Professional Documents
Culture Documents
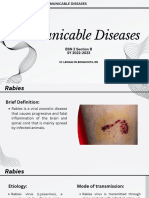
Rabies: Lyssa Virus. Genus Name of Rhabdoviridae
Rabies: Lyssa Virus. Genus Name of Rhabdoviridae
Uploaded by
Fhaye LitucoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Rabies: Lyssa Virus. Genus Name of Rhabdoviridae
Rabies: Lyssa Virus. Genus Name of Rhabdoviridae
Uploaded by
Fhaye LitucoCopyright:
Available Formats
RABIES 3.
Larygneal Spasms
4. convulsions
I. Definition 5. delirium
Is a viral disease that cause acute After a symptom-free incubation period that
encephalitis (inflammation of the brain) in ranges from 10 days to a year or longer (the
warm-blooded average is 30 to 50 days)
1. Malaise
2. Loss of appetite
II.Etiology 3. Fatigue
Lyssa virus. Genus name of Rhabdoviridae 4. Headache
5. Fever
Two to 10 days later, signs of nervous
III.Mode of Transmission system damage appear.
Travels to the brain by following the 1. Hyperactivity and hypersensitivity
peripheral nerves 2. Disorientation
Animal bite 3. Hallucination
4. Seizures
5. Paralysis
IV.Incubation Period 6. Difficulty of breathing
1. The incubation period of the disease VI. Pathognomonic Sign
is usually a few months in humans, Hydrophobia, a morbid fear of water
depending on the distance the virus
must travel to reach the central VII.Diagnostic Test
nervous system.
1. Treatment after exposure, known as
2. Once the rabies virus reaches the
post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP), is
central nervous system and
highly successful in preventing the
symptoms begin to show, the
disease if administered promptly,
infection is effectively untreatable
generally within ten days of
and usually fatal within days.
infection.[1] Thoroughly washing the
wound as soon as possible with soap
V.Signs and Symptoms and water for approximately five
minutes is very effective at reducing
1. fever the number of viral particles. “If
2. Insomia available, a virucidal antiseptic such
as povidone-iodine, iodine tincture,
aqueous iodine solution, or alcohol Purified chick embryo cell vaccine
(ethanol) should be applied after (PCECV)
washing. Exposed mucous
membranes such as eyes, nose or
mouth should be flushed well with IX. Prevention and Control
water
2. Some recent work has shown that 1. Vero cell rabies vaccine
during lethal rabies infection, the
2. A recombinant vaccine called V-RG has
blood-brain barrier (BBB) does not
been successfully used in Belgium, France,
allow anti-viral immune cells to
Germany, and the disease if administered
enter the brain, the primary site of
promptly, generally within ten years of
rabies virus replication.[25] This
infection.
aspect contributes to the
pathogenicity of the virus and X.Nursing Management
artificially increasing BBB
permeability promotes viral 1. Treatment after exposure, known as
clearance.[26] Opening the BBB post- exposure prophylaxis (PEP), is
during rabies infection has been highly successful in preventing the
suggested as a possible novel disease of administered promptly,
approach to treating the disease, even generally within then days of
though no attempts have yet been infection
made to determine whether or not 2. No matter where the wound
this treatment could be successful. authorities emphasize that the first
and most valuable preventive
measure is through cleaning of the
VII.Drug of Choice site with soap and water
The Imovax® Rabies Vaccine, The virus is 3. If rabies vaccine treatment is called
harvested from infected human diploid cells, for, it should be started as soon as
MRC-5 strain, concentrated by ultrafiltration possible after exposure. Counting the
