Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Worksheet 3: Lesson 7.4: Mutation
Worksheet 3: Lesson 7.4: Mutation
Uploaded by
Faith Martina Amando0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pageRadiation can cause genetic mutations in organisms in two main ways:
1. Directly by transferring enough energy to break bonds in DNA molecules, damaging the strands which can lead to mutations if not properly repaired.
2. Indirectly by transferring energy to other molecules like water, causing them to form reactive intermediates that can then interact with and damage DNA, also potentially causing mutations.
While most mutations are harmless, some mutations occurring in coding regions of DNA (exons) can be harmful, though in rare cases random mutations may provide benefits that help a species survive.
Original Description:
Science Mutation
Original Title
Science-10-7.4-Worksheet
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentRadiation can cause genetic mutations in organisms in two main ways:
1. Directly by transferring enough energy to break bonds in DNA molecules, damaging the strands which can lead to mutations if not properly repaired.
2. Indirectly by transferring energy to other molecules like water, causing them to form reactive intermediates that can then interact with and damage DNA, also potentially causing mutations.
While most mutations are harmless, some mutations occurring in coding regions of DNA (exons) can be harmful, though in rare cases random mutations may provide benefits that help a species survive.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pageWorksheet 3: Lesson 7.4: Mutation
Worksheet 3: Lesson 7.4: Mutation
Uploaded by
Faith Martina AmandoRadiation can cause genetic mutations in organisms in two main ways:
1. Directly by transferring enough energy to break bonds in DNA molecules, damaging the strands which can lead to mutations if not properly repaired.
2. Indirectly by transferring energy to other molecules like water, causing them to form reactive intermediates that can then interact with and damage DNA, also potentially causing mutations.
While most mutations are harmless, some mutations occurring in coding regions of DNA (exons) can be harmful, though in rare cases random mutations may provide benefits that help a species survive.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Unit 7: Effects of Electromagnetic Waves on the
Environment • Grade 10
Lesson 7.4: Mutation
Worksheet 3
Name: Luke Emanuel L. Amando Date:
Rating:
Grade and Section: 10- St. John
General Instructions: Answer the following in essay format. (5 points per item)
1. Is genetic mutation totally harmful to organisms?
Mutations can be harmful, neutral, or advantageous. The majority of
2.
mutations are point mutations, which alter the DNA sequence at a single point.
Mutations occur when the base sequence on the DNA strand changes. Most
mutations have no effect because they occur in introns, also known as "junk
DNA." However, some mutations occur on exons, and these are the ones that
can be potentially harmful to the organism, though in some exceptional cases
random mutations can be beneficial, and pressured mutations are almost always
beneficial to a species' survival. Harmful mutations can occur as a result of semi-
conservative replication errors or prolonged exposure to certain types of
radiation. Some exon mutations have no effect because they are "silent
mutations" in which the bases change but still code for the same amino acid. For
example, if GTC changes to GTT, there will be no noticeable difference because
both of these triplets code for the same thing, glutamine.
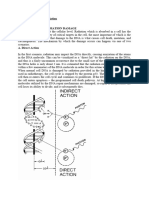
How does radiation cause mutation?
Radiation can transfer energy to molecules such as DNA, causing bonds to
break. In any case, when radiation interacts with molecules in the cell, it loses
energy. When radiation has enough energy to free an electron from an atom, it
can cause mutation. Then it is referred to as ionizing radiation. In contrast to
microwaves and light, which are both forms of radiation but have less energy.
Bonds can be broken when an electron is released from a molecule. Radiation
can cause mutations in two different ways:
1. Direct effect : radiation breaks bonds in DNA, this breaks the strands and
mutation can occur when it is not properly repaired.
2. Indirect effect : radiation causes other molecules to lose an electron; these
molecules (reactive intermediates) can then interact with DNA to cause
mutation.
