Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHAP 6: Changes Around Us: 6 (CBSE) Future Group Tuitions Science
CHAP 6: Changes Around Us: 6 (CBSE) Future Group Tuitions Science
Uploaded by
Swapnil ChaudhariOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAP 6: Changes Around Us: 6 (CBSE) Future Group Tuitions Science
CHAP 6: Changes Around Us: 6 (CBSE) Future Group Tuitions Science
Uploaded by
Swapnil ChaudhariCopyright:
Available Formats
6th (CBSE) FUTURE GROUP TUITIONS SCIENCE
CHAP 6: Changes Around Us
Some changes can be reversed and some cannot be reversed.
A change may occur by heating a substance or by mixing it with some other.
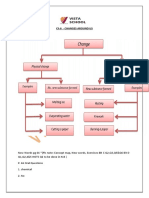
Types of changes:
o Reversible change: A change in which the initial substance can be obtained back by
reversing the action. Example: folding of paper, dissolving sugar in water, etc.
o Non-irreversible change: Change in which the initial substance cannot be obtained
back by reversing the action. Example: burning of paper, grinding grains etc.
o Physical change: Changes in the form of substance but not in chemical identity. No
new substance formed. Changes are sometimes reversible. Example: breaking a log
of wood.
o Chemical changes: Changes in which substance is transformed into new substance.
Initial substance is lost. Change is always irreversible. Example: burning a log of
wood.
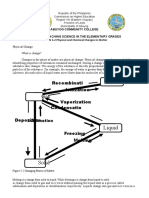
Ways by which changes occur:
o Boiling and Condensation:
1) Boiling: The rapid vaporization of a liquid when it is heated to its boiling point.
2) Condensation: The change of water vapor into liquid water on cooling.
o Heating of metal:
1) Process in which a metal is heated to a certain temperature and the cooled in a
particular manner to alter its internal structure for obtaining desired degree of
physical and mechanical properties such as brittleness, hardness, and softness.
o Freezing and Melting:
1) Freezing: The process in which a liquid turns into solid when its temperature is
lowered.
2) Melting: The process in which a solid converts to a liquid by applying heat.
Future Group Tuitions 1
You might also like
- 2 JYs YHe XG V87 Jue OIKM6Document1 page2 JYs YHe XG V87 Jue OIKM6anjuranarana01No ratings yet
- Chapter - 6: Changes Around Us: Basic Concepts - A Flow ChartDocument26 pagesChapter - 6: Changes Around Us: Basic Concepts - A Flow ChartSupriya CNo ratings yet
- NOTES ON Changes in Non-Living Things 2022Document2 pagesNOTES ON Changes in Non-Living Things 2022Samuel AjanaNo ratings yet
- ResourceDocument2 pagesResourceSHAISTA AFREEN TEACHERNo ratings yet
- MAT TER: 1.-IntroductionDocument9 pagesMAT TER: 1.-IntroductionMay FairNo ratings yet
- Science Notes For MidtermDocument9 pagesScience Notes For MidtermLeoNo ratings yet
- Good Morning Grade 4 Rosal!: Science 4 Quarter 1 - Week 5Document30 pagesGood Morning Grade 4 Rosal!: Science 4 Quarter 1 - Week 5Erica May GarciaNo ratings yet
- How Things Change & React With One Another: Physical and Chemical ChangesDocument6 pagesHow Things Change & React With One Another: Physical and Chemical ChangesBharatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6. Changes Around UsDocument9 pagesChapter 6. Changes Around UsYoshita ShahNo ratings yet
- Changes in Matter: Department of Mathematics and ScienceDocument20 pagesChanges in Matter: Department of Mathematics and ScienceAsru RojamNo ratings yet
- Changes Around Us Science - Class-ViDocument28 pagesChanges Around Us Science - Class-ViAmit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Changes Around UsDocument16 pagesChapter 6-Changes Around UsSanchita KunwerNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 8 Chemistry Selina Solution Chapter 2 Physical and Chemical ChangesDocument4 pagesICSE Class 8 Chemistry Selina Solution Chapter 2 Physical and Chemical ChangesRajesh ShenoyNo ratings yet
- ICSE Selina Class 8 Chemistry Chapter 2Document10 pagesICSE Selina Class 8 Chemistry Chapter 2Den Angelica DungoNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 6 - Chapter 06Document11 pagesExp SC 6 - Chapter 06megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Changes in Non-Living Things: Physical ChangeDocument3 pagesChanges in Non-Living Things: Physical ChangeR1dereNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Changes: AnswerDocument11 pagesPhysical and Chemical Changes: Answerchivukula KarthikNo ratings yet
- Condensation DefinitionDocument6 pagesCondensation DefinitionMathea Lyf Aire ElordeNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical ChangeDocument4 pagesPhysical and Chemical ChangeArmaan Noorani100% (1)
- Aldrich Nathanael Homework 16th September 2023 (Already Done)Document1 pageAldrich Nathanael Homework 16th September 2023 (Already Done)fauziNo ratings yet
- I. State True or FalseDocument2 pagesI. State True or Falsevijay pal shivranNo ratings yet
- Properties of Solid, Liquid and GasDocument11 pagesProperties of Solid, Liquid and GasLe VuongNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 CH 6 Changes Around UsDocument3 pagesGrade 6 CH 6 Changes Around UsBrijeshNo ratings yet