and is inactivated by beta-propiolactone. first day of vaccine treatment as day
One dose of reconstituted vaccine contains 0 on days 0, 3, 7, 14
less than 100 mg albumin, less than 150 μg 4. The first dose of rabies vaccine is
neomycin sulfate and 20 μg of phenol red given as soon as possible after
indicator. This vaccine must only be used exposure, with additional doses on
intramuscularly and as a single dose vial. days three, seven and fourteen after
the first
5. Patients who have previously
VIII.Immunization received pre-exposure vaccination do
not receive the immunoglobulin,
Human diploid cell vaccine (HDCV)
only the post-exposure vaccinations
on day 0 and 2
XI. Possible Nursing Diagnosis
1. High risk for infection transmission
2. Knowledge deficit
3. Altered body temperature related to
presence of infection
4. Dehydration related to refusal to take
liquids secondary to throat spasms
and fear of spasmodic attacks
SUBMITTED BY
JESSANT J. DEBLOIS
BSN3G
SUBMITTED TO
MR. ARMANDO DELOS
SANTOS, RN, MAN
You might also like
- TS Vaccine Stability Table PDFDocument17 pagesTS Vaccine Stability Table PDFDimitrios DalagiorgosNo ratings yet
- Rabies Case StudyDocument6 pagesRabies Case StudySheryll Almira Hilario100% (1)
- TuberculosisDocument5 pagesTuberculosiscecil100% (6)
- RabiesDocument28 pagesRabiesrouhanbinrashidNo ratings yet
- RabiesDocument4 pagesRabiesJamie FabianiaNo ratings yet
- Pcfm-Enterovirus InfectionsDocument7 pagesPcfm-Enterovirus InfectionsZarene AnnNo ratings yet
- 17 Agromed Tutor 2Document22 pages17 Agromed Tutor 2FatimahNo ratings yet
- ChickenpoxDocument23 pagesChickenpoxLukman HikimNo ratings yet
- FlipchartDocument24 pagesFlipchartSamantha Ishi LimNo ratings yet
- INTESTINAL INFECTIONS BhmsDocument5 pagesINTESTINAL INFECTIONS BhmsBhavithra. PNo ratings yet
- RabiesDocument48 pagesRabiesSarah AliNo ratings yet
- Finals 3Document5 pagesFinals 3Fau Fau DheoboNo ratings yet
- Rabies: Dr. Amany Ahmed IbrahimDocument31 pagesRabies: Dr. Amany Ahmed IbrahimMohammed Abd ElfattahNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care For A Family Caring For Children With Infectious DiseaseDocument4 pagesNursing Care For A Family Caring For Children With Infectious DiseasekdfhjfhfNo ratings yet
- DengueDocument2 pagesDengueAhana CherianNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseasesp.170 199Document30 pagesCommunicable Diseasesp.170 199Gary Largosa GallardoNo ratings yet
- Theory PointersDocument89 pagesTheory Pointerslala byuNo ratings yet
- General Medicine 3Document60 pagesGeneral Medicine 3Zeyad AlhaimiNo ratings yet
- Infectious DiseasesDocument4 pagesInfectious DiseasesLily BettyNo ratings yet
- Rabies VaccinesDocument2 pagesRabies VaccinesmadebagussnNo ratings yet
- Report DraftDocument8 pagesReport DraftJeremel MalanumNo ratings yet
- MIcrobial Infection of The BloodDocument7 pagesMIcrobial Infection of The BloodseahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 43: Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has An Infectious DisorderDocument12 pagesChapter 43: Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has An Infectious DisorderAlyssaGrandeMontimorNo ratings yet
- B9781416049197X50014 B9781416049197503534 MainDocument2 pagesB9781416049197X50014 B9781416049197503534 MainMANGNo ratings yet
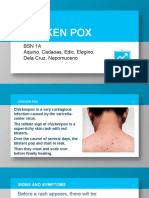
- Chicken Pox: BSN 1A Aquino, Cadaoas, Edic, Elegino, Dela Cruz, NepomucenoDocument20 pagesChicken Pox: BSN 1A Aquino, Cadaoas, Edic, Elegino, Dela Cruz, NepomucenoRayza MaglaqueNo ratings yet
- Rabies: NAME: Duaa Amer Abed U.O.A C.O.PharmacyDocument8 pagesRabies: NAME: Duaa Amer Abed U.O.A C.O.PharmacyTee bagNo ratings yet
