Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 6: Accounting Policies: Learning Outcomes
Unit 6: Accounting Policies: Learning Outcomes
Uploaded by
sajedulOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 6: Accounting Policies: Learning Outcomes
Unit 6: Accounting Policies: Learning Outcomes
Uploaded by
sajedulCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
70 PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE OF ACCOUNTING
UNIT 6 : ACCOUNTING POLICIES
LEARNING OUTCOMES
After studying this unit, you will be able to :
w Understand the meaning of ‘Accounting Policies’.
w Familiarize with the situations under which selection from different accounting policies is required.
w Grasp the conditions where change in accounting policy can be made and the consequences arising
from such changes.
Selection of Accounting Policies
UNIT OVERVIEW
Based
on
Prudence Substance over
Materiality
Form
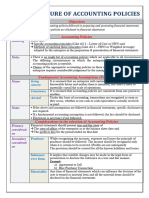
6.1 MEANING OF ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Accounting Policies refer to specific accounting principles and methods of applying these principles adopted
by the enterprise in the preparation and presentation of financial statements. Policies are based on various
accounting concepts, principles and conventions that have already been explained in Unit 2 of Chapter 1.
There is no single list of accounting policies, which are applicable to all enterprises in all circumstances.
Enterprises operate in diverse and complex environmental situations and so they have to adopt various
policies. The choice of specific accounting policy appropriate to the specific circumstances in which the
enterprise is operating, calls for considerate judgement by the management. ICAI has been trying to reduce
the number of acceptable accounting policies through Guidance Notes and Accounting Standards in its
combined efforts with the government, other regulatory agencies and progressive managements. Already
it has achieved some progress in this respect.
The areas wherein different accounting policies are frequently encountered can be given as follows:
(1) Valuation of inventories;
(2) Valuation of investments.
© The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK 1.71
This list should not be taken as exhaustive but is only illustrative. As the course will progress, students will
see the intricacies of the various accounting policies.
Suppose an enterprise holds some investments in the form of shares of a company at the end of an accounting
period. For valuation of shares, the enterprise may adopt FIFO, average method etc. The method selected
by that enterprise for valuation is called an accounting policy. Different enterprises may adopt different
accounting policies. Likewise, different methods of providing depreciation on fixed assets, i.e. Straight line,
written down, etc. are available to the business enterprises which will lead to different depreciation amounts.
6.2 SELECTION OF ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Choice of accounting policy is an important policy decision which affects the performance measurement
as well as financial position of the business entity. Selection of inappropriate accounting policy may lead to
understatement or overstatement of performance and financial position. Thus, accounting policy should be
selected with due care after considering its effect on the financial performance of the business enterprise
from the angle of various users of accounts.
It is believed that no unified and exhaustive list of accounting policies can be suggested which has
universal application. Three major characteristics which should be considered for the purpose of selection
and application of accounting policies. viz.,Prudence, Substance over form, and Materiality. The financial
statements should be prepared on the basis of such accounting policies, which exhibit true and fair view of
state of affairs of Balance Sheet and the Profit & Loss Account.
Examples wherein selection from a set of accounting policies is made, can be given as follows:–
1. Inventories are valued at cost except for finished goods and by-products. Finished goods are valued at
lower of cost or market value and by-products are valued at net realizable value.
2. Investments (long term) are valued at their acquisition cost. Provision for permanent diminution in
value has been made wherever necessary.
Sometimes a wrong or inappropriate treatment is adopted for items in Balance Sheet, or Profit & Loss
Account, or other statement. Disclosure of the treatment adopted is necessary in any case, but disclosure
cannot rectify a wrong or inappropriate treatment.
6.3 CHANGE IN ACCOUNTING POLICIES
A change in accounting policies should be made in the following conditions:
(a) It is required by some statute or for compliance with an Accounting Standard.
(b) Change would result in more appropriate presentation of financial statement.
