Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1ST SA BIOCHEMISTRY - Almendras
1ST SA BIOCHEMISTRY - Almendras
Uploaded by
Cherry DagohoyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1ST SA BIOCHEMISTRY - Almendras
1ST SA BIOCHEMISTRY - Almendras
Uploaded by
Cherry DagohoyCopyright:
Available Formats
1st SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT
GENERAL BIOCHEMISTRY
MTY1109
INSTRUCTIONS:
Choose the letter with the BEST answer.
RATIONALIZED every choice in the choices of each question WHY IT IS THE
CORRECT/INCORRECT answer.
5 points each item. TOTAL OF 100 POINTS
1. Which of the following is considered as structural polysaccharide?
A. Heparin C. Hyaluronic acid E. Glucose
B. Cellulose D. Starch
Explanation: They range in structure from linear to highly branched. Examples include
storage polysaccharides such as starch and glycogen, and structural polysaccharides such as
cellulose and chitin.
2. They are known as subtype of diastereomers whose molecules differ only in the
configuration at one chiral center.
A. Monomers C. Isomers E. None of the Above
B. Epimers D. All of the above
Explanation: the chiral center where each molecule differs is where their absolute
configuration is opposite that of the other pair.
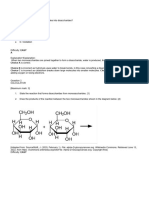
3. Which of the following structures is that of an L-monosaccharide?
A. B. C. D.
4. What is the relationship between D-Galactose and L-Galactose?
A. Diastereomers C. Epimers E. Geometrical isomers
B. Enantiomers D. Cis-trans isomers
Explanation: So D-glucose and D-galactose are diastereomers. They have the same
connectivity but are different optical isomers that are not enantiomers.
5. Which of the following disaccharides has the same β (1 to 4) linkage.
A. Sucrose and Maltose
B. Maltose and Cellobiose
C. Mannose and Sucrose
D. Lactose and Cellobiose
E. Cellulose and Fructose
Explanation: Common Disaccharides. Sucrose, lactose, and maltose are
common dietary components. Lactose, the disaccharide of milk, consists of
galactose joined to glucose by a β-1,4-glycosidic linkage. Lactose is
hydrolyzed to these monosaccharides by lactase in human beings.
6. The only achiral amino acid.
A. Glu B. Gln C. Gly D. Glc E. Gle
1st SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT
GENERAL BIOCHEMISTRY
MTY1109
Explanation: Glycine is the only amino acid with no asymmetric (chiral) carbon because it has two
hydrogens attached to alpha carbon.
7. Regeneration of the Carboxyl and Amino group of amino acids upon addition of water.
A. Protein Denaturation C. Protein Hydrolysis E. Protein Hydration
B. Peptide formation D. Peptide Hydrogenation
Explanation: A peptide bond is a chemical bond formed between two
molecules when the carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the amino
group of the other molecule, releasing a molecule of water (H2O). This is a
dehydration synthesis reaction (also known as a condensation reaction), and
usually occurs between amino acids.
8. Which of the following statements about protein structure is correct?
A. The sequence of amino acids in a protein is its tertiary structure
B. The sequence of amino acids in a protein is its secondary structure
C. Cross-links formed by oxidation of -SH groups of cysteine to form disulfide bridges
render the amino acid unavailable to digestion.
D. Cross-links between the amino group of lysine and the carboxyl group of glutamate
render the amino acid(s) unavailable for digestion.
E. All proteins have the same secondary structure
Explanation: Tertiary structure is the next level of complexity in protein folding. Tertiary
structure is the three dimensional structure of a protein. While individual amino acids in
the primary sequence can interact with one another to form secondary structures such
as helices and sheets and individual amino acids from distant parts of the primary
sequence can intermingle via charge-charge, hydrophobic, disulfide, or other
interactions, the formation of these bonds and interactions, the formation of these bonds
and interactions will serve to change shape of the overall protein.
9. Statement 1: Insulin and Glucagon are transport proteins that regulates blood glucose.
Statement 2: Hemoglobin is classified as multimeric and has a tertiary structure.
A. Both statements are correct.
B. Both statements are incorrect.
C. 1st statement is correct; 2nd is incorrect.
D. 1st statement is incorrect; 2nd is correct.
Insulin helps cells absorb glucose, reducing blood sugar and providing the cells with
glucose for energy. When blood sugar levels are too low, the pancreas release glucagon
instructs the liver to release stored glucose, which causes blood sugar to rise.