- Lucid Chart ManuscriptDocument11 pagesLucid Chart ManuscriptCyrill Alexandria TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Top Communicable Diseases in The Philippines 2019Document4 pagesTop Communicable Diseases in The Philippines 2019Nicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease (Introduction Part 2) : Period of DeclineDocument6 pagesCommunicable Disease (Introduction Part 2) : Period of Declinefiel borataNo ratings yet
- The Pathogenesis of German Measles and MeaslesDocument3 pagesThe Pathogenesis of German Measles and Measlessailajanekkanti03No ratings yet
- MMR ImmunizationDocument43 pagesMMR ImmunizationkukuruziNo ratings yet
- Vaccine (Infant, Child)Document5 pagesVaccine (Infant, Child)Nursing LectureNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 LEC Alterations With Infectious Inflammatory and Immunologic Responses PDFDocument18 pagesNCM 109 LEC Alterations With Infectious Inflammatory and Immunologic Responses PDFcalliemozartNo ratings yet
- VITALSIGNSIMMUNIZATIONDocument6 pagesVITALSIGNSIMMUNIZATIONGlaiza Mae TuralbaNo ratings yet
- Cedid San Pablo Ied Ambiente Artistico Comunicativo English 10Th Sent To The EmailDocument6 pagesCedid San Pablo Ied Ambiente Artistico Comunicativo English 10Th Sent To The Emaildiego suarezNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases 2Document12 pagesInfectious Diseases 2Jean GolezNo ratings yet
- MCN Nursing Care of A Family Care For Children With Infectious DisordersDocument21 pagesMCN Nursing Care of A Family Care For Children With Infectious DisorderscalliemozartNo ratings yet
- Epi PampletDocument2 pagesEpi Pamplet2AACENAS, Julia Stephanie A.No ratings yet
- CHN ReviewersDocument5 pagesCHN ReviewersAngelina Nicole G. TungolNo ratings yet
- Lerelyn Case Reading4Document53 pagesLerelyn Case Reading4Ma Lerelyn DatinguinooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Communicable Diseases 2ND Sem 2022 2023Document10 pagesChapter 1 Communicable Diseases 2ND Sem 2022 2023Lovelyn Cantollas EugenioNo ratings yet
- Rabies & Snake BiteDocument32 pagesRabies & Snake BiteJoy BogadorNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Central ObjectivesDocument6 pagesLesson Plan: Central Objectivesprabha krishnan100% (2)
- Q3-PPT-HEALTH8 - Week 1 (Stages of Infection)Document45 pagesQ3-PPT-HEALTH8 - Week 1 (Stages of Infection)JungieNo ratings yet
- Medical Virology Dr. Saif AL-Mayah: Rabies Virus Disease:This Virus Causes Rabies. Important PropertiesDocument9 pagesMedical Virology Dr. Saif AL-Mayah: Rabies Virus Disease:This Virus Causes Rabies. Important PropertiesAtheer AlabdyNo ratings yet
- Micro para Finals ReviewerDocument7 pagesMicro para Finals ReviewerJoshua UveroNo ratings yet
- Airborne InfectionsDocument31 pagesAirborne InfectionskishorebinrajsNo ratings yet
- RabiesDocument25 pagesRabiesAdindapauliaNo ratings yet
- Variola Virus: (Smallpox)Document3 pagesVariola Virus: (Smallpox)Maya OlinNo ratings yet
- Rabies: Prophylaxis If The Animal Can BeDocument1 pageRabies: Prophylaxis If The Animal Can BeAlna Shelah IbañezNo ratings yet
- COPY Q3-PPT-HEALTH8 - Week 1.2 (Stages of Infection)Document24 pagesCOPY Q3-PPT-HEALTH8 - Week 1.2 (Stages of Infection)JungieNo ratings yet
- rabiesDocument12 pagesrabiesDivya DharshiniNo ratings yet
- Diseases at A Glance by Dr. NK Sharma Chapter: Human Health & DiseaseDocument5 pagesDiseases at A Glance by Dr. NK Sharma Chapter: Human Health & DiseaseRahul DixitNo ratings yet
- Rabies PDFDocument8 pagesRabies PDFKathryne May JinonNo ratings yet
- Microbiology : 2 SemesterDocument8 pagesMicrobiology : 2 Semestermadison DeliNo ratings yet
- AnalysisDocument4 pagesAnalysisfortuneayaNo ratings yet
