Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 1 Differential Equations Intro
Lesson 1 Differential Equations Intro
Uploaded by
eulaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 1 Differential Equations Intro
Lesson 1 Differential Equations Intro
Uploaded by
eulaCopyright:
Available Formats
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
Independent
(ODE/PDE)
Non-linear
Dependent
variable
variable
Linear/
Degree
Order
Type
- is an equation that contains an unknown function and some of Given
its derivatives.
- is an equation that involves one or more derivates, or 1. ( x − 1) dy + sin ydx = 0
differentials. d 2x dx
2. 2
− 6x2 = 2 xy 3
dy dy
Linear Differential Equations
z z
3. y 2 + ( 2 x − 5) = e −2 x +1
- are those in w/c the dependent variable and its derivatives x y
occur in the 1st degree and are not multiplied together. d 4x d 2x
3
4. 3 4 + x 2 2 − 5 y = 0
dy dy
General Linear Equation of the nth order
5. 5 xy '− 1 = 1 + 3 y '''
n n −1 n−2 3
d y d y d y t 2t
P0 ( x ) + P1 ( x ) n −1 + P2 ( x ) n − 2 + ... + Pn ( x ) y = R ( x )
2
dx n
dx dx 6. 4 − 7 2 = 0
where P0 , P1 , P2 ,..., Pn and R are function of x only.
ELIMINATION OF ARBITRARY CONSTANTS
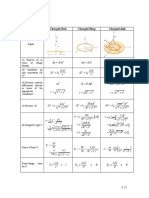
Types of Differential equation
RULES
1. Ordinary differential equation (ODE) – is that in w/c all the 1. The number of differentiating the given equation is the same as
differential coefficients have reference to a single independent the number of arbitrary constants to be eliminated.
variable. 2. The order of the differential equation is the same as the number of
arbitrary constant present in the equation.
2. Partial differential equation (PDE) – is that in w/c there are two or 3. The desired equation is free from arbitrary constants.
more independent variables and partial differential coefficients
with respect to any of them. Example
1. Eliminate c from the equation c ( y − 3x ) = e−2 x
Degree and Order of Differential equation
2. Eliminate c1 and c2 c from the equation 2. y = c1e −4 x + c2 e 3 x
The order of a differential equation is the order of the highest 3. Eliminate c1 and c2 c from the equation y = c1 cos 3 x + c2 sin 3 x + e x
derivative that occurs in the equation. 4. Find the solution to sin ( cx − y ) = 2 x free from c.
5. Eliminate d and k from equation 3x 2 − ( y − k ) = d 2 .
2
The degree of a differential equation is the exponent of the highest
power of the highest order derivative, after the equation has been cleared 6. Eliminate a from equation e a sin 3 x = cos 2 y .
of fractions & radicals in the dependent variable and its derivatives.
Prepared by: R. C. RIVERA, M.Sc.
