Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Photosyenthesis - 2
Types of Photosyenthesis - 2
Uploaded by
shaista iqbalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Photosyenthesis - 2
Types of Photosyenthesis - 2
Uploaded by
shaista iqbalCopyright:
Available Formats
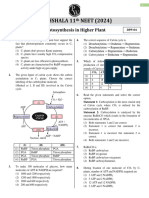
C3 C4 CAM
TYPES OF -> CO2 ATTACH WITH -> CO2 is -> CAM
PHOTOSYNTHESIS RUBP (5CARBON converted into OCCURS IN
LOWER WATER
IN DESERT PLANTS MOLECULE) WHICH Oxaloacetate CONDITIONS
ARE CONVERTED (4 carbon) and -> OCCURS IN 2
INTO 2 MOLECULES then into sugar.
STAGES
OF PGA (3 CARBON) -> C4 plant use C3
-> CO2 is
-> DIURNAL PROCESS photosynthesis converted into
and Kranz malic acid (1st)
-> LOW CO2 to 02 -> CO2 is
anatomy
Ratio released from
segregate the
-> Lower level of malic acid to
cells with C3
form sugar (2nd)
photosynthetic photosynthesis -> Temporal
efficiency than C4 and C4 strategy for C3
photosynthesis photosynthesis
Plants
->Autotrophic organisms which
occur in the open spaces between
higher plants are called Biological
Biological Soil crust soil crust.
-> They are of 3 Types; Biological
crust (Formed by combination of
cyanobacteria, algae, lichens,
mosses, bacteria, and fungi),
Mechanical and chemical crust
(formed by clays or salts in the
soils).
->They are capable of
withstanding desiccation and
suspending
respiration.
Annual Plants
Annual plants are plants which live for one growing season or year and then survive
until the following growing season as seeds.
Desert annuals have little capacity for photosynthetic acclimation, unlik evergreen
species. They are also unable to handle severe drought
Some annuals are amphiphytic, that is, they may be annual or perennial depending
on local environmental conditions. For example, several species of the grass genus
Stipagrostis are perennial under moderate conditions but are annual when
conditions become more extreme.
Annuals can be classified as Winter and Summer Annuals.
Winter Annuals have short height, single layered leaves close to soil which are highly
dissected.
Summer Annuals have comparatively more height, follow solar tracking with leaves
that are displayed along the entire vertical length of the stem and are smaller in size
You might also like
- Carbon Cycle GizmoDocument5 pagesCarbon Cycle GizmoDana Ramirez-Zamora100% (1)
- Project Report On Coconut Shell Charcoal/activated CarbonDocument7 pagesProject Report On Coconut Shell Charcoal/activated CarbonEIRI Board of Consultants and Publishers100% (1)
- 001 v5 (Basic, BX)Document42 pages001 v5 (Basic, BX)Joseph Bontrager100% (1)
- Crop Ecology - Productivity and Management in Agricultural Systems - (2011) Queensland Recomendation-275-295Document21 pagesCrop Ecology - Productivity and Management in Agricultural Systems - (2011) Queensland Recomendation-275-295CarolinaNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument25 pagesCarbon Cyclegracewrites4uNo ratings yet
- EC07 Energy Nutrient RelationsDocument29 pagesEC07 Energy Nutrient Relationsevahhassane2003No ratings yet
- Science f2 Chapter2Document8 pagesScience f2 Chapter2manusia takgunaNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Microorganisms in Environmental ProtectionDocument24 pagesBiotechnology Microorganisms in Environmental Protectionaiga1090No ratings yet
- C3_and_C4_PhotosynthesisDocument6 pagesC3_and_C4_Photosynthesismphomakh7No ratings yet
- Biology12 NotesDocument6 pagesBiology12 NotesDelightful TineNo ratings yet
