Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Stroboscope Writing Material
Stroboscope Writing Material
Uploaded by
Tejpreet Singh BediCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Pass Ultrasound Physics Exam Study Guide ReviewFrom EverandPass Ultrasound Physics Exam Study Guide ReviewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- AGS-688 ManualDocument60 pagesAGS-688 Manualvatcslav0% (1)
- Stroboscope With RPM Indicator Full ReportDocument26 pagesStroboscope With RPM Indicator Full Reportthreephasefault100% (2)
- Torsion Meter PartialDocument22 pagesTorsion Meter PartialSam Ompad100% (1)
- Objective: Equipment:: Lab Report 5Document3 pagesObjective: Equipment:: Lab Report 5Rida NasirNo ratings yet
- T 3Document4 pagesT 3नेपाली नेवरि प्रसन्नNo ratings yet
- UTI BrochureDocument2 pagesUTI BrochureKaye de LeonNo ratings yet
- 4 StroboscopeDocument3 pages4 StroboscopeKamal Mahal0% (5)
- Theory of Operation of Rate SensorsDocument4 pagesTheory of Operation of Rate SensorsPhạm Ngọc HòaNo ratings yet
- Turbine Speed MeasurementDocument26 pagesTurbine Speed MeasurementAyyar Kandasamy100% (4)
- Describe The Construction of A Electromagnetic Velocity Sensor and Explain Its WorkingDocument8 pagesDescribe The Construction of A Electromagnetic Velocity Sensor and Explain Its WorkingJiten Thakur100% (1)
- Stepper Motor ReportDocument19 pagesStepper Motor ReportIan Bagunas100% (2)
- Experimental Technique in AutomobileDocument12 pagesExperimental Technique in AutomobileVivekDhameliyaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Tachometers and Digital TachometerDocument15 pagesMechanical Tachometers and Digital TachometerAllen GeorgeNo ratings yet
- HW3Document2 pagesHW3cx18717315873No ratings yet
- Stroboscope: Non-Contact Speed Measurement High Intensity Flashes Direct Speed Reading in RPM No Shaft ModificationDocument1 pageStroboscope: Non-Contact Speed Measurement High Intensity Flashes Direct Speed Reading in RPM No Shaft ModificationVarunNo ratings yet
- Stepper MotorsDocument53 pagesStepper MotorsirfancardiagnosticNo ratings yet
- PIC NotesDocument17 pagesPIC Notessvyas7872No ratings yet
- Basic Principle of Mechanical Torsion MeterDocument4 pagesBasic Principle of Mechanical Torsion MeterKranthi KumarNo ratings yet
- DT2289Document5 pagesDT2289shijirbatNo ratings yet
- Measure of Angular VelocityDocument12 pagesMeasure of Angular VelocityAshley_Rulzzzzzzz100% (2)
- Sound MeasurementDocument27 pagesSound MeasurementVarad DateNo ratings yet
- AC Induction Motor MonitoringDocument4 pagesAC Induction Motor MonitoringAnonymous PVXBGg9TNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Vibration and Strain MeasurementDocument12 pagesUnit 5 Vibration and Strain Measurement08 Dadarkar Mujtaba MEANo ratings yet
- Speed Measurement CH 1Document42 pagesSpeed Measurement CH 1unknown730407No ratings yet
- Vibration - Electrical or Mechanical - EASADocument3 pagesVibration - Electrical or Mechanical - EASAGilbNo ratings yet
- Angle Measurement Using Hall Sensor PDFDocument3 pagesAngle Measurement Using Hall Sensor PDFAlok MajhiNo ratings yet
- Servo MotorsDocument27 pagesServo Motorsc_archana100% (1)
- Ultrasonic MotorDocument11 pagesUltrasonic MotorShivang AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Food Microbiology & Microbial Techniques - Fsr2002: Niraj Singh M.Tech-Fsqm I SEM I.D.No. (RA1812036010015)Document14 pagesFood Microbiology & Microbial Techniques - Fsr2002: Niraj Singh M.Tech-Fsqm I SEM I.D.No. (RA1812036010015)Niraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Linear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT)Document10 pagesLinear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT)Sam WaikarNo ratings yet
