Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cheat Sheet For G Field
Cheat Sheet For G Field
Uploaded by
Kok Soon ChongOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cheat Sheet For G Field
Cheat Sheet For G Field
Uploaded by
Kok Soon ChongCopyright:
Available Formats
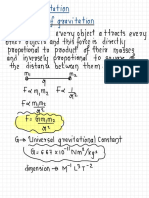
Newton’s Law of Gravitation
Gravitation Field
o Every point mass attracts another point mass with a force that is proportional to
the product of the 2 masses and inversely proportional to the square of the o A region of space surrounding a body possessing mass, in which any other body
distance between them. that has mass will experience a force of attraction.
o Gravitational Field Strength g (at a point in a gravitational field) is defined as the
mm m m Fg : is a vector, formula give the magnitude of
Fg ∝ 1 2 2 ⇒ Fg = G 1 2 2 the force only.
gravitational force per unit mass acting on a mass placed at that point.
r r : always attractive, acts along the joining Fg M g : vector
-11
G: 6.67 x 10 Nm kg
2 -2
the 2 centres of mass g= ⇒ g =G : SI unit: N kg
-1
Fg = mg m-1 2
Unit of Fg : N : to find resultant Fg due to multiple r : to find resultant g at a point, use vector addition.
masses, use vector addition. g / N kg
Fg / N
4 Inside Earth (r < RE): g = 4 Gπρr ⇒ g ∝ r
Inside Earth (r < RE): F = Gmπρr ⇒ F ∝ r
mg 9.81
g g 3
3
ME 1
M Em 1 Outside Earth (r>RE): g =G ⇒g∝ 2
Outside Earth (r>RE): Fg = G 2
⇒ Fg ∝ 2 r/m r 2
r
r r RE
RE r/m Factors affecting measurements of g
o Earth’s density not being uniform
dU
F =− GRAVITATION o Earth is not a sphere but bulging at the equator
g dr o Rotation of Earth (apparent g = g’)
At the equator:
Gravitational Potential Energy Fnet = ma
o Work done by an external force in bringing the mass from infinity to that point in
a gravitational field. mg
mg − N = mRE ω 2
U : scalar mg ' = mg − mRω 2
mm
U = −G 1 2 : SI unit : J
r : to find resultant U, use algebraic addition. N (= mg’) g ' = g − Rω 2
U is always negative. Since the gravitational force is attractive, work must be dφ
o
U g =−
done by external force to bring it to infinity. As infinity is taken to be zero
(reference), any other point in the g-field will have less GPE, hence negative. φ= dr
OR Since the gravitational force is attractive, positive work is done by the
m
Gravitational Potential
gravitational force to bring the mass from infinity to that point. Hence negative o Work done per unit mass by an external force in bringing that body from infinity to
work is done by the external force, GPE is negative. that point in a gravitational field.
o dU → negative of gradient of U-r
φ : scalar
Fg = − U M -1
curve gives the gravitational φ = = −G : SI unit : J kg
dr force F .
g m r : to find resultant φ, use algebraic addition.
o φ is always negative, as reference point, where φ = 0, is taken to be at infinity.
Motion and G-field
o Escape Velocity
Equipotential lines
1 M m 2GM E
mve ≥ G E → ve ≥
2
2 r r Gravitional. field lines
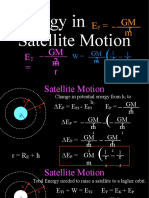
o Orbiting Satellite E/J
ET = KE + GPE
M Em v2 GM E
Fnet = ma → G 2 = m → v= KE
r r r
r/m
2π 4π 3
2 RE
M m Motion and G-field (cont’d)
or G E2 = mrω 2 = mr → T 2 = R → T 2 ∝ R3 ET o Geostationary Orbit: above a fixed point on Earth.
r T GM E GPE
Conditions:
o Total Mechanical Energy of Satellite Period = 24 hrs
1 GM E m GM E m GM E m In plane of equator
ET = KE + GPE = + (− )=− Moving from wst to east.