10. Zwitterion form of Alanine:
A. B. C. D.
Explanation: An amino acid zwitterion arising from transfer of a proton from the carboxy to the
amino group of alanine; major species at pH 7.3.
11. Energy is primarily stored in the body in the form of ________.
A. Cholesterol C. Triglycerides E. Fatty acid salts
B. Lipoproteins D. Free fatty acids
Explanation: Triglycerides: The major form of fat stored by the body.
A triglyceride consists of three molecules of fatty acid combined with a
1st SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT
GENERAL BIOCHEMISTRY
MTY1109
molecule of the alcohol glycerol. Triglycerides serve as the backbone of
many types of lipids (fats). Triglycerides come from the food we eat as well
as from being produced by the body.
12. Which of the following is a characteristic of both triacylglycerols and
glycerophospholipids?
A. Both contain carboxyl groups and are amphipathic.
B. Both contain fatty acids and are saponifiable.
C. Both contain glycerol and ether bonds.
D. Both can be negatively charged at cellular pH.
E. Both contain one or more ester bonds.
The main constituents of membrane bilayers often called phospholipids, an imprecise
term, as other lipids contains phosphate.
13. Which of the following is true?
A. Polyunsaturated fatty acids tend to bend, causing less packing, thus making
them softer than their saturated counterparts.
B. A cis-monounsaturated fatty acid has the same 3D structure as their
unsaturated counterparts.
C. The more unsaturated a fatty acid is, the higher its melting point.
D. The melting point of fatty acids is not dependent on the number of carbons in
their chain.
Explanation: The geometry of the double bond is almost always a cis configuration in
natural fatty acids. These molecules do not "stack" very well. The intermolecular interactions are
much weaker than saturated molecules. As a result, the melting points are much lower
for unsaturated fatty acids.
14. Prostaglandin is involved in all of the following EXCEPT:
I. Relaxing and contracting smooth muscle
II. Platelet aggregation
III. hypersensitivity responses
IV. Raising body temperature
A. I only C. III only E. I & IV only
B. II only D. II & III only
Explanation: Prostaglandis likewise leukotriens are proinflammatory mediators resulting
from metabolic degradation of the arachidonic acid originating from membrane
phospholipids
15. Oxidation of ________ leads to formation of _________.
A. Saturated FAs; Ketones
B. Unsaturated FAs; Aldehydes
C. Cholesterol; Carboxylic acids
D. Triglycerides; Fatty acid soaps
E. Lipids cannot be oxidized.
Explanation: The oxidation of long-chain fatty acids to acetyl-CoA is a central energy-
yielding pathway in animals, may protists, and some bacteria. The electrons removed
during fatty acid oxidation pass through the mitochondrial respiratory chain, driving ATP
synthesis, and the acetyl-CoA produced from the fatty acids may be completely oxidized
to CO2 via the citric acid cycle.
16. The concept of "induced fit" refers to the fact that:
A. Enzyme specificity is induced by enzyme-substrate binding.
1st SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT
GENERAL BIOCHEMISTRY
MTY1109
B. Enzyme-substrate binding induces an increase in the reaction entropy, thereby
catalyzing the reaction.
C. Enzyme-substrate binding induces movement along the reaction coordinate to
the transition state.
D. Substrate binding may induce a conformational change in the enzyme, which
then brings catalytic groups into proper orientation.
E. All of these
Explanation: The concept of "induced fit" refers to the fact that: A) enzyme
specificity is induced by enzyme-substrate binding. ... enzyme-substrate
binding induces an increase in the reaction entropy, thereby catalyzing the
reaction.
17. Statements:
(1) An apoenzyme, by itself, has no biochemical activity.
(2) Urease is an example of an enzyme with absolute specificity.
(3) All enzymes have names that end in -ase.
A. All three statements are true.
B. Two of three statements are true.
C. One of three statements are true.
D. None of these are true.
The ability of enzyme to bind with specific substrate or catalyze a specific set of
chemical reaction’s is called “enzyme specificity”. Some enzymes have an intrinsic
property of binding with only one substrate and catalyzing a single reaction. Enzymes
have the names that end in –ose.
18. Fischer’s ‘lock and key’ model of the enzyme action implies that:
A. The active site is complementary in shape to that of substance only after
interaction.
B. The active site is complementary in shape to that of substance
C. Substrates change conformation prior to active site interaction
D. The active site is flexible and adjusts to substrate
E. None of these
Explanation: The shape of an enzyme's active site is complementary to
the shape of its specific substrate or substrates. This means they
can fit together. Science presenter Jon Chase demonstrates the action of the
enzyme catalase, produced by the liver, in breaking down hydrogen peroxide
into water and oxygen.
