Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Analysis of Financial Statement
Analysis of Financial Statement
Uploaded by
Fleur BeauxbatonCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument6 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisValtteri Itäranta0% (2)
- 02 Fs AnalysisDocument14 pages02 Fs AnalysisWilsonNo ratings yet
- Balance SheetDocument30 pagesBalance SheetBhuvan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Ratio Analysis PresentationDocument27 pagesFinancial Statement Ratio Analysis Presentationkarimhisham100% (1)
- Final T Y B Com Syllabus 75-25 With New QP Semester V and VI 02-05-2014Document35 pagesFinal T Y B Com Syllabus 75-25 With New QP Semester V and VI 02-05-2014vinodgupta1146966100% (2)
- Financial Statement Analysis Ratios and Formulas (Flashcards)Document52 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis Ratios and Formulas (Flashcards)Blesilda OracoyNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument9 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisSneha Giji SajiNo ratings yet
- Accounting Ratios: Dr. Pradeep Kumar, Assistant Professor, Imce, SrmuDocument14 pagesAccounting Ratios: Dr. Pradeep Kumar, Assistant Professor, Imce, Srmukushagra guptaNo ratings yet
- Financial RatiosDocument3 pagesFinancial Ratiospv12356No ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument22 pagesRatio AnalysismAnisH MNo ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument46 pagesRatio AnalysisPsyonaNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument23 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisEmmaryl PogadoNo ratings yet
- RatioAnalysis ContentDocument27 pagesRatioAnalysis ContentTeh PohkeeNo ratings yet
- Activity Ratios: By: Rabindra GouriDocument9 pagesActivity Ratios: By: Rabindra GouriRabindra DasNo ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument8 pagesRatio AnalysisrahulborntobewildNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis: by Aditi RodeDocument36 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis: by Aditi RodegrshneheteNo ratings yet
- Financial AnalysisDocument24 pagesFinancial AnalysisMuskaan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Financial Management Slides 2.3Document10 pagesFinancial Management Slides 2.3honathapyarNo ratings yet
- RATIO AnalysisDocument36 pagesRATIO AnalysisRishika MadhukarNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument39 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisJoshua Naragdag ColladoNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance & International Controlling (BPO) : Home Work 2 On The Balance Sheet and The Important RatiosDocument7 pagesCorporate Finance & International Controlling (BPO) : Home Work 2 On The Balance Sheet and The Important RatiosNitish RawatNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument55 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisPravin UntooNo ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument16 pagesRatio AnalysisNakul GoyalNo ratings yet
- 4 Financial Statement AnalysisDocument13 pages4 Financial Statement AnalysisAdnan RizviNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis: Accounting For ManagersDocument30 pagesRatio Analysis: Accounting For ManagersVishal JogiNo ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument21 pagesRatio AnalysisRasha rubeenaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Financial AccountingDocument44 pagesBasics of Financial AccountingVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument38 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisRoyal HikariNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Business Studies 2nd Cycle Test Revision Guide PDFDocument5 pagesIGCSE Business Studies 2nd Cycle Test Revision Guide PDFMariam TadiliNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis: Ratio Analysis: A Ratio: Is Defined As AnDocument19 pagesRatio Analysis: Ratio Analysis: A Ratio: Is Defined As AnSaugata PoaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Evaluation of Financial PerformanceDocument36 pagesChapter 2 Evaluation of Financial PerformanceUsha PeruNo ratings yet
- 11 Ratio Analysis PowerPointToPdfDocument11 pages11 Ratio Analysis PowerPointToPdfLexNo ratings yet
- Liquidity ManagementDocument54 pagesLiquidity Managementansary75No ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis - APDocument31 pagesRatio Analysis - APPrachi SinghNo ratings yet
