Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mix Design Guide: ACI NEDUET Students Chapter
Mix Design Guide: ACI NEDUET Students Chapter
Uploaded by
Asad AshfaqOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mix Design Guide: ACI NEDUET Students Chapter
Mix Design Guide: ACI NEDUET Students Chapter
Uploaded by
Asad AshfaqCopyright:
Available Formats
[Type here]
aggregates. They are not the major contributor
MIX DESIGN of strength but to have stronger concrete
strength voids are to be filled with fine
GUIDE aggregate making it dense and more durable.
ACI NEDUET Students Chapter
acineduetstudentschapter@gmail.com C. Coarse Aggregate
Coarse aggregate are the bigger pieces of stone
and cover up most of the volume in concrete.
1.Introduction They provide tremendous strength to concrete
and give it rock like strength. Stone, basalt,
The American Concrete Institute (ACI) is a
gravel and shingle are used as coarse
standard producing organization like ASTM
aggregates in concrete making it more durable
and AWS. The ACI mix design method is
and load resistant. Well graded aggregates
one of the best basic concrete mix design
should be used for a more consistent and
methods available today. This section is a
efficient mix.
general outline of the ACI standard
proportioning method with specific emphasis
on concrete beam casting. Moreover, It
emphasis on the general concepts one should D. Water
have and certain procedures for concrete mix
design. We will be following “Standard Water is used in ratio with that of the
Practice for Selecting cement however excessive water can
Proportions for Normal, Heavyweight and Mass increase the porosity of the concrete.
Concrete (ACI 211. 9-91) approved by ACI Water creates a paste with cement to
committee 211. bond the concrete together drying out
and hardening the mix. This water
should be free of solid particles and
2.Concrete components
contamination. For concrete water, pH of
3-9 is acceptable but 7.2-7.6 is
A. Cement recommended for best results.
Cement is the adhesive material in concrete that
creates bonding strength between the E. Admixtures
aggregates. Cement reacts with water in the dry
Admixtures are the chemical addition to
mix and takes certain time to harden the
the concrete that are used for different
concrete sealing the ingredients together and
functions. Admixtures such as
forming the strengthened mass. Normally OPC
superplasticizers are used to increase the
is used but for special conditions cement types
workability of concrete. In the same way
may vary.
admixtures can be added to increase or
decrease the rate of reaction and to
B. Fine Aggregate lessen the water content in concrete.
They are added in small quantities as
The sand and small particles of silt that are required and vary dependent on the
called fine aggregates are used in concrete to function needed.
create a homogenous consistent texture of
concrete and to fill in the voids between coarse
TEAM RESEARCH: TENURE 2020-2021
[Type here]
3.ACI Concrete Mix Design (Codes and
Specifications)
ACI Specification
ACI has a variety of codes to provide
detailed guidelines and specifications for
the design of various concrete mix
designs.
For instance, ACI 318 (refer to Chapter
19) refers to the three major concepts for
concrete Reference: ACI Method of concrete mix
(a) Limits for the minimum compressive design
strength
(f’c) for the design of Concrete
Referring to Table 19.2.1.1 Certain formulations have also been included in
the codes.
(b) Concrete Durability
The heading encompasses various
factors for effective durability.
Definition states that the factor of
durability depends upon the
endurance of a cementitious material
towards fluid propagation.
TEAM RESEARCH: TENURE 2020-2021
[Type here]
These details and use of chart for the evaluation of mix
design are further elaborated in this document as we
proceed further.
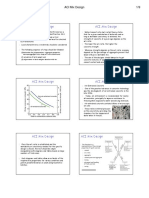
4. Maximum water content (chart/table)
The quantity of water per unit volume of concrete required
to produce a given slump is dependent on the maximum
Coarse Aggregate size, the shape and grading of both
Coarse aggregate and Fine aggregate, as well as the amount
of entrained air.
Table 1 shows Approximate mixing water (lb/yd3) and
Air content for different slumps and nominal maximum
sizes of aggregates for non-air content concrete.
Reference: ACI Mix Design
Reference: ACI Method of concrete mix design
ACI 211 (refer to Chapter 6) include all the necessary
data and charts along with the specified methods
for designing the concrete.