- A Stepper Motor Is A "Pulse-Driven" Motor That Changes The Angular Position of The Rotor in "Steps" It Is A Digital Electromechanical Device DefineDocument35 pagesA Stepper Motor Is A "Pulse-Driven" Motor That Changes The Angular Position of The Rotor in "Steps" It Is A Digital Electromechanical Device DefineSupriya RakshitNo ratings yet
- Accelerometers Versus Velocity Sensors - What's The Difference 2Document1 pageAccelerometers Versus Velocity Sensors - What's The Difference 2Nelson Arul NathanNo ratings yet
- Module 4 3Document24 pagesModule 4 3Atharva KhadseNo ratings yet
- AC MachinesDocument22 pagesAC MachinesUtkarsh ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Stepper MotorDocument39 pagesUnit-1 Stepper MotorkoundinyaNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Induction MotorDocument21 pagesThree Phase Induction MotorM R Tarun RameshkumarNo ratings yet
- Advances in MetrologyDocument40 pagesAdvances in Metrologymanoj kumar GNo ratings yet
- Cs SeminarDocument15 pagesCs SeminarMoti GamachuNo ratings yet
- II yr/III Sem/Mech/EEE 2 Marks With Answers Unit-IIDocument5 pagesII yr/III Sem/Mech/EEE 2 Marks With Answers Unit-IIanunilaNo ratings yet
- 2 Vibn Analysis BasicsDocument117 pages2 Vibn Analysis BasicsTanoj PatroNo ratings yet
- ENCODERSDocument11 pagesENCODERSRabi khanNo ratings yet
- Brushless DC MotorDocument6 pagesBrushless DC Motorpsksiva13No ratings yet
- Design and Development of A Fluxgate MagnetometerDocument5 pagesDesign and Development of A Fluxgate Magnetometerdr_oxide2No ratings yet
- Principles of Measurement and Instrumentation EKT 112: OscilloscopeDocument40 pagesPrinciples of Measurement and Instrumentation EKT 112: OscilloscopesambavaleNo ratings yet
- Photo Transistor: Dr.A.Anbarasi Associate Professor Department of Physics CuddaloreDocument14 pagesPhoto Transistor: Dr.A.Anbarasi Associate Professor Department of Physics CuddaloreHema HemaNo ratings yet
- AU2140097 HomeActivity3Document1 pageAU2140097 HomeActivity3niyati.p1No ratings yet
- Robot Actuators and Feedback Components (Main7)Document82 pagesRobot Actuators and Feedback Components (Main7)tarasasanka33% (6)
- Measurement of VelocityDocument59 pagesMeasurement of VelocityYogeshBhatt100% (1)
- Unit 4 Laser and Advances in MetrologyDocument74 pagesUnit 4 Laser and Advances in MetrologyS. SARGUNA THAMIZHAN MECHNo ratings yet
- Electric DrivesDocument16 pagesElectric DrivesvigneshNo ratings yet
- Stepper Motor BasicsDocument11 pagesStepper Motor BasicsrvpilotNo ratings yet
- Group 6 GyroscopeDocument17 pagesGroup 6 GyroscopePhenias ManyashaNo ratings yet
- UoGx ECEg4155 Chapter 7 8Document45 pagesUoGx ECEg4155 Chapter 7 8Abdi ExplainsNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Vibration & Axial DisplacementDocument6 pagesMeasurement of Vibration & Axial DisplacementSatNo ratings yet
- AC MotorDocument18 pagesAC MotorNAVNEET GUPTANo ratings yet
- Noise and Vibration Analysis of Elevator Traction Machine: Ryo Kawasaki Yasuo HIRONAKA Masaharu NISHIMURADocument9 pagesNoise and Vibration Analysis of Elevator Traction Machine: Ryo Kawasaki Yasuo HIRONAKA Masaharu NISHIMURAyounesNo ratings yet
- Training Program On Vibration AnalysisDocument92 pagesTraining Program On Vibration AnalysisDurga Prasad Padhy100% (2)
- Stepper Motor - Types, Advantages and ApplicationsDocument2 pagesStepper Motor - Types, Advantages and ApplicationsBilalNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor (ALL TOPICS)Document33 pagesInduction Motor (ALL TOPICS)Ramprakash89% (18)
- EM214Induction Motorchapter 3Document46 pagesEM214Induction Motorchapter 3mahrusNo ratings yet