Change in accounting policy may have a material effect on the items of financial statements. For example,
if depreciation method is changed from straight-line method to written-down value method, or if cost
formula used for inventory valuation is changed from weighted average to FIFO, or if interest is capitalized
which was earlier not in practice, or if proportionate amount of interest is changed to inventory which was
earlier not the practice, all these may increase or decrease the net profit. Unless the effect of such change
in accounting policy is quantified, the financial statements may not help the users of accounts. Therefore, it
is necessary to quantify the effect of change on financial statement items like assets, liabilities, profit/loss.
© The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India
1.72 PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE OF ACCOUNTING
For Example, Omega Enterprises revised its accounting policy relating to valuation of inventories to include
applicable production overheads.
SUMMARY
w Accounting Policies refer to specific accounting principles and methods of applying these principles
adopted by the enterprise in the preparation and presentation of financial statements. Policies are
based on various accounting concepts, principles and conventions.
w Three major characteristics which should be considered for the purpose of selection and application of
accounting policies. viz., Prudence, Substance over form, and Materiality.
w A change in accounting policies should be made in the following conditions:
(a) It is required by some statute or for compliance with an Accounting Standard.
(b) Change would result in more appropriate presentation of financial statement.
TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE
Multiple Choice Questions
1. A change in accounting policy is justified
(a) To comply with accounting standard and law.
(b) To ensure more appropriate presentation of the financial statement of the enterprise.
(c) All of the above.
2. Accounting policy for inventories of Xeta Enterprises states that inventories are valued at the lower
of cost determined on weighted average basis or net realizable value. Which accounting principle is
followed in adopting the above policy?
(a) Materiality. (b) Prudence.
(c) Substance over form.
3. The areas wherein different accounting policies can be adopted are
(a) Providing depreciation. (b) Valuation of inventories.
(c) Both the option.
4. Selection of an inappropriate accounting policy decision may
(a) Overstate the performance and financial position of a business entity.
(b) Understate/overstate the performance and financial position of a business entity.
(c) Overstate the performance of a business entity.
© The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK 1.73
5. Accounting policies refer to specific accounting
(a) Principles. (b) Methods of applying those principles.
(c) Both (a) and (b).
Theoretical Questions
1. Define Accounting Policies in brief. Identify few areas wherein different accounting policies are
frequently encountered.
2. “Change in accounting policy may have a material effect on the items of financial statements.” Explain
the statement with the help of an example.
ANSWERS/HINTS
Multiple Choice Questions
(1) (c), (2) (b), (3) (c), (4) (b), (5) (c)
Theoretical Questions
1. Accounting Policies refer to specific accounting principles and methods of applying these principles
adopted by the enterprise in the preparation and presentation of financial statements. For details, refer
para 6.1.
2. Change in accounting policy may have a material effect on the items of financial statements. For
example, if depreciation method is changed from straight-line method to written-down value method,
or if cost formula used for inventory valuation is changed from weighted average to FIFO. Unless the
effect of such change in accounting policy is quantified, the financial statements may not help the users
of accounts.