Classify of the following equations according to their
You might also like
- Ode Ie Cov Balwan SirDocument229 pagesOde Ie Cov Balwan SirRrq HolitosNo ratings yet
- Component-Based Reduced Basis Simulations: White PaperDocument16 pagesComponent-Based Reduced Basis Simulations: White PaperJ T Mendonça SantosNo ratings yet
- Ordinary Diff Erential Equations: Chapter HighlightsDocument25 pagesOrdinary Diff Erential Equations: Chapter HighlightsPRABHAKAR KUMARNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations Review MaterialDocument5 pagesDifferential Equations Review MaterialIsmael SalesNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document34 pagesUnit 3Eren YeagerNo ratings yet
- Differential EqnsDocument61 pagesDifferential Eqnssnehaagarwal0411No ratings yet
- Aimstutorial (VSAQ)Document4 pagesAimstutorial (VSAQ)SalmanAnjansNo ratings yet
- Análisis Sistemas Electromagnéticos en Ingeniería de ProcesosDocument2 pagesAnálisis Sistemas Electromagnéticos en Ingeniería de ProcesosMariana García BarradasNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations - Mind MapsDocument2 pagesDifferential Equations - Mind MapsHarsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- DE For EEDocument6 pagesDE For EEPaul Simon NacisNo ratings yet
- Maths II PDFDocument88 pagesMaths II PDFRohit KumarNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2019-20 MAT1011 ETH VL2019201005249 Reference Material II 19-Sep-2019 Solved-Problems Double-and-Triple-Integrals-2 PDFDocument18 pagesFALLSEM2019-20 MAT1011 ETH VL2019201005249 Reference Material II 19-Sep-2019 Solved-Problems Double-and-Triple-Integrals-2 PDFabhist chuhan100% (1)
- Differential EquationsDocument12 pagesDifferential EquationsJoshua Carlo EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Ma1512 Cheatsheet Summary Differential Equations For EngineeringDocument4 pagesMa1512 Cheatsheet Summary Differential Equations For EngineeringDennis SorianoNo ratings yet
- Analysis in Several Variables II ExamDocument9 pagesAnalysis in Several Variables II ExamDiegoNo ratings yet
- 3 8 Solved ProblemsDocument1 page3 8 Solved ProblemsJim Lee LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 2Document88 pagesMathematics 2avsharma7777No ratings yet
- IntegrationDocument7 pagesIntegrationapi-516387140No ratings yet
- Implicit Differentiation HandoutDocument3 pagesImplicit Differentiation HandoutFuck youNo ratings yet
- Differential EquationsDocument69 pagesDifferential EquationsMohammed ShameeriNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 2Document88 pagesMathematics 2Hui HuiNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument4 pages1 IntroductiongmbnlykamaeNo ratings yet
- 1lecture NotesDocument67 pages1lecture Notessamuel_07No ratings yet
- Introduction To Differential EquationsDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Differential EquationsGeanno PolinagNo ratings yet
- Intro DEDocument17 pagesIntro DEGeanno PolinagNo ratings yet
- Ac Slidesp2Document418 pagesAc Slidesp2Mert DUMANNo ratings yet
- DifferentialDocument52 pagesDifferentialEric Justin Tan CarreonNo ratings yet
- Integral GaussianaDocument2 pagesIntegral GaussianaPalacios Rivera Miguel de JesúsNo ratings yet
- Apendice Factores de FormaDocument11 pagesApendice Factores de FormaNicolasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Differential EquationDocument43 pagesIntroduction To Differential EquationSufi TechNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 2 Quantum 40 Slashbyte 41Document90 pagesMathematics 2 Quantum 40 Slashbyte 41ANAS KHANNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Ordinary Differential Equations: Dr. Waqas Aleem Assistant Professor (MNS-UET, Multan)Document12 pagesIntroduction To Ordinary Differential Equations: Dr. Waqas Aleem Assistant Professor (MNS-UET, Multan)Sehry SyedNo ratings yet
- Soln Final Math154 2010Document5 pagesSoln Final Math154 2010yasemin güneytepeNo ratings yet
- chpt.1 OdeDocument23 pageschpt.1 OdesaisreeNo ratings yet
- Theme 5 - 1 Notes DifferentiationDocument20 pagesTheme 5 - 1 Notes Differentiationxhxjjvzt2fNo ratings yet