- Apply Good Dispensing Principles - NEW-1Document49 pagesApply Good Dispensing Principles - NEW-1abelashe2No ratings yet
- Timing Calibration Harness AssemblyDocument5 pagesTiming Calibration Harness Assemblyflordeliz jimenez rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 Energy Transport With Energy DissipationDocument16 pagesLecture 11 Energy Transport With Energy DissipationFarahin Burhan100% (1)
- GP MCQ 6Document4 pagesGP MCQ 6Marta MoreiraNo ratings yet
- # Sample Quotation Copy For Go Kart SparesDocument3 pages# Sample Quotation Copy For Go Kart SparessaqibNo ratings yet
- 4th Quarter ExamDocument2 pages4th Quarter ExamMa. Cynthia San JuanNo ratings yet
- Foodsupplements 6-3-2019Document282 pagesFoodsupplements 6-3-2019TalalAlamoudiNo ratings yet
- Kakuban - The Esoteric Meaning of Amida 2Document4 pagesKakuban - The Esoteric Meaning of Amida 2Rhys SchauwekerNo ratings yet
- 08-03-17 EditionDocument28 pages08-03-17 EditionSan Mateo Daily JournalNo ratings yet
- Jillian Gaviani FSC Booth DesignDocument7 pagesJillian Gaviani FSC Booth DesignMuthana JalladNo ratings yet
- PhySciSHS Q4 Week1Document46 pagesPhySciSHS Q4 Week1Roseman TumaliuanNo ratings yet
- DD Soft Copy and Hard Copy Recieved Details Journal Review Process 21 April 2014 8 PM1Document34 pagesDD Soft Copy and Hard Copy Recieved Details Journal Review Process 21 April 2014 8 PM1Puneet AjalNo ratings yet
- Alternador AVK - DSG DIG Instalacion Servicio y MantenimientoDocument595 pagesAlternador AVK - DSG DIG Instalacion Servicio y MantenimientoMartin FloresNo ratings yet
- IOL Calculation in Complex Corneal ConditionsDocument8 pagesIOL Calculation in Complex Corneal ConditionsShimaa MersalNo ratings yet
- CSTSN5Document2 pagesCSTSN5nileshcw51No ratings yet
- Mercedes Actros Head FAHES - Vehicle Inspection Result 25-02-24Document1 pageMercedes Actros Head FAHES - Vehicle Inspection Result 25-02-24Sreeja LinNo ratings yet
- Loughborough Junction Minutes 16 February 2009Document5 pagesLoughborough Junction Minutes 16 February 2009Loughborough JunctionNo ratings yet
- A Study On Distribution Strategies of Hindustan Unilever Limited by Rajnikant GharatDocument31 pagesA Study On Distribution Strategies of Hindustan Unilever Limited by Rajnikant GharatRajnikant GharatNo ratings yet
- Best Control For FliesDocument30 pagesBest Control For FliesDavidNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Daily Lesson PlanDocument14 pagesDepartment of Education: Daily Lesson PlanSharlene Jane Roque AporboNo ratings yet
- EW-3500-C and D EW-4200-C and D Marine Diesel Generators: Ntec EST NCDocument27 pagesEW-3500-C and D EW-4200-C and D Marine Diesel Generators: Ntec EST NCGeorgiNo ratings yet
- p350 38Document430 pagesp350 38Mark CheneyNo ratings yet
- 12.1 LeesGreen BWMS Equipment and Maintenance Manual v2.1Document71 pages12.1 LeesGreen BWMS Equipment and Maintenance Manual v2.1Huy Lễ NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Verbs List SoundDocument16 pagesVerbs List SoundEliana Zapata RuedaNo ratings yet
- AA SL Test 1Document3 pagesAA SL Test 1Ejaz Ahmad100% (1)
- Madam Butterfly (Okusama Chou) - Erotic PoetryDocument22 pagesMadam Butterfly (Okusama Chou) - Erotic PoetrygamahucherNo ratings yet
- Published Article 2Document17 pagesPublished Article 2Bharathi RajaNo ratings yet
Stroboscope Writing Material
Stroboscope Writing Material
Uploaded by
Tejpreet Singh BediOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Stroboscope Writing Material
Stroboscope Writing Material
Uploaded by
Tejpreet Singh BediCopyright:
Available Formats
Thus whenever a hole comes in line with the light source and sensor, a pulse is generated.