2 r r 2r
You might also like
- Cheat Sheet For E-FieldDocument2 pagesCheat Sheet For E-FieldKok Soon ChongNo ratings yet
- 2014-15 Solutions To Practice Problems - Groundwater Permeability and Seepage Part 3Document13 pages2014-15 Solutions To Practice Problems - Groundwater Permeability and Seepage Part 3Kok Soon Chong50% (2)
- Practice Problems - Groundwater Permeability and Seepage Part 2Document2 pagesPractice Problems - Groundwater Permeability and Seepage Part 2Kok Soon ChongNo ratings yet
- Gravitational Field Concise NotesDocument2 pagesGravitational Field Concise Notes2A620langdiNo ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument20 pagesPhysics NotesDani AdonaiNo ratings yet
- Gravitation - PCDocument36 pagesGravitation - PCFor YoutubeNo ratings yet
- (8032) DPP Gravitation eDocument6 pages(8032) DPP Gravitation eIshaan TandonNo ratings yet
- Formulae GravitationDocument5 pagesFormulae Gravitationchinmaykumarmohanty9No ratings yet
- GravitationDocument21 pagesGravitationTrivedi MokshNo ratings yet
- GravitationDocument18 pagesGravitationRaju GautamNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 12Document1 pageChapter2 12jstbnceNo ratings yet
- Chap3 NotesDocument8 pagesChap3 NotesSiow En YiNo ratings yet
- GravitationDocument2 pagesGravitationhavertz291aNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Gravity 2020 05 13 WedDocument29 pagesChapter 3 Gravity 2020 05 13 WedChong Chee SianNo ratings yet
- H2 Physics Gravitation SummaryDocument1 pageH2 Physics Gravitation SummaryAudrey Jong0% (1)
- Day 9 GravitationDocument13 pagesDay 9 GravitationDivyanshi SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint - GravityDocument9 pagesPowerpoint - GravityAtharvvaNo ratings yet
- 08 Gravitation Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument5 pages08 Gravitation Formula Sheets Quizrrchucha kumarNo ratings yet
- Gravitation TestDocument13 pagesGravitation TestHaa KksakNo ratings yet
- Gravitation: Chapter - 00Document19 pagesGravitation: Chapter - 00BhagyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document16 pagesChapter 12Fahmi MomoNo ratings yet
- (Rise Up) - Gravitation - Aug 29Document88 pages(Rise Up) - Gravitation - Aug 29lipeba7201No ratings yet
- CAIE Physics A-Level: Topic 8: Gravitational FieldsDocument6 pagesCAIE Physics A-Level: Topic 8: Gravitational Fieldsmughees_itcompNo ratings yet
- Gravitational Fields & Circular MotionDocument3 pagesGravitational Fields & Circular Motionmptneuro2024No ratings yet
- Gravitation NoteDocument28 pagesGravitation NotePranav AjithNo ratings yet
- 5 - Gravitation-01 - TheoryDocument16 pages5 - Gravitation-01 - TheoryRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - GravitationDocument13 pagesChapter 8 - GravitationAman Singh RaoNo ratings yet
- 07 Gravitation Revision Notes QuizrrDocument32 pages07 Gravitation Revision Notes QuizrrChu ChuNo ratings yet
- Gravitation LNDocument42 pagesGravitation LNMinnuNo ratings yet
- 982 Topper 21 101 3 4 127 Gravitation Up201610281257 1477639670 5874Document12 pages982 Topper 21 101 3 4 127 Gravitation Up201610281257 1477639670 5874rishi manoj100% (1)
- 3.1 Newton's Universal Law of GravitationDocument6 pages3.1 Newton's Universal Law of GravitationCart KartikaNo ratings yet
- 08 Gravitation Formula Sheets Getmarks AppDocument6 pages08 Gravitation Formula Sheets Getmarks Appmishrabhishek7701No ratings yet
- Gravitation: Grade: 11 A, A1, B Subject: PhysicsDocument41 pagesGravitation: Grade: 11 A, A1, B Subject: PhysicsChunkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Universal GravitationDocument29 pagesChapter 1 - Universal GravitationDanny CherishNo ratings yet
- GRAVITATION-Shafee Sir.Document20 pagesGRAVITATION-Shafee Sir.jimmyemandeeNo ratings yet
- Every Equations-Deriving and PracDocument30 pagesEvery Equations-Deriving and PracArishaNo ratings yet
