Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 viewsBasic Information Tech
Basic Information Tech
Uploaded by
Buse 7Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Quarter 3 - Module 1-W1&W2: Computer Systems Servicing (CSS)Document18 pagesQuarter 3 - Module 1-W1&W2: Computer Systems Servicing (CSS)AC Balio100% (5)
- Aio 1 PPTDocument24 pagesAio 1 PPT22206186No ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document51 pagesChapter 03oCloudiiNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Introduction To ComputersDocument26 pagesTopic 1 Introduction To ComputersAdelah AdelNo ratings yet
- Software Development Units (BooksRack - Net)Document174 pagesSoftware Development Units (BooksRack - Net)leonor bunga bungaNo ratings yet
- Binary Shift: (P) Practical (T) Theory (3) Denotes Number of LessonsDocument9 pagesBinary Shift: (P) Practical (T) Theory (3) Denotes Number of LessonsWalid SassiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Advanced Topics - AccessibleDocument61 pagesChapter 10 - Advanced Topics - AccessibleMd Mozasser RahmanNo ratings yet
- Introduction & Matrix Multiplication: 6.172 Performance Engineering of Software SystemsDocument69 pagesIntroduction & Matrix Multiplication: 6.172 Performance Engineering of Software SystemsAcker ChannelNo ratings yet
- Base 64 Character Encoding and Decoding ModelingDocument7 pagesBase 64 Character Encoding and Decoding ModelingShashi TiwariNo ratings yet
- L 04 Chapter02 v03Document68 pagesL 04 Chapter02 v03verdah.inam2005No ratings yet
- DES and AES - 2017Document107 pagesDES and AES - 2017bangal marathaNo ratings yet
- Bca Semester-I - 2 PDFDocument9 pagesBca Semester-I - 2 PDFThink AlienNo ratings yet
- Bca Semester-I - 2 PDFDocument9 pagesBca Semester-I - 2 PDFThink AlienNo ratings yet
- Bca Semester-I 2vvhDocument9 pagesBca Semester-I 2vvhThink AlienNo ratings yet
- Data Storage ManipulationDocument69 pagesData Storage ManipulationZiya Can OğuzNo ratings yet
- Laudon Mis15 PPT Ch07Document48 pagesLaudon Mis15 PPT Ch07Sanh NguyệtNo ratings yet
- 21AC - What's New in Db2 For I PDFDocument47 pages21AC - What's New in Db2 For I PDFVenkatasubramanian SivagnanasundaramNo ratings yet
- Quick Study Notes On ComputersDocument3 pagesQuick Study Notes On ComputersraanaarNo ratings yet
- DatabaseDocument20 pagesDatabasemalik.krittikaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International As & A Level 9618 Computer Science Syllabus For Examination in 2024 and 2025Document20 pagesCambridge International As & A Level 9618 Computer Science Syllabus For Examination in 2024 and 2025Om Parkash Sarwan Bheel100% (1)
- Chapter1 AcaDocument26 pagesChapter1 AcaKusuma P ChandrashekharNo ratings yet
- C.S Project WrongDocument31 pagesC.S Project Wrongtejeswaran m100% (1)
- Important Computer Awareness Capsule For IBPS RRB PO-Clerk Mains 2017-www - Ibpsguide.com PDFDocument50 pagesImportant Computer Awareness Capsule For IBPS RRB PO-Clerk Mains 2017-www - Ibpsguide.com PDFDileep SaiNo ratings yet
- 3 4 ComputerPartsDocument51 pages3 4 ComputerPartsArun KorathNo ratings yet
- Instructions: Language of The Machine: Computer Architecture - CS401Document65 pagesInstructions: Language of The Machine: Computer Architecture - CS401Refik YalcinNo ratings yet
- Information Systems Today: Chapter # 2Document51 pagesInformation Systems Today: Chapter # 2abdullah altwjreNo ratings yet
- CSM 151 - Lec1 - 2024Document69 pagesCSM 151 - Lec1 - 2024GodfredNo ratings yet
- Ig Cs Checklist All 2024Document49 pagesIg Cs Checklist All 20241417186624No ratings yet
- Week-5 Microsoft Access By: Shafiullah Lecturer CS/ITDocument11 pagesWeek-5 Microsoft Access By: Shafiullah Lecturer CS/ITMuhammad ShehzadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document59 pagesChapter 3thu phanNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between A 32-Bit and A 64-Bit OS - QuoraDocument1 pageWhat Is The Difference Between A 32-Bit and A 64-Bit OS - Quorafadzai marechaNo ratings yet
- Ictl 2Document33 pagesIctl 2promise01nyanisaNo ratings yet