- C3 Carbon Fixation - WikipediaDocument8 pagesC3 Carbon Fixation - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Membrane Bioreactor Technology For Small Water Treatment UtilitiesDocument16 pagesHybrid Membrane Bioreactor Technology For Small Water Treatment UtilitiesMaria Alejandra AyudeNo ratings yet
- FotosíntesisDocument37 pagesFotosíntesisAndrés Reinoso SánchezNo ratings yet
- IPPTA 164-39-45 Effluent Treatment byDocument7 pagesIPPTA 164-39-45 Effluent Treatment byShamimNo ratings yet
- R NaveDocument1 pageR NaveBereket YitayawNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Biogeochemical CycleDocument31 pages2.3 Biogeochemical CyclePAVITRA A/P THEVINDRAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Gehs 6030 Env - Micro1Document52 pagesGehs 6030 Env - Micro1Sneha GNo ratings yet
- Tulane University School of PH&TM Global Environmental Health SciencesDocument52 pagesTulane University School of PH&TM Global Environmental Health SciencesLizet MejiaNo ratings yet
- Atkin L7 - Oct 26 2023Document33 pagesAtkin L7 - Oct 26 2023joelypamelaandersonNo ratings yet
- C2 C3 C4 & Cam Variations On The Theme of PhotosynthesisDocument20 pagesC2 C3 C4 & Cam Variations On The Theme of PhotosynthesisKoons KoonsNo ratings yet
- 11 - Atom CycleDocument57 pages11 - Atom Cycleppg.ditamaulina99730No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in C4 PlantsDocument5 pagesPhotosynthesis in C4 PlantsErvin Ade PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Proses Dekomposisi Bahan Organik: Bakteri Aerob HeterotropikDocument38 pagesProses Dekomposisi Bahan Organik: Bakteri Aerob HeterotropikiahfafaNo ratings yet
- Name: - Date: - Block: - AP Biology Notes For Cell Energetics 5 Kreb's Cycle and Electron Transport ChainDocument36 pagesName: - Date: - Block: - AP Biology Notes For Cell Energetics 5 Kreb's Cycle and Electron Transport ChainMinh NguyenNo ratings yet
- The Element Carbon - An InfographicDocument2 pagesThe Element Carbon - An InfographicGERALD ANGELO BUDUANNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MBR O-1141Document25 pagesIntroduction To MBR O-1141Madhusudanan78No ratings yet
- Crystal Academy: EcosystemDocument3 pagesCrystal Academy: EcosystemShalynee SuthaharNo ratings yet
- Adsorption of Copper From Aqueous Solution by Activated Carbons Obtained by Pyrolisis of Cassava PeelDocument6 pagesAdsorption of Copper From Aqueous Solution by Activated Carbons Obtained by Pyrolisis of Cassava PeelevinNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Water Agricultural Water: Animal Farming Operations: Groundwater Quality IssuesDocument105 pagesAgricultural Water Agricultural Water: Animal Farming Operations: Groundwater Quality IssuesAndré OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Nutrient CyclesDocument2 pagesNutrient Cycles030929No ratings yet
- Pollution 1Document2 pagesPollution 1Arslan RasheedNo ratings yet
- Pollution 1Document2 pagesPollution 1Arslan RasheedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8, 9 & 10 Study Guide AnswersDocument10 pagesChapter 8, 9 & 10 Study Guide AnswersAbbas khanNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - DPP 04 (Of Lec 07) - Sequence No. 48 - Pathshala 11th NEET 2024Document3 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher Plants - DPP 04 (Of Lec 07) - Sequence No. 48 - Pathshala 11th NEET 2024priyanshuranjanroutNo ratings yet
- David Faure, InThinking Carbon Cycle Activity. IB BiologyDocument13 pagesDavid Faure, InThinking Carbon Cycle Activity. IB BiologyGeorge KoukouvesNo ratings yet