TEAM RESEARCH: TENURE 2020-2021
[Type here]
Reference: ACI Mix Design Reference: ACI Method of concrete mix design
The details for the slump requirement for different types of Table 2 shows Approximate mixing water
(lb/yd3) and
structures have also been specified precisely. Air content for different slumps and nominal
maximum sizes of aggregates for air content concrete.
TEAM RESEARCH: TENURE 2020-2021
[Type here]
Reference: ACI Mix Design
Reference: ACI Mix Design
Reference: ACI Mix Design However, a minimum cement content is
required to ensure good finish ability,
5. Calculation for cementitious material workability, and strength.
content
A. CALCULATION OF CEMENT
CONTENT: B. FINE AGGREGATE CONTENT:
Once the water content and the w/c ratio is
determined, the amount of cement per unit There are two standard methods to establish
volume of the concrete is found by dividing the fine aggregate content, the mass method
the estimated water content by the w/c ratio. and the volume method. We will use the
Weight of cement= Weight of Water "volume" method. "Volume" Method is the
w/c preferred method, as it is a somewhat more
exact procedure .The volume of fine
aggregates is found by subtracting the volume
TEAM RESEARCH: TENURE 2020-2021
[Type here]
Reference: ACI Mix Design
Reference: ACI Mix Design
6. Selection of water cement ratio depending on
of cement, water, air, and coarse aggregate Table 4 shows The percent of coarse
from the total concrete volume. Then once the aggregate to concrete for a maximum size
volume is known, the weights of each and fineness modulus.
ingredient can be calculated from specific
gravity. The volume occupied in concrete by
any ingredient can be calculated by dividing
its weight to density of that material.
Table 3 shows Volume of each ingredient
in concrete.
Reference: ACI Mix Design
C. COARSE AGGREGATE CONTENT:
The most economical concrete will have as
much as possible space occupied by Coarse
aggregate since it will require no cement in
the space filled by Coarse aggregate. strength and slump test
Coarse aggregate volumes are based on
oven-dry rodded weights obtained in Water Cement Ratio depending on Slump
accordance with ASTM C 29. The value Test:
from the table multiplied by the dry-rodded
unit weight (the oven-dry (OD) weight of
coarse aggregate required per cubic foot of
concrete). To convert from OD to saturated
surface dry (SSD) weights, multiply by [1 +
absorption capacity (AC)].
TEAM RESEARCH: TENURE 2020-2021
[Type here]
There is no direct relation of W/C ratio with of aggregates can be taken as per the
slump. Rather the method we follow to following table.
calculate cement content is such as, 1st we Reference: ACI Method of concrete mix
calculate water content by the help of below design
Reference: ACI Method of concrete mix design
7. Mix calculation (Example calculations)
mentioned two tables. And then we calculate Water Cement Ratio depending on strength of
the W/C ratio depending upon compressive concrete:
strength of concrete required. In the end by
the help of W/C ratio and water content Now when the water content is known from
obtained we calculate Cement content. If the the above table, and we do know the
slump is not specified, it can be taken from compressive strength which is required for
the following table depending upon the type our structure, we can select the appropriate
of construction we aim to do. W/C ratio from the following table.
Reference: ACI Method of concrete mix
design
ACI Mix Design Example #1
Now when the slump is known or taken from
Consider the following example: The 28-
the above table, the approximate mixing
day compressive strength should be 4,000
water and air content requirements for
psi. The slump should be between 3 and 4
different slumps and nominal maximum sizes
TEAM RESEARCH: TENURE 2020-2021
[Type here]
in. and the maximum aggregate size should Coarse Aggregate: Bulk specific gravity
not exceed 1 in. The coarse and fine (SSD) = 2.70; absorption capacity = 1.1%;
aggregates in the storage bins are wet. The dry-rodded unit weight = 105 lb./ft.3
properties of the materials are as follows: surface moisture = 1% Fine Aggregate:
Cement : Type I, specific gravity = 3.15 Bulk specific
gravity (SSD) = 2.67; absorption capacity = 1.3%; fineness
modulus = 2.70; surface moisture = 1.5%
TEAM RESEARCH: TENURE 2020-2021
[Type here]
NOTE: The reference of the above example has been
mentioned in the reference’s section.