- Big Data and The Next WaveDocument46 pagesBig Data and The Next WaveJAGA ADHINo ratings yet
- Big Data Streams Analytics: Challenges, Analysis, and ApplicationsDocument55 pagesBig Data Streams Analytics: Challenges, Analysis, and ApplicationsMd Zahid HossainNo ratings yet
- Big DataDocument25 pagesBig DataVIJAYA PRABA PNo ratings yet
- Cs Sem 1 SummaryDocument28 pagesCs Sem 1 SummaryJian Hong OoNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering: ECE 4240 - Microprocessor InterfacingDocument3 pagesFaculty of Engineering: ECE 4240 - Microprocessor InterfacingDheereshNo ratings yet
- MIPS Processor R3000: RegistersDocument76 pagesMIPS Processor R3000: Registersmalik Al kadahNo ratings yet
- ch-1 Part 1Document31 pagesch-1 Part 1Kalayu RedaeNo ratings yet
- EE379K/EE394V Smart Grids:: Ross Baldick, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Spring 2017Document9 pagesEE379K/EE394V Smart Grids:: Ross Baldick, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Spring 2017tt_aljobory3911No ratings yet
- New N5 Summary NotesDocument12 pagesNew N5 Summary NotessuresampatsNo ratings yet
- Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm: Telecommunications, The Internet, and Wireless TechnologyDocument54 pagesManagement Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm: Telecommunications, The Internet, and Wireless TechnologyHammad HassanNo ratings yet
- Tancet 2017 Ca - SsDocument28 pagesTancet 2017 Ca - SssellappasivaNo ratings yet
- Micro (2) - 9 The Math Coprocessor Part-1 29-3-2024Document14 pagesMicro (2) - 9 The Math Coprocessor Part-1 29-3-2024Zaid PeroNo ratings yet
- Effect of Data Skewness and Workload Balance in Parallel Data MiningDocument17 pagesEffect of Data Skewness and Workload Balance in Parallel Data MiningSaurabh BhondeNo ratings yet
- 168 - An Enhanced Hybrid Cryptographic Algorithm For Security of Text - Paper ID - IJ61010735Document8 pages168 - An Enhanced Hybrid Cryptographic Algorithm For Security of Text - Paper ID - IJ61010735Bhavik RanaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NetworkingDocument30 pagesIntroduction To NetworkingJakia ChyNo ratings yet
- OSI Reference Model: Reference Model Was Created by The International Organization ForDocument37 pagesOSI Reference Model: Reference Model Was Created by The International Organization ForMoris SungaNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Why Binary and How We Interpret ItDocument16 pagesLecture - Why Binary and How We Interpret ItmeNo ratings yet
- Basic Microprocessor Architectural ConceptsDocument12 pagesBasic Microprocessor Architectural ConceptsMK100% (2)
- Cryptography and Network SecurityDocument53 pagesCryptography and Network SecurityAarindam RainaNo ratings yet
- WP012 64bit Software PortingDocument8 pagesWP012 64bit Software PortingAnanya TanejaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Premendra Kumar Sahu Asst. ProfessorDocument46 pagesUnit 1: Premendra Kumar Sahu Asst. ProfessorPremendra SahuNo ratings yet
- 64 Bit ComputingDocument15 pages64 Bit ComputingDawod Shaaban Al-SulifanieNo ratings yet
- A 64 B R E B C (REBC3) : ITS Otor Nhanced Lock IpherDocument16 pagesA 64 B R E B C (REBC3) : ITS Otor Nhanced Lock IpherAIRCC - IJNSANo ratings yet
- BCS 011Document4 pagesBCS 011chaitanya lakkakulaNo ratings yet
- Computer Basic and PC Software AssignmentDocument28 pagesComputer Basic and PC Software AssignmentBishaz ShiwakotiNo ratings yet
- 15 An Insight Into Ip AddressingDocument9 pages15 An Insight Into Ip Addressing12a03thongphamhuuNo ratings yet
- Lec 01Document20 pagesLec 01Saqib RiazNo ratings yet
- 21 - 03 - 2023 Financial Accounting IIDocument40 pages21 - 03 - 2023 Financial Accounting IIBuse 7No ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document61 pagesLecture 2Buse 7No ratings yet
- 18 and 19 Group AccountsDocument27 pages18 and 19 Group AccountsBuse 7No ratings yet
- Tedarik Zinciri Vize NotDocument10 pagesTedarik Zinciri Vize NotBuse 7No ratings yet
- ITB 396 COGM-COGS Example 3Document1 pageITB 396 COGM-COGS Example 3Buse 7No ratings yet
- Sample QuestionnaireDocument4 pagesSample QuestionnaireBuse 7No ratings yet