19. It decreases enzyme activity by binding at a site other than the active site.
A. Reversible Competitive inhibitor
B. Reversible Noncompetitive inhibitor
C. Irreversible inhibitor
D. Positive regulator
E. Negative regulator
Explanation:In noncompetitive inhibition, an inhibitor molecule binds to
the enzyme at a location other than the active site (an allosteric site). The
substrate can still bind to the enzyme, but the inhibitor changes the shape of
the enzyme so it is no longer in optimal position to catalyze the reaction.
20. Statements:
(1) Enzymes undergo all of the reactions of proteins including denaturation.
(2) Vitamin E, a cholesterol derivative, can be synthesized in the skin by sunlight
irradiation.
1st SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT
GENERAL BIOCHEMISTRY
MTY1109
(3) The optimum pH for enzyme activity within the human body is always within the
physiological pH range of 7.0 to 7.5.
A. All three statements are true.
B. Two of three statements are true.
C. One of three statements are true.
D. None of these are true.
Explanation: Denaturation can be brought about in various ways. Proteins are denatured
by treatment with alkaline or acid, oxidizing or reducing agents, and certain organic
solvents Interesting among denaturing agents are those that affect the secondary and
tertiary structure without affecting the primary structure. The agents most frequently
used for this purpose are urea and guanidinium chloride.
You might also like
- BIOL 200 Molecular Biology Lecture NotesDocument44 pagesBIOL 200 Molecular Biology Lecture NotesDantong JiaNo ratings yet
- Bộ đề 1 ôn TestAsDocument56 pagesBộ đề 1 ôn TestAsÁnh Tuyết Lê Thị0% (1)
- Ganong Textbook of Medical PhysiologyDocument98 pagesGanong Textbook of Medical PhysiologyJanie-Vi Gorospe100% (1)
- Biochemistry MCQsDocument19 pagesBiochemistry MCQsschxzerrydawn100% (2)
- AP Biology Study Guide PDFDocument80 pagesAP Biology Study Guide PDFnax nittleman100% (4)
- Biochemistry Stage Exam Main PaperDocument21 pagesBiochemistry Stage Exam Main PaperDkt Pius KpchirchirNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry - Biomolecules AssignmentDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry - Biomolecules Assignmentsyed0% (1)
- Biochemistry QuizDocument6 pagesBiochemistry QuizPatrick Ngo'nga Chifwema100% (1)
- Unit 2 Chemical Basis of Life ReviewDocument2 pagesUnit 2 Chemical Basis of Life ReviewKamal NaserNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-01 Class - 12 Chemistry (Biomolecules)Document6 pagesCbse Test Paper-01 Class - 12 Chemistry (Biomolecules)SivakumarNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Biomolecules Questions Answers PDFDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Biomolecules Questions Answers PDFLakshmi DesikanNo ratings yet
- Chebme2 Q1 031715Document6 pagesChebme2 Q1 031715MEOW41No ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY - PACOP VioletDocument53 pagesBIOCHEMISTRY - PACOP VioletExequiel BoriborNo ratings yet
- Lab Investigation Discussion QuestionsDocument2 pagesLab Investigation Discussion QuestionsParisa YahyaieNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules (AS Level Bio)Document35 pagesBiological Molecules (AS Level Bio)DrMufaddal RampurwalaNo ratings yet
- Org Chem II Guiding QuestionsDocument10 pagesOrg Chem II Guiding QuestionsMesfen MeleseNo ratings yet
- Topic-1A (Food and Health) (Autosaved) - 20-40Document21 pagesTopic-1A (Food and Health) (Autosaved) - 20-40lisaNo ratings yet
- Biochem-Samplex LeDocument12 pagesBiochem-Samplex LeCarlos NiñoNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology and Biochemical EngineeringDocument46 pagesBiotechnology and Biochemical EngineeringPauline PongaseNo ratings yet
- 1-BIOCHEM-PRELIM-Shiftings-Carbohydrate-Chem-Enzymes-Energy-Metabolism-Porphyrins (1 DC)Document14 pages1-BIOCHEM-PRELIM-Shiftings-Carbohydrate-Chem-Enzymes-Energy-Metabolism-Porphyrins (1 DC)MICHAEL DELIVANo ratings yet
- Biochemistry (VIOLET)Document53 pagesBiochemistry (VIOLET)BRYAN BALDOMERONo ratings yet
- First Biology ExamsDocument16 pagesFirst Biology Examsmaysissa172No ratings yet
- Biomolecules ImpDocument22 pagesBiomolecules ImpmrdaddydaddaNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Basis of LifeDocument13 pagesThe Chemical Basis of Lifezulfikarleghari100% (1)
