe PDFJasdeepSinghNo ratings yet
- Bryce Gilmore - An Introduction To The Methods of WD GannDocument11 pagesBryce Gilmore - An Introduction To The Methods of WD Gannenvieme100% (4)
Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 14
Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 14
Uploaded by
Pierre-Cécil KönigOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 14
Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 14
Uploaded by
Pierre-Cécil KönigCopyright:
Available Formats
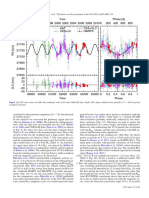
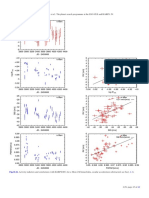
A&A 552, A78 (2013)
Year Phase [d]
1992 1994 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 2010 0 50 100 150 200 250 300
17200
P=307.2 d CES+LC
CORALIE CES+VLC
17150 AAT HARPS
17100
RV [m/s]
17050
17000
16950
16900
16850
100
O-C [m/s]
50
0
-50
-100
49000 50000 51000 52000 53000 54000 55000 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
Time Phase
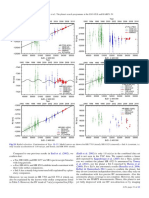
Fig. 9. (Left) RV time series for ι Hor combined with AAT and CORALIE data. (Right) RVs phase folded to the period of P = 307 d and the
residuals (bottom).
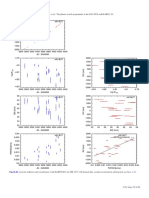
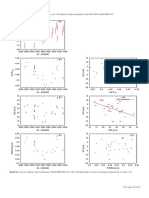
0.29 ζ 2 Ret: given the very similar stellar parameters of the binary
ι Hor (G0V) pair ζ 1 Ret and ζ 2 Ret, del Peloso et al. (2000) already
0.28 HARPS
SMARTS pointed out the baffling fact of their very different activity
Mount Wilson S-index
0.27 566 d
630 d
level. We do not find any significant RV excess variability
0.26 for ζ 2 Ret. However, there is a significant RV-FHWM corre-
0.25 lation and all three activity indicators seem to exhibit a small
0.24 trend, which might be either due to a magnetic cycle or in-
0.23
strumental (cf. τ Cet).
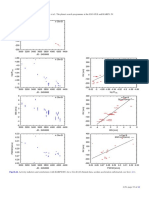
$ Eri: Hatzes et al. (2000) announced a planet in an eccentric
0.22
orbit (e = 0.6) around this active star. Benedict et al. (2006)
0.21 refined the orbital solution and combined the RVs with as-
0.2 trometric observations with the HST Fine Guidance Sensor
3000 3500 4000 4500 5000 5500 indicating an orbital inclination of i = 30◦ . Likewise, Reffert
JD - 2450000 & Quirrenbach (2011) derived a similar value for the incli-
Fig. 10. S-index measurements for ι Hor. Metcalfe et al. (2010) pub- nation and an upper mass limit of 6.1 MJup using H
lished the SMARTS data (blue open circles) and the 566 d period (dot- astrometry and the RV orbit solution.
ted line). The formal best fit for the combined data set is 630 d (dashed However, in the periodogram for $ Eri (Fig. 14) we cannot
line). find any evidence for the long-period planet (P = 2500 d)
suggested by Hatzes et al. (2000) whose orbital solution is
plotted in Fig. 20 for comparison. Due to the higher preci-
sion of our data, the combined rms is 8.2 m/s for fitting a
exceeds the predicted value140 ± 7 m/s/dex for a magnetic constant, while Hatzes et al. (2000) list an rms ranging from
cycle (Sect. 4.5, assuming 5746±27 K and [Fe/H] = −0.22 ± 11 to 22 m/s for different instruments in the residuals of their
0.05 from del Peloso et al. 2000). r = 0.88 indicates that Keplerian model. $ Eri is an active star and all three activity
the
√ subtraction of this correlation will reduce the scatter by indicators are variable, and the BIS shows an anti-correlation
1 − r2 to 5.9 m/s. ζ 1 Ret has the largest log R#HK -variations with RV. The stellar rotation period is 11.2 d (Donahue et al.