- CSR SustainabilityDocument34 pagesCSR SustainabilityBuse 7No ratings yet
- Operations Management: Sustainability and Supply Chain ManagementDocument38 pagesOperations Management: Sustainability and Supply Chain ManagementBuse 7No ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document31 pagesLecture 3Buse 7No ratings yet
- The Contemporary Business Environment: Usiness AMEDocument7 pagesThe Contemporary Business Environment: Usiness AMEBuse 7No ratings yet
- Opportunities and Obstacles For Foreign Investors in Turkish Real EstateDocument71 pagesOpportunities and Obstacles For Foreign Investors in Turkish Real EstateBuse 7No ratings yet
- Handouts Chapter 15Document33 pagesHandouts Chapter 15Buse 7No ratings yet
- ML 3 15 Principles of Leadership and Management Practice Test Mark SchemeDocument6 pagesML 3 15 Principles of Leadership and Management Practice Test Mark SchemeBuse 7No ratings yet
- ML 3 2 Principles of People Management Practice Test Mark SchemeDocument6 pagesML 3 2 Principles of People Management Practice Test Mark SchemeBuse 7No ratings yet
- Handouts Chapter 14Document35 pagesHandouts Chapter 14Buse 7No ratings yet
- Basic Economic ConceptsDocument1 pageBasic Economic ConceptsBuse 7No ratings yet
- Handouts Chapter 12Document30 pagesHandouts Chapter 12Buse 7No ratings yet
- Graphs and FunctionsDocument38 pagesGraphs and FunctionsBuse 7No ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument39 pagesMathematicsBuse 7No ratings yet
- Mathematics I Egiovanis@adu - Edu.trDocument59 pagesMathematics I Egiovanis@adu - Edu.trBuse 7No ratings yet
- Glossary - Chapter 18 Artistic EffectsDocument4 pagesGlossary - Chapter 18 Artistic EffectsBuse 7No ratings yet
- Glossary - Chapter 12Document3 pagesGlossary - Chapter 12Buse 7No ratings yet
- SD Hackman Leading TeamsDocument13 pagesSD Hackman Leading TeamsIliana SanmartinNo ratings yet
- Experiencing Postsocialist CapitalismDocument251 pagesExperiencing Postsocialist CapitalismjelisNo ratings yet
- Sebp7383 05 00 Allcd - 9Document837 pagesSebp7383 05 00 Allcd - 9Roland Culla100% (1)
- Shapes of NailsDocument14 pagesShapes of NailsIyannNo ratings yet
- Mic 2 Mkii Installation Instructions and Reference Handbook 4189320057 UkDocument70 pagesMic 2 Mkii Installation Instructions and Reference Handbook 4189320057 Ukkamel kamelNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Sience - Body PartsDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Sience - Body Partsapi-307376252No ratings yet
- Support/downloads or Scan Above QR Code For Detailed Policy WordingDocument10 pagesSupport/downloads or Scan Above QR Code For Detailed Policy Wordingraj VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Steffes 5100 Tech Data SheetDocument4 pagesSteffes 5100 Tech Data SheetcringsredNo ratings yet
- Deodorization - W. de Greyt and M. KellensDocument43 pagesDeodorization - W. de Greyt and M. KellensGabriel VoglarNo ratings yet
- REVISING EXERCISES 1baDocument3 pagesREVISING EXERCISES 1baAlvaro LorcaNo ratings yet
- Entry Level Linguist ResumeDocument4 pagesEntry Level Linguist Resumejbzhnbyhf100% (1)
- B.inggris-Daily ActivitiesDocument11 pagesB.inggris-Daily ActivitiesDadang SopianNo ratings yet
- Experimental and Numerical Modeling of Cavitation ErosionDocument11 pagesExperimental and Numerical Modeling of Cavitation ErosionКонстантин ФинниковNo ratings yet
- How To Improve Battery Life of Your Galaxy Note 10 and Note 10Document18 pagesHow To Improve Battery Life of Your Galaxy Note 10 and Note 10rainpcruzNo ratings yet
- Tera Spin PK-1500 Series PK-1600 40 Weighting Arms Jul-2018Document14 pagesTera Spin PK-1500 Series PK-1600 40 Weighting Arms Jul-2018deepakNo ratings yet
- Genuine Eaton Vicker HidrauDocument28 pagesGenuine Eaton Vicker HidrauJenner Volnney Quispe ChataNo ratings yet
- Create Database Taller-AdalbertoDocument2 pagesCreate Database Taller-AdalbertoAdalberto GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Pentaho CE Vs EE ComparisonDocument4 pagesPentaho CE Vs EE Comparisonbangipool100% (1)