- Session 15-21-Assessment of Credit - Working Capital & Term LendingDocument60 pagesSession 15-21-Assessment of Credit - Working Capital & Term LendingHaardik GandhiNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis (Ratio) PresentationDocument19 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis (Ratio) Presentationyellowcat910% (1)
- Chapter 13Document6 pagesChapter 13Hareem Zoya WarsiNo ratings yet
- Bank Ratio Analysis v.2Document30 pagesBank Ratio Analysis v.2moe.jee6173100% (1)
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument14 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisAllona BatonghinogNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting - An Introduction: DR Vandana Bhama FORE School of Management, DelhiDocument30 pagesFinancial Accounting - An Introduction: DR Vandana Bhama FORE School of Management, DelhiShavik BaralNo ratings yet
- Ratios: by Prafful Bhalerao Roll No. 04Document26 pagesRatios: by Prafful Bhalerao Roll No. 04Rahul KadamNo ratings yet
- Module 8 (FINP7)Document4 pagesModule 8 (FINP7)David VillaNo ratings yet
- 04 Fs Analysis With StudentDocument10 pages04 Fs Analysis With StudentarianasNo ratings yet
- Unit - Vi Ratio AnalysisDocument49 pagesUnit - Vi Ratio Analysisshekkari akhilNo ratings yet
- Finanacial Statements: Balance Sheet & Profit and Loss AccountDocument26 pagesFinanacial Statements: Balance Sheet & Profit and Loss AccountAshok SeerviNo ratings yet
- Sessions 10 11 RatiosDocument21 pagesSessions 10 11 Ratiosadharsh veeraNo ratings yet
- Financial RatiosDocument35 pagesFinancial RatiosLetsah Bright100% (1)
- Annual ReportDocument5 pagesAnnual Reportmengjun0987654311No ratings yet
- Financial Management Re Vie WeDocument60 pagesFinancial Management Re Vie WeferroalNo ratings yet
- Working Capital ManagementDocument64 pagesWorking Capital ManagementPrerna SinhaNo ratings yet
- Activity RatiosDocument7 pagesActivity RatiosSUBIR100% (1)
- Ratio AnalysisDocument37 pagesRatio AnalysisKaydawala Saifuddin 20No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Financial Statements-1Document39 pagesLecture 3 - Financial Statements-1ikhsanNo ratings yet
- The Balance SheetDocument101 pagesThe Balance SheethakomoNo ratings yet
- Liquidity of Short-Term Assets Related Debt-Paying Ability: Mehwish KiranDocument33 pagesLiquidity of Short-Term Assets Related Debt-Paying Ability: Mehwish KiranAlina ZubairNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis 2Document4 pagesFinancial Analysis 2Meynard AguilarNo ratings yet
- NTCC Summer Internship: Semester 7Document11 pagesNTCC Summer Internship: Semester 7Ayush MishraNo ratings yet
- Finanacial Statements: Balance Sheet & Profit and Loss AccountDocument26 pagesFinanacial Statements: Balance Sheet & Profit and Loss AccountRichard AustinNo ratings yet
- Financial Statements & Cash Flow AnalysisDocument15 pagesFinancial Statements & Cash Flow AnalysisMeidrick Rheeyonie Gialogo AlbaNo ratings yet
- Business Metrics and Tools; Reference for Professionals and StudentsFrom EverandBusiness Metrics and Tools; Reference for Professionals and StudentsNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting and Reporting Study Guide NotesFrom EverandFinancial Accounting and Reporting Study Guide NotesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Curso DE Finanzas Corporativas. Material Tomado De: Financial Statements and Ratio AnalysisDocument58 pagesCurso DE Finanzas Corporativas. Material Tomado De: Financial Statements and Ratio AnalysisCArmen CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Common Stock Analysis and ValuationDocument5 pagesChapter 7 Common Stock Analysis and Valuationbibek100% (1)
- Report On Financial Analysis of Textile Industry of BangladeshDocument39 pagesReport On Financial Analysis of Textile Industry of BangladeshSaidur0% (2)
- Fundamental Analysis of Banking SectorsDocument56 pagesFundamental Analysis of Banking Sectorssidhant kumarNo ratings yet
- FABM 2 HANDOUTS 1st QRTRDocument17 pagesFABM 2 HANDOUTS 1st QRTRDanise PorrasNo ratings yet
- Manish Manral - A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE OF SELECTED AUTOMOBILE COMPANIES WITH ASHOKA LEYLAND LTD. (PANTNAGAR)Document90 pagesManish Manral - A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE OF SELECTED AUTOMOBILE COMPANIES WITH ASHOKA LEYLAND LTD. (PANTNAGAR)Ankit TiwariNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratios QuizDocument4 pagesFinancial Ratios QuizHamieWave TVNo ratings yet