and a quite high jitter estimate of 3.8 m/s within our sample. 1996; Fröhlich 2007). On a short time scale of 85 min its
A78, page 14 of 62
You might also like
- Great Mysteries of Our World (Reading and Training)Document5 pagesGreat Mysteries of Our World (Reading and Training)Alexander Rodriguez100% (4)
- P2132000 eDocument7 pagesP2132000 eJohn Escobar100% (1)
- Aw tf80scDocument5 pagesAw tf80scÁlvaro MéndezNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 13Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 13Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 11Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 11Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Sasw 1Document4 pagesSasw 1زوبير شطيNo ratings yet
- Kichael Carley Acoustics-40-43Document4 pagesKichael Carley Acoustics-40-43eki7777No ratings yet
- Non-Newtonian Flow in Annuli: of ofDocument6 pagesNon-Newtonian Flow in Annuli: of ofLaura NathaliaNo ratings yet
- R Zero-Offset P-P Reflection Coefficient, R Zero-Offset S-Wave Reflection CoefficientDocument14 pagesR Zero-Offset P-P Reflection Coefficient, R Zero-Offset S-Wave Reflection CoefficientYannick Ange Karmel THIERONo ratings yet
- Jamieson 1969Document2 pagesJamieson 1969Iraqi stormNo ratings yet
- BGR Bipolar JSSC 1976 IntegratedDocument4 pagesBGR Bipolar JSSC 1976 Integratedgupt_82No ratings yet
- Prediction of Wave Reflection From Rock Structures: An Integration of Field & Laboratory DataDocument10 pagesPrediction of Wave Reflection From Rock Structures: An Integration of Field & Laboratory Datamarufuddin0No ratings yet
- A Review of AVO Analysis PDFDocument24 pagesA Review of AVO Analysis PDFMohamed Abdel-FattahNo ratings yet
- A Review of AVO AnalysisDocument10 pagesA Review of AVO AnalysisYves Emmanuel KouadioNo ratings yet
- Ambraseys - Simpson - Prediction of Vertical Response Spectra in Europe PDFDocument12 pagesAmbraseys - Simpson - Prediction of Vertical Response Spectra in Europe PDFMartin Dario Mazo QuingrejoNo ratings yet
- Stability of Bodewadt FlowDocument8 pagesStability of Bodewadt FlowAmmara RaoNo ratings yet
- Erratum: "Habitable Zones Around Main-Sequence Stars: New Estimates"Document3 pagesErratum: "Habitable Zones Around Main-Sequence Stars: New Estimates"Leonidas ValenciaNo ratings yet
- PanelDocument3 pagesPanelPavan KishoreNo ratings yet
- Online 603Document5 pagesOnline 603renatogeo14No ratings yet
- AtmosphereDocument48 pagesAtmosphereVikram C KNo ratings yet
- On The Property (Z) : E H. ZariouhDocument11 pagesOn The Property (Z) : E H. Zariouhaznay zakariaeNo ratings yet
- ELE302 - PreLab 3Document21 pagesELE302 - PreLab 3hughjass39.99No ratings yet
- BBAAV Abs2Document4 pagesBBAAV Abs2Tps TaquillaNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 16Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 16Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Fabry-Perot Resonator For Hard X-Rays: Shih-Lin ChangDocument53 pagesFabry-Perot Resonator For Hard X-Rays: Shih-Lin ChangAshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Direct Numerical Simulations of Vortex Rings at Re: Michaelbergdorf, Petroskoumoutsakos AnthonyleonardDocument11 pagesDirect Numerical Simulations of Vortex Rings at Re: Michaelbergdorf, Petroskoumoutsakos AnthonyleonardShakib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Morsi 1972Document17 pagesMorsi 1972Julio HerreraNo ratings yet
- Qwitt Diode AnalysisDocument19 pagesQwitt Diode AnalysisAghna Tiyas MandalNo ratings yet
- Steven Miller Et Al - Infrared Emissions of H3 + in The Atmosphere of Jupiter in The 2.1 and 4.0 Micron RegionDocument20 pagesSteven Miller Et Al - Infrared Emissions of H3 + in The Atmosphere of Jupiter in The 2.1 and 4.0 Micron RegionPassammNo ratings yet
- Galaxies: Gamma-Ray Astrophysics in The Time DomainDocument17 pagesGalaxies: Gamma-Ray Astrophysics in The Time DomainRyu- MikaNo ratings yet
- Extended Elastic Impedance-TheoryDocument18 pagesExtended Elastic Impedance-TheorykodogsaktiNo ratings yet
- EMT 2 Marks and 16 Marks-Question BankDocument30 pagesEMT 2 Marks and 16 Marks-Question BankBright Tendai ChingwenaNo ratings yet
- Analisis - Angulo de Dominio de La Amplitud - AVODocument18 pagesAnalisis - Angulo de Dominio de La Amplitud - AVOfiebritosNo ratings yet
- EMF (Khaled Elbeltagy - 201605178)Document6 pagesEMF (Khaled Elbeltagy - 201605178)alaa AlsabehNo ratings yet
- AVO Attibute Analysis Reservoir CharacterizationDocument14 pagesAVO Attibute Analysis Reservoir CharacterizationAjendra SinghNo ratings yet
