Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adobe Scan 13-Nov-2021
Adobe Scan 13-Nov-2021
Uploaded by
Kruthi BalajiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Biological Science Canadian 2nd Edition Freeman Test Bank 1Document36 pagesBiological Science Canadian 2nd Edition Freeman Test Bank 1conniemcphersonaeporxsmkbNo ratings yet
- Amoeba Sisters Dihybrid FOILDocument1 pageAmoeba Sisters Dihybrid FOILAlejandra Monteagudo ReyzabalNo ratings yet
- Lect 3 Gene Segregation and Interaction PDFDocument10 pagesLect 3 Gene Segregation and Interaction PDFdhonaNo ratings yet
- Chap 5Document11 pagesChap 5Parshvi TyagiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Genetic VariationsDocument8 pagesPrinciples of Genetic VariationsDipangkar SarkarNo ratings yet
- S ENG POI COMPLETE 23 Dec GA SirDocument37 pagesS ENG POI COMPLETE 23 Dec GA SirDave JuneNo ratings yet
- GENETICS - 21.05.21 & 22.05.21 - MASE2 MergedDocument310 pagesGENETICS - 21.05.21 & 22.05.21 - MASE2 MergedHarshit VermaNo ratings yet
- Law of Inheritance and PEDIGREEDocument74 pagesLaw of Inheritance and PEDIGREECharlene SuliganNo ratings yet
- Lec - General Zoology #1Document2 pagesLec - General Zoology #1Nu Ri LeeNo ratings yet
- M1 Introdcution To GeneticsDocument4 pagesM1 Introdcution To GeneticsBrylle Angelo PolintanNo ratings yet
- Terms To Know in Mendelian GeneticsDocument2 pagesTerms To Know in Mendelian GeneticsDoris C. Brucales100% (1)
- Life Sciences Grade 12 Genetics Concepts Virtual Lesson PowerPoint NotesDocument19 pagesLife Sciences Grade 12 Genetics Concepts Virtual Lesson PowerPoint Notescrisseldah1No ratings yet
- 1 GeneticsDocument18 pages1 GeneticssifawanjiNo ratings yet
- Epistasis: XpinkDocument2 pagesEpistasis: XpinkSamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 (Gene Actions)Document32 pagesLecture 1 (Gene Actions)Anil YadavNo ratings yet
- Population Genetics Booklet Y13Document83 pagesPopulation Genetics Booklet Y13hummy18No ratings yet
- Agents of DiseasesDocument3 pagesAgents of DiseasesRaymart DomingoNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Bio CH 3 Inheritance and VariationsDocument21 pagesClass 12 Bio CH 3 Inheritance and VariationsShreyash ApshingeNo ratings yet
- Biology: Genetics & Inheritance III: Genetic Basis For Variation IDocument27 pagesBiology: Genetics & Inheritance III: Genetic Basis For Variation ITimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27Document58 pagesChapter 27Konishko DeyNo ratings yet
- "Mendelian Genetics": General Biology 2 ReviewerDocument5 pages"Mendelian Genetics": General Biology 2 ReviewerFayza Jalil Balading100% (1)
- Cytogen Lesson 1Document3 pagesCytogen Lesson 1STEM-A CHRISTINE TRIBUNALONo ratings yet
- 4 - Q - Genetic InheritanceDocument22 pages4 - Q - Genetic InheritanceNOOR JANNAH FIRDOUSE BINTI ISMAIL KM-Pensyarah100% (1)
- General Biology Genetics, Proteins, Origins of Life & BiotechnologyDocument31 pagesGeneral Biology Genetics, Proteins, Origins of Life & BiotechnologyAlexis Carla GahumanNo ratings yet
- Heredity Class 10 NEETDocument25 pagesHeredity Class 10 NEETPixcasso 21No ratings yet
- HEREDITARYDocument8 pagesHEREDITARYSiti Hajar RevillaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Mendelian Laws of InheritanceDocument31 pagesLecture 1 - Mendelian Laws of InheritancekibzwanjikuNo ratings yet
- Mendels LawDocument21 pagesMendels LawDemi CamsolNo ratings yet
- Test ReviewDocument2 pagesTest Reviewapi-296852092No ratings yet