- Tutorial 3 MCQs SolutionsDocument4 pagesTutorial 3 MCQs SolutionsEmmanuel ChendaNo ratings yet
- 生化CH06-08 選擇Document36 pages生化CH06-08 選擇dennis980012No ratings yet
- Biochem Final Examination 2007Document8 pagesBiochem Final Examination 2007PinayMD OnHoldNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 20 MCQs-1Document6 pagesBiochemistry 20 MCQs-1Muhammadsiddique khanNo ratings yet
- ChoDocument10 pagesChoLohith HanumNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry - Biomolecules AssignmentDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry - Biomolecules AssignmentTanu BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 1st Semester BSN Mcqs For Practice AD, Educational Platform-1Document6 pagesBiochemistry 1st Semester BSN Mcqs For Practice AD, Educational Platform-1Prince Masroor Ali Abro100% (2)
- Chemistry Formula Chapter14 BiomoleculesDocument13 pagesChemistry Formula Chapter14 BiomoleculesAnup GoelNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules-Hard: A: B: C: DDocument5 pagesBiological Molecules-Hard: A: B: C: DManqabat WalayNo ratings yet
- Problems Fluid MosaickeyDocument7 pagesProblems Fluid MosaickeyBatrisyia AdNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice 2Document5 pagesMultiple Choice 2emmaNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 BiomoleculesDocument13 pagesNCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 BiomoleculesVidyakulNo ratings yet
- Concepts in Biochemistry2Document38 pagesConcepts in Biochemistry2atefmaboodNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 9 ch9 Class 11Document4 pagesWorksheet 9 ch9 Class 11akilapaul17682No ratings yet
- Bio ImpDocument10 pagesBio Implinngeshwar BNo ratings yet
- BCH Finals 1Document12 pagesBCH Finals 1roxanne.viriNo ratings yet
- Biology SL 2025 Uniform & Function - Carbohydrates and LipidsDocument35 pagesBiology SL 2025 Uniform & Function - Carbohydrates and LipidsAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument41 pagesCarbohydratesJowe VarnalNo ratings yet
- A. Stanley MillerDocument14 pagesA. Stanley MillerCourtney JachnaNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules AS LevelDocument16 pagesBiological Molecules AS LevelAmal ZahraNo ratings yet
- Natural Product ExamDocument2 pagesNatural Product Examgemechu gebisaNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument66 pagesBiochemistryKenny RaganasNo ratings yet
- CH - 14 BiomoleculesDocument14 pagesCH - 14 BiomoleculesAnmolNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Chapter End ActivitiesDocument4 pagesBiochemistry Chapter End ActivitiesBethNo ratings yet
- Chapt02 - lectureMOD 1Document27 pagesChapt02 - lectureMOD 1Kristin ElderNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 - Biomolecules Important Questions 2022-23Document22 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 - Biomolecules Important Questions 2022-23Archanaa PadmavathiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 08 - Lipids Membranes-TestDocument10 pagesChapter - 08 - Lipids Membranes-Testendang dian lestariNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Organic MoleculesDocument7 pagesThe Chemistry of Organic MoleculesPangkat DalawaNo ratings yet
- BemcqDocument1 pageBemcqJohn Andrew GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Lipids Lesson 3: The Cell MembraneDocument12 pagesUnit 3 Lipids Lesson 3: The Cell MembraneValenzuela Allene GraceNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For The Dental Hygienists Guide To Nutritional Care 5th Edition by Stegeman DownloadDocument14 pagesTest Bank For The Dental Hygienists Guide To Nutritional Care 5th Edition by Stegeman Downloadwhitneycoxmrtsgiwdkx100% (25)
- UntitledDocument9 pagesUntitledaisha atikaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Review 2Document14 pagesBiochemistry Review 2deelol99No ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: B. RibosomeDocument6 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: B. RibosomeChiku MteghaNo ratings yet
- Revisi0on Sheet E Lec 4 CarbohydratesDocument4 pagesRevisi0on Sheet E Lec 4 Carbohydratesmahmoud nasserNo ratings yet