These
pulses are counted/ measured through an electronic counter.
The number of pulses generated depends upon the following factors:
i. The number of holes in the disc;
ii. The shaft speed.
Since the number of holes is fixed, therefore, the number of pulses generated depends on the
speed of the shaft only. The electronic counter may therefore be calibrated in terms of speed
(r.p.m.)
Fig. Photo-electric tachometer
Stroboscope: The working principle of stroboscope is that if a repeating event is only viewed
when at one particular point in its cycle it appears to be stationary. A mark is made on rotating
shaft, and a flashing light is subjected on the shaft. The frequency of the flashing is one very
short flash per revolution.
To determine the shaft speed we increases the frequency of flashing gradually from small value
until the rotating shaft appears to be stationary, then note the frequency. The frequency then
doubled, if there is still one apparent stationary image, the frequency is again doubled. This
continued until two images appear 180 degrees apart. When first appear for these two images the
flash frequency is twice the speed of rotation.
Stroboscopes are used to measure angular speed between 600 to 20000 rpm. Its advantage is that
it doesn’t need to make contact with the rotating shaft.
Fig. Shaft speed measurement using Stroboscope
Prepared by Mr. Anil Kumar Gillawat, Asst. Prof., MED
Finding exact value of speed: Single line image is obtained by adjusting the stroboscope at its
highest flashing frequency (fm). The flashing rate is gradually reduced and the flashing
frequencies are noted for all single line images (m different flashing rates).
f m f 1 m 1
N
f m f1
If the shaft rotates at speed slightly higher than the primary speed, the pattern appears to rotate
slowly forward. On the other hand, If the shaft rotates at speed slightly less than the primary
speed, the pattern appears to rotate in the reverse direction to that of the direction of rotation of
shaft.
Advantages:
1. Imposes no load on the shaft hence no power loss.
2. Non-contact type hence, no attachments needed.
3. Convenient to use for spot checks on machinery speeds and laboratory work.
Disadvantages:
1. The variable frequency oscillator circuit cannot be stabilized to give a fixed
frequency hence less accurate than digital meters.