- EXOS Quick Guide - Cheat SheetDocument19 pagesEXOS Quick Guide - Cheat Sheetmaverick2689No ratings yet
- Channel DecisionsDocument30 pagesChannel Decisionsuzmatabassum1996No ratings yet
- Bcsbi Pictorial BookDocument24 pagesBcsbi Pictorial BookMALAYADRI DUARINo ratings yet
- PLC - HMI Lab #4 22W1Document2 pagesPLC - HMI Lab #4 22W1crazyjmprNo ratings yet
- CCC-BMG MOON 3-2 - Within Dwarvenholm v2.0Document30 pagesCCC-BMG MOON 3-2 - Within Dwarvenholm v2.0MarianoNo ratings yet
- 3I Grading Rubric For Output PresentationDocument2 pages3I Grading Rubric For Output PresentationBinibining Michelle CenizaNo ratings yet
- Qsi540-600Document74 pagesQsi540-600Lorenzo RossiNo ratings yet
- About BITS CmdletsDocument3 pagesAbout BITS CmdletsvashsauNo ratings yet
- DX-790-960-65-16.5i-M Model: A79451600v02: Antenna SpecificationsDocument2 pagesDX-790-960-65-16.5i-M Model: A79451600v02: Antenna SpecificationsakiselNo ratings yet
- Testing ChecklistDocument3 pagesTesting ChecklistAnurag YadavNo ratings yet
- BRR Course 5Document19 pagesBRR Course 5Wade SperryNo ratings yet
Basic Information Tech
Basic Information Tech
Uploaded by
Buse 70 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views32 pagesOriginal Title
basic information tech
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views32 pagesBasic Information Tech
Basic Information Tech
Uploaded by
Buse 7Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 32
GO!
All in One Computer Concepts and
Applications
Third Edition
Chapter 1
Computers and
Information Processing
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Learning Objectives (1 of 2)
• Recognize Computers
• Explain the Functions of a Computer
• Describe How Computers Represent Data Using
Binary Codes
• Describe the Evolution of Computer Systems
• List the Various Types and Characteristics of Personal
Computers
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Learning Objectives (2 of 2)
• Give Examples of Other Personal Computing Devices
• List the Various Types and Characteristics of Multiuser
Computers
• Explain the Safe and Efficient Use of Technology
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Recognize Computers (1 of 2)
• Data + Processing = Information
• Ubiquitous computing (ubicomp)
• Smart homes
• Embedded computers
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Recognize Computers (2 of 2)
• Convergence
– Mobile payment systems
• Green computing
– Smart appliances
– Smart grid
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
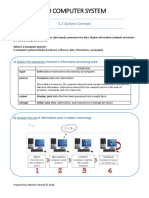
Explain the Functions of a Computer
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Describe How Computers Represent Data
Using Binary Codes (1 of 4)
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Describe How Computers Represent Data
Using Binary Codes (1 of 4)
With one switch, 2 options:
ON and OFF
With 2 switches, the
possibilities ‘increase by a
factor of 2( 22=4) and so on…
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Describe How Computers Represent Data
Using Binary Codes (1 of 4)
A Binary Code Using 8 Switches, Or Bits, Has 256
Different Possible Combinations
Number Of Bits
Possibilities Power of Two
(Switches)
2 to the 1
1 2 21
2 squared
2 4 22
2 cubed
3 8 23
2 to the 4
4 16 24
2 to the 5
5 32 25
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Describe How Computers Represent Data
Using Binary Codes (2 of 4)
A Binary Code Using 8 Switches, Or Bits, Has 256
Different Possible Combinations
Number Of Bits
Possibilities Power of Two
(Switches)
2 to the 6
6 64 26
2 to the 7
7 128 27
2 to the 8
8 256
28
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Describe How Computers Represent Data
Using Binary Codes (1 of 4)
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Describe How Computers Represent Data
Using Binary Codes (1 of 4)
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Describe How Computers Represent Data
Using Binary Codes (3 of 4)
The Standard Decimal Prefixes to Measure Data
Unit Number of Bytes
Bit (b) 11 over 8
8
Byte (B) 1
Kilobyte (KB) 1,000
Megabyte (MB) 1 million
Gigabyte (GB) 1 billion
Terabyte (TB) 1 trillion