You might also like
- En Proefexamen VOL VCA QuestionsDocument15 pagesEn Proefexamen VOL VCA QuestionsshaheerNo ratings yet
- Bushong Chapter 31 Challenge Questions AnswersDocument3 pagesBushong Chapter 31 Challenge Questions AnswersDiana Jean CaimolNo ratings yet
- Radiation Biology LectureDocument39 pagesRadiation Biology LectureBipin UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Internasional PicotDocument6 pagesJurnal Internasional PicotTHE COMUNITAS PASAPUA ANGKATAN 2017100% (1)
- The Hazards of Dead LegsDocument1 pageThe Hazards of Dead LegsAshfaq KhanNo ratings yet
- NOTES FOR RTT Biological EffectsDocument6 pagesNOTES FOR RTT Biological EffectsRadhika BindNo ratings yet
- Biological Effects of Ionizing RadiationDocument22 pagesBiological Effects of Ionizing RadiationCharlemyne Quevedo LachanceNo ratings yet
- 3 Molecular and Cellular RadbiologyDocument46 pages3 Molecular and Cellular RadbiologyAngelo RamosNo ratings yet
- Ionization and Cell DamageDocument2 pagesIonization and Cell DamageMomo ItachiNo ratings yet
- MutationDocument35 pagesMutationemail4ishanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 18Document21 pagesLecture 7 18AshMere MontesinesNo ratings yet
- Module 6 IQ1Document69 pagesModule 6 IQ1TasnimaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Radiations and Properties of X-RaysDocument57 pagesElectromagnetic Radiations and Properties of X-RaysRosette DawoudNo ratings yet
- RADIOBIODocument5 pagesRADIOBIObenjoNo ratings yet
- Basic Biologic Interactions of RadiationDocument28 pagesBasic Biologic Interactions of RadiationAyu FadhilahNo ratings yet
- X Rays, Gamma Rays, Cosmic Rays: Types of MutagensDocument9 pagesX Rays, Gamma Rays, Cosmic Rays: Types of MutagensNi Wayan SuliartiniNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 2 - Bioradiation Radiation Biology - Mechanisms - 1Document7 pagesLecture - 2 - Bioradiation Radiation Biology - Mechanisms - 1Naglaa MostafaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 031Document2 pagesChapter 031Zaid juttNo ratings yet
- 1 - 1 - AnswersDocument2 pages1 - 1 - Answersjasmine.tran26No ratings yet
- Radiation EffectDocument35 pagesRadiation Effectaiimsjdh acadNo ratings yet
- Genetic Change Study NotesDocument38 pagesGenetic Change Study NotesPierre BenardNo ratings yet
- Roent Prelims CompiledDocument7 pagesRoent Prelims CompiledALYXXA FEMME ORDANEZANo ratings yet
- Dna Replication and MutationDocument4 pagesDna Replication and MutationmichsantosNo ratings yet
- 259 FullDocument6 pages259 Fullmohammedfahadtvm493No ratings yet
- Radiobiological EffectsDocument60 pagesRadiobiological EffectsJie DVNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Nuclear ChemistryDocument3 pagesAssignment of Nuclear ChemistryMubashir Hassan KhanNo ratings yet
- Gene Repair: Metabolic Activities Environmental FactorsDocument8 pagesGene Repair: Metabolic Activities Environmental FactorsAbbas TalibNo ratings yet
- Dna and Protein EssayDocument3 pagesDna and Protein Essayapi-248018975No ratings yet
- Biological Effects of Radiation (Physics)Document13 pagesBiological Effects of Radiation (Physics)Josiah Dave CalumpangNo ratings yet
- Radiobiology&ProtectionDocument75 pagesRadiobiology&ProtectionsabreennafiyaNo ratings yet
- DNA and MutationsDocument13 pagesDNA and MutationspiaNo ratings yet
- Dimple ImDocument4 pagesDimple ImBilooyNo ratings yet
- What Happens When Your DNA Is Damaged?Document4 pagesWhat Happens When Your DNA Is Damaged?海祁No ratings yet
- Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation-2022Document138 pagesBiological Effects of Ionizing Radiation-2022Waleed TayyabNo ratings yet
- L1 Radbio Midterm Rad EffectsDocument4 pagesL1 Radbio Midterm Rad Effectsfrancoise wyanet rualoNo ratings yet
- Science 10 q3 MUTATIONDocument33 pagesScience 10 q3 MUTATIONLeah Beth CañedoNo ratings yet
- Radio BiologyDocument7 pagesRadio BiologyLucelle CoquillaNo ratings yet
- Units of Radiation DoseDocument20 pagesUnits of Radiation DoseMadduri NithamNo ratings yet
- ANANDocument11 pagesANANAron JaroNo ratings yet
- Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation: En. Mohd Fahmi B Mohd YusofDocument45 pagesBiological Effects of Ionizing Radiation: En. Mohd Fahmi B Mohd YusofFahmi BestNo ratings yet
- Draft Praktikum KimiaDocument16 pagesDraft Praktikum KimiafatinNo ratings yet
- RadbioDocument10 pagesRadbioHans LlanetaNo ratings yet
- Biological Risk, Radiation ProtectionDocument37 pagesBiological Risk, Radiation Protection202210034No ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument3 pagesClass Notessrijal kunwarNo ratings yet
- 13 3 PowerPointDocument17 pages13 3 PowerPointDeena SriyazzNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Genetic ChangeDocument12 pagesModule 6 - Genetic ChangeHSC CoachNo ratings yet
- Radio Biophysics Level 3Document74 pagesRadio Biophysics Level 3Naglaa MostafaNo ratings yet