- Coalbed Methane (CBM) : Prepared by Dr. Ajay Suri For Course PEE 18102Document341 pagesCoalbed Methane (CBM) : Prepared by Dr. Ajay Suri For Course PEE 18102ajay suriNo ratings yet
- Fistum CamDocument11 pagesFistum CamMellya RizkiNo ratings yet
- Plants, Food and Man - 03-10-13Document4 pagesPlants, Food and Man - 03-10-13Shadeen ScottNo ratings yet
- Biochem LectureDocument35 pagesBiochem Lectureallaniguekate25No ratings yet
- Sludge Mngment, Anaerobic Treatment and Aquatic Plant SystemsDocument33 pagesSludge Mngment, Anaerobic Treatment and Aquatic Plant SystemsAndrew Marquez DonaireNo ratings yet
- Presentation Waste Water TreatmentDocument69 pagesPresentation Waste Water TreatmentAkilaNo ratings yet
- Bioremediation 141123233153 Conversion Gate01Document30 pagesBioremediation 141123233153 Conversion Gate01Mdhe asif alamNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Carbon Sequestration by Algae in Domestic Sewage and Industrial EffluentDocument3 pagesComparative Study of Carbon Sequestration by Algae in Domestic Sewage and Industrial EffluentBalakumar KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Science Rev LT 1Document1 pageScience Rev LT 1JoyceNo ratings yet
- Et Al.: Economics, Business, Marketing, PolicyDocument1 pageEt Al.: Economics, Business, Marketing, PolicyMaria Jose CuellarNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower Problems and Chemical DosingDocument2 pagesCooling Tower Problems and Chemical Dosingvela vanNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle PPT For WebsiteDocument43 pagesCarbon Cycle PPT For WebsiteDavid LiuNo ratings yet
- Trif Imperial College FinalDocument347 pagesTrif Imperial College FinalJitendra SainiNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Degradation MicroorganismDocument11 pagesAerobic Degradation MicroorganismSARA VELEZ BRAVONo ratings yet
- Types of PhotosyntheseDocument6 pagesTypes of PhotosyntheseZain ul abdin QureshiNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Study Material C4 Cycle OnwardsDocument6 pagesPhotosynthesis Study Material C4 Cycle OnwardsmoonyNo ratings yet
- Moving Bed Biofilm Reactors - Paper Industry WorldDocument4 pagesMoving Bed Biofilm Reactors - Paper Industry WorldMahmudul HasanNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals Fundamentals Fundamentals of Crop Science of Crop Science of Crop ScienceDocument39 pagesFundamentals Fundamentals Fundamentals of Crop Science of Crop Science of Crop ScienceAlthea DoradoNo ratings yet
- Plant Adaptations To The Environment: Part 2: Physiological and Symbiotic AdaptationsDocument21 pagesPlant Adaptations To The Environment: Part 2: Physiological and Symbiotic AdaptationsSheelendra Mangal BhattNo ratings yet
- Fermentation (Bokashi) Versus Composting of Organic Waste Materials: Consequences For Nutrient Losses and CO - FootprintDocument3 pagesFermentation (Bokashi) Versus Composting of Organic Waste Materials: Consequences For Nutrient Losses and CO - FootprintVictor BotiganNo ratings yet
- OUTLINEDocument1 pageOUTLINEeducationalpurpose00No ratings yet
- CRPSCI 1100-Module5Document14 pagesCRPSCI 1100-Module5carbonel.carlaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Finals ReviewerDocument3 pagesChemistry Finals ReviewerPercival ArcherNo ratings yet
- Sludge Treatment and DisposalDocument16 pagesSludge Treatment and Disposalsandhya bhattiNo ratings yet