- (L4) - Gravitation - 23rd Oct.Document64 pages(L4) - Gravitation - 23rd Oct.Ritwik Kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- Gravitational and Electric FieldsDocument8 pagesGravitational and Electric FieldsMordecai ChimedzaNo ratings yet
- Lecture14 Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesDocument3 pagesLecture14 Equilibrium of Rigid BodieshuzaifaalyanhfNo ratings yet
- "Gravity Beyond Einstein"-Series: Gravitomagnetism - Successes in Explaining The CosmosDocument41 pages"Gravity Beyond Einstein"-Series: Gravitomagnetism - Successes in Explaining The Cosmossipora1No ratings yet
- Ic Sol w07d3 1Document8 pagesIc Sol w07d3 1sushant sharmaNo ratings yet
- Fields and ForcesDocument1 pageFields and ForcesSohamNo ratings yet
- Outline in General Physics I: Q2 Lesson 2: Newtonian Understanding of GravityDocument8 pagesOutline in General Physics I: Q2 Lesson 2: Newtonian Understanding of GravityWilliam NavsNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five Class 9thDocument11 pagesChapter Five Class 9thAliNo ratings yet
- Derivation and NumericalsDocument13 pagesDerivation and Numericalspiravi66No ratings yet
- Gravitation Class 11 Notes CBSE Physics Chapter 8 PDFDocument23 pagesGravitation Class 11 Notes CBSE Physics Chapter 8 PDFAyush singhNo ratings yet
- Gravitation Revision Notes (JEE Mains)Document33 pagesGravitation Revision Notes (JEE Mains)SHREYANo ratings yet
- 6 GravitationDocument6 pages6 Gravitationjustinboy68049No ratings yet
- @aakashallen: GravitationDocument17 pages@aakashallen: GravitationRamakrishna ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chapter-8 GravitationDocument18 pagesChapter-8 GravitationsarahNo ratings yet
- Pres 5 Energy Changes - KeyDocument7 pagesPres 5 Energy Changes - KeyJoey BryanNo ratings yet
- 22a. Gravitation (Neon) GKK GaruDocument31 pages22a. Gravitation (Neon) GKK GaruPathan KausarNo ratings yet
- GravitationDocument17 pagesGravitationRamesh SdNo ratings yet
- GravitationDocument4 pagesGravitationvivek.vmcavNo ratings yet
- GravitationDocument15 pagesGravitationvemalanarasimharaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05Document11 pagesChapter 05api-3728553No ratings yet
- Gravitation and Kepler's LawsDocument18 pagesGravitation and Kepler's LawsAaditya Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-physics-Plus One Chapter8Document12 pagesHsslive-physics-Plus One Chapter8kavya shreeNo ratings yet
- CH 6. Gravitation (Phy +1)Document52 pagesCH 6. Gravitation (Phy +1)Thè WondërNo ratings yet
- Module 10: Gravitation: Kepler's LawDocument13 pagesModule 10: Gravitation: Kepler's Lawapi-3766872No ratings yet
- Hsslive - Plus One Chapter 7 - 2024Document9 pagesHsslive - Plus One Chapter 7 - 2024ritheshparas39No ratings yet
- Strong Rigidity of Locally Symmetric Spaces. (AM-78), Volume 78From EverandStrong Rigidity of Locally Symmetric Spaces. (AM-78), Volume 78No ratings yet
- Cohomology of Quotients in Symplectic and Algebraic Geometry. (MN-31), Volume 31From EverandCohomology of Quotients in Symplectic and Algebraic Geometry. (MN-31), Volume 31No ratings yet
- 1 0 (9.8) 2 S T 1 0 (5.8) 2 S T 1 1 2.0 (9.8) (5.8) 2 2 T T 60 170 TanDocument4 pages1 0 (9.8) 2 S T 1 0 (5.8) 2 S T 1 1 2.0 (9.8) (5.8) 2 2 T T 60 170 TanKok Soon ChongNo ratings yet
- Ker Ker Liq Total Bea Liq Total Bea Liq Liq Liq Liq Liq LiqDocument6 pagesKer Ker Liq Total Bea Liq Total Bea Liq Liq Liq Liq Liq LiqKok Soon ChongNo ratings yet
- JC2 Physics H2 2018 JurongDocument85 pagesJC2 Physics H2 2018 JurongKok Soon ChongNo ratings yet
- JC2 Physics H2 2018 MilleniaDocument84 pagesJC2 Physics H2 2018 MilleniaKok Soon ChongNo ratings yet
- 2018 PU3 H2 PHY PE2 Mark Scheme: Paper 1 (30 Marks)Document3 pages2018 PU3 H2 PHY PE2 Mark Scheme: Paper 1 (30 Marks)Kok Soon ChongNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet - Circular MotionDocument1 pageCheat Sheet - Circular MotionKok Soon ChongNo ratings yet