- AQA Biology: 1 Biological Molecules SupportDocument7 pagesAQA Biology: 1 Biological Molecules SupportYasen SalemNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Biological MoleculesDocument15 pagesTopic 1 - Biological MoleculesannabelbithellNo ratings yet
- BroteinsDocument54 pagesBroteinsIbrahim Adel zaidNo ratings yet
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- BK.1 TamarrawDocument3 pagesBK.1 TamarrawCherry DagohoyNo ratings yet
- Dagohoy, Louis John P. Attendance To WRP Online ActivitiesDocument3 pagesDagohoy, Louis John P. Attendance To WRP Online ActivitiesCherry DagohoyNo ratings yet
- CaserealDocument2 pagesCaserealCherry DagohoyNo ratings yet
- 1 INTRODUCTION - Basic Ethical ConceptsDocument8 pages1 INTRODUCTION - Basic Ethical ConceptsCherry DagohoyNo ratings yet
- AwDocument6 pagesAwCherry DagohoyNo ratings yet
- 3 Freedom, Law and ConscienceDocument7 pages3 Freedom, Law and ConscienceCherry DagohoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Bioethical Themes in The Midst of Life - AIDSDocument3 pagesChapter 8: Bioethical Themes in The Midst of Life - AIDSCherry DagohoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Ethical TheoriesDocument10 pagesChapter 2: Ethical TheoriesCherry DagohoyNo ratings yet
- Determinacion de AminoacidosDocument8 pagesDeterminacion de AminoacidosNilo Michael Robles CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Bio Biological Molecules AlevelsDocument28 pagesBio Biological Molecules AlevelsMunazzagulNo ratings yet
- Isolation, Qualitative Color Reaction and Alkaline Hydrolysis of Gluten From YeastDocument5 pagesIsolation, Qualitative Color Reaction and Alkaline Hydrolysis of Gluten From YeastHeather Gutierrez100% (3)
- DOPA BiomoleculesDocument9 pagesDOPA Biomoleculesantaryami barikNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of MilkDocument128 pagesChemistry of MilksakshiNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Nutrition Science and Applications 2nd Edition Smolin Test Bank Full ChapterDocument49 pages(Download PDF) Nutrition Science and Applications 2nd Edition Smolin Test Bank Full Chapterclipaeyska8100% (10)
- PACOP ItemsDocument11 pagesPACOP ItemsKathryn Faith MalabagNo ratings yet
- Biochem Reviewer ProteinsDocument27 pagesBiochem Reviewer Proteinsram castilloNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Chapter # 1 EnzymesDocument10 pagesBiochemistry Chapter # 1 EnzymesUsman AhmadNo ratings yet
- Gupta Keratin DavidPub 2012Document7 pagesGupta Keratin DavidPub 2012shreyapersonal20No ratings yet
- Chapter-2 - InglesDocument21 pagesChapter-2 - InglesVivi GaviriaNo ratings yet
- Nutrients: Milk and Dairy Products and Their Nutritional Contribution To The Average Polish DietDocument19 pagesNutrients: Milk and Dairy Products and Their Nutritional Contribution To The Average Polish DietMuhammad RehmanNo ratings yet
- Basic of Proteins - JMCMDocument48 pagesBasic of Proteins - JMCMNeil Vincent De AsisNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Proteins and EnzymesDocument4 pagesProblem Set Proteins and EnzymesJayvee BillonesNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry For Psychiatry Students by Abayneh EDocument123 pagesBiochemistry For Psychiatry Students by Abayneh Egobez temariNo ratings yet
- PROTEINSDocument17 pagesPROTEINSAbhijat Jha100% (1)
- 9701 w13 QP 4 PDFDocument60 pages9701 w13 QP 4 PDFstevan joeNo ratings yet
- Group AssignmentDocument9 pagesGroup AssignmentRenee Dwi Permata MessakaraengNo ratings yet
- The Devil in The MilkDocument3 pagesThe Devil in The Milksham9787578027No ratings yet
- AAA App NotesDocument4 pagesAAA App NotesPriasalesNo ratings yet
- Insects 11 00876Document13 pagesInsects 11 00876nguoidiquaNo ratings yet
- BiochemDocument7 pagesBiochemRyan TurnerNo ratings yet
- Determination of Protein Content SpectrophotometricallyDocument10 pagesDetermination of Protein Content SpectrophotometricallyTsabit AlbananiNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 4.1Document4 pagesExperiment No. 4.1Rianne Danielle CarsulaNo ratings yet
- AmberTools13 Cpptraj PtrajDocument91 pagesAmberTools13 Cpptraj PtrajmayankgiaNo ratings yet
- Peptides Book CalbiochemDocument30 pagesPeptides Book Calbiochemmankm21No ratings yet
- MEDF1012A Amino Acids and ProteinsDocument48 pagesMEDF1012A Amino Acids and ProteinsminhyunxiiiiNo ratings yet