- L. Euler. The Transformation of Certain Differential Equations, Which Do Not Permit The Separation of VariablesDocument5 pagesL. Euler. The Transformation of Certain Differential Equations, Which Do Not Permit The Separation of VariablesJorgeGrajalesRiveraNo ratings yet
- 2nd Exam D.E.1 NotesDocument4 pages2nd Exam D.E.1 NotesVince Carlo C GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chap 01Document79 pagesChap 01Muhammad HamzaNo ratings yet
- MIT Int Bee 2025 Mock ProblemsDocument6 pagesMIT Int Bee 2025 Mock Problemsfarsamuels183No ratings yet
- Differential Equation ModuleDocument3 pagesDifferential Equation Modulemark jefferson castroNo ratings yet
- Pde 240509154448 9589657aDocument20 pagesPde 240509154448 9589657adrfrehmanNo ratings yet
- DE 1.2 Elimination of Arbitrary ConstantsDocument14 pagesDE 1.2 Elimination of Arbitrary ConstantsJewel Janine LlanesNo ratings yet
- Differential EquationsDocument30 pagesDifferential EquationsParminder singh parmarNo ratings yet
- 3 8 Solved Problems PDFDocument1 page3 8 Solved Problems PDFEli m. paredesNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 First Order Differential EquationsDocument49 pagesCHAPTER 4 First Order Differential EquationsPaih DtNo ratings yet
- B.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering Mathematics-IDocument15 pagesB.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering Mathematics-IDarshil GalaiyaNo ratings yet
- Differential CoefficientsDocument4 pagesDifferential CoefficientsVedika ShahNo ratings yet
- Eng Math 501e - 2011 2012 Fall - Week1 - Applications PDFDocument2 pagesEng Math 501e - 2011 2012 Fall - Week1 - Applications PDFcherkessNo ratings yet
- Unit # 01 (Part - I) : JEE-PhysicsDocument11 pagesUnit # 01 (Part - I) : JEE-PhysicsgauravNo ratings yet
- Business Mathematics: Definations 1. VariablesDocument20 pagesBusiness Mathematics: Definations 1. Variablesتنویر منیرNo ratings yet
- Week 14 (Part 4) - Integrals Yielding Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsDocument12 pagesWeek 14 (Part 4) - Integrals Yielding Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsqweqweNo ratings yet
- Ordinary Differential Equation: Second YearDocument23 pagesOrdinary Differential Equation: Second Yearخيرالله عبد حسين محمدNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Differential EquationsDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Differential EquationsEricka Mae FedereNo ratings yet
- Differential Eqn.Document22 pagesDifferential Eqn.Vinaya AnilNo ratings yet
- ExerciseDocument3 pagesExerciseThùy Dung TrầnNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document23 pagesWeek 1吉利蘇No ratings yet
- GaussianWavepacket PDFDocument5 pagesGaussianWavepacket PDFMonte CarloNo ratings yet
- Sol T2Document2 pagesSol T2Sohini RoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document67 pagesChapter 3Bexultan MustafinNo ratings yet
- Maths IIDocument88 pagesMaths IIAnish Kushwaha (Anshu)No ratings yet
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Neisseria and Moraxella - HANDOUTSDocument10 pagesNeisseria and Moraxella - HANDOUTSeulaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Families of CurveDocument16 pagesLesson 2 Families of CurveeulaNo ratings yet
- Linear Equations of The First OrderDocument1 pageLinear Equations of The First OrdereulaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document5 pagesChapter 4eulaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document5 pagesChapter 4eulaNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Science in Electronics Engineering (Bsece) : Program DescriptionDocument13 pagesBachelor of Science in Electronics Engineering (Bsece) : Program DescriptioneulaNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Modeling of Melting and Freezing Processes PDFDocument34 pagesMathematical Modeling of Melting and Freezing Processes PDFAjit KambleNo ratings yet
- Stability Theory (Math45031/65031) : Dr. Joel Daou University of Manchester First Semester 2021/22Document69 pagesStability Theory (Math45031/65031) : Dr. Joel Daou University of Manchester First Semester 2021/22Achuan ChenNo ratings yet
- MENG4391 SyllabusDocument3 pagesMENG4391 SyllabusThanh PhanNo ratings yet
- UnitDocument93 pagesUnitprasanthwong100% (1)
- Tutorialsheet 01 PDFDocument2 pagesTutorialsheet 01 PDFsanjay_dutta_5No ratings yet