8. References:
TEAM RESEARCH: TENURE 2020-2021
[Type here]
http://www.ce.memphis.edu/1112/notes/project_2/beam/
A CI_mix_design.pdf
https://theconstructor.org/practical-guide/aci-
methodconcrete-mix-design/7196/
TEAM RESEARCH: TENURE 2020-2021
You might also like
- Method Statement For Construction of GirderDocument5 pagesMethod Statement For Construction of GirderAsad AshfaqNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument20 pagesPDFsimiyu cciNo ratings yet
- 2012 BRAKES VSA System Components - TL PDFDocument114 pages2012 BRAKES VSA System Components - TL PDFsoftallNo ratings yet
- Concrete Technology, 2nd Edition Book by A M Neville and J J BrooksDocument460 pagesConcrete Technology, 2nd Edition Book by A M Neville and J J BrooksAsad Ashfaq100% (2)
- Eco-efficient Rendering Mortars: Use of Recycled MaterialsFrom EverandEco-efficient Rendering Mortars: Use of Recycled MaterialsNo ratings yet
- API 5l x42 Pipe Specification Data SheetDocument1 pageAPI 5l x42 Pipe Specification Data SheetIván López PavezNo ratings yet
- Angel of GroznyDocument348 pagesAngel of GroznySportyANK100% (1)
- Performance of A High-Solidity Wells Turbine For An OWC Wave Power PlantDocument6 pagesPerformance of A High-Solidity Wells Turbine For An OWC Wave Power PlantAna Elisa Rodrigues do CoutoNo ratings yet
- Bts Site Installation Involve Many StagesDocument47 pagesBts Site Installation Involve Many StagesAvinash Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- ACI Mix DesignDocument10 pagesACI Mix DesignDwinto RachmatNo ratings yet
- ACIMix DesignDocument10 pagesACIMix DesignJAZPAKNo ratings yet
- Week .11 & 12 Mix DesignDocument62 pagesWeek .11 & 12 Mix Designhafsaayaz30100% (1)
- Design of M100 Grade ACI MethodDocument3 pagesDesign of M100 Grade ACI MethodGaurav PatilNo ratings yet
- Designing Concrete Mixtures Designing Concrete Mixtures: CIVL 1112 ACI Mix Design /10Document10 pagesDesigning Concrete Mixtures Designing Concrete Mixtures: CIVL 1112 ACI Mix Design /10Muhammad Ave SenaNo ratings yet
- Training Programe On Concret Mixdesign and Concrete WorkDocument48 pagesTraining Programe On Concret Mixdesign and Concrete Workkoiljoshua100% (1)
- HO - CB 352 CM Part - 4A - Fresh Properties of ConcreteDocument8 pagesHO - CB 352 CM Part - 4A - Fresh Properties of ConcreteAmjad Wael Yahia FayedNo ratings yet
- PRC 2 Lab Manual-Job 2Document14 pagesPRC 2 Lab Manual-Job 2Toqeer KhanNo ratings yet
- Lec 15 - Concrete Mix ProportioningDocument73 pagesLec 15 - Concrete Mix Proportioningmansoor azamNo ratings yet
- ACI Mix DesignDocument9 pagesACI Mix Designbahran tibebuNo ratings yet
- ACI Mix DesignDocument9 pagesACI Mix DesignManuelNo ratings yet
- Concrete Mix Design Beng 2021Document31 pagesConcrete Mix Design Beng 2021musinguzi robertNo ratings yet
- A Review of Concrete Mix Designs: November 2017Document6 pagesA Review of Concrete Mix Designs: November 2017ESTIAQ AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Concrete Mix Proportioning As Per Is 10262 2009Document7 pagesConcrete Mix Proportioning As Per Is 10262 2009yaminNo ratings yet
- 23 PDFDocument4 pages23 PDFWilliam PerkinsNo ratings yet
- CIB13831Document11 pagesCIB13831ahmedNo ratings yet
- ACI Mix Design ACI Mix DesignDocument9 pagesACI Mix Design ACI Mix DesignChris OltonNo ratings yet
- Miniproject Concrete - Literature ReviewDocument28 pagesMiniproject Concrete - Literature ReviewMadav BalgobinNo ratings yet
- Mix Design of Structural Self-Compacting Concrete Using Void-Bulk Density MethodDocument11 pagesMix Design of Structural Self-Compacting Concrete Using Void-Bulk Density MethodPtpgStucNo ratings yet
- Lightweight Concrete MixDocument12 pagesLightweight Concrete MixgunjanatulbansalNo ratings yet