- PC Progress Report 1.1Document27 pagesPC Progress Report 1.1Kok Soon ChongNo ratings yet
- PC Progress Report 1 Rev01Document33 pagesPC Progress Report 1 Rev01Kok Soon ChongNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems - Shear Strength (II)Document2 pagesPractice Problems - Shear Strength (II)Kok Soon ChongNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems - Groundwater Permeability and Seepage Part 1Document2 pagesPractice Problems - Groundwater Permeability and Seepage Part 1Kok Soon ChongNo ratings yet
- Conditions of BalanceDocument4 pagesConditions of BalanceKhalil Ali0% (1)
- Second Summative Test Science 6 Quarter 3Document1 pageSecond Summative Test Science 6 Quarter 3Jari CruzNo ratings yet
- 5 6311935473514185809Document145 pages5 6311935473514185809s kr100% (1)
- Three Phase Induction MotorDocument4 pagesThree Phase Induction MotorAimi Al-YahyaNo ratings yet
- LOCG-GEN-Guideline-003 Rev 0 - Marine Lifting PDFDocument28 pagesLOCG-GEN-Guideline-003 Rev 0 - Marine Lifting PDFJohn PetterNo ratings yet
- Kisssoft 0315 Product Description en PDFDocument112 pagesKisssoft 0315 Product Description en PDFhrrypnNo ratings yet
- CH 12Document24 pagesCH 12Roberta Moraes MarcondesNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1-Equivalent Force System-1 PDFDocument3 pagesAssignment 1-Equivalent Force System-1 PDFShaurya Baghel0% (1)
- The Difference Between Asynchronous and Synchronous MotorsDocument6 pagesThe Difference Between Asynchronous and Synchronous MotorsShiva Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- 5 AC Machimes-Synchronous MachineDocument36 pages5 AC Machimes-Synchronous MachineJohannes Butar-butarNo ratings yet
- Chap10 CapacitorsDocument22 pagesChap10 Capacitorsbree789No ratings yet
- Central ForcesDocument19 pagesCentral ForcesSri Endah DewiNo ratings yet
- Name(s) :: UP MbengwanaDocument6 pagesName(s) :: UP MbengwanasamuelNo ratings yet
- 5054 s16 Ms 21 PDFDocument6 pages5054 s16 Ms 21 PDFKritish RamnauthNo ratings yet
- Codigo Ansi de Funciones de ProteccionesDocument5 pagesCodigo Ansi de Funciones de ProteccionesGerman SchwabNo ratings yet
- Noah Grinberg - Speed Vs Slope LabDocument2 pagesNoah Grinberg - Speed Vs Slope Lablisa grinbergNo ratings yet
- Vi. Fluid Friction in Steady One Dimensional FlowDocument38 pagesVi. Fluid Friction in Steady One Dimensional FlowAlna LiviaNo ratings yet
- PS 113 Exam 2 NAME - SecDocument4 pagesPS 113 Exam 2 NAME - SecDestiny Kit ManuelNo ratings yet
- PowerLogic PM5000 Series - METSEPM5110Document3 pagesPowerLogic PM5000 Series - METSEPM5110ramos valdan murcielagoNo ratings yet
- 1.0 FUNDAMENTALS of VIBRATION 1.1 What Is Vibration? Mechanical VibrationDocument56 pages1.0 FUNDAMENTALS of VIBRATION 1.1 What Is Vibration? Mechanical VibrationLuis Balducci100% (1)
- Numerical Wave TankDocument25 pagesNumerical Wave TankRida FatimaNo ratings yet
- Motion Mountain: The Adventure of PhysicsDocument1,366 pagesMotion Mountain: The Adventure of PhysicsGoembaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines II UNIT 2Document34 pagesElectrical Machines II UNIT 2mkrasan0% (1)
- ProjectileDocument3 pagesProjectileAnanya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Engineering AssistantDocument9 pagesEngineering AssistantKrishna ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- An Automatic Transmission For Bicycles: A Simulation: Article in PressDocument10 pagesAn Automatic Transmission For Bicycles: A Simulation: Article in PressSP CreationsNo ratings yet
- Current TransformerDocument5 pagesCurrent TransformerJenny AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Converter Fed DC Motor-2Document3 pagesConverter Fed DC Motor-2Aayush PatidarNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of BiomechanicsDocument36 pagesFundamentals of BiomechanicsAlan Magpantay0% (1)
- (B-Tech Elt Course Outline) Physics I - GS111Document2 pages(B-Tech Elt Course Outline) Physics I - GS111sherry420No ratings yet