- Changes in MatterDocument6 pagesChanges in MatterNoorwashilaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Changes in MatterDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Changes in Matterreinalizaf.171022No ratings yet
- Changes Around Us-6Document3 pagesChanges Around Us-6aairakapoor aairakapoorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Physical and Chemical ChangesDocument4 pagesChapter 2: Physical and Chemical ChangesNaqvi play'sNo ratings yet
- NSC U4 Matter Part IIIDocument14 pagesNSC U4 Matter Part IIIAmaia TeranNo ratings yet
- Study Material Class 6 Chemistry Study of ChangesDocument8 pagesStudy Material Class 6 Chemistry Study of Changesdruhin.milly2017No ratings yet
- Chemistry Worksheet Class 7 On Chapter 6 Physical and Chemical Changes With Answers Set 1Document5 pagesChemistry Worksheet Class 7 On Chapter 6 Physical and Chemical Changes With Answers Set 1soumyasahacidNo ratings yet
- IodinDocument7 pagesIodinMizni Zaharanil HilmiNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Chem Phy Chem Changes Part A 1626539808Document2 pagesClass 7 Chem Phy Chem Changes Part A 1626539808Darshan PadmapriyaNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 7 - Chapter 06Document13 pagesExp SC 7 - Chapter 06megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- 647bfb2b3d4f0-Changes in Matter Part 1 2Document8 pages647bfb2b3d4f0-Changes in Matter Part 1 2Erandi Kusala AmarasiriNo ratings yet
- BAB II PEMBAHASAN 2.1 Pengertian Materi 2.2 Sifat-Sifat MateriDocument9 pagesBAB II PEMBAHASAN 2.1 Pengertian Materi 2.2 Sifat-Sifat MateriBestman PashaNo ratings yet
- Change of Phase in Matter-Physical ChangeDocument41 pagesChange of Phase in Matter-Physical ChangeJulie BalogoNo ratings yet
- 25 BD 40 Eff 2 CaDocument25 pages25 BD 40 Eff 2 Cakaramkurdish2No ratings yet
- Neena Haridas: Physical ScienceDocument25 pagesNeena Haridas: Physical ScienceAbby Pinugu Lacerna IINo ratings yet
- Neena Haridas: Physical ScienceDocument25 pagesNeena Haridas: Physical ScienceAbby Pinugu Lacerna IINo ratings yet
- CH 6.changes Around Us - NotesDocument5 pagesCH 6.changes Around Us - Notesswetha swithinNo ratings yet
- 1) Freezing 2) Condensation 3) Vaporisation 4) MeltingDocument5 pages1) Freezing 2) Condensation 3) Vaporisation 4) MeltingxyzNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Changes NotesDocument11 pagesPhysical and Chemical Changes NotesRaghavendra BetakerurNo ratings yet
- Properties of Matter and Changes in MatterDocument55 pagesProperties of Matter and Changes in MatterPrinces April ArrezaNo ratings yet
- 01 05 JournalDocument3 pages01 05 JournalAkshay KarthikNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Physical and Chemical ChangesDocument3 pages5.2 Physical and Chemical ChangesGrace SalarNo ratings yet
- Physicalchemicalchange 140825133215 Phpapp02Document25 pagesPhysicalchemicalchange 140825133215 Phpapp02nicole.levy.ctcNo ratings yet
- Changes in Matter and Properties of MaterialsDocument2 pagesChanges in Matter and Properties of Materialsmiguelangel.torneroNo ratings yet
- Neena Haridas: Physical ScienceDocument25 pagesNeena Haridas: Physical ScienceAnjali RaoNo ratings yet
- Physicalchemical ChangesDocument17 pagesPhysicalchemical ChangesAira YamuyamNo ratings yet
- Changes in Matter: Lesson 5Document20 pagesChanges in Matter: Lesson 5Siyamala NagarajuNo ratings yet
- Changes in MatterDocument17 pagesChanges in MatteretrimayssaNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical ChangesDocument15 pagesPhysical and Chemical ChangesSalemah MeshalNo ratings yet
- Changes Around Us NotesDocument5 pagesChanges Around Us NotesMohit ThakurNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PDFDocument73 pagesChemistry PDFRagini khargNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical ChangesDocument3 pagesPhysical and Chemical ChangesAbhyudaya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Physical N Chemical ChangesDocument16 pagesPhysical N Chemical Changessarahudi100% (4)
- Science 5 Quarter 1 Module 3 Week 3Document6 pagesScience 5 Quarter 1 Module 3 Week 3Vhacie TorresNo ratings yet
- Changes Around UsDocument2 pagesChanges Around UsPranav ShindeNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Reactions : 6th Grade Chemistry Book | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandPhysical and Chemical Reactions : 6th Grade Chemistry Book | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Chap 5: Separation of Substances: 6 (CBSE) Future Group Tuitions ScienceDocument2 pagesChap 5: Separation of Substances: 6 (CBSE) Future Group Tuitions ScienceSwapnil ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 05 Political Science Panchayati RajDocument1 pageChapter - 05 Political Science Panchayati RajSwapnil ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 04 Political Science Key Elements of A Democratic GovernmentDocument2 pagesChapter - 04 Political Science Key Elements of A Democratic GovernmentSwapnil ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Future Excellence Academy: 9 (ICSE) Maths Date: 09/12/2020 Class Test (Chap 26 & 27) Marks: 20Document2 pagesFuture Excellence Academy: 9 (ICSE) Maths Date: 09/12/2020 Class Test (Chap 26 & 27) Marks: 20Swapnil ChaudhariNo ratings yet