- LTTechNote1 TelescopeThroughputDocument13 pagesLTTechNote1 TelescopeThroughputJaduqueNo ratings yet
- Seismic Reservoir Characterisation: 6.1 Amplitude-Versus-Offset (AVO)Document10 pagesSeismic Reservoir Characterisation: 6.1 Amplitude-Versus-Offset (AVO)umairNo ratings yet
- Ndata 07331Document4 pagesNdata 07331niciu86No ratings yet
- 2022 SenDocument25 pages2022 SenPavan YadavNo ratings yet
- Cloud Spectral ReflectanceDocument5 pagesCloud Spectral ReflectancevmaximusNo ratings yet
- NOE0415380416 ch041Document7 pagesNOE0415380416 ch041Umed Abd-alsatarNo ratings yet
- Solvable Examples of Drift and Diffusion of Ions in Non-Uniform Electric FieldsDocument18 pagesSolvable Examples of Drift and Diffusion of Ions in Non-Uniform Electric FieldsMilan StepanovNo ratings yet
- Bond Valence Parameters Inorganic StructuresDocument4 pagesBond Valence Parameters Inorganic StructuresDavid MartinezNo ratings yet
- Test Document 9Document17 pagesTest Document 9Ufuk YazganNo ratings yet
- Localized Electrons With Wien2kDocument34 pagesLocalized Electrons With Wien2kAbu Alhabayeb HabeebNo ratings yet
- Steven Miller and Jonathan Tennyson - First Principles Calculation of The Molecular Constants of H3 +, H2D +, D2H + and D3 +Document10 pagesSteven Miller and Jonathan Tennyson - First Principles Calculation of The Molecular Constants of H3 +, H2D +, D2H + and D3 +TreaxmeANo ratings yet
- Spectral Imaging: Shock Fronts and Plasma InstabilitiesDocument5 pagesSpectral Imaging: Shock Fronts and Plasma InstabilitiesxdumpNo ratings yet
- AstroDocument20 pagesAstrosekharNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document24 pagesChapter 7Jordan A Guerra ANo ratings yet
- Analysis of Micro-Doppler SignaturesDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Micro-Doppler Signaturesnachiketakumar8882No ratings yet
- Russell 2010Document57 pagesRussell 2010a1341365100% (2)
- Exact Coherent StatesDocument12 pagesExact Coherent StatesDeborah MbaNo ratings yet
- Turbulence and Standing Waves in Oscillatory Chemical Reactions With Global CouplingDocument7 pagesTurbulence and Standing Waves in Oscillatory Chemical Reactions With Global CouplingVikram VenkatesanNo ratings yet
- The Capacity Spectrum Method As A Tool For Seismic DesignDocument8 pagesThe Capacity Spectrum Method As A Tool For Seismic DesignNIE100% (2)
- Smith 1979Document10 pagesSmith 1979urgent urgentNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0021925818648859 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0021925818648859 MainAli RazaNo ratings yet
- Bianca M. Dinelli Et Al - Bands of H3 + Up To 4-Nu-2 Rovibrational Transitions From First Principles CalculationsDocument8 pagesBianca M. Dinelli Et Al - Bands of H3 + Up To 4-Nu-2 Rovibrational Transitions From First Principles CalculationsPassammNo ratings yet
- RD Sharma Mcqs 2023-2024 Class 12 (R.D.sharMA) (Z-Library)Document547 pagesRD Sharma Mcqs 2023-2024 Class 12 (R.D.sharMA) (Z-Library)hemNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 9Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 9Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Anderson 1991Document8 pagesAnderson 1991Joel D. CruzNo ratings yet
- Crowe, 1988 - Effect of Particle Size On Modulating Turbulent IntensityDocument7 pagesCrowe, 1988 - Effect of Particle Size On Modulating Turbulent IntensityAlainIslasNo ratings yet
- Integrated Imaging of the Earth: Theory and ApplicationsFrom EverandIntegrated Imaging of the Earth: Theory and ApplicationsMax MoorkampNo ratings yet
- Physics Is SexyDocument2 pagesPhysics Is SexyPierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 49Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 49Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 53Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 53Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 45Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 45Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 51Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 51Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 46Document62 pagesZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 46Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 26Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 26Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 41Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 41Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 43Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 43Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 37Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 37Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- ! HK ! HK Log RHK RV Log RHK BIS RV BisDocument1 page! HK ! HK Log RHK RV Log RHK BIS RV BisPierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 39Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 39Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 30Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 30Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 21Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 21Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 33Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 33Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 29Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 29Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Table A.3. Offset Differences C: VLC LCDocument1 pageTable A.3. Offset Differences C: VLC LCPierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 22Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 22Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 23Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 23Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 22Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 22Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 21Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 21Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 18Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 18Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Solar SystemDocument13 pagesSolar Systemapi-286973255No ratings yet
- Cool Doody Thesis by SlidesgoDocument49 pagesCool Doody Thesis by SlidesgoLestariBonitaNo ratings yet
- Lamb'S Tales From ShakespeareDocument1 pageLamb'S Tales From ShakespearegiamegiNo ratings yet
- Legends of The SithDocument142 pagesLegends of The SithJason SturgeonNo ratings yet
- CH 04Document48 pagesCH 04Jabez Daniel GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Assignment TrigonometryDocument6 pagesAssignment TrigonometryAbdirisaq MohamedNo ratings yet
- List of Horoscope Name in Hindi and English - राशी के नामDocument1 pageList of Horoscope Name in Hindi and English - राशी के नामjoans smithNo ratings yet
- Mathabx SymbolsDocument6 pagesMathabx SymbolsGokul VijayanNo ratings yet
- LKS2 The Northern Lights Differentiated Reading Comprehension ActivityDocument15 pagesLKS2 The Northern Lights Differentiated Reading Comprehension ActivityZuhre CalisirNo ratings yet
- 11812.phedon Bilek - SibylDocument9 pages11812.phedon Bilek - SibylBuku Soul100% (5)
- Chinese and Western Combinations Aquarius (Tiger) Month Combination With Rat YearDocument2 pagesChinese and Western Combinations Aquarius (Tiger) Month Combination With Rat YearMary RoseNo ratings yet
- Comparing AdjectivesDocument2 pagesComparing AdjectivesJorge JimenezNo ratings yet
- UnkulunkuluDocument62 pagesUnkulunkuluTsegawbeztoNo ratings yet
- Sun in 1st House - Lagna - Ascendant Love, Career, MarriageDocument5 pagesSun in 1st House - Lagna - Ascendant Love, Career, MarriageSri KayNo ratings yet
- Relationships With ParentsDocument2 pagesRelationships With ParentsVaraha Mihira100% (2)
- The Void of Course MoonDocument8 pagesThe Void of Course MoonLiladhar GaurNo ratings yet
- Physicalscience12 q2 Mod1 Earthisnotthecenteroftheuniverse v4Document29 pagesPhysicalscience12 q2 Mod1 Earthisnotthecenteroftheuniverse v4Grantmars Arelacse67% (3)
- Special RelativityDocument236 pagesSpecial RelativityAndrei Avadani100% (3)
- Sankalpam and Cosmic CycleDocument4 pagesSankalpam and Cosmic Cycleraj83% (6)
- Ivo Labbé Et Al - Understanding Galaxy AssemblyDocument7 pagesIvo Labbé Et Al - Understanding Galaxy AssemblyLukoeNo ratings yet
- Astro Calculations and Impacts Based On DegreesDocument8 pagesAstro Calculations and Impacts Based On Degreesravi goyalNo ratings yet
- Anomalous Structures On The MoonDocument6 pagesAnomalous Structures On The Moondlazar_1No ratings yet
- Super Stargazer Guide BookDocument8 pagesSuper Stargazer Guide Bookarivalagan13No ratings yet
- How To Choose Binoculars: 1.choosing Binoculars For The First TimeDocument3 pagesHow To Choose Binoculars: 1.choosing Binoculars For The First TimesnclgsraoNo ratings yet
- Planisphere 45N en PDFDocument6 pagesPlanisphere 45N en PDFLiviu FerariuNo ratings yet
- Me PDFDocument581 pagesMe PDFJasdeepSinghNo ratings yet
- Bryce Gilmore - An Introduction To The Methods of WD GannDocument11 pagesBryce Gilmore - An Introduction To The Methods of WD Gannenvieme100% (4)