- VRL SoftDocument55 pagesVRL SoftManoj A Talikoti100% (2)
- Project Report On Ratio Analysis of Kamal Solvent Extractions PVT Ltd.Document48 pagesProject Report On Ratio Analysis of Kamal Solvent Extractions PVT Ltd.Kapil MishraNo ratings yet
- Financial Statements and Ratio Analysis: ChapterDocument25 pagesFinancial Statements and Ratio Analysis: Chapterkarim67% (3)
- Ms9107a - Financial Statements AnalysisDocument7 pagesMs9107a - Financial Statements AnalysisCelestaire LeeNo ratings yet
- Finance Assignment Ratio - Financial ManagementDocument9 pagesFinance Assignment Ratio - Financial ManagementKelly Brook100% (3)
- Acc CIA2Document22 pagesAcc CIA2Aleena Clare ThomasNo ratings yet
- CFO-Forum MCEV Principles and Guidance April 2016Document31 pagesCFO-Forum MCEV Principles and Guidance April 2016apluNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument26 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisRahul DewakarNo ratings yet
- Avenue Supermarts Limited: (D-MART)Document15 pagesAvenue Supermarts Limited: (D-MART)Mayur0% (1)
- 13th Feb 2022 - MR CKR Presentation For How To Be AnalystDocument30 pages13th Feb 2022 - MR CKR Presentation For How To Be Analystaditya162100% (1)
- FINMAN2 ReviewerDocument17 pagesFINMAN2 ReviewerKYLA MARIE BLANDONo ratings yet
- Management Accounting Concept and Application by Cabrera PDFDocument29 pagesManagement Accounting Concept and Application by Cabrera PDFMar-ramos Ramos50% (6)
- FM AssignmentDocument12 pagesFM AssignmentNurul Ariffah100% (1)
- Sabah Credit CorporationDocument14 pagesSabah Credit CorporationYff DickNo ratings yet
- 13 Ratio Analysis of Shree Cement & Ambuja CementDocument35 pages13 Ratio Analysis of Shree Cement & Ambuja Cementsatyamchy141No ratings yet
- Analysis of Financial Performance of Plantation SubSector Companies Listed On The Indonesia StockDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Financial Performance of Plantation SubSector Companies Listed On The Indonesia StockInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- A Project Report ON: Ratio Analysis Super Spinning Mills LTDDocument66 pagesA Project Report ON: Ratio Analysis Super Spinning Mills LTDHari Krishna ReddyNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis of Masan Company Masan GroupDocument24 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis of Masan Company Masan GroupTammy DaoNo ratings yet
- 633833334841206250Document57 pages633833334841206250Ritesh Kumar Dubey100% (1)
- Financial Statements Analysis and Long-Term Planning: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument31 pagesFinancial Statements Analysis and Long-Term Planning: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwindaisuke_kazukiNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis R I L: Assignment OnDocument19 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis R I L: Assignment OnRavi JaiswalNo ratings yet
Analysis of Financial Statement
Analysis of Financial Statement
Uploaded by
Fleur BeauxbatonOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Analysis of Financial Statement
Analysis of Financial Statement
Uploaded by
Fleur BeauxbatonCopyright:
Available Formats
Analysis of Financial Statements
Tools of Financial Statement Analysis
Horizontal Analysis – is a technique for evaluating a series of financial statement data over
a period of time.
Vertical Analysis – is a technique for evaluating financial statement data that expresses
each item
in a financial statement in terms of percent of a base amount.
Ratio Analysis – expresses relationship among selected items of financial statement data.
Financial Ratios:
Tests of Liquidity – refers to company’s ability to pay its current liabilities as they fall due
Tests of Solvency – ability of the company to pay its debts
Tests of Profitability – measurements of degree of success (or failure) of profit-directed
activities of a firm or division thereof.
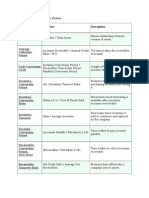
Tests of Liquidity:
• Current ratio (banker’s ratio, Working capital ratio)
It is a measure of adequacy of working capital. It is the primary test of solvency to meet
current obligations from current assets.
= Current assets / Current liabilities
• Quick ratio (Acid Test Ratio)
It measures the number of times that the current liabilities could be paid with the available
cash and near cash items. Quick assets refer to all current assets except inventories and
prepaid expenses.
