Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 17
Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 17
Uploaded by
Pierre-Cécil KönigOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 17
Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 17
Uploaded by
Pierre-Cécil KönigCopyright:
Available Formats
M. Zechmeister et al.: The planet search programme at the ESO CES and HARPS. IV.
Year Year
1992 1994 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 2010 1992 1994 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 2010
9450 23220
ζ Tuc (F9V)
CES+LC 23200
CES+VLC
9400 HARPS 23180
RV [m/s]
23160
RV [m/s]
9350
23140
β Hyi (G2IV)
23120 CES+LC
9300 CES+VLC
23100 HARPS
2.7 m/s/yr
P=4338 d
9250 23080
49000 50000
51000 52000 53000 54000 55000 49000 50000 51000 52000 53000 54000 55000
BJD - 2 400 000 BJD - 2 400 000
Year Year
1992 1994 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 2010 1992 1994 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 2010
-10600 12000
11980 ν Phe (F8V)
CES+LC
CES+VLC
-10650 11960 HARPS
11940
RV [m/s]
RV [m/s]
-10700 11920
11900
-10750 11880
HR 209 (G1V)
CES+LC
CES+VLC 11860
HARPS
-10800 11840
49000 50000
51000 52000 53000 54000 55000 49000 50000
51000 52000 53000 54000 55000
BJD - 2 400 000 BJD - 2 400 000
Year Year
1992 1994 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 2010 1992 1994 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 2010
27800 -16480
27780 τ Cet (G8V)
CES+LC
-16500 CES+VLC
27760 HARPS
27740 -16520
RV [m/s]
RV [m/s]
27720
27700 -16540
27680 HR 506 (F9V)
CES+LC -16560
CES+VLC
27660 HARPS
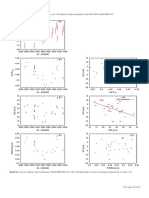
P=963.0 d
27640 -16580
49000 50000 51000 52000 53000 54000 55000 49000 50000 51000 52000 53000 54000 55000
BJD - 2 400 000 BJD - 2 400 000
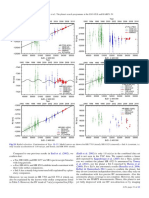
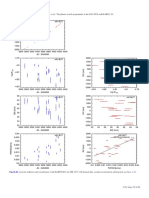
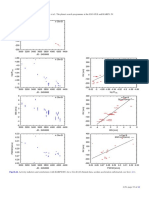
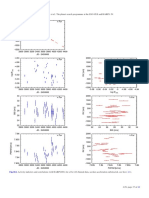
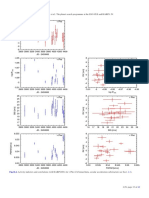
Fig. 19. Radial velocity time series (unbinned data). The error bars depict the internal measurement errors ∆RVi , i.e. not including jitter. LC (green
open circles) and VLC (blue open diamonds) data are displayed with their measured offsets. Jumps in the curves indicates the difference between
the measured (Sect. 3.5) and fitted (Sect. 4) LC-VLC offset. HARPS data are in red filled circles. The solid lines indicate significant models, while
dashed lines illustrate less or non-significant alternative models. All models include secular acceleration. Model curves are shown for β Hyi (trend
and long-period sinusoid, see text for discussion), and HR 506 (sinusoid).
(Sect. 4.3, Table 5). Also, there is a marginally significant li- artificial, however an additional (positive or negative) con-
near correlation of the RVs with BIS and FWHM and there- tribution to the trend by activity cannot be excluded. After
fore stellar activity could contribute to the trend as well. removing the trend, there is no significant correlation or ex-
HR 6416: GJ 666 B can explain the trend of 9.4 m/s (Sect. 4.3, cess variability.
