Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ST - John'S School, Greater Noida West Class IX Science
ST - John'S School, Greater Noida West Class IX Science
Uploaded by
India Tech with AstitvaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ST - John'S School, Greater Noida West Class IX Science
ST - John'S School, Greater Noida West Class IX Science
Uploaded by
India Tech with AstitvaCopyright:
Available Formats
ST.
JOHN’S SCHOOL,
Greater Noida West
Class IX
Science
CHAPTER 6
TISSUES ( Intext and back exercise)
1: What is a tissue?
Ans: Tissue is a group of cells that are similar in structure and are organised together to perform a specific
task.
2: What is the utility of tissues in multi-cellular organisms?
Ans: In unicellular organisms, a single cell performs all the basic functions such as respiration, movement,
excretion, digestion, etc. But in multicellular organisms, cells are grouped to form tissues. These tissues are
specialised to carry out a particular function at a definite place in the body. For example, the muscle cells
form muscular tissues which helps in movement, nerve cells form the nervous tissue which helps in
transmission of messages. This is known as division of labour in multicellular organisms. It is because of
this division of labour that multicellular organisms are able to perform all functions efficiently.
1: Name types of simple tissues.
Ans: Simple permanent tissues are of three types:
1. Parenchyma,
2. Collenchyma,
3.Sclerenchyma.
Parenchyma tissue is of further two types
1. Aerenchyma
2. chlorenchyma.
2: Where is apical meristem found?
Ans: Apical meristem is present at the growing tips of stems and roots. Their main function is to initiate
growth in new cells of seedlings, at the tip of roots, and shoots.
3: Which tissue makes up the husk of coconut?
Ans: The husk of a coconut is made up of sclerenchyma tissue.
4: What are the constituents of phloem?
Ans: Phloem is the food conducting tissue in plants. It is made up of four components:
(i) Sieve tubes
(ii) Companion cells
(iii) Phloem parenchyma
(iv) Phloem fibres
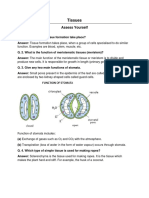
1: Name the tissue responsible for movement in our body.
Ans: The muscular tissue is responsible for movement in our body.
2:What does a neuron look like?
Ans: A neuron consists of a cell body with a nucleus and cytoplasm. It has two important extensions
known as the axon and dendrites. An axon is a long thread-like extension of nerve cells that transmits
impulses away from the cell body. Dendrites, on the other hand, are thread-like extensions of cell body that
receive nerve impulses. Thus, the axon transmits impulses away from the cell body, whereas the dendrite
receives nerve impulses. This coordinated function helps in transmitting impulses very quickly.
Nerve cell
3: Give three features of cardiac muscles.
Ans: Three features of cardiac muscles are:
(i) Cardiac muscles are involuntary muscles that contract rapidly, but do not get fatigued.
(ii) The cells of cardiac muscles are cylindrical, branched, and uninucleate.
(iii) They control the contraction and relaxation of the heart.
4: What are the functions of areolar tissue?
Ans: Functions of areolar tissue:
(i) It helps in supporting internal organs.
(ii) It helps in repairing the tissues of the skin and muscles.
BACK EXERCISE (Animal Tissues)
Question 6:
Diagrammatically show the difference between the three types of muscle fibres.
Ans: The three types of muscle fibres are: Striated muscles, smooth muscles (unstriated muscle fibre), and
cardiac muscles.
Striated muscle fibres Unstriated muscle fibres
Cardiac muscle fibres
Question 7:
What is the specific function of the cardiac muscle?
Ans: The specific function of the cardiac muscle is to control the contraction and relaxation of the heart.
Question 8:
Differentiate between striated, unstriated and cardiac muscles on the basis of their structure and
site/location in the body.