- MutationDocument4 pagesMutationReymark NovecioNo ratings yet
- Mutation: Physical Sciences Dept. College of Science de La Salle University-Dasmariñas Cavite March 15, 2010Document5 pagesMutation: Physical Sciences Dept. College of Science de La Salle University-Dasmariñas Cavite March 15, 2010Aki OtaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 5 - Elements of Radiation BiologyDocument46 pagesLecture - 5 - Elements of Radiation Biologyhannan alnzi100% (1)
- 5705 EnglishDocument6 pages5705 EnglishAmnaNo ratings yet
- Basic Review of Radiation Biology and TerminologyDocument7 pagesBasic Review of Radiation Biology and TerminologyAjay MohanNo ratings yet
- Genetic Mutations - Notes - FILL INDocument6 pagesGenetic Mutations - Notes - FILL INPaulína PalčinskáNo ratings yet
- GelelctroDocument11 pagesGelelctro99manu99No ratings yet
- Science10 Q3 Ver4 Mod5Document32 pagesScience10 Q3 Ver4 Mod5Berliese FriasNo ratings yet
- Radiation Biology: Presented By: Aarya.H.NairDocument83 pagesRadiation Biology: Presented By: Aarya.H.NairAARYANo ratings yet
- Chap 11Document18 pagesChap 11sanchitNo ratings yet
- DNA MutationsDocument44 pagesDNA MutationsYashika A.No ratings yet
- 13,3 MutationsDocument6 pages13,3 MutationsSanaa SamkoNo ratings yet
- GelelctroDocument11 pagesGelelctroDrDeepak PawarNo ratings yet
- Early and Late Side-Effects in Radiation TherapyDocument6 pagesEarly and Late Side-Effects in Radiation Therapyungthu39No ratings yet
- B. Diagram: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors EtiologyDocument3 pagesB. Diagram: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors EtiologyJenness VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Common Forms of Anemia: Diagnosis and Management in Clinical PracticeDocument4 pagesCommon Forms of Anemia: Diagnosis and Management in Clinical PracticerivegaucheNo ratings yet
- Mycosia CYOADocument20 pagesMycosia CYOAAnother Random PersonNo ratings yet
- Archive 1 BDocument24 pagesArchive 1 BJan FowlerNo ratings yet
- 5Document4 pages5Kelli BaldwinNo ratings yet
- Pt. Restu Cahaya Sejahtera Farma: Daftar Harga Jual BarangDocument17 pagesPt. Restu Cahaya Sejahtera Farma: Daftar Harga Jual BarangGhriya ReynathaNo ratings yet
- Contoh Paragraf Bahasa InggrisDocument2 pagesContoh Paragraf Bahasa Inggrisnurdyah ayu oktavianiNo ratings yet
- Fda TindamaxDocument8 pagesFda TindamaxLuis Antonio Camacho CamachoNo ratings yet
- Nutra Puding Buah NagaDocument2 pagesNutra Puding Buah NagaUun RochmawatiNo ratings yet
- Initial Data Base For Family Nursing Practice A. Family Structure, Characteristics, and DynamicsDocument11 pagesInitial Data Base For Family Nursing Practice A. Family Structure, Characteristics, and DynamicsRoshin TejeroNo ratings yet
- Mapeh e - Class RecordDocument54 pagesMapeh e - Class RecordAnne Panlibuton TuanteNo ratings yet
- 2022.01.07.22268919v1.full Omicron 7 EneroDocument31 pages2022.01.07.22268919v1.full Omicron 7 EneroNancy Grisell RamirezNo ratings yet
- A Buddhist Perspective On Health and SpiritualityDocument3 pagesA Buddhist Perspective On Health and Spiritualityedi_wsNo ratings yet
- Fdarcharting 120314214902 Phpapp02Document5 pagesFdarcharting 120314214902 Phpapp02John Louie SolitarioNo ratings yet
- 30thang4 Mac Dinh Chi TPHCMDocument8 pages30thang4 Mac Dinh Chi TPHCMQuoc Hoang HuyNo ratings yet
- Lab Policies KOH Prep For Fungal Elements Affiliate Lab 8649 4Document3 pagesLab Policies KOH Prep For Fungal Elements Affiliate Lab 8649 4Geby JeonNo ratings yet
- Final Dental MechatronicsDocument2 pagesFinal Dental MechatronicsSanjai Uthup ThomasNo ratings yet
- Fungal Mycotoxin ConnectionDocument2 pagesFungal Mycotoxin Connectionapi-3695725100% (1)
- American Egg Board - Specifics About Eggs PDFDocument3 pagesAmerican Egg Board - Specifics About Eggs PDFashrafuli_44No ratings yet
- Panel Hospital PPN Updated 08-06-2018 PDFDocument4 pagesPanel Hospital PPN Updated 08-06-2018 PDFشہزاد حفیظNo ratings yet
- Ethnobotany of Southern Balochistan - Godman and GhafoorDocument104 pagesEthnobotany of Southern Balochistan - Godman and Ghafoorsaadayaz100% (2)
- Thyroid Nodules: What Is The Thyroid Gland?Document3 pagesThyroid Nodules: What Is The Thyroid Gland?sougataNo ratings yet
- MealsOnSteelArticle2011 Scott StevensonDocument6 pagesMealsOnSteelArticle2011 Scott Stevensonelsozo100% (1)
- Wintering & Quarantine Ponds: Dr. Soibam Khogen SinghDocument23 pagesWintering & Quarantine Ponds: Dr. Soibam Khogen SinghGen SoibamNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Occidental Mindoro State CollegeDocument8 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Occidental Mindoro State CollegeDendenna NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Hearing Screening Pediatrics 2009Document14 pagesHearing Screening Pediatrics 2009Francisco ValleNo ratings yet
- Indore PPT 4 Tier II Sar CRM 8-06-2018Document62 pagesIndore PPT 4 Tier II Sar CRM 8-06-2018Pallavi JayramNo ratings yet