- 7 Priciple of Genetic 1Document22 pages7 Priciple of Genetic 1beyonduckNo ratings yet
- Learning Competencies: Predict Genotypes and Phenotypes of Parents and Offspring Using The Laws of InheritanceDocument33 pagesLearning Competencies: Predict Genotypes and Phenotypes of Parents and Offspring Using The Laws of InheritanceRichmon AlamanNo ratings yet
- 08 Handout 2Document3 pages08 Handout 2Kent BlazinNo ratings yet
- Session 2.1 Mendel's Laws of InheritanceDocument47 pagesSession 2.1 Mendel's Laws of InheritanceJayas Maria De PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Plant BreedingDocument39 pagesPlant BreedingCRISTY MAE JANDAYANNo ratings yet
- Section 5 Genes and InheritanceDocument100 pagesSection 5 Genes and InheritanceCAYTANO JIMENEZ ARELLYNo ratings yet
- P O I A V: Reason For Selecting Garden Pea PlantDocument22 pagesP O I A V: Reason For Selecting Garden Pea PlantDr. Remya RanjithNo ratings yet
- Geneticbio IDocument40 pagesGeneticbio IRonilyn Dela Cruz TraycoNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics ReviewerDocument9 pagesCytogenetics ReviewerClaire GonoNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Bio400Document16 pages5.2 Bio400m-5243143No ratings yet
- Ch12a Mendelian GeneticsDocument34 pagesCh12a Mendelian Geneticseshu 1No ratings yet
- Genetics Foldables 1Document4 pagesGenetics Foldables 1api-523679344No ratings yet
- Extensions of Mendelian InheritanceDocument30 pagesExtensions of Mendelian InheritanceWONG JIE MIN MoeNo ratings yet
- History of Genetics: GamosDocument5 pagesHistory of Genetics: GamoskenmassNo ratings yet
- Mendelian GeneticsDocument4 pagesMendelian GeneticsArcelle BraganzaNo ratings yet
- Big Words!!: Homozygous Vs Heterozygous Dominant Vs RecessiveDocument5 pagesBig Words!!: Homozygous Vs Heterozygous Dominant Vs RecessiveMarj MendezNo ratings yet
- Mendel's Law of Segregation: 4 3 SemesterDocument37 pagesMendel's Law of Segregation: 4 3 SemesterShaker MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Genetics NotesDocument20 pagesGenetics Noteslebohangcandy8No ratings yet
- Genetics and InheritanceDocument78 pagesGenetics and Inheritanceapi-202349222No ratings yet
- Geneticbio IDocument21 pagesGeneticbio IZainulNo ratings yet
- 3 Genetics Notes - VocabulariespptDocument48 pages3 Genetics Notes - VocabulariespptVickyNo ratings yet
- BIO 2 2nd SemDocument7 pagesBIO 2 2nd SemKelly Misha NoolNo ratings yet
- Inheritance Patterns and Genetic VariationDocument25 pagesInheritance Patterns and Genetic Variationvalentina castilloNo ratings yet
- Principles of Inheritance and VariationDocument33 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance and Variationtghome9988No ratings yet
- Genbio 2 ReviewerDocument8 pagesGenbio 2 ReviewerLarvin Andrei E. BechaydaNo ratings yet
- Mendelian Genetics FullDocument41 pagesMendelian Genetics Fullniranjanyadawad14No ratings yet
- HeredityDocument13 pagesHeredityKristóf KovácsNo ratings yet
- Ch14 LEC Mendel 2016editDocument85 pagesCh14 LEC Mendel 2016editMark Jason EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Introduction To GeneticsDocument4 pagesChapter 4: Introduction To Geneticsnd555No ratings yet
- Unit 1 ADocument58 pagesUnit 1 ANishant MishraNo ratings yet
- 3.4 - InheritanceDocument6 pages3.4 - InheritanceJulieta vazquezNo ratings yet
- Human and Population Genetics: M. K. Tadjudin Fakultas Kedokteran Dan Ilmu Kesehatan UIN Syarif HidayatullahDocument125 pagesHuman and Population Genetics: M. K. Tadjudin Fakultas Kedokteran Dan Ilmu Kesehatan UIN Syarif HidayatullahMaskur Fahmi ÄdibasNo ratings yet