Ans:
Striated muscle Unstriated muscle Cardiac muscle
On the basis of structure:
Cells are cylindrical Cells are long Cells are cylindrical
Cells are not branched Cells are not branched Cells are branched
Cells are multinucleate Cells are uninucleate Cells are uninucleate
Alternate light and dark There are no bands present Faint bands are present
bands are present
Its ends are blunt Its ends are tapering Its ends are flat and wavy
On the basis of location:
These muscles are present in These muscles control the These muscles control the
body parts such as hands, movement of food in the contraction and relaxation of
legs, tongue, etc. alimentary canal, the the heart
contraction and relaxation of
blood vessels, etc.
Question 9:
Draw a labelled diagram of a neuron.
Ans:
Structure of a neuron
Question 10:
Name the following:
(a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth.
(b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans.
(c) Tissue that transports food in plants.
(d) Tissue that stores fat in our body.
(e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix.
(f) Tissue present in the brain.
Ans:
(a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth → Epithelial tissue
(b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans → Tendons
(c) Tissue that transports food in plants → Phloem
(d) Tissue that stores fat in our body → Adipose tissue
(e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix → Blood
(f) Tissue present in the brain → Nervous tissue
Question 11:
Identify the type of tissue in the following: bone, lining of kidney tubule
Ans:
Bone: Connective tissue
Lining of kidney tubule: Cuboidal epithelial tissue
You might also like
- Human Body StructureDocument72 pagesHuman Body Structuredeepak dwivedi94% (16)
- Chapter 6 BiologyDocument8 pagesChapter 6 BiologyMohammed mahfuzNo ratings yet
- PD 4 WJ SBJ UE7 XAASH4 U KZDocument11 pagesPD 4 WJ SBJ UE7 XAASH4 U KZPrincy GuptaNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument11 pagesTissuesManveethNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 - Tissues - .Document9 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 - Tissues - .AshchatNo ratings yet
- 9 Science Imp ch6 3Document8 pages9 Science Imp ch6 3deepakNo ratings yet
- Aakash Institute: NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 TissuesDocument13 pagesAakash Institute: NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 TissuesNischay MahamanaNo ratings yet
- Tissues Solved Examples Solved Example ICSE 0213445d 59d1 4ef6 9586 3cf7638047b9Document5 pagesTissues Solved Examples Solved Example ICSE 0213445d 59d1 4ef6 9586 3cf7638047b9akanksha0102guptaNo ratings yet
- Tissue Mat PDFDocument13 pagesTissue Mat PDFAyushman TripathyNo ratings yet
- Tissues Notes Class IxDocument7 pagesTissues Notes Class Ixishaan singhNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On TissuesDocument5 pagesWorksheet On TissuesBryan AmoresNo ratings yet
- Exercise-6.1: NCERT Solution For Class 9 Science - Chapter 6 TissuesDocument9 pagesExercise-6.1: NCERT Solution For Class 9 Science - Chapter 6 TissuesShah RukhNo ratings yet
- CHAPTERDocument5 pagesCHAPTERmustafasamim518No ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument14 pagesAnimal Tissuesjitendragandhi250No ratings yet
- TissueDocument6 pagesTissuers6xhffn49No ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Type: AnswerDocument15 pagesMultiple Choice Type: Answeranisur198287No ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Gen BioDocument4 pagesLesson 4 Gen Biokookie bunnyNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4. AnswersDocument5 pagesExperiment 4. AnswersChristian Roy CNo ratings yet
- Class 9TH Biology TissueDocument4 pagesClass 9TH Biology TissueChirag KashyapNo ratings yet