2. Cannot be used where ambient light is above a certain level.
3. Requires well defined lighting conditions for efficient operations
4. Errors are caused due to slight variation in the frequency.
You might also like
- Pass Ultrasound Physics Exam Study Guide ReviewFrom EverandPass Ultrasound Physics Exam Study Guide ReviewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- AGS-688 ManualDocument60 pagesAGS-688 Manualvatcslav0% (1)
- Stroboscope With RPM Indicator Full ReportDocument26 pagesStroboscope With RPM Indicator Full Reportthreephasefault100% (2)
- Torsion Meter PartialDocument22 pagesTorsion Meter PartialSam Ompad100% (1)
- Objective: Equipment:: Lab Report 5Document3 pagesObjective: Equipment:: Lab Report 5Rida NasirNo ratings yet
- T 3Document4 pagesT 3नेपाली नेवरि प्रसन्नNo ratings yet
- UTI BrochureDocument2 pagesUTI BrochureKaye de LeonNo ratings yet
- 4 StroboscopeDocument3 pages4 StroboscopeKamal Mahal0% (5)
- Theory of Operation of Rate SensorsDocument4 pagesTheory of Operation of Rate SensorsPhạm Ngọc HòaNo ratings yet
- Turbine Speed MeasurementDocument26 pagesTurbine Speed MeasurementAyyar Kandasamy100% (4)
- Describe The Construction of A Electromagnetic Velocity Sensor and Explain Its WorkingDocument8 pagesDescribe The Construction of A Electromagnetic Velocity Sensor and Explain Its WorkingJiten Thakur100% (1)
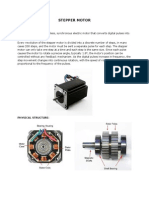
- Stepper Motor ReportDocument19 pagesStepper Motor ReportIan Bagunas100% (2)
- Experimental Technique in AutomobileDocument12 pagesExperimental Technique in AutomobileVivekDhameliyaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Tachometers and Digital TachometerDocument15 pagesMechanical Tachometers and Digital TachometerAllen GeorgeNo ratings yet
- HW3Document2 pagesHW3cx18717315873No ratings yet
- Stroboscope: Non-Contact Speed Measurement High Intensity Flashes Direct Speed Reading in RPM No Shaft ModificationDocument1 pageStroboscope: Non-Contact Speed Measurement High Intensity Flashes Direct Speed Reading in RPM No Shaft ModificationVarunNo ratings yet
- Stepper MotorsDocument53 pagesStepper MotorsirfancardiagnosticNo ratings yet
- PIC NotesDocument17 pagesPIC Notessvyas7872No ratings yet
- Basic Principle of Mechanical Torsion MeterDocument4 pagesBasic Principle of Mechanical Torsion MeterKranthi KumarNo ratings yet
- DT2289Document5 pagesDT2289shijirbatNo ratings yet
- Measure of Angular VelocityDocument12 pagesMeasure of Angular VelocityAshley_Rulzzzzzzz100% (2)
- Sound MeasurementDocument27 pagesSound MeasurementVarad DateNo ratings yet
- AC Induction Motor MonitoringDocument4 pagesAC Induction Motor MonitoringAnonymous PVXBGg9TNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Vibration and Strain MeasurementDocument12 pagesUnit 5 Vibration and Strain Measurement08 Dadarkar Mujtaba MEANo ratings yet
- Speed Measurement CH 1Document42 pagesSpeed Measurement CH 1unknown730407No ratings yet
- Vibration - Electrical or Mechanical - EASADocument3 pagesVibration - Electrical or Mechanical - EASAGilbNo ratings yet
- Angle Measurement Using Hall Sensor PDFDocument3 pagesAngle Measurement Using Hall Sensor PDFAlok MajhiNo ratings yet
- Servo MotorsDocument27 pagesServo Motorsc_archana100% (1)
- Ultrasonic MotorDocument11 pagesUltrasonic MotorShivang AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Food Microbiology & Microbial Techniques - Fsr2002: Niraj Singh M.Tech-Fsqm I SEM I.D.No. (RA1812036010015)Document14 pagesFood Microbiology & Microbial Techniques - Fsr2002: Niraj Singh M.Tech-Fsqm I SEM I.D.No. (RA1812036010015)Niraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Linear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT)Document10 pagesLinear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT)Sam WaikarNo ratings yet