© The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India
You might also like
- Erpnext TutorialDocument131 pagesErpnext TutorialPrapto Nugroho S100% (1)
- Scm. LupinDocument8 pagesScm. LupinSanjib Biswas100% (1)
- VMI Process in OracleDocument13 pagesVMI Process in OraclePraWinNo ratings yet
- Unit - 6 Accounting Policies: Learning OutcomesDocument4 pagesUnit - 6 Accounting Policies: Learning OutcomesTanyaNo ratings yet
- Accounting PoliciesDocument6 pagesAccounting PoliciesShalini TiwariNo ratings yet
- AS-1 Disclosure of Accounting Policies: CMA S. BaskaranDocument11 pagesAS-1 Disclosure of Accounting Policies: CMA S. BaskaranS. BaskaranNo ratings yet
- Finance Project PrintDocument23 pagesFinance Project PrintYash ParekhNo ratings yet
- Module 014 Week005-Statement of Changes in Equity, Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and ErrorsDocument9 pagesModule 014 Week005-Statement of Changes in Equity, Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errorsman ibeNo ratings yet
- As-1 Disclosure of Accounting PoliciesDocument7 pagesAs-1 Disclosure of Accounting PoliciesPrakash_Tandon_583No ratings yet
- Accounting Standard 1Document7 pagesAccounting Standard 1api-3828505No ratings yet
- As1 CaDocument2 pagesAs1 CaĐėvıł ĶıñgNo ratings yet
- As 8 Alc PoliciesDocument50 pagesAs 8 Alc PoliciesAkhil AkhyNo ratings yet
- Final CHP T 2Document152 pagesFinal CHP T 2Marikrishna Chandran CA100% (1)
- Accounting Standard (AS) 1 (Issued 1979) : Disclosure of Accounting PoliciesDocument5 pagesAccounting Standard (AS) 1 (Issued 1979) : Disclosure of Accounting PoliciesSuhasini GummeNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Overview of Accounting Standards: After Studying This Unit, You Will Be Able ToDocument138 pagesUnit 2: Overview of Accounting Standards: After Studying This Unit, You Will Be Able Totauseefalam917100% (1)
- Disclosure of Accounting PoliciesDocument7 pagesDisclosure of Accounting PoliciesgimmyjoyNo ratings yet
- 74888bos60524 cp4 U1Document50 pages74888bos60524 cp4 U1Bala Guru Prasad TadikamallaNo ratings yet
- Disclosure of Accounting PoliciesDocument8 pagesDisclosure of Accounting Policiesabdullah0331No ratings yet
- IND AS 8 Raw PDFDocument41 pagesIND AS 8 Raw PDFrajesh reddyNo ratings yet
- Ind As On Measurement Based On Accounting PoliciesDocument38 pagesInd As On Measurement Based On Accounting Policiespulkitddude_24114888No ratings yet
- Disclosure of Accounting PoliciesDocument7 pagesDisclosure of Accounting PoliciesSatesh Kumar KonduruNo ratings yet
- Accounting Standard (AS) 1: (Issued 1979)Document7 pagesAccounting Standard (AS) 1: (Issued 1979)anoop_mishra1986No ratings yet
- Accounting Standard PoliciesDocument4 pagesAccounting Standard Policiesashishoraon789835No ratings yet
- Advancd Acc Ca Inter cp-4Document15 pagesAdvancd Acc Ca Inter cp-4Pooja Suresh BNo ratings yet
- Accounting Standard (As) 1 Disclosure Ofaccounting Policies: (Issued 1979)Document3 pagesAccounting Standard (As) 1 Disclosure Ofaccounting Policies: (Issued 1979)Sonali PuriNo ratings yet
- IFA II Chap - 5 2016Document15 pagesIFA II Chap - 5 2016teddymaru7No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Accounting Policies PDFDocument8 pagesChapter 11 Accounting Policies PDFAthena LansangNo ratings yet
- Chap2 As 1 Disclosure of Accounting PoliciesDocument3 pagesChap2 As 1 Disclosure of Accounting PoliciesAashutosh PatodiaNo ratings yet
- 3 Overview of Accounting StandardsDocument136 pages3 Overview of Accounting StandardsAlok Kumar100% (1)
- LKAS 8 Accounting Policies (New)Document33 pagesLKAS 8 Accounting Policies (New)Kogularamanan NithiananthanNo ratings yet
- As1 171222Document6 pagesAs1 171222spikysanchitNo ratings yet
- Accounting Standard (AS) 1 (Issued 1979) : Disclosure of Accounting PoliciesDocument4 pagesAccounting Standard (AS) 1 (Issued 1979) : Disclosure of Accounting Policiessaradindu123No ratings yet