- MAHANDocument9 pagesMAHANKANT JAMES D. MAHANNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues NotesDocument9 pagesAnimal Tissues Notesvedantgodbole9No ratings yet
- Tissue Solutions Textual Questions and Answers: Is Called A TissueDocument11 pagesTissue Solutions Textual Questions and Answers: Is Called A TissueMr Pan GamingNo ratings yet
- 3 Animal Tissues Structure and FunctionDocument16 pages3 Animal Tissues Structure and FunctionIce ShadowNo ratings yet
- Section and ChapDocument3 pagesSection and ChapJISAS CLIMAXNo ratings yet
- Chapter Science-9 CombinedDocument20 pagesChapter Science-9 CombinedAnushkaNo ratings yet
- Samarjeet FA-1 Activity ScienceDocument16 pagesSamarjeet FA-1 Activity ScienceSamarjeet BaliyanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan (Animal Tissues)Document9 pagesLesson Plan (Animal Tissues)Gomez Agustin Leslie100% (1)
- Chapter 7th TissueDocument6 pagesChapter 7th Tissuenakulvyan708No ratings yet
- Cell Types and Cell Modification: LessonDocument6 pagesCell Types and Cell Modification: Lessonjoshiah glennNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues: TissueDocument4 pagesAnimal Tissues: TissuePrasad SwaminathanNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY TISSUE NOTESpdfDocument30 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY TISSUE NOTESpdfYego EdwinNo ratings yet
- Pines City Colleges Medical Laboratory Science Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory ManualDocument9 pagesPines City Colleges Medical Laboratory Science Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory ManualLynch Devin Kirtug-SalengNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document7 pagesModule 3fiids.castroNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument13 pagesAnimal TissuescbseiscNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 4 Module Cell Types and Cell ModificationsDocument7 pagesActivity No. 4 Module Cell Types and Cell ModificationsAryan Jovic DomingoNo ratings yet
- Tissues CLASS 9 CBSEDocument11 pagesTissues CLASS 9 CBSEAdvait Abraham AbhilashNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet 4 Classification of Tissues A28 Group1Document6 pagesWork Sheet 4 Classification of Tissues A28 Group1Japet Floyd Alipio100% (1)
- Tissues Class 9Document13 pagesTissues Class 9Richa Nawani KaushikNo ratings yet
- Name: House: Study Questions: The Skeletal SystemDocument2 pagesName: House: Study Questions: The Skeletal SystemCharlie HorowitzNo ratings yet
- Science 6 TG q2Document112 pagesScience 6 TG q2Pinaka ShungaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 Module 4Document26 pagesGen Bio 1 Module 4AQUINO JAYSON KIERNo ratings yet
- What Is A Tissue? Ans:: Class: 9 (Science) Tissues Chapter - 2Document21 pagesWhat Is A Tissue? Ans:: Class: 9 (Science) Tissues Chapter - 2The Silent RepentantNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues: Epithelial Tissue Is Made Up of Layers of Tightly Packed Cells That Line The SurfacesDocument3 pagesAnimal Tissues: Epithelial Tissue Is Made Up of Layers of Tightly Packed Cells That Line The SurfacesJamesNo ratings yet
- DLP Format 1ST Cot 2020 2021Document4 pagesDLP Format 1ST Cot 2020 2021Dione Patrick MiñozaNo ratings yet
- Tissues: Assess YourselfDocument16 pagesTissues: Assess YourselfGamer JiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledJonathan (Jonny)No ratings yet
- Selina Concise Biology Solutions Class 7 Chapter 1 Plant and Animal TissuesDocument12 pagesSelina Concise Biology Solutions Class 7 Chapter 1 Plant and Animal TissuesAKSHAJ AGGARWALNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE - 6 - TG - Q2.docx Filename - UTF-8''SCIENCE 6 TG Q2Document103 pagesSCIENCE - 6 - TG - Q2.docx Filename - UTF-8''SCIENCE 6 TG Q2אנג' ליקהNo ratings yet