- 01 - European Option Under Stochastic Interest Rate and Local VolatilityDocument21 pages01 - European Option Under Stochastic Interest Rate and Local VolatilityAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Niraj Kumar: Study of Sloshing Effects in A Cylindrical Tank With and Without Baffles Under Linear AccelerationDocument31 pagesNiraj Kumar: Study of Sloshing Effects in A Cylindrical Tank With and Without Baffles Under Linear AccelerationSaurabh Suman100% (1)
- Document 1: Eligibility Requirements: M.Sc./P.G. Diploma Course in Industrial AutomationDocument14 pagesDocument 1: Eligibility Requirements: M.Sc./P.G. Diploma Course in Industrial AutomationRantharu AttanayakeNo ratings yet
- FEM Lecture 3 Method of Weighted ResidualsDocument10 pagesFEM Lecture 3 Method of Weighted ResidualsHuma BaigNo ratings yet
- On The Exponential Solution of Differential Equations For A Linear Operator PDFDocument25 pagesOn The Exponential Solution of Differential Equations For A Linear Operator PDFzhihong zuoNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1Sanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- An Estimation of A Billet Temperature During Reheating Furnace OperationDocument8 pagesAn Estimation of A Billet Temperature During Reheating Furnace OperationpabloNo ratings yet
- AdvancedNumericalDifferentialEquationSolvingInMathematica PDFDocument372 pagesAdvancedNumericalDifferentialEquationSolvingInMathematica PDFJMATALLANAARENASNo ratings yet
- Pde 1707.02568Document13 pagesPde 1707.02568heavywaterNo ratings yet
- EE2462 Engineering Math III (Part 1) : Associate ProfessorDocument125 pagesEE2462 Engineering Math III (Part 1) : Associate ProfessorCastro HamiltonNo ratings yet
- Santiago Marquez Damian PHD ThesisDocument231 pagesSantiago Marquez Damian PHD ThesisHans JensenNo ratings yet
- Be Mechanical Engineering Cbcs Syllabus 2015 16 OnwardsDocument492 pagesBe Mechanical Engineering Cbcs Syllabus 2015 16 OnwardsRAKESH RAVINo ratings yet
- Boundary Element Methods: Judit Gonzalez-Santana Machel Higgins Kirsten StephensDocument42 pagesBoundary Element Methods: Judit Gonzalez-Santana Machel Higgins Kirsten StephensME-MNG-15 RameshNo ratings yet
- MA6351Document73 pagesMA6351Selva KumarNo ratings yet
- PDE TextbookDocument310 pagesPDE Textbookrashid khanNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Pile Foundation of An Underground Building Under The Influence of Tunnel Using PLAXIS 3DDocument39 pagesAnalysis of Pile Foundation of An Underground Building Under The Influence of Tunnel Using PLAXIS 3DHari RamNo ratings yet
- Universiti Malaysia Perlis Eqt 203: Engineering Mathematics Iii Chapter 1: Partial Differential Equations Tutorial 1Document5 pagesUniversiti Malaysia Perlis Eqt 203: Engineering Mathematics Iii Chapter 1: Partial Differential Equations Tutorial 1Tholasi GanapathyNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transform of Partial DerivativesDocument6 pagesLaplace Transform of Partial DerivativesShashi KanthNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Electric Fields Underneath and On Conductor Surfaces of Ultra High Voltage Transmission LinesDocument8 pagesCalculation of Electric Fields Underneath and On Conductor Surfaces of Ultra High Voltage Transmission LinesAhmed Taleb SheblNo ratings yet
- Advanced Numerical Differential Equation Solving in Mathematica Part 1Document184 pagesAdvanced Numerical Differential Equation Solving in Mathematica Part 1Luis ZavalaNo ratings yet
- M.E. Power Electronics and Drives Anna University Syllabus Reg 2021Document31 pagesM.E. Power Electronics and Drives Anna University Syllabus Reg 2021Daniel LakNo ratings yet
- Computer Algebra Recipes - An Advanced Guide To Scientific Modeling Richard H Enns (Springer 2007 372S With Maple)Document372 pagesComputer Algebra Recipes - An Advanced Guide To Scientific Modeling Richard H Enns (Springer 2007 372S With Maple)Óscarillo ValdésNo ratings yet
- IskandaraniDocument216 pagesIskandaraniLeyner cardenas mercadoNo ratings yet
- Ordinary and Partial Differential Equation Routines in C, C++, Fortran, Java, Maple, and MDocument7 pagesOrdinary and Partial Differential Equation Routines in C, C++, Fortran, Java, Maple, and MAhmed Salah KamelNo ratings yet