- Advanced GeneticsDocument12 pagesAdvanced GeneticsRose Anne ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- ABO Blood Type WorksheetDocument4 pagesABO Blood Type WorksheetJed MarceloNo ratings yet
- Genetics 1.0 Quick ?Document7 pagesGenetics 1.0 Quick ?Brother's IdiasNo ratings yet
- Multiple AllelesDocument11 pagesMultiple Allelessulha mNo ratings yet
- Classical (Mendelian) GeneticsDocument32 pagesClassical (Mendelian) GeneticsKOMAL FATIMANo ratings yet
- Handout - Hardy Weinberg Practice QuestionsDocument7 pagesHandout - Hardy Weinberg Practice Questionsapi-295865486No ratings yet
- Julianne Mercolita - Activity 9 Gen 2021Document4 pagesJulianne Mercolita - Activity 9 Gen 2021Julianne MercolitaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Notes: Mendel and The Gene IdeaDocument32 pagesChapter 14 Notes: Mendel and The Gene IdeailubtvxqNo ratings yet
- Cyto311 - Lec-Week 9 - Mendelian Genetics Part 2Document3 pagesCyto311 - Lec-Week 9 - Mendelian Genetics Part 2Jayvhie Gulane LayanNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument8 pagesGenetics무루파털뭉치No ratings yet
- 2nd Demo For COT in Science 8Document4 pages2nd Demo For COT in Science 8Rea Christymae Duran100% (2)
- Board Pattern Test-1Document4 pagesBoard Pattern Test-1dakshahirwar0708No ratings yet
- Hardy Weinberg Practice Problem KEY 12-13Document2 pagesHardy Weinberg Practice Problem KEY 12-13DontsArtNo ratings yet
- 2015 Genetics From Genes To Genomes 5th Edition 5th Edition Test BankDocument38 pages2015 Genetics From Genes To Genomes 5th Edition 5th Edition Test Bankzacharyjackson20051996pbd100% (45)
- Station 1 MEIOSIS: Unit 4 Genetics Test ReviewDocument6 pagesStation 1 MEIOSIS: Unit 4 Genetics Test Reviewapi-375285021No ratings yet
- Cot Lesson Plan GeneticsDocument10 pagesCot Lesson Plan GeneticsPrincess Ronquillo - DuqueNo ratings yet
- Sample QnsDocument38 pagesSample Qnsn039No ratings yet
- Punnett Square Practice - Worksheet 2Document4 pagesPunnett Square Practice - Worksheet 2api-502781581No ratings yet
- And Variation Genetics: Heredity: ScienceDocument15 pagesAnd Variation Genetics: Heredity: ScienceMichelle Casayuran - Regala100% (2)
- Mono Hybrid Cross WorksheetDocument1 pageMono Hybrid Cross Worksheetlisah5245No ratings yet
- Dragon Genetics Lab-Part 2 & 3-Remote UlvDocument5 pagesDragon Genetics Lab-Part 2 & 3-Remote UlvstellaNo ratings yet
- G9 Science - Lesson 3 Non Mendelian InheritanceDocument1 pageG9 Science - Lesson 3 Non Mendelian InheritanceClarice Jenn MaltoNo ratings yet
- Module 1.GENETICSDocument10 pagesModule 1.GENETICSamerhasnor pandapatanNo ratings yet
- 2-Mendel's Laws of InheritenceDocument19 pages2-Mendel's Laws of InheritenceSajin Sali100% (1)
- 02genetic 05Document9 pages02genetic 05Hafif0% (1)
- Department of Education: Learning Material in Science 9Document4 pagesDepartment of Education: Learning Material in Science 9Jed MatetNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Genetic Principles in Blood BankingDocument20 pages1.1 Genetic Principles in Blood BankingVermillion ZedNo ratings yet
Adobe Scan 13-Nov-2021
Adobe Scan 13-Nov-2021
Uploaded by
Kruthi BalajiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Adobe Scan 13-Nov-2021
Adobe Scan 13-Nov-2021
Uploaded by
Kruthi BalajiCopyright:
Available Formats
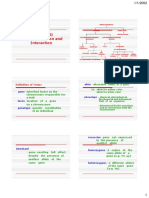
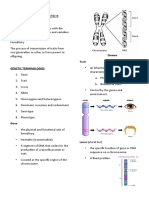
-Seed shape, round and Genetic constituent of
wrinkled
-Seed colour, yellow and green
organisms