- Accounting Policies1Document4 pagesAccounting Policies1szn1No ratings yet
- Unit Number/ Heading Learning OutcomesDocument10 pagesUnit Number/ Heading Learning OutcomesariesNo ratings yet
- Pas 8 Cfas PDFDocument6 pagesPas 8 Cfas PDFAndreaaAAaa TagleNo ratings yet
- IAS-8 Accounting Policies, Change in Accounting Estimates and Errors ObjectiveDocument6 pagesIAS-8 Accounting Policies, Change in Accounting Estimates and Errors ObjectiveAbdullah Al Amin MubinNo ratings yet
- As1-Diclosure of Accounting PoliciesDocument6 pagesAs1-Diclosure of Accounting PoliciesDharmesh MistryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 Policies Estimates and ErrorsDocument28 pagesChapter 18 Policies Estimates and ErrorsHammad Ahmad100% (1)
- What Is Accounting PrinciplesDocument17 pagesWhat Is Accounting PrinciplesvicenteferrerNo ratings yet
- 64707d8be4b079489dc30f9c OriginalDocument12 pages64707d8be4b079489dc30f9c OriginalArish HilalNo ratings yet
- PAS 8 - Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and ErrorsDocument37 pagesPAS 8 - Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and ErrorsPeralta Renn JethroNo ratings yet
- PAS 8 - Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and ErrorsDocument11 pagesPAS 8 - Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and ErrorsKrizzia DizonNo ratings yet
- Other Standards: 1 IAS 8 Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates & ErrorsDocument7 pagesOther Standards: 1 IAS 8 Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates & Errorshafeez azizNo ratings yet
- PolicyDocument52 pagesPolicyHagere EthiopiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 (Cfas) PDFDocument3 pagesChapter 12 (Cfas) PDFVince Pereda100% (2)
- Accounting Policies and ErrorsDocument32 pagesAccounting Policies and ErrorsTia Li100% (1)
- 1 As Disclouser of Accounting PoliciesDocument6 pages1 As Disclouser of Accounting Policiesanisahemad1178No ratings yet
- Exp Posure D Draft: A Accounti Ing Stan Ndard (A AS) 5 (Re Evised)Document15 pagesExp Posure D Draft: A Accounti Ing Stan Ndard (A AS) 5 (Re Evised)ratiNo ratings yet
- ACC2001 Lecture 5Document50 pagesACC2001 Lecture 5michael krueseiNo ratings yet
- IAS 8 Diana Maruf AnasDocument24 pagesIAS 8 Diana Maruf AnasLamis ShalabiNo ratings yet
- Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and ErrorsDocument29 pagesAccounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and ErrorsSheda AshrafNo ratings yet
- Review Materials: Prepared By: Junior Philippine Institute of Accountants UC-Banilad Chapter F.Y. 2019-2020Document33 pagesReview Materials: Prepared By: Junior Philippine Institute of Accountants UC-Banilad Chapter F.Y. 2019-2020AB CloydNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Accounting Standard 1Document9 pagesPresentation On Accounting Standard 1ritusexyNo ratings yet
- FRS 18, Accounting PoliciesDocument8 pagesFRS 18, Accounting PoliciesveemaswNo ratings yet
- 4 MFRS108Document34 pages4 MFRS108Dont RushNo ratings yet
- Accounting Concepts/conventions and Policies: Always On The Exam!! MCQ?Document30 pagesAccounting Concepts/conventions and Policies: Always On The Exam!! MCQ?veemaswNo ratings yet
- As-1: Disclosure of Accounting Policies: ObjectivesDocument58 pagesAs-1: Disclosure of Accounting Policies: ObjectivesAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- Engagement Essentials: Preparation, Compilation, and Review of Financial StatementsFrom EverandEngagement Essentials: Preparation, Compilation, and Review of Financial StatementsNo ratings yet
- Master Budgeting and Forecasting for Hospitality Industry-Teaser: Financial Expertise series for hospitality, #1From EverandMaster Budgeting and Forecasting for Hospitality Industry-Teaser: Financial Expertise series for hospitality, #1No ratings yet
- Annual Update and Practice Issues for Preparation, Compilation, and Review EngagementsFrom EverandAnnual Update and Practice Issues for Preparation, Compilation, and Review EngagementsNo ratings yet