- CC Mix Design by KLPDocument59 pagesCC Mix Design by KLPstruban8337100% (1)
- Seminar ReportDocument21 pagesSeminar ReportTheWatchdogs WatchdogNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Mix Proportioning of High Strength Concrete Using Doe and Aci Method IJERTCONV4IS30028Document3 pagesComparative Study of Mix Proportioning of High Strength Concrete Using Doe and Aci Method IJERTCONV4IS30028Hanan IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Project On Concrete Mix Design For Various Grades of ConcreteDocument22 pagesProject On Concrete Mix Design For Various Grades of ConcreteMohammad Rizwan KhanNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Strength at Early Ages ofDocument5 pagesEvaluation of Strength at Early Ages ofHishmat EzzelarabNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Workability and Fresh Concrete I: StructureDocument12 pagesUnit 5 Workability and Fresh Concrete I: StructureFredrick ChombaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-Mix DesignDocument51 pagesChapter 5-Mix DesignJaphet LudovickNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document32 pagesChapter 2Md Ashiqur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Concrete Mix Design by IS, ACI and BS Methods: A Comparative AnalysisDocument4 pagesConcrete Mix Design by IS, ACI and BS Methods: A Comparative AnalysisDP SinghNo ratings yet
- JCR Paper-2Document4 pagesJCR Paper-2gopierode4No ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document4 pagesAssignment 2Naneth SabangNo ratings yet
- Mix Design of ConcreteDocument14 pagesMix Design of ConcreteShashank PatoleNo ratings yet
- CVE171 Lecture 5.2Document47 pagesCVE171 Lecture 5.2Mlkhr lgndbNo ratings yet
- ACI Mix DesignDocument9 pagesACI Mix DesignShafiqullah GowharyNo ratings yet
- ACI Mix Design PDFDocument9 pagesACI Mix Design PDFHanniel MadramootooNo ratings yet
- CIVL 1101 Introduction To Concrete 7/10Document1 pageCIVL 1101 Introduction To Concrete 7/10Srikar AvrNo ratings yet
- CT Unit 3Document19 pagesCT Unit 3Online AdoroNo ratings yet
- Theeffectofcement PDFDocument8 pagesTheeffectofcement PDFLaur HaxhiuNo ratings yet
- High Strength Concrete Mix DesignDocument3 pagesHigh Strength Concrete Mix DesignNasir ShahNo ratings yet
- Curing Methods and Their Effects On TheDocument4 pagesCuring Methods and Their Effects On Theshiraz ahmedNo ratings yet
- Estimates of Self-Compacting Concrete Potential' DurabilityDocument9 pagesEstimates of Self-Compacting Concrete Potential' DurabilityNiou MekkiNo ratings yet
- Mix Design FinalDocument8 pagesMix Design FinalAreaya mahetemNo ratings yet
- Concrete Mix Design Concrete Mix Design: Presentation LayoutDocument28 pagesConcrete Mix Design Concrete Mix Design: Presentation LayoutKris dNo ratings yet
- Ajwad Et Al 2018 - Assessing Strengthening ConcreteDocument4 pagesAjwad Et Al 2018 - Assessing Strengthening ConcreteJavsarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Concrete Material & MixtureDocument10 pagesChapter 1 - Concrete Material & MixtureNezrinNo ratings yet
- Concrete Mix Design Using Crushed SandDocument22 pagesConcrete Mix Design Using Crushed SandOlaolu Olalekan50% (2)
- ACI Mix DesignDocument9 pagesACI Mix DesignAbdul Hamid BhattiNo ratings yet
- 1a ++CONCRETE+AND+STEEL+Construction+Material+ReviewDocument23 pages1a ++CONCRETE+AND+STEEL+Construction+Material+ReviewMochizou OojiNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Concrete Mix Design StrengthDocument4 pagesFactors Affecting Concrete Mix Design StrengthmanishNo ratings yet
- ACI Mix Design ACI Mix DesignDocument7 pagesACI Mix Design ACI Mix Designomar alvaradoNo ratings yet