Seven contrasting -Flower colour, violet and white
Homozygote- identical pair
traits in Mendel's Pod shape, full and constricted
Genotype of alleles
-Pod colour, green and yellow
experiments -Flower position, axial and
Heterozygote- dissimilar pair:
terminal
-Stem height, tall and dwarf of alleles -.-
- - - - ---
p p
External and morphological
appearance of a tralt
Unit ofinheritance Dominant trat- which is
Genes Responsible for expression Phenotype expressed in both homozygotes
and heterozygotes
ofany trait
Recessive trait- which is only
expressed in homozygotes
Inheritance study of only
one character
Variants of a gene present at
Alleles the same locus on Monohybrid cross Phenotypic ratio- 3:1
homologous chromosomes
Genotypic ratio- 1:2:1
Inheritance study of two
characters
Dihybrid cross Phenotypic ratio- 9:3:3:1 The male and female
Reciprocal cross parents are changed
Genotypic ratio-
1:2:1:2:4:2:1:2:1.
Dominant traitdoes not
p p
completely mask the recessive
Cross of filial1 or Fi trait pP
Back cross Incomplete
heLear
progeny with any parent Fi phenotype does not
resembleany parent, instead,
dominance showsa blending of alleles
Eg. Antirthinum (snapdragon),
Mirabilis jalapa
Cross of Fi progeny with the
recessive homozygous parent More than one alleles for a
gene or character
Test cross Used to determine genotype of Multiple alleles
Fi individual showing dominant E.g. ABO blood group, gene,
phenotype Iexist in three forms
A gene, which controls more
than one characters
Chromosomal theory Sutton and Boveri Pleiotropic genes
of inheritance E.g.A defective gene
causing phenylketonuria
--.
TH Morgan coined theterm When a gene suppresses
Association of genes in close the effect of non-allelic gene
proximity on the same
Linkage chromosomes Epistasis E.g. hair colour and
baldness, wheat kernel
Closely linked genes show low
recombination and mostly colour, coat colour in horses
inherited together
- - - - - - - - - -
Inheritance of a trait Different types of gametes
controlled by many genes produced by males
Polygenic Male heterogamety
inheritance E.g. skin colour, height in E.g. XO in insects, XY in
humans humans and Drosophila
Different types of gametes
Female produced by females
heterogamety E.g. ZW in birds
Colour blindness X-linked recessive
--
Development of an
individual from an App
unfertilised egg
Parthenogenesis E.g. male drones of honey
Haemophilia X-linked recessive
bees contain haploid Lear
chromosomes
Change in the DNA sequence
due to deletion, insertion or
substitution
Autosomal recessive
Point mutation- change in single
Mutation base pair in DNA, e.g. sickle cell
Glu (GAG) changes to
anaemia Sickle-cell anaemia Val (GUG) at the 6th
Frame-shift mutation-due to position codon of B-globin;
deletion or insertion of base chain of haemoglobin
--- Lpairs
Gain of a full set of
Autosomal recessive
chromosomes
Caused by mutation in the gene
Phenylketonuria coding for enzyme
phenylalanine hydroxylase,
Polyploidy Caused when cytokinesis
does not follow karyokinesis
which converts phenylalanine too
tyrosine Common in plants
Autosomal recessive
App
Defective genes for a or B
globin chains of haemoglobin
Down's syndrome Trisomy of 21st
Thalassemia a-Thalassemia- HBA1 and chromosome
HBA2 gene on chromosome 16
B-Thalassemia- gene HBB on
chromosome 11
Loss or gain of an extra
chromosome
Additional X chromosome
Klinefelter's
Caused when chromatids fail to
Aneuploidy segregate during cell division syndrome XXY
E.g. Down's syndrome, Turner's
syndrome, etc.