= Quick assets / Current Liabilities
• Receivables turnover
It is the time required to complete one collection cycle from the time receivables are
recorded, then collected, to the time new receivables are recorded again.
= Net (credit) sales / Average receivables
• Average age of receivables (average collection period or days ‘sales in receivables)
It indicates the average number of days during which the company must wait before
receivables are collected.
= 360 days / Receivables turnover
• Inventory turnover
It measures the number of times that the inventory is replaced during the period.
= Cost of goods sold / Average merchandise inventory
• Average age of inventory (Inventory Conversion Period or Days’ sales in inventory)
It indicates the average number of days during which the company must wait before the
inventories are sold
= 360 days / Inventory turnover
• Normal Operating Cycle
= Average age of Receivables + Average age of Inventory
• Trade Payables Turnover
= Net credit purchases/Average Trade Payables
• Average age of Trade Payables
It indicates the length of time during which payables remain unpaid.
= 360days/ Payables turnover
• Current Assets Turnover
It measures the movement and utilization of current assets to meet operating
requirements.
= Cost of sales + Operating Expenses **/Average current assets
** Exclude depreciation, amortization and other expenses related to long term
assets.
Tests of Solvency:
• Times Interest Earned - It determines the extent to which operations cover interest
expense
=EBIT/Interest Expense
• Debt-Equity Ratio - Proportion of assets provided by creditors compared to that
provided by owners
=Total Liabilities/Total SHE
• Debt Ratio - Proportion of total assets provided by creditors
=Total Liabilities/Total Assets
• Equity Ratio - Proportion of total assets provided by owners
=Total SHE/Total Assets
You might also like
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument6 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisValtteri Itäranta0% (2)
- 02 Fs AnalysisDocument14 pages02 Fs AnalysisWilsonNo ratings yet
- Balance SheetDocument30 pagesBalance SheetBhuvan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Ratio Analysis PresentationDocument27 pagesFinancial Statement Ratio Analysis Presentationkarimhisham100% (1)
- Final T Y B Com Syllabus 75-25 With New QP Semester V and VI 02-05-2014Document35 pagesFinal T Y B Com Syllabus 75-25 With New QP Semester V and VI 02-05-2014vinodgupta1146966100% (2)
- Financial Statement Analysis Ratios and Formulas (Flashcards)Document52 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis Ratios and Formulas (Flashcards)Blesilda OracoyNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument9 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisSneha Giji SajiNo ratings yet
- Accounting Ratios: Dr. Pradeep Kumar, Assistant Professor, Imce, SrmuDocument14 pagesAccounting Ratios: Dr. Pradeep Kumar, Assistant Professor, Imce, Srmukushagra guptaNo ratings yet
- Financial RatiosDocument3 pagesFinancial Ratiospv12356No ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument22 pagesRatio AnalysismAnisH MNo ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument46 pagesRatio AnalysisPsyonaNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument23 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisEmmaryl PogadoNo ratings yet
- RatioAnalysis ContentDocument27 pagesRatioAnalysis ContentTeh PohkeeNo ratings yet
- Activity Ratios: By: Rabindra GouriDocument9 pagesActivity Ratios: By: Rabindra GouriRabindra DasNo ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument8 pagesRatio AnalysisrahulborntobewildNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis: by Aditi RodeDocument36 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis: by Aditi RodegrshneheteNo ratings yet
- Financial AnalysisDocument24 pagesFinancial AnalysisMuskaan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Financial Management Slides 2.3Document10 pagesFinancial Management Slides 2.3honathapyarNo ratings yet
- RATIO AnalysisDocument36 pagesRATIO AnalysisRishika MadhukarNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument39 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisJoshua Naragdag ColladoNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance & International Controlling (BPO) : Home Work 2 On The Balance Sheet and The Important RatiosDocument7 pagesCorporate Finance & International Controlling (BPO) : Home Work 2 On The Balance Sheet and The Important RatiosNitish RawatNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument55 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisPravin UntooNo ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument16 pagesRatio AnalysisNakul GoyalNo ratings yet