- 9th Bio MTG Tissue QuesDocument13 pages9th Bio MTG Tissue QuesData ShareNo ratings yet
- Competency 11Document26 pagesCompetency 11Charis RebanalNo ratings yet
- Tissues - NotesDocument14 pagesTissues - Notesphysicsbooks.storeNo ratings yet
- Class 9 - CH6 TissuesDocument9 pagesClass 9 - CH6 Tissuesv.nikolikjNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Musculo-Skeletal System Q2, Week 1Document8 pagesLesson 1: Musculo-Skeletal System Q2, Week 1Grace Micah Dayucos CaisioNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument5 pagesAnimal TissueRoopaNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Science CH 6Document7 pagesClass 9 Science CH 6Priyanka PanwarNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions for Class 9 March 28 Science Chapter 6 Tissues CompressedDocument11 pagesNcert Solutions for Class 9 March 28 Science Chapter 6 Tissues Compressedcdiya9463No ratings yet
- Tissue ClassworkDocument5 pagesTissue ClassworkRajesh Kanna A亗No ratings yet
- Module 2 AnaphysioDocument32 pagesModule 2 AnaphysioJomarie RamirezNo ratings yet
- ST - John'S School Greater Noida West Subject: Science CLASS IX: BIOLOGY (2020 - 21) Chapter - 6 Tissues (Answer Key - 2)Document6 pagesST - John'S School Greater Noida West Subject: Science CLASS IX: BIOLOGY (2020 - 21) Chapter - 6 Tissues (Answer Key - 2)India Tech with AstitvaNo ratings yet
- Very Short Answer Type Questions Class IXDocument4 pagesVery Short Answer Type Questions Class IXIndia Tech with AstitvaNo ratings yet
- Class Viii ASSIGNMENT 1 (Answer Key)Document3 pagesClass Viii ASSIGNMENT 1 (Answer Key)India Tech with AstitvaNo ratings yet
- Word 2010 Tutorial 8 1Document20 pagesWord 2010 Tutorial 8 1India Tech with AstitvaNo ratings yet
- St. John'S School Greater Noida WestDocument2 pagesSt. John'S School Greater Noida WestIndia Tech with AstitvaNo ratings yet
- St. John'S School Greater Noida WestDocument3 pagesSt. John'S School Greater Noida WestIndia Tech with AstitvaNo ratings yet
- Class 8 History Chapter1 Part1 NotesDocument3 pagesClass 8 History Chapter1 Part1 NotesIndia Tech with AstitvaNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Hist Rebel NotesDocument4 pagesClass 8 Hist Rebel NotesIndia Tech with Astitva100% (1)
- Class 8 History Chapter1 Assignment SheetDocument1 pageClass 8 History Chapter1 Assignment SheetIndia Tech with Astitva100% (1)
- Class 8 Judiciary Assignment Sheet AnswersDocument3 pagesClass 8 Judiciary Assignment Sheet AnswersIndia Tech with Astitva50% (2)
- Athletics Track EventDocument6 pagesAthletics Track EventIndia Tech with AstitvaNo ratings yet
- It So Happened Notes CH.2 Children at WorkDocument1 pageIt So Happened Notes CH.2 Children at WorkIndia Tech with AstitvaNo ratings yet
- St. John'S School Greater Noida West: Chapter-1 Crop Production and Management Date Notes Subject-Science Class-ViiiDocument3 pagesSt. John'S School Greater Noida West: Chapter-1 Crop Production and Management Date Notes Subject-Science Class-ViiiIndia Tech with AstitvaNo ratings yet
- Alai DarwazaDocument1 pageAlai DarwazaIndia Tech with Astitva0% (1)
- St. John'S School Greater Noida WestDocument3 pagesSt. John'S School Greater Noida WestIndia Tech with AstitvaNo ratings yet
- St. John'S School Greater Noida West CLASS: VIII-A (2020 - 21) Subject - Science Chapter - 3 Synthetic Fibres and PlasticsDocument6 pagesSt. John'S School Greater Noida West CLASS: VIII-A (2020 - 21) Subject - Science Chapter - 3 Synthetic Fibres and PlasticsIndia Tech with AstitvaNo ratings yet
- St. John'S School Greater Noida WestDocument3 pagesSt. John'S School Greater Noida WestIndia Tech with AstitvaNo ratings yet