- "The Language of Business: How Accounting Tells Your Story" "A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding, Interpreting, and Leveraging Financial Statements for Personal and Professional Success"From Everand"The Language of Business: How Accounting Tells Your Story" "A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding, Interpreting, and Leveraging Financial Statements for Personal and Professional Success"No ratings yet
- The Balanced Scorecard: Turn your data into a roadmap to successFrom EverandThe Balanced Scorecard: Turn your data into a roadmap to successRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Difference Between Net Realizable Value and Fair Value Less Cost To SellDocument3 pagesDifference Between Net Realizable Value and Fair Value Less Cost To SellgdegirolamoNo ratings yet
- 5 - Getting Started For Simulation ProjectDocument22 pages5 - Getting Started For Simulation ProjectDaniel TjeongNo ratings yet
- Marketing ChannelsDocument563 pagesMarketing ChannelsAlinna100% (3)
- Cost Control: Business ExpensesDocument3 pagesCost Control: Business Expensessamuel villaNo ratings yet
- TB Special - PDF 15 & 16Document12 pagesTB Special - PDF 15 & 16Rabie HarounNo ratings yet
- TheoriesDocument11 pagesTheoriesJanella PatriziaNo ratings yet
- Mcdonalds in IndiaDocument20 pagesMcdonalds in IndiaAnupam KhandreNo ratings yet
- Canada UFEDocument26 pagesCanada UFESam MkandwireNo ratings yet
- 1831 73 4303 1 10 20220907Document12 pages1831 73 4303 1 10 20220907Jordan KopongNo ratings yet
- Bba PDFDocument50 pagesBba PDFLakhan KumarNo ratings yet
- EB - Romney - AIS13wm 405 440 1 5Document5 pagesEB - Romney - AIS13wm 405 440 1 5Mayang SariNo ratings yet
- DistributionDocument32 pagesDistributionRahul KhannaNo ratings yet
- CA Pranav Dedhia - Costing Theory Smart Notes (CA Inter)Document20 pagesCA Pranav Dedhia - Costing Theory Smart Notes (CA Inter)MlNo ratings yet
- Inventory EOQDocument50 pagesInventory EOQKaneki KenNo ratings yet
- 8 Wastes of Lean Manufacturing - DOWNTIME - TIMWOODSDocument20 pages8 Wastes of Lean Manufacturing - DOWNTIME - TIMWOODStemaquijaNo ratings yet
- Assortment Rotation and The Value of Concealment: Kris Johnson Ferreira Joel GohDocument44 pagesAssortment Rotation and The Value of Concealment: Kris Johnson Ferreira Joel GohIgna BNo ratings yet
- What Is Demand Forecasting? and Why It Is Important For Your BusinessDocument10 pagesWhat Is Demand Forecasting? and Why It Is Important For Your BusinessSadaqat AkNo ratings yet
- Absorption Vs Marginal CostingDocument24 pagesAbsorption Vs Marginal CostingPoint BlankNo ratings yet
- Kabale University: Course Work Submitted By: Tubirore EricDocument5 pagesKabale University: Course Work Submitted By: Tubirore EriciamsacrisNo ratings yet
- Channel DesignDocument17 pagesChannel DesignPooja Tripathi100% (1)
- QuestionPaperDec 2010Document50 pagesQuestionPaperDec 2010Md.Reza HussainNo ratings yet
- $3,200 Units X 3 Foot Per Unit $55,650 / 10,500 Feet $5.30 Per FootDocument41 pages$3,200 Units X 3 Foot Per Unit $55,650 / 10,500 Feet $5.30 Per FootLyra EscosioNo ratings yet
- Intra Firm Ratio Analysis of Financial Statements of Bharti Realty Holdings Ltd.Document37 pagesIntra Firm Ratio Analysis of Financial Statements of Bharti Realty Holdings Ltd.DevNo ratings yet
- Departmental Wise Measurable Master - 2Document13 pagesDepartmental Wise Measurable Master - 2VenkatesanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Operations Management: Dr. Erlita C. Guerra, Mba, MpaDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Operations Management: Dr. Erlita C. Guerra, Mba, MpaJessa BasadreNo ratings yet
- Aggregate PlanningDocument29 pagesAggregate PlanningkushalNo ratings yet
- Mohammed Othman Ezzat CV A.005Document4 pagesMohammed Othman Ezzat CV A.005Medo O. EzzatNo ratings yet