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Describe How Computers Represent Data
Using Binary Codes (4 of 4)
The Standard Decimal Prefixes to Measure Data
Unit Number of Bytes
Petabyte (PB) 1,000 TB
Exabyte (EB) 1,000 PB
Zettabyte (ZB) 1,000 EB
Yottabyte (YB) 1,000 ZB
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Describe the Evolution of Computer
Systems (1 of 2)
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Describe the Evolution of Computer
Systems (1 of 2)
• Analytical Engine–19th century
• Turing machines–1936
• Turing test–1950
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Describe the Evolution of Computer
Systems (1 of 2)
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Describe the Evolution of Computer
Systems (2 of 2)
• First generation: ENIAC–1943-1946
• Second generation: Transistors–1950s
• Third generation: Integrated circuits–1960s
• Fourth generation: Microprocessor–1970s
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Describe the Evolution of Computer
Systems (2 of 2)
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
List the Various Types and Characteristics
of Personal Computers (1 of 3)
• Personal computer • Notebook
– Netbook
• Desktop computer
– Subnotebook
– Workstation
– All-in-one computer • Laptop
• Tablet computer
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
List the Various Types and Characteristics
of Personal Computers (3 of 3)
Comparing Personal Computers
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Give Examples of Other Personal
Computing Devices (1 of 2)
Mobile devices:
– Smartphones
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Give Examples of Other Personal
Computing Devices (1 of 2)
Mobile devices:
– E-readers
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Give Examples of Other Personal
Computing Devices (1 of 2)
Mobile devices: GPS
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Give Examples of Other Personal
Computing Devices (2 of 2)
• Video game system
– Game console
– Game controller
• Video game simulation
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
List the Various Types and Characteristics
of Multiuser Computers (1 of 3)
Multiuser computers:
– Centralized resources and security
– More powerful computers
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
List the Various Types and Characteristics
of Multiuser Computers (2 of 3)
• Midrange computers
• Mainframes
• Enterprise servers
• Supercomputers
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
List the Various Types and Characteristics
of Multiuser Computers (3 of 3)
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Explain the Safe and Efficient Use of
Technology
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Summary
• We are currently experiencing ubiquitous computing
and convergence
• In the information processing cycle, data is converted
into information
• Personal computers include desktops and portable
devices
• Multiuser computers are accessed by clients
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Questions
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Copyright
Copyright © 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
You might also like
- Quarter 3 - Module 1-W1&W2: Computer Systems Servicing (CSS)Document18 pagesQuarter 3 - Module 1-W1&W2: Computer Systems Servicing (CSS)AC Balio100% (5)
- Aio 1 PPTDocument24 pagesAio 1 PPT22206186No ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document51 pagesChapter 03oCloudiiNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Introduction To ComputersDocument26 pagesTopic 1 Introduction To ComputersAdelah AdelNo ratings yet
- Software Development Units (BooksRack - Net)Document174 pagesSoftware Development Units (BooksRack - Net)leonor bunga bungaNo ratings yet
- Binary Shift: (P) Practical (T) Theory (3) Denotes Number of LessonsDocument9 pagesBinary Shift: (P) Practical (T) Theory (3) Denotes Number of LessonsWalid SassiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Advanced Topics - AccessibleDocument61 pagesChapter 10 - Advanced Topics - AccessibleMd Mozasser RahmanNo ratings yet