-
A gene, which controls more:
Monosomy, one of the than one characters
sex chromosome is
Turner's syndrome missing
Pleiotropic genes E.g. A defective gene
causing phenylketonuria
XO
Stable trait inheritance for When a gene suppresses
several generations on self- the effect of non-allelic gene
fertilisation
Epistasis E.g. hair colour and
True breeding plantHomozygous for traits baldness, wheat kernel
colour, coat colour in horses
Produces similar offsprings
on self-fertilisation
Different types of gametes
produced by males
Male heterogamety
E.g. XO in insects, XY in
humans and Drosophila
You might also like
- Biological Science Canadian 2nd Edition Freeman Test Bank 1Document36 pagesBiological Science Canadian 2nd Edition Freeman Test Bank 1conniemcphersonaeporxsmkbNo ratings yet
- Amoeba Sisters Dihybrid FOILDocument1 pageAmoeba Sisters Dihybrid FOILAlejandra Monteagudo ReyzabalNo ratings yet
- Lect 3 Gene Segregation and Interaction PDFDocument10 pagesLect 3 Gene Segregation and Interaction PDFdhonaNo ratings yet
- Chap 5Document11 pagesChap 5Parshvi TyagiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Genetic VariationsDocument8 pagesPrinciples of Genetic VariationsDipangkar SarkarNo ratings yet
- S ENG POI COMPLETE 23 Dec GA SirDocument37 pagesS ENG POI COMPLETE 23 Dec GA SirDave JuneNo ratings yet
- GENETICS - 21.05.21 & 22.05.21 - MASE2 MergedDocument310 pagesGENETICS - 21.05.21 & 22.05.21 - MASE2 MergedHarshit VermaNo ratings yet
- Law of Inheritance and PEDIGREEDocument74 pagesLaw of Inheritance and PEDIGREECharlene SuliganNo ratings yet
- Lec - General Zoology #1Document2 pagesLec - General Zoology #1Nu Ri LeeNo ratings yet
- M1 Introdcution To GeneticsDocument4 pagesM1 Introdcution To GeneticsBrylle Angelo PolintanNo ratings yet
- Terms To Know in Mendelian GeneticsDocument2 pagesTerms To Know in Mendelian GeneticsDoris C. Brucales100% (1)
- Life Sciences Grade 12 Genetics Concepts Virtual Lesson PowerPoint NotesDocument19 pagesLife Sciences Grade 12 Genetics Concepts Virtual Lesson PowerPoint Notescrisseldah1No ratings yet
- 1 GeneticsDocument18 pages1 GeneticssifawanjiNo ratings yet
- Epistasis: XpinkDocument2 pagesEpistasis: XpinkSamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 (Gene Actions)Document32 pagesLecture 1 (Gene Actions)Anil YadavNo ratings yet
- Population Genetics Booklet Y13Document83 pagesPopulation Genetics Booklet Y13hummy18No ratings yet
- Agents of DiseasesDocument3 pagesAgents of DiseasesRaymart DomingoNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Bio CH 3 Inheritance and VariationsDocument21 pagesClass 12 Bio CH 3 Inheritance and VariationsShreyash ApshingeNo ratings yet
- Biology: Genetics & Inheritance III: Genetic Basis For Variation IDocument27 pagesBiology: Genetics & Inheritance III: Genetic Basis For Variation ITimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27Document58 pagesChapter 27Konishko DeyNo ratings yet
- "Mendelian Genetics": General Biology 2 ReviewerDocument5 pages"Mendelian Genetics": General Biology 2 ReviewerFayza Jalil Balading100% (1)
- Cytogen Lesson 1Document3 pagesCytogen Lesson 1STEM-A CHRISTINE TRIBUNALONo ratings yet
- 4 - Q - Genetic InheritanceDocument22 pages4 - Q - Genetic InheritanceNOOR JANNAH FIRDOUSE BINTI ISMAIL KM-Pensyarah100% (1)
- General Biology Genetics, Proteins, Origins of Life & BiotechnologyDocument31 pagesGeneral Biology Genetics, Proteins, Origins of Life & BiotechnologyAlexis Carla GahumanNo ratings yet
- Heredity Class 10 NEETDocument25 pagesHeredity Class 10 NEETPixcasso 21No ratings yet