Table 5). A trend is a sufficient model. The residuals do not HR 8323: the listed significant period of 1372 d is caused by a
exhibit significant excess variability. stellar magnetic cycle. All three activity indicators show si-
HR 7703: a trend is a sufficient model and the value of 3.6 m/s milar variations and strong correlations with RVs (Fig. B.30,
(Sect. 4.3, Table 5) can be explained by GJ 783 B. Therefore Tables A.4 and A.5). The observed slope of 98 ± 10 m/s/dex
the formally significant RV-log R!HK correlation should be (Table A.4) agrees well with the predicted RV-log R!HK
A78, page 17 of 62
You might also like
- Sandvik DL431-7C: Underground Drill RigDocument4 pagesSandvik DL431-7C: Underground Drill RiglidoNo ratings yet
- Tesmec 2012 PDFDocument104 pagesTesmec 2012 PDFStalyn Jaer Tarrillo Mendoza100% (3)
- Astral Sorcery (Minecraft)Document82 pagesAstral Sorcery (Minecraft)Christian JimenezNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Science Exam Revision Questions - Sets 1-5Document25 pagesYear 9 Science Exam Revision Questions - Sets 1-5dayahnNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 17Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 17Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 18Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 18Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 20Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 20Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 20Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 20Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 21Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 21Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 21Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 21Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 19Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 19Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Hiab 322 Hiduo: Capacity 30 TMDocument2 pagesHiab 322 Hiduo: Capacity 30 TMjose_raico2285No ratings yet
- Ttd3 600tv PDFDocument1 pageTtd3 600tv PDFarxo_9No ratings yet
- Airport Information: Details For Jorge Chavez IntlDocument48 pagesAirport Information: Details For Jorge Chavez IntlultimatedroiidNo ratings yet
- Hiab XS1055 Loadchart CWDocument4 pagesHiab XS1055 Loadchart CWmaciste bonitaNo ratings yet
- Sequential Estimate SanJoseDocument7 pagesSequential Estimate SanJoseFOEBE MARREY MANUELNo ratings yet
- Pisco 2022Document11 pagesPisco 2022Gabriel RojasNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Rymsa TGA2D3-800TVDocument1 pageDatasheet Rymsa TGA2D3-800TVOscar CanonNo ratings yet
- YarrakDocument20 pagesYarrakİ. Çağlar YILDIRIMNo ratings yet
- 15112739-TB-C01-00 24al PSTDocument6 pages15112739-TB-C01-00 24al PSTdheeraj SureshNo ratings yet
- Grupo 200 enDocument90 pagesGrupo 200 enSergio Quintana Rodriguez100% (1)
- Fusing Equipment: Types K, T, H, and N Fuse Links Coordination TablesDocument1 pageFusing Equipment: Types K, T, H, and N Fuse Links Coordination TablesJuan Camilo Ramirez AriasNo ratings yet
- Daikin Ducable Unit 5 5tr To 16 7trDocument2 pagesDaikin Ducable Unit 5 5tr To 16 7trరాజా రావు చామర్తిNo ratings yet
- Transformer Applications PDFDocument18 pagesTransformer Applications PDFtoots guiaoNo ratings yet
- جافا عملي qDocument22 pagesجافا عملي qكيمو تيكNo ratings yet
- Terna FGD With Pressure Thrust Nozzle LoadsDocument94 pagesTerna FGD With Pressure Thrust Nozzle LoadsVaniya GoelNo ratings yet
- Ansa Price ListDocument1 pageAnsa Price ListPrakash RajNo ratings yet
- LFKCDocument17 pagesLFKCcheldya rodriguesNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Excel WorksheetDocument2 pagesNew Microsoft Excel WorksheetpratikNo ratings yet
- Miller Toy Company Manufactures A Plastic Swimming PoolDocument10 pagesMiller Toy Company Manufactures A Plastic Swimming Poollaale dijaanNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 22Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 22Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 22Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 22Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Solar Dealer Price ListDocument7 pagesSolar Dealer Price Listpal rajNo ratings yet
- ImensiupdateDocument4 pagesImensiupdateAlterSon Grafi KalayNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi Guide Book 101Document1 pageMitsubishi Guide Book 101Ismail MohammadNo ratings yet
- Oasis Ms11m EngDocument1 pageOasis Ms11m EngChris TianNo ratings yet