- Introduction & Matrix Multiplication: 6.172 Performance Engineering of Software SystemsDocument69 pagesIntroduction & Matrix Multiplication: 6.172 Performance Engineering of Software SystemsAcker ChannelNo ratings yet
- Base 64 Character Encoding and Decoding ModelingDocument7 pagesBase 64 Character Encoding and Decoding ModelingShashi TiwariNo ratings yet
- L 04 Chapter02 v03Document68 pagesL 04 Chapter02 v03verdah.inam2005No ratings yet
- DES and AES - 2017Document107 pagesDES and AES - 2017bangal marathaNo ratings yet
- Bca Semester-I - 2 PDFDocument9 pagesBca Semester-I - 2 PDFThink AlienNo ratings yet
- Bca Semester-I - 2 PDFDocument9 pagesBca Semester-I - 2 PDFThink AlienNo ratings yet
- Bca Semester-I 2vvhDocument9 pagesBca Semester-I 2vvhThink AlienNo ratings yet
- Data Storage ManipulationDocument69 pagesData Storage ManipulationZiya Can OğuzNo ratings yet
- Laudon Mis15 PPT Ch07Document48 pagesLaudon Mis15 PPT Ch07Sanh NguyệtNo ratings yet
- 21AC - What's New in Db2 For I PDFDocument47 pages21AC - What's New in Db2 For I PDFVenkatasubramanian SivagnanasundaramNo ratings yet
- Quick Study Notes On ComputersDocument3 pagesQuick Study Notes On ComputersraanaarNo ratings yet
- DatabaseDocument20 pagesDatabasemalik.krittikaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International As & A Level 9618 Computer Science Syllabus For Examination in 2024 and 2025Document20 pagesCambridge International As & A Level 9618 Computer Science Syllabus For Examination in 2024 and 2025Om Parkash Sarwan Bheel100% (1)
- Chapter1 AcaDocument26 pagesChapter1 AcaKusuma P ChandrashekharNo ratings yet
- C.S Project WrongDocument31 pagesC.S Project Wrongtejeswaran m100% (1)
- Important Computer Awareness Capsule For IBPS RRB PO-Clerk Mains 2017-www - Ibpsguide.com PDFDocument50 pagesImportant Computer Awareness Capsule For IBPS RRB PO-Clerk Mains 2017-www - Ibpsguide.com PDFDileep SaiNo ratings yet
- 3 4 ComputerPartsDocument51 pages3 4 ComputerPartsArun KorathNo ratings yet
- Instructions: Language of The Machine: Computer Architecture - CS401Document65 pagesInstructions: Language of The Machine: Computer Architecture - CS401Refik YalcinNo ratings yet
- Information Systems Today: Chapter # 2Document51 pagesInformation Systems Today: Chapter # 2abdullah altwjreNo ratings yet
- CSM 151 - Lec1 - 2024Document69 pagesCSM 151 - Lec1 - 2024GodfredNo ratings yet
- Ig Cs Checklist All 2024Document49 pagesIg Cs Checklist All 20241417186624No ratings yet
- Week-5 Microsoft Access By: Shafiullah Lecturer CS/ITDocument11 pagesWeek-5 Microsoft Access By: Shafiullah Lecturer CS/ITMuhammad ShehzadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document59 pagesChapter 3thu phanNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between A 32-Bit and A 64-Bit OS - QuoraDocument1 pageWhat Is The Difference Between A 32-Bit and A 64-Bit OS - Quorafadzai marechaNo ratings yet
- Ictl 2Document33 pagesIctl 2promise01nyanisaNo ratings yet
- Big Data and The Next WaveDocument46 pagesBig Data and The Next WaveJAGA ADHINo ratings yet
- Big Data Streams Analytics: Challenges, Analysis, and ApplicationsDocument55 pagesBig Data Streams Analytics: Challenges, Analysis, and ApplicationsMd Zahid HossainNo ratings yet
- Big DataDocument25 pagesBig DataVIJAYA PRABA PNo ratings yet
- Cs Sem 1 SummaryDocument28 pagesCs Sem 1 SummaryJian Hong OoNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering: ECE 4240 - Microprocessor InterfacingDocument3 pagesFaculty of Engineering: ECE 4240 - Microprocessor InterfacingDheereshNo ratings yet
- MIPS Processor R3000: RegistersDocument76 pagesMIPS Processor R3000: Registersmalik Al kadahNo ratings yet
- ch-1 Part 1Document31 pagesch-1 Part 1Kalayu RedaeNo ratings yet
- EE379K/EE394V Smart Grids:: Ross Baldick, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Spring 2017Document9 pagesEE379K/EE394V Smart Grids:: Ross Baldick, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Spring 2017tt_aljobory3911No ratings yet
- New N5 Summary NotesDocument12 pagesNew N5 Summary NotessuresampatsNo ratings yet
- Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm: Telecommunications, The Internet, and Wireless TechnologyDocument54 pagesManagement Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm: Telecommunications, The Internet, and Wireless TechnologyHammad HassanNo ratings yet
- Tancet 2017 Ca - SsDocument28 pagesTancet 2017 Ca - SssellappasivaNo ratings yet
- Micro (2) - 9 The Math Coprocessor Part-1 29-3-2024Document14 pagesMicro (2) - 9 The Math Coprocessor Part-1 29-3-2024Zaid PeroNo ratings yet
- Effect of Data Skewness and Workload Balance in Parallel Data MiningDocument17 pagesEffect of Data Skewness and Workload Balance in Parallel Data MiningSaurabh BhondeNo ratings yet
- 168 - An Enhanced Hybrid Cryptographic Algorithm For Security of Text - Paper ID - IJ61010735Document8 pages168 - An Enhanced Hybrid Cryptographic Algorithm For Security of Text - Paper ID - IJ61010735Bhavik RanaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NetworkingDocument30 pagesIntroduction To NetworkingJakia ChyNo ratings yet
- OSI Reference Model: Reference Model Was Created by The International Organization ForDocument37 pagesOSI Reference Model: Reference Model Was Created by The International Organization ForMoris SungaNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Why Binary and How We Interpret ItDocument16 pagesLecture - Why Binary and How We Interpret ItmeNo ratings yet
- Basic Microprocessor Architectural ConceptsDocument12 pagesBasic Microprocessor Architectural ConceptsMK100% (2)
- Cryptography and Network SecurityDocument53 pagesCryptography and Network SecurityAarindam RainaNo ratings yet
- WP012 64bit Software PortingDocument8 pagesWP012 64bit Software PortingAnanya TanejaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Premendra Kumar Sahu Asst. ProfessorDocument46 pagesUnit 1: Premendra Kumar Sahu Asst. ProfessorPremendra SahuNo ratings yet
- 64 Bit ComputingDocument15 pages64 Bit ComputingDawod Shaaban Al-SulifanieNo ratings yet
- A 64 B R E B C (REBC3) : ITS Otor Nhanced Lock IpherDocument16 pagesA 64 B R E B C (REBC3) : ITS Otor Nhanced Lock IpherAIRCC - IJNSANo ratings yet
- BCS 011Document4 pagesBCS 011chaitanya lakkakulaNo ratings yet
- Computer Basic and PC Software AssignmentDocument28 pagesComputer Basic and PC Software AssignmentBishaz ShiwakotiNo ratings yet
- 15 An Insight Into Ip AddressingDocument9 pages15 An Insight Into Ip Addressing12a03thongphamhuuNo ratings yet
- Lec 01Document20 pagesLec 01Saqib RiazNo ratings yet
- 21 - 03 - 2023 Financial Accounting IIDocument40 pages21 - 03 - 2023 Financial Accounting IIBuse 7No ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document61 pagesLecture 2Buse 7No ratings yet
- 18 and 19 Group AccountsDocument27 pages18 and 19 Group AccountsBuse 7No ratings yet
- Tedarik Zinciri Vize NotDocument10 pagesTedarik Zinciri Vize NotBuse 7No ratings yet
- ITB 396 COGM-COGS Example 3Document1 pageITB 396 COGM-COGS Example 3Buse 7No ratings yet
- Sample QuestionnaireDocument4 pagesSample QuestionnaireBuse 7No ratings yet
- CSR SustainabilityDocument34 pagesCSR SustainabilityBuse 7No ratings yet
- Operations Management: Sustainability and Supply Chain ManagementDocument38 pagesOperations Management: Sustainability and Supply Chain ManagementBuse 7No ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document31 pagesLecture 3Buse 7No ratings yet
- The Contemporary Business Environment: Usiness AMEDocument7 pagesThe Contemporary Business Environment: Usiness AMEBuse 7No ratings yet
- Opportunities and Obstacles For Foreign Investors in Turkish Real EstateDocument71 pagesOpportunities and Obstacles For Foreign Investors in Turkish Real EstateBuse 7No ratings yet
- Handouts Chapter 15Document33 pagesHandouts Chapter 15Buse 7No ratings yet
- ML 3 15 Principles of Leadership and Management Practice Test Mark SchemeDocument6 pagesML 3 15 Principles of Leadership and Management Practice Test Mark SchemeBuse 7No ratings yet
- ML 3 2 Principles of People Management Practice Test Mark SchemeDocument6 pagesML 3 2 Principles of People Management Practice Test Mark SchemeBuse 7No ratings yet