- A Stepper Motor Is A "Pulse-Driven" Motor That Changes The Angular Position of The Rotor in "Steps" It Is A Digital Electromechanical Device DefineDocument35 pagesA Stepper Motor Is A "Pulse-Driven" Motor That Changes The Angular Position of The Rotor in "Steps" It Is A Digital Electromechanical Device DefineSupriya RakshitNo ratings yet
- Accelerometers Versus Velocity Sensors - What's The Difference 2Document1 pageAccelerometers Versus Velocity Sensors - What's The Difference 2Nelson Arul NathanNo ratings yet
- Module 4 3Document24 pagesModule 4 3Atharva KhadseNo ratings yet
- AC MachinesDocument22 pagesAC MachinesUtkarsh ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Stepper MotorDocument39 pagesUnit-1 Stepper MotorkoundinyaNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Induction MotorDocument21 pagesThree Phase Induction MotorM R Tarun RameshkumarNo ratings yet
- Advances in MetrologyDocument40 pagesAdvances in Metrologymanoj kumar GNo ratings yet
- Cs SeminarDocument15 pagesCs SeminarMoti GamachuNo ratings yet
- II yr/III Sem/Mech/EEE 2 Marks With Answers Unit-IIDocument5 pagesII yr/III Sem/Mech/EEE 2 Marks With Answers Unit-IIanunilaNo ratings yet
- 2 Vibn Analysis BasicsDocument117 pages2 Vibn Analysis BasicsTanoj PatroNo ratings yet
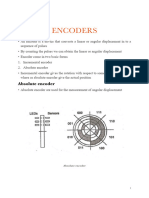
- ENCODERSDocument11 pagesENCODERSRabi khanNo ratings yet
- Brushless DC MotorDocument6 pagesBrushless DC Motorpsksiva13No ratings yet
- Design and Development of A Fluxgate MagnetometerDocument5 pagesDesign and Development of A Fluxgate Magnetometerdr_oxide2No ratings yet
- Principles of Measurement and Instrumentation EKT 112: OscilloscopeDocument40 pagesPrinciples of Measurement and Instrumentation EKT 112: OscilloscopesambavaleNo ratings yet
- Photo Transistor: Dr.A.Anbarasi Associate Professor Department of Physics CuddaloreDocument14 pagesPhoto Transistor: Dr.A.Anbarasi Associate Professor Department of Physics CuddaloreHema HemaNo ratings yet
- AU2140097 HomeActivity3Document1 pageAU2140097 HomeActivity3niyati.p1No ratings yet
- Robot Actuators and Feedback Components (Main7)Document82 pagesRobot Actuators and Feedback Components (Main7)tarasasanka33% (6)
- Measurement of VelocityDocument59 pagesMeasurement of VelocityYogeshBhatt100% (1)
- Unit 4 Laser and Advances in MetrologyDocument74 pagesUnit 4 Laser and Advances in MetrologyS. SARGUNA THAMIZHAN MECHNo ratings yet
- Electric DrivesDocument16 pagesElectric DrivesvigneshNo ratings yet
- Stepper Motor BasicsDocument11 pagesStepper Motor BasicsrvpilotNo ratings yet
- Group 6 GyroscopeDocument17 pagesGroup 6 GyroscopePhenias ManyashaNo ratings yet
- UoGx ECEg4155 Chapter 7 8Document45 pagesUoGx ECEg4155 Chapter 7 8Abdi ExplainsNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Vibration & Axial DisplacementDocument6 pagesMeasurement of Vibration & Axial DisplacementSatNo ratings yet
- AC MotorDocument18 pagesAC MotorNAVNEET GUPTANo ratings yet
- Noise and Vibration Analysis of Elevator Traction Machine: Ryo Kawasaki Yasuo HIRONAKA Masaharu NISHIMURADocument9 pagesNoise and Vibration Analysis of Elevator Traction Machine: Ryo Kawasaki Yasuo HIRONAKA Masaharu NISHIMURAyounesNo ratings yet
- Training Program On Vibration AnalysisDocument92 pagesTraining Program On Vibration AnalysisDurga Prasad Padhy100% (2)