- Class IX Science Why Do We Fall Ill PPT Module 3 - 3Document17 pagesClass IX Science Why Do We Fall Ill PPT Module 3 - 3Sandeep Kumar100% (2)
- CHN Midterm ReviewerDocument54 pagesCHN Midterm ReviewerJoi PreconesNo ratings yet
- Animal BiteDocument51 pagesAnimal BiteJo-Ann Marie MendozaNo ratings yet
- Childhood Infectious DiseasesDocument17 pagesChildhood Infectious DiseasesRNStudent1No ratings yet
- The Wuhan Coronavirus: Survival Manual and Concise Guide to COVID-19 (Symptoms, Outbreak, and Prevention in 2020)From EverandThe Wuhan Coronavirus: Survival Manual and Concise Guide to COVID-19 (Symptoms, Outbreak, and Prevention in 2020)No ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion ConsentDocument2 pagesBlood Transfusion ConsentShejil BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- PseudorabiesDocument23 pagesPseudorabiesSyikin Zolkefly100% (1)
- Basic Concepts - IntroductionDocument18 pagesBasic Concepts - IntroductionDj ArofNo ratings yet
- ClostridumDocument30 pagesClostridumFrancesca VargasNo ratings yet
- 7 - Anthelmintic DrugsDocument70 pages7 - Anthelmintic DrugsTogu NaiposposNo ratings yet
- Subcutaneous & Systemic MycosesDocument7 pagesSubcutaneous & Systemic MycosesDee GeeNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer AwarenessDocument14 pagesCervical Cancer AwarenessMDI detNo ratings yet
- Criteria Donor of BloodDocument3 pagesCriteria Donor of Bloodapi-269388039No ratings yet
- Antifungal Agents MBCHBD III - July 2021Document36 pagesAntifungal Agents MBCHBD III - July 2021KudzaisheNo ratings yet
- .Nursing Care Plan Poliomyelitis - 1713521478901Document10 pages.Nursing Care Plan Poliomyelitis - 1713521478901Joseph MuzabulaNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 1 Leishmaniasis-A-Review-On-Parasite-Vector-And-Reservoir-HostDocument6 pagesKelompok 1 Leishmaniasis-A-Review-On-Parasite-Vector-And-Reservoir-HostPanji SetyawanNo ratings yet
- MS LectureDocument5 pagesMS LectureAntoinette PeleñaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Home Vaccine Order 1-19-22Document3 pagesNursing Home Vaccine Order 1-19-22WXYZ-TV Channel 7 DetroitNo ratings yet
- What Is Chlamydia?: Sexually Transmitted DiseaseDocument3 pagesWhat Is Chlamydia?: Sexually Transmitted Diseaseflex gyNo ratings yet
- Japan's Statistic Bureau of Japan 2021Document95 pagesJapan's Statistic Bureau of Japan 2021Ren SuzakuNo ratings yet
- STI Risk & CondomsDocument5 pagesSTI Risk & CondomsAdams LoveNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Anti Viral DrugsDocument5 pagesAssignment - Anti Viral DrugsmziabdNo ratings yet
- (Konsultayo FAQ 2020) RabiesDocument5 pages(Konsultayo FAQ 2020) RabiesJay SmithNo ratings yet
- Topical Antibiotics For Skin InfectionsDocument4 pagesTopical Antibiotics For Skin InfectionsniklukNo ratings yet
- Parasitology NotesDocument5 pagesParasitology NotesAyaAlforque100% (1)
- LP Ena-1-60 PDFDocument60 pagesLP Ena-1-60 PDFEnaNo ratings yet
- Vibrio Cholerae That Causes CholeraDocument15 pagesVibrio Cholerae That Causes CholerayslovillanuevaNo ratings yet
- ISY-401 ManualDocument1 pageISY-401 ManualmcpaulfreemanNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics InfectionDocument75 pagesPediatrics InfectionHikufe JesayaNo ratings yet
- NystatinDocument3 pagesNystatinapi-3797941100% (3)
- Chickenpox - A Rare Case Involing Periodontal Tissues: ASE EportDocument4 pagesChickenpox - A Rare Case Involing Periodontal Tissues: ASE EportTunggul BagusNo ratings yet
- Black DeathDocument16 pagesBlack DeathMae DañoNo ratings yet
- Streptococcus Pneumoniae S. PneumoniaeDocument18 pagesStreptococcus Pneumoniae S. PneumoniaeadrianNo ratings yet