- Comparacion de CentrifugasDocument1 pageComparacion de CentrifugasRicardo VillarNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Excavators: Major Component Weights 323D2 LDocument4 pagesHydraulic Excavators: Major Component Weights 323D2 Lali alilouNo ratings yet
- NPD1 Training - PTPL - Smart Modular Gearbox - Apr 2020 PDFDocument20 pagesNPD1 Training - PTPL - Smart Modular Gearbox - Apr 2020 PDFShyam J Vyas0% (1)
- 7.5. Esquema de Simulación Batería M-400 - 1000 PsigDocument1 page7.5. Esquema de Simulación Batería M-400 - 1000 PsigRichard GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Catalog Mounting Kits Topworx en 82212Document8 pagesCatalog Mounting Kits Topworx en 82212Jezie ReyesNo ratings yet
- Multi Inverter Split Spec Mideas 2022Document1 pageMulti Inverter Split Spec Mideas 2022Guadamuz NicoNo ratings yet
- Carrier AmbionDocument2 pagesCarrier AmbionknaidooNo ratings yet
- (Latest) Edc Ffa Long QuestionDocument11 pages(Latest) Edc Ffa Long QuestionputeriNo ratings yet
- Clamshell Bucket Type: Twice CylindersDocument3 pagesClamshell Bucket Type: Twice CylindersTran Trong PhuNo ratings yet
- Capital Allowance 2Document7 pagesCapital Allowance 2hassaanzafar032No ratings yet
- NC Rotary Tables: Standard TypeDocument2 pagesNC Rotary Tables: Standard TypeNathan ChenNo ratings yet
- (DOWN 22) : Baltic Supramax Index 2488 OWS Chrs Ows Chrs FFA Supramax Tess 52 28/32000Document1 page(DOWN 22) : Baltic Supramax Index 2488 OWS Chrs Ows Chrs FFA Supramax Tess 52 28/32000Kashif SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- FDD Lte Bands & Frequencies Lte Band Number Band Name Downlink (MHZ) Uplink (MHZ) Width OF Band (MHZ) Duplex Spacing (MHZ) Band GAP (MHZ)Document7 pagesFDD Lte Bands & Frequencies Lte Band Number Band Name Downlink (MHZ) Uplink (MHZ) Width OF Band (MHZ) Duplex Spacing (MHZ) Band GAP (MHZ)Alpha2000No ratings yet
- Rental & Purchase Product List: Baskets Modular SystemsDocument1 pageRental & Purchase Product List: Baskets Modular SystemsManuelNo ratings yet
- Product Specifications Product Specifications: Electrical PropertiesDocument3 pagesProduct Specifications Product Specifications: Electrical PropertiesСергей МирошниченкоNo ratings yet
- محاضرات الطرق - الرابع - part5 PDFDocument3 pagesمحاضرات الطرق - الرابع - part5 PDFAlexander TuringanNo ratings yet
- Product Specifications Product Specifications: Electrical PropertiesDocument3 pagesProduct Specifications Product Specifications: Electrical PropertiesMariNo ratings yet
- Laser Cutting Machine Main Accessories Price ListDocument1 pageLaser Cutting Machine Main Accessories Price Listjaiveer.comNo ratings yet
- ETD Commander First Officer Date Reg Vt-Ai Despatcher Extra Fuel Wind Dir Wind SPDDocument21 pagesETD Commander First Officer Date Reg Vt-Ai Despatcher Extra Fuel Wind Dir Wind SPDGAVASHKARNo ratings yet
- HXPM8X3WWW1717065T2CT28 MTS78 PDFDocument1 pageHXPM8X3WWW1717065T2CT28 MTS78 PDFПётр НовиковNo ratings yet
- Car Customs Mar 2018Document29 pagesCar Customs Mar 2018josephkhouryNo ratings yet
- LTG Comparative r4-12.12.2009Document1 pageLTG Comparative r4-12.12.2009Jennifer CombsNo ratings yet
- Rate List of Umiya Residency: Note - 2 Years Advance Maintainance To Be Paid at The Time of PossessionDocument4 pagesRate List of Umiya Residency: Note - 2 Years Advance Maintainance To Be Paid at The Time of PossessionVISHNU DEVELOPERSNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 51Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 51Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Physics Is SexyDocument2 pagesPhysics Is SexyPierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 39Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 39Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 49Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 49Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 53Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 53Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 46Document62 pagesZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 46Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 41Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 41Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Table A.3. Offset Differences C: VLC LCDocument1 pageTable A.3. Offset Differences C: VLC LCPierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 37Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 37Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 45Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 45Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 30Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 30Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 43Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 43Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 29Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 29Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 33Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 33Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 22Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 22Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 26Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 26Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 23Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 23Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- ! HK ! HK Log RHK RV Log RHK BIS RV BisDocument1 page! HK ! HK Log RHK RV Log RHK BIS RV BisPierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 21Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 21Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 21Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 21Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 22Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 22Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 18Document1 pageZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 18Pierre-Cécil KönigNo ratings yet
- Prehistoric PeriodDocument14 pagesPrehistoric PeriodSimon BacsalNo ratings yet
- Greek God - ApolloDocument56 pagesGreek God - ApolloObNo ratings yet
- Sun in CancerDocument7 pagesSun in CancerJames PerezNo ratings yet
- Graduation ProgramDocument16 pagesGraduation ProgramTiffany Kate Juan Lintao-MangadapNo ratings yet
- Notes On Predictive Nirayan Astrology - Part IDocument285 pagesNotes On Predictive Nirayan Astrology - Part IANTHONY WRITER100% (4)
- 17 01 2021 Mumbai SM UxzDocument8 pages17 01 2021 Mumbai SM UxzaneezkunjuNo ratings yet
- Standard Candles in AstrophysicsDocument9 pagesStandard Candles in AstrophysicsRobert LoganNo ratings yet
- Lecture CH 1 Nature of ScienceDocument12 pagesLecture CH 1 Nature of ScienceRoberto Pereira da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Purpose: The Purpose of This Activity Is To Become More Familiar With Kepler's Laws of PlanetaryDocument5 pagesPurpose: The Purpose of This Activity Is To Become More Familiar With Kepler's Laws of PlanetaryREGINA SANTIAGONo ratings yet
- Astrological Profile of Rapists and MurdererDocument7 pagesAstrological Profile of Rapists and MurdererJatinder Sandhu100% (1)
- Sarvali On DigbalaDocument14 pagesSarvali On DigbalapiyushNo ratings yet
- The Rinri ProjectDocument35 pagesThe Rinri ProjectBoris Petrovic100% (3)
- What Are Black Holes - NASADocument5 pagesWhat Are Black Holes - NASAAntónia AmbrusNo ratings yet
- Nikola Tesla - Harnessing Electricity PDFDocument147 pagesNikola Tesla - Harnessing Electricity PDFTavi GrigNo ratings yet
- The Cosmic Origin of ElementsDocument38 pagesThe Cosmic Origin of ElementsCHYNNE ASHLEY CABANESNo ratings yet
- Cusp or KP ChartDocument7 pagesCusp or KP ChartKrishna CHNo ratings yet
- Section 3.2Document2 pagesSection 3.2Sidemen For LifeNo ratings yet
- Federation Spaceflight ChronologyDocument152 pagesFederation Spaceflight ChronologyJehu Torres Esquivel100% (3)
- Untitled Screenplay PDFDocument3 pagesUntitled Screenplay PDFJonathon BookerNo ratings yet
- 2014 Final Examnamibian P191PRE MEDICAL FOUNDATIONDocument14 pages2014 Final Examnamibian P191PRE MEDICAL FOUNDATIONLiloyi LupiyaNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 Homework #15Document2 pagesPhysics 2 Homework #15Joseph IvanchukNo ratings yet
- Learn Arabic Grammar - Lesson 2Document5 pagesLearn Arabic Grammar - Lesson 2Islamic Treasure100% (1)
- Can I Get A JobDocument4 pagesCan I Get A Jobsumit_mailmeNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Spectrum Lab Student SheetDocument4 pagesHydrogen Spectrum Lab Student Sheets bNo ratings yet
- MUFON UFO Journal - August 1987Document24 pagesMUFON UFO Journal - August 1987Carlos RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Mars 101Document4 pagesMars 101BR RedNo ratings yet
- Gujarat State Government Public Holiday List 2019Document1 pageGujarat State Government Public Holiday List 2019Parth ShahNo ratings yet
- Indian CalendarDocument49 pagesIndian Calendararavindiyengar1977No ratings yet