- Stepper Motor - Types, Advantages and ApplicationsDocument2 pagesStepper Motor - Types, Advantages and ApplicationsBilalNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor (ALL TOPICS)Document33 pagesInduction Motor (ALL TOPICS)Ramprakash89% (18)
- EM214Induction Motorchapter 3Document46 pagesEM214Induction Motorchapter 3mahrusNo ratings yet
- Apply Good Dispensing Principles - NEW-1Document49 pagesApply Good Dispensing Principles - NEW-1abelashe2No ratings yet
- Timing Calibration Harness AssemblyDocument5 pagesTiming Calibration Harness Assemblyflordeliz jimenez rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 Energy Transport With Energy DissipationDocument16 pagesLecture 11 Energy Transport With Energy DissipationFarahin Burhan100% (1)
- GP MCQ 6Document4 pagesGP MCQ 6Marta MoreiraNo ratings yet
- # Sample Quotation Copy For Go Kart SparesDocument3 pages# Sample Quotation Copy For Go Kart SparessaqibNo ratings yet
- 4th Quarter ExamDocument2 pages4th Quarter ExamMa. Cynthia San JuanNo ratings yet
- Foodsupplements 6-3-2019Document282 pagesFoodsupplements 6-3-2019TalalAlamoudiNo ratings yet
- Kakuban - The Esoteric Meaning of Amida 2Document4 pagesKakuban - The Esoteric Meaning of Amida 2Rhys SchauwekerNo ratings yet
- 08-03-17 EditionDocument28 pages08-03-17 EditionSan Mateo Daily JournalNo ratings yet
- Jillian Gaviani FSC Booth DesignDocument7 pagesJillian Gaviani FSC Booth DesignMuthana JalladNo ratings yet
- PhySciSHS Q4 Week1Document46 pagesPhySciSHS Q4 Week1Roseman TumaliuanNo ratings yet
- DD Soft Copy and Hard Copy Recieved Details Journal Review Process 21 April 2014 8 PM1Document34 pagesDD Soft Copy and Hard Copy Recieved Details Journal Review Process 21 April 2014 8 PM1Puneet AjalNo ratings yet
- Alternador AVK - DSG DIG Instalacion Servicio y MantenimientoDocument595 pagesAlternador AVK - DSG DIG Instalacion Servicio y MantenimientoMartin FloresNo ratings yet
- IOL Calculation in Complex Corneal ConditionsDocument8 pagesIOL Calculation in Complex Corneal ConditionsShimaa MersalNo ratings yet
- CSTSN5Document2 pagesCSTSN5nileshcw51No ratings yet
- Mercedes Actros Head FAHES - Vehicle Inspection Result 25-02-24Document1 pageMercedes Actros Head FAHES - Vehicle Inspection Result 25-02-24Sreeja LinNo ratings yet
- Loughborough Junction Minutes 16 February 2009Document5 pagesLoughborough Junction Minutes 16 February 2009Loughborough JunctionNo ratings yet
- A Study On Distribution Strategies of Hindustan Unilever Limited by Rajnikant GharatDocument31 pagesA Study On Distribution Strategies of Hindustan Unilever Limited by Rajnikant GharatRajnikant GharatNo ratings yet
- Best Control For FliesDocument30 pagesBest Control For FliesDavidNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Daily Lesson PlanDocument14 pagesDepartment of Education: Daily Lesson PlanSharlene Jane Roque AporboNo ratings yet
- EW-3500-C and D EW-4200-C and D Marine Diesel Generators: Ntec EST NCDocument27 pagesEW-3500-C and D EW-4200-C and D Marine Diesel Generators: Ntec EST NCGeorgiNo ratings yet
- p350 38Document430 pagesp350 38Mark CheneyNo ratings yet
- 12.1 LeesGreen BWMS Equipment and Maintenance Manual v2.1Document71 pages12.1 LeesGreen BWMS Equipment and Maintenance Manual v2.1Huy Lễ NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Verbs List SoundDocument16 pagesVerbs List SoundEliana Zapata RuedaNo ratings yet
- AA SL Test 1Document3 pagesAA SL Test 1Ejaz Ahmad100% (1)
- Madam Butterfly (Okusama Chou) - Erotic PoetryDocument22 pagesMadam Butterfly (Okusama Chou) - Erotic PoetrygamahucherNo ratings yet
- Published Article 2Document17 pagesPublished Article 2Bharathi RajaNo ratings yet