- HEREDITARYDocument8 pagesHEREDITARYSiti Hajar RevillaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Mendelian Laws of InheritanceDocument31 pagesLecture 1 - Mendelian Laws of InheritancekibzwanjikuNo ratings yet
- Mendels LawDocument21 pagesMendels LawDemi CamsolNo ratings yet
- Test ReviewDocument2 pagesTest Reviewapi-296852092No ratings yet
- 7 Priciple of Genetic 1Document22 pages7 Priciple of Genetic 1beyonduckNo ratings yet
- Learning Competencies: Predict Genotypes and Phenotypes of Parents and Offspring Using The Laws of InheritanceDocument33 pagesLearning Competencies: Predict Genotypes and Phenotypes of Parents and Offspring Using The Laws of InheritanceRichmon AlamanNo ratings yet
- 08 Handout 2Document3 pages08 Handout 2Kent BlazinNo ratings yet
- Session 2.1 Mendel's Laws of InheritanceDocument47 pagesSession 2.1 Mendel's Laws of InheritanceJayas Maria De PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Plant BreedingDocument39 pagesPlant BreedingCRISTY MAE JANDAYANNo ratings yet
- Section 5 Genes and InheritanceDocument100 pagesSection 5 Genes and InheritanceCAYTANO JIMENEZ ARELLYNo ratings yet
- P O I A V: Reason For Selecting Garden Pea PlantDocument22 pagesP O I A V: Reason For Selecting Garden Pea PlantDr. Remya RanjithNo ratings yet
- Geneticbio IDocument40 pagesGeneticbio IRonilyn Dela Cruz TraycoNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics ReviewerDocument9 pagesCytogenetics ReviewerClaire GonoNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Bio400Document16 pages5.2 Bio400m-5243143No ratings yet
- Ch12a Mendelian GeneticsDocument34 pagesCh12a Mendelian Geneticseshu 1No ratings yet
- Genetics Foldables 1Document4 pagesGenetics Foldables 1api-523679344No ratings yet
- Extensions of Mendelian InheritanceDocument30 pagesExtensions of Mendelian InheritanceWONG JIE MIN MoeNo ratings yet
- History of Genetics: GamosDocument5 pagesHistory of Genetics: GamoskenmassNo ratings yet
- Mendelian GeneticsDocument4 pagesMendelian GeneticsArcelle BraganzaNo ratings yet
- Big Words!!: Homozygous Vs Heterozygous Dominant Vs RecessiveDocument5 pagesBig Words!!: Homozygous Vs Heterozygous Dominant Vs RecessiveMarj MendezNo ratings yet
- Mendel's Law of Segregation: 4 3 SemesterDocument37 pagesMendel's Law of Segregation: 4 3 SemesterShaker MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Genetics NotesDocument20 pagesGenetics Noteslebohangcandy8No ratings yet
- Genetics and InheritanceDocument78 pagesGenetics and Inheritanceapi-202349222No ratings yet
- Geneticbio IDocument21 pagesGeneticbio IZainulNo ratings yet
- 3 Genetics Notes - VocabulariespptDocument48 pages3 Genetics Notes - VocabulariespptVickyNo ratings yet
- BIO 2 2nd SemDocument7 pagesBIO 2 2nd SemKelly Misha NoolNo ratings yet
- Inheritance Patterns and Genetic VariationDocument25 pagesInheritance Patterns and Genetic Variationvalentina castilloNo ratings yet
- Principles of Inheritance and VariationDocument33 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance and Variationtghome9988No ratings yet
- Genbio 2 ReviewerDocument8 pagesGenbio 2 ReviewerLarvin Andrei E. BechaydaNo ratings yet
- Mendelian Genetics FullDocument41 pagesMendelian Genetics Fullniranjanyadawad14No ratings yet
- HeredityDocument13 pagesHeredityKristóf KovácsNo ratings yet
- Ch14 LEC Mendel 2016editDocument85 pagesCh14 LEC Mendel 2016editMark Jason EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Introduction To GeneticsDocument4 pagesChapter 4: Introduction To Geneticsnd555No ratings yet