- 4 Financial Statement AnalysisDocument13 pages4 Financial Statement AnalysisAdnan RizviNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis: Accounting For ManagersDocument30 pagesRatio Analysis: Accounting For ManagersVishal JogiNo ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument21 pagesRatio AnalysisRasha rubeenaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Financial AccountingDocument44 pagesBasics of Financial AccountingVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument38 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisRoyal HikariNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Business Studies 2nd Cycle Test Revision Guide PDFDocument5 pagesIGCSE Business Studies 2nd Cycle Test Revision Guide PDFMariam TadiliNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis: Ratio Analysis: A Ratio: Is Defined As AnDocument19 pagesRatio Analysis: Ratio Analysis: A Ratio: Is Defined As AnSaugata PoaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Evaluation of Financial PerformanceDocument36 pagesChapter 2 Evaluation of Financial PerformanceUsha PeruNo ratings yet
- 11 Ratio Analysis PowerPointToPdfDocument11 pages11 Ratio Analysis PowerPointToPdfLexNo ratings yet
- Liquidity ManagementDocument54 pagesLiquidity Managementansary75No ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis - APDocument31 pagesRatio Analysis - APPrachi SinghNo ratings yet
- Session 15-21-Assessment of Credit - Working Capital & Term LendingDocument60 pagesSession 15-21-Assessment of Credit - Working Capital & Term LendingHaardik GandhiNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis (Ratio) PresentationDocument19 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis (Ratio) Presentationyellowcat910% (1)
- Chapter 13Document6 pagesChapter 13Hareem Zoya WarsiNo ratings yet
- Bank Ratio Analysis v.2Document30 pagesBank Ratio Analysis v.2moe.jee6173100% (1)
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument14 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisAllona BatonghinogNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting - An Introduction: DR Vandana Bhama FORE School of Management, DelhiDocument30 pagesFinancial Accounting - An Introduction: DR Vandana Bhama FORE School of Management, DelhiShavik BaralNo ratings yet
- Ratios: by Prafful Bhalerao Roll No. 04Document26 pagesRatios: by Prafful Bhalerao Roll No. 04Rahul KadamNo ratings yet
- Module 8 (FINP7)Document4 pagesModule 8 (FINP7)David VillaNo ratings yet
- 04 Fs Analysis With StudentDocument10 pages04 Fs Analysis With StudentarianasNo ratings yet
- Unit - Vi Ratio AnalysisDocument49 pagesUnit - Vi Ratio Analysisshekkari akhilNo ratings yet
- Finanacial Statements: Balance Sheet & Profit and Loss AccountDocument26 pagesFinanacial Statements: Balance Sheet & Profit and Loss AccountAshok SeerviNo ratings yet
- Sessions 10 11 RatiosDocument21 pagesSessions 10 11 Ratiosadharsh veeraNo ratings yet
- Financial RatiosDocument35 pagesFinancial RatiosLetsah Bright100% (1)
- Annual ReportDocument5 pagesAnnual Reportmengjun0987654311No ratings yet
- Financial Management Re Vie WeDocument60 pagesFinancial Management Re Vie WeferroalNo ratings yet
- Working Capital ManagementDocument64 pagesWorking Capital ManagementPrerna SinhaNo ratings yet
- Activity RatiosDocument7 pagesActivity RatiosSUBIR100% (1)
- Ratio AnalysisDocument37 pagesRatio AnalysisKaydawala Saifuddin 20No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Financial Statements-1Document39 pagesLecture 3 - Financial Statements-1ikhsanNo ratings yet
- The Balance SheetDocument101 pagesThe Balance SheethakomoNo ratings yet
- Liquidity of Short-Term Assets Related Debt-Paying Ability: Mehwish KiranDocument33 pagesLiquidity of Short-Term Assets Related Debt-Paying Ability: Mehwish KiranAlina ZubairNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis 2Document4 pagesFinancial Analysis 2Meynard AguilarNo ratings yet
- NTCC Summer Internship: Semester 7Document11 pagesNTCC Summer Internship: Semester 7Ayush MishraNo ratings yet
- Finanacial Statements: Balance Sheet & Profit and Loss AccountDocument26 pagesFinanacial Statements: Balance Sheet & Profit and Loss AccountRichard AustinNo ratings yet