- Rare Earth Coordination Chemistry: Fundamentals and ApplicationsFrom EverandRare Earth Coordination Chemistry: Fundamentals and ApplicationsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- 0262693135Document359 pages0262693135zipperblues100% (4)
- Class 7th ScienceDocument5 pagesClass 7th ScienceSonu YadavNo ratings yet
- Reading Power 6 Skill ADocument42 pagesReading Power 6 Skill AJenelou delapenaNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom (L2) - 2nd JuneDocument43 pagesPlant Kingdom (L2) - 2nd JuneUpal PramanickNo ratings yet
- BIO104 General Ecology Laboratory 5 Group GDocument6 pagesBIO104 General Ecology Laboratory 5 Group GAllan Jr. Agao-AgaoNo ratings yet
- Aizen y Feinsinger.1994Document23 pagesAizen y Feinsinger.1994Alexis Centeno CuellarNo ratings yet
- B2 Questions and AnswersDocument22 pagesB2 Questions and Answersinaayairshad.17No ratings yet
- Belgian Mum Cultural InfoDocument8 pagesBelgian Mum Cultural InfoLAUM1No ratings yet
- DLL - Science 5 - Q2 - W7Document11 pagesDLL - Science 5 - Q2 - W7Mae Minnette Mark DizonNo ratings yet
- Summative Test Ecosystem 1Document1 pageSummative Test Ecosystem 1Jonalvin KE67% (3)
- Lesson Plan Sir MarcosDocument7 pagesLesson Plan Sir MarcosJhon AgustinNo ratings yet
- Student's Booklet - The Classification of Living ThingsDocument8 pagesStudent's Booklet - The Classification of Living ThingsRafa Rguez PerezNo ratings yet
- Unit OneDocument3 pagesUnit OneSondos SamehNo ratings yet
- 2nd PT in Science 6 Teacher Made TestDocument8 pages2nd PT in Science 6 Teacher Made TestDanski PomilarNo ratings yet
- Science DLP Parts of PlantsDocument8 pagesScience DLP Parts of PlantsMishell AbejeroNo ratings yet
- The Pathogenic Fungi On Cempaka (Magnolia Elegans (Blume) H. Keng) Leaves at Various Altitudes in Agroforestry SystemsDocument4 pagesThe Pathogenic Fungi On Cempaka (Magnolia Elegans (Blume) H. Keng) Leaves at Various Altitudes in Agroforestry SystemsVidtraNo ratings yet
- Science 6 DLP 21 Importance of ForestDocument10 pagesScience 6 DLP 21 Importance of ForestMonica Morales MaañoNo ratings yet
- Jaiviko A Product of Amrit OrganicDocument7 pagesJaiviko A Product of Amrit OrganicJohn RaiNo ratings yet
- 1 ReviewerDocument5 pages1 ReviewerDear PrudenceNo ratings yet
- Advanced Agro-Hydro-Meteorology: A MSC Course For Students of Atmospheric SciencesDocument7 pagesAdvanced Agro-Hydro-Meteorology: A MSC Course For Students of Atmospheric Sciencesبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Capstone RRL 01 14 18Document8 pagesCapstone RRL 01 14 18Joshua De Leon100% (2)
- How Grass Grows Final 2Document2 pagesHow Grass Grows Final 2gorekaNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Science Annual Exam 2023-2024 The Srijan SchoolDocument6 pagesClass 7 Science Annual Exam 2023-2024 The Srijan SchoolmanishNo ratings yet
- Academic Reading Test 11-22Document13 pagesAcademic Reading Test 11-22Muhammad FiazNo ratings yet
- Gardening - Planning The GardenDocument4 pagesGardening - Planning The Gardencontadino_impazzitoNo ratings yet
- Natural Farming Manual (Complete Imo & Other Technique)Document10 pagesNatural Farming Manual (Complete Imo & Other Technique)rodefren100% (6)
- Ch-7 - Bio 10th - Life Process - Revision AssignmentDocument8 pagesCh-7 - Bio 10th - Life Process - Revision AssignmentDharmendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Anais Malcolm SumnerDocument17 pagesAnais Malcolm SumnerCoreHardNo ratings yet
- Seed GerminationDocument2 pagesSeed GerminationJohn Carl de LoyolaNo ratings yet