- Handouts Chapter 14Document35 pagesHandouts Chapter 14Buse 7No ratings yet
- Basic Economic ConceptsDocument1 pageBasic Economic ConceptsBuse 7No ratings yet
- Handouts Chapter 12Document30 pagesHandouts Chapter 12Buse 7No ratings yet
- Graphs and FunctionsDocument38 pagesGraphs and FunctionsBuse 7No ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument39 pagesMathematicsBuse 7No ratings yet
- Mathematics I Egiovanis@adu - Edu.trDocument59 pagesMathematics I Egiovanis@adu - Edu.trBuse 7No ratings yet
- Glossary - Chapter 18 Artistic EffectsDocument4 pagesGlossary - Chapter 18 Artistic EffectsBuse 7No ratings yet
- Glossary - Chapter 12Document3 pagesGlossary - Chapter 12Buse 7No ratings yet
- SD Hackman Leading TeamsDocument13 pagesSD Hackman Leading TeamsIliana SanmartinNo ratings yet
- Experiencing Postsocialist CapitalismDocument251 pagesExperiencing Postsocialist CapitalismjelisNo ratings yet
- Sebp7383 05 00 Allcd - 9Document837 pagesSebp7383 05 00 Allcd - 9Roland Culla100% (1)
- Shapes of NailsDocument14 pagesShapes of NailsIyannNo ratings yet
- Mic 2 Mkii Installation Instructions and Reference Handbook 4189320057 UkDocument70 pagesMic 2 Mkii Installation Instructions and Reference Handbook 4189320057 Ukkamel kamelNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Sience - Body PartsDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Sience - Body Partsapi-307376252No ratings yet
- Support/downloads or Scan Above QR Code For Detailed Policy WordingDocument10 pagesSupport/downloads or Scan Above QR Code For Detailed Policy Wordingraj VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Steffes 5100 Tech Data SheetDocument4 pagesSteffes 5100 Tech Data SheetcringsredNo ratings yet
- Deodorization - W. de Greyt and M. KellensDocument43 pagesDeodorization - W. de Greyt and M. KellensGabriel VoglarNo ratings yet
- REVISING EXERCISES 1baDocument3 pagesREVISING EXERCISES 1baAlvaro LorcaNo ratings yet
- Entry Level Linguist ResumeDocument4 pagesEntry Level Linguist Resumejbzhnbyhf100% (1)
- B.inggris-Daily ActivitiesDocument11 pagesB.inggris-Daily ActivitiesDadang SopianNo ratings yet
- Experimental and Numerical Modeling of Cavitation ErosionDocument11 pagesExperimental and Numerical Modeling of Cavitation ErosionКонстантин ФинниковNo ratings yet
- How To Improve Battery Life of Your Galaxy Note 10 and Note 10Document18 pagesHow To Improve Battery Life of Your Galaxy Note 10 and Note 10rainpcruzNo ratings yet
- Tera Spin PK-1500 Series PK-1600 40 Weighting Arms Jul-2018Document14 pagesTera Spin PK-1500 Series PK-1600 40 Weighting Arms Jul-2018deepakNo ratings yet
- Genuine Eaton Vicker HidrauDocument28 pagesGenuine Eaton Vicker HidrauJenner Volnney Quispe ChataNo ratings yet
- Create Database Taller-AdalbertoDocument2 pagesCreate Database Taller-AdalbertoAdalberto GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Pentaho CE Vs EE ComparisonDocument4 pagesPentaho CE Vs EE Comparisonbangipool100% (1)
- EXOS Quick Guide - Cheat SheetDocument19 pagesEXOS Quick Guide - Cheat Sheetmaverick2689No ratings yet
- Channel DecisionsDocument30 pagesChannel Decisionsuzmatabassum1996No ratings yet
- Bcsbi Pictorial BookDocument24 pagesBcsbi Pictorial BookMALAYADRI DUARINo ratings yet
- PLC - HMI Lab #4 22W1Document2 pagesPLC - HMI Lab #4 22W1crazyjmprNo ratings yet
- CCC-BMG MOON 3-2 - Within Dwarvenholm v2.0Document30 pagesCCC-BMG MOON 3-2 - Within Dwarvenholm v2.0MarianoNo ratings yet
- 3I Grading Rubric For Output PresentationDocument2 pages3I Grading Rubric For Output PresentationBinibining Michelle CenizaNo ratings yet
- Qsi540-600Document74 pagesQsi540-600Lorenzo RossiNo ratings yet
- About BITS CmdletsDocument3 pagesAbout BITS CmdletsvashsauNo ratings yet
- DX-790-960-65-16.5i-M Model: A79451600v02: Antenna SpecificationsDocument2 pagesDX-790-960-65-16.5i-M Model: A79451600v02: Antenna SpecificationsakiselNo ratings yet
- Testing ChecklistDocument3 pagesTesting ChecklistAnurag YadavNo ratings yet
- BRR Course 5Document19 pagesBRR Course 5Wade SperryNo ratings yet