- A Cell Crossword PuzzleDocument2 pagesA Cell Crossword PuzzleRichelyn Che0% (1)
- All About NailDocument40 pagesAll About NailChrizzieTaasanNo ratings yet
- CattleDocument3 pagesCattleNatalia Lopez RobredoNo ratings yet
- Ion AmpliSeq Cancer Hotspot Panel FlyerDocument2 pagesIon AmpliSeq Cancer Hotspot Panel FlyerAt ManeNo ratings yet
- 1983 - Jenkins. Revision of Hamadryas. Bul Allyn MusDocument146 pages1983 - Jenkins. Revision of Hamadryas. Bul Allyn MusArturo R M PérezNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit OutlineDocument56 pagesBiology Unit OutlineSreeya DasNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Notes - SLU Lictag FrancesDocument49 pagesParasitology Notes - SLU Lictag FrancesJmarc JubiladoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System & Major Organs (1-4)Document6 pagesEndocrine System & Major Organs (1-4)april lou andrea sorillaNo ratings yet
- Cells 08 01419Document35 pagesCells 08 01419dzaky fadhilNo ratings yet
- Y-8 RespirationDocument29 pagesY-8 Respirationsamor20102002No ratings yet
- ReferencesDocument62 pagesReferencesCaleb NyamoraNo ratings yet
- PBH Requirements PDFDocument2 pagesPBH Requirements PDFAyat HasanNo ratings yet
- Activity 4. Culture Media PreparationDocument4 pagesActivity 4. Culture Media PreparationRoan Eam TanNo ratings yet
- 8.3 Worksheet KEY-7Document3 pages8.3 Worksheet KEY-7Jordan EspirituNo ratings yet
- Helichrysum Umbreculigerum Better Than CBDDocument373 pagesHelichrysum Umbreculigerum Better Than CBDAthina Margatina100% (1)
- Cellrespphotopuzzle Pre ApDocument2 pagesCellrespphotopuzzle Pre Apapi-155864611No ratings yet
- R Hsa 69173Document3 pagesR Hsa 69173zzrot1No ratings yet
- Good Food Label Worksheet - Angie 2012Document3 pagesGood Food Label Worksheet - Angie 2012Dwi SuprionoNo ratings yet
- Chaos Theory, Evolution and The CreationDocument39 pagesChaos Theory, Evolution and The CreationDennis MurphyNo ratings yet
- Student Project: Applications of Exponential Functions: Pure Mathematics 30Document8 pagesStudent Project: Applications of Exponential Functions: Pure Mathematics 30Pie PeyNo ratings yet
- GENBIO2 - Lesson - The Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument2 pagesGENBIO2 - Lesson - The Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyJazmaine SimbulanNo ratings yet
- Dot Blot ProtocolDocument2 pagesDot Blot ProtocolSuki BlytheNo ratings yet
- ArticuloDocument7 pagesArticuloCarlosGuevaraPáezNo ratings yet
- Probiotic Strains in American Probiotic ProductsDocument2 pagesProbiotic Strains in American Probiotic ProductsexpandNo ratings yet
- Filedate - 468download Ebook Biological Macromolecules Bioactivity and Biomedical Applications PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesFiledate - 468download Ebook Biological Macromolecules Bioactivity and Biomedical Applications PDF Full Chapter PDFnancy.budzynski543100% (35)
- Electro-Chemiluminescence Immunoassay (ECLIA) For The in Vitro Quantitative Determination of Total Triiodothyronine in Serum and PlasmaDocument2 pagesElectro-Chemiluminescence Immunoassay (ECLIA) For The in Vitro Quantitative Determination of Total Triiodothyronine in Serum and PlasmaNkimsearNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Review On Metabolic SyndromeDocument36 pagesA Comprehensive Review On Metabolic SyndromekotraeNo ratings yet
- Worksheet: Cellular Respiration & Cell EnergyDocument4 pagesWorksheet: Cellular Respiration & Cell Energyclaryl alexaNo ratings yet
- BIOL200 Midterm Review Session 2022WT1 - V2Document72 pagesBIOL200 Midterm Review Session 2022WT1 - V2Parveen BrarNo ratings yet
- BMSC 230 Online Quizzes Module 4-6Document12 pagesBMSC 230 Online Quizzes Module 4-6Brennan J.G. Kumitch0% (1)