- Unit 1 ADocument58 pagesUnit 1 ANishant MishraNo ratings yet
- 3.4 - InheritanceDocument6 pages3.4 - InheritanceJulieta vazquezNo ratings yet
- Human and Population Genetics: M. K. Tadjudin Fakultas Kedokteran Dan Ilmu Kesehatan UIN Syarif HidayatullahDocument125 pagesHuman and Population Genetics: M. K. Tadjudin Fakultas Kedokteran Dan Ilmu Kesehatan UIN Syarif HidayatullahMaskur Fahmi ÄdibasNo ratings yet
- Advanced GeneticsDocument12 pagesAdvanced GeneticsRose Anne ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- ABO Blood Type WorksheetDocument4 pagesABO Blood Type WorksheetJed MarceloNo ratings yet
- Genetics 1.0 Quick ?Document7 pagesGenetics 1.0 Quick ?Brother's IdiasNo ratings yet
- Multiple AllelesDocument11 pagesMultiple Allelessulha mNo ratings yet
- Classical (Mendelian) GeneticsDocument32 pagesClassical (Mendelian) GeneticsKOMAL FATIMANo ratings yet
- Handout - Hardy Weinberg Practice QuestionsDocument7 pagesHandout - Hardy Weinberg Practice Questionsapi-295865486No ratings yet
- Julianne Mercolita - Activity 9 Gen 2021Document4 pagesJulianne Mercolita - Activity 9 Gen 2021Julianne MercolitaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Notes: Mendel and The Gene IdeaDocument32 pagesChapter 14 Notes: Mendel and The Gene IdeailubtvxqNo ratings yet
- Cyto311 - Lec-Week 9 - Mendelian Genetics Part 2Document3 pagesCyto311 - Lec-Week 9 - Mendelian Genetics Part 2Jayvhie Gulane LayanNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument8 pagesGenetics무루파털뭉치No ratings yet
- 2nd Demo For COT in Science 8Document4 pages2nd Demo For COT in Science 8Rea Christymae Duran100% (2)
- Board Pattern Test-1Document4 pagesBoard Pattern Test-1dakshahirwar0708No ratings yet
- Hardy Weinberg Practice Problem KEY 12-13Document2 pagesHardy Weinberg Practice Problem KEY 12-13DontsArtNo ratings yet
- 2015 Genetics From Genes To Genomes 5th Edition 5th Edition Test BankDocument38 pages2015 Genetics From Genes To Genomes 5th Edition 5th Edition Test Bankzacharyjackson20051996pbd100% (45)
- Station 1 MEIOSIS: Unit 4 Genetics Test ReviewDocument6 pagesStation 1 MEIOSIS: Unit 4 Genetics Test Reviewapi-375285021No ratings yet
- Cot Lesson Plan GeneticsDocument10 pagesCot Lesson Plan GeneticsPrincess Ronquillo - DuqueNo ratings yet
- Sample QnsDocument38 pagesSample Qnsn039No ratings yet
- Punnett Square Practice - Worksheet 2Document4 pagesPunnett Square Practice - Worksheet 2api-502781581No ratings yet
- And Variation Genetics: Heredity: ScienceDocument15 pagesAnd Variation Genetics: Heredity: ScienceMichelle Casayuran - Regala100% (2)
- Mono Hybrid Cross WorksheetDocument1 pageMono Hybrid Cross Worksheetlisah5245No ratings yet
- Dragon Genetics Lab-Part 2 & 3-Remote UlvDocument5 pagesDragon Genetics Lab-Part 2 & 3-Remote UlvstellaNo ratings yet
- G9 Science - Lesson 3 Non Mendelian InheritanceDocument1 pageG9 Science - Lesson 3 Non Mendelian InheritanceClarice Jenn MaltoNo ratings yet
- Module 1.GENETICSDocument10 pagesModule 1.GENETICSamerhasnor pandapatanNo ratings yet
- 2-Mendel's Laws of InheritenceDocument19 pages2-Mendel's Laws of InheritenceSajin Sali100% (1)
- 02genetic 05Document9 pages02genetic 05Hafif0% (1)
- Department of Education: Learning Material in Science 9Document4 pagesDepartment of Education: Learning Material in Science 9Jed MatetNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Genetic Principles in Blood BankingDocument20 pages1.1 Genetic Principles in Blood BankingVermillion ZedNo ratings yet