- Financial Statements & Cash Flow AnalysisDocument15 pagesFinancial Statements & Cash Flow AnalysisMeidrick Rheeyonie Gialogo AlbaNo ratings yet
- Business Metrics and Tools; Reference for Professionals and StudentsFrom EverandBusiness Metrics and Tools; Reference for Professionals and StudentsNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting and Reporting Study Guide NotesFrom EverandFinancial Accounting and Reporting Study Guide NotesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Curso DE Finanzas Corporativas. Material Tomado De: Financial Statements and Ratio AnalysisDocument58 pagesCurso DE Finanzas Corporativas. Material Tomado De: Financial Statements and Ratio AnalysisCArmen CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Common Stock Analysis and ValuationDocument5 pagesChapter 7 Common Stock Analysis and Valuationbibek100% (1)
- Report On Financial Analysis of Textile Industry of BangladeshDocument39 pagesReport On Financial Analysis of Textile Industry of BangladeshSaidur0% (2)
- Fundamental Analysis of Banking SectorsDocument56 pagesFundamental Analysis of Banking Sectorssidhant kumarNo ratings yet
- FABM 2 HANDOUTS 1st QRTRDocument17 pagesFABM 2 HANDOUTS 1st QRTRDanise PorrasNo ratings yet
- Manish Manral - A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE OF SELECTED AUTOMOBILE COMPANIES WITH ASHOKA LEYLAND LTD. (PANTNAGAR)Document90 pagesManish Manral - A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE OF SELECTED AUTOMOBILE COMPANIES WITH ASHOKA LEYLAND LTD. (PANTNAGAR)Ankit TiwariNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratios QuizDocument4 pagesFinancial Ratios QuizHamieWave TVNo ratings yet
- VRL SoftDocument55 pagesVRL SoftManoj A Talikoti100% (2)
- Project Report On Ratio Analysis of Kamal Solvent Extractions PVT Ltd.Document48 pagesProject Report On Ratio Analysis of Kamal Solvent Extractions PVT Ltd.Kapil MishraNo ratings yet
- Financial Statements and Ratio Analysis: ChapterDocument25 pagesFinancial Statements and Ratio Analysis: Chapterkarim67% (3)
- Ms9107a - Financial Statements AnalysisDocument7 pagesMs9107a - Financial Statements AnalysisCelestaire LeeNo ratings yet
- Finance Assignment Ratio - Financial ManagementDocument9 pagesFinance Assignment Ratio - Financial ManagementKelly Brook100% (3)
- Acc CIA2Document22 pagesAcc CIA2Aleena Clare ThomasNo ratings yet
- CFO-Forum MCEV Principles and Guidance April 2016Document31 pagesCFO-Forum MCEV Principles and Guidance April 2016apluNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument26 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisRahul DewakarNo ratings yet
- Avenue Supermarts Limited: (D-MART)Document15 pagesAvenue Supermarts Limited: (D-MART)Mayur0% (1)
- 13th Feb 2022 - MR CKR Presentation For How To Be AnalystDocument30 pages13th Feb 2022 - MR CKR Presentation For How To Be Analystaditya162100% (1)
- FINMAN2 ReviewerDocument17 pagesFINMAN2 ReviewerKYLA MARIE BLANDONo ratings yet
- Management Accounting Concept and Application by Cabrera PDFDocument29 pagesManagement Accounting Concept and Application by Cabrera PDFMar-ramos Ramos50% (6)
- FM AssignmentDocument12 pagesFM AssignmentNurul Ariffah100% (1)
- Sabah Credit CorporationDocument14 pagesSabah Credit CorporationYff DickNo ratings yet
- 13 Ratio Analysis of Shree Cement & Ambuja CementDocument35 pages13 Ratio Analysis of Shree Cement & Ambuja Cementsatyamchy141No ratings yet
- Analysis of Financial Performance of Plantation SubSector Companies Listed On The Indonesia StockDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Financial Performance of Plantation SubSector Companies Listed On The Indonesia StockInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- A Project Report ON: Ratio Analysis Super Spinning Mills LTDDocument66 pagesA Project Report ON: Ratio Analysis Super Spinning Mills LTDHari Krishna ReddyNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis of Masan Company Masan GroupDocument24 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis of Masan Company Masan GroupTammy DaoNo ratings yet
- 633833334841206250Document57 pages633833334841206250Ritesh Kumar Dubey100% (1)
- Financial Statements Analysis and Long-Term Planning: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument31 pagesFinancial Statements Analysis and Long-Term Planning: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwindaisuke_kazukiNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis R I L: Assignment OnDocument19 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis R I L: Assignment OnRavi JaiswalNo ratings yet