- Concrete Mix DesignDocument22 pagesConcrete Mix DesignIvo StanilovNo ratings yet
- Mix DesignDocument10 pagesMix DesignMary Emalaine SerranoNo ratings yet
- Concrete-Block Manufacture - Processes and MachinesFrom EverandConcrete-Block Manufacture - Processes and MachinesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Fabrication of Materials: Materials TechnologyFrom EverandThe Fabrication of Materials: Materials TechnologyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Elastic, Plastic and Yield Design of Reinforced StructuresFrom EverandElastic, Plastic and Yield Design of Reinforced StructuresNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Pipe Culvert by Anil KumarDocument2 pagesMethod Statement For Pipe Culvert by Anil KumarAsad AshfaqNo ratings yet
- Aashto T 193Document11 pagesAashto T 193Asad AshfaqNo ratings yet
- To Determine Specific Gravity of SoilDocument12 pagesTo Determine Specific Gravity of SoilAsad AshfaqNo ratings yet
- Plate Load TestDocument2 pagesPlate Load TestAsad AshfaqNo ratings yet
- Daily Site Diary: Task Description Status WBS CodeDocument2 pagesDaily Site Diary: Task Description Status WBS CodeAsad AshfaqNo ratings yet
- Ind - Niftytotalmarket - List 2Document17 pagesInd - Niftytotalmarket - List 2filmyhariNo ratings yet
- Power System Lab QuizDocument2 pagesPower System Lab QuizVipin KumarNo ratings yet
- UCCN2003 TCP/IP Internetworking UCCN2243 Internetworking Principles & PracticesDocument10 pagesUCCN2003 TCP/IP Internetworking UCCN2243 Internetworking Principles & PracticesKahtheresh MuruganNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 4.Document7 pagesLab Report 4.Usman Ali Usman AliNo ratings yet
- Versace Unisex Sunglasses VE 2140 100287 214ODocument1 pageVersace Unisex Sunglasses VE 2140 100287 214Oklejsishahaj2022No ratings yet
- Ifedc 2022 Rock TypingDocument17 pagesIfedc 2022 Rock TypingpetrolognewsNo ratings yet
- Dinner MenuDocument2 pagesDinner MenueatlocalmenusNo ratings yet
- TechnicalProposal 20130710B Rev0Document3 pagesTechnicalProposal 20130710B Rev0JomaargNo ratings yet
- Astm G32 - 10Document19 pagesAstm G32 - 10ABINASH BEHERANo ratings yet
- Chef Danielle Peita Graham InterviewDocument2 pagesChef Danielle Peita Graham InterviewSeah Pei JunNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11: 19 Oct 2022 Instructor: Prof Larry Li: Fairchild Republic A-10 Thunderbolt IIDocument24 pagesLecture 11: 19 Oct 2022 Instructor: Prof Larry Li: Fairchild Republic A-10 Thunderbolt IItl xNo ratings yet
- (Leafospirosis Deadly Disease From Rat: Fiqh Al-Hadith-Based Analysis) Leptospirosis Wabak Maut Dari Tikus: Analisis Berasaskan Fiqh Al-HadithDocument16 pages(Leafospirosis Deadly Disease From Rat: Fiqh Al-Hadith-Based Analysis) Leptospirosis Wabak Maut Dari Tikus: Analisis Berasaskan Fiqh Al-Hadith0050 MUHAMMAD HAIKAL BIN SAHARINo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan ExampleDocument2 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan Exampleapi-357485951No ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science ADM 21-30 ReviewerDocument10 pagesEarth and Life Science ADM 21-30 ReviewerABEGAEL ARINDAENGNo ratings yet
- Nihon Kohden BSM-2300 - Service ManualDocument207 pagesNihon Kohden BSM-2300 - Service ManualĐức Cường100% (2)
- Computer Graphics I UNIT NotesDocument24 pagesComputer Graphics I UNIT Notesgouse1210100% (1)
- Study Master Life Sciences Teachers Guide Grade 10 9781107380509ARDocument225 pagesStudy Master Life Sciences Teachers Guide Grade 10 9781107380509ARmiltonellkayNo ratings yet
- Beirut Madinati Full Program enDocument32 pagesBeirut Madinati Full Program endevonchildNo ratings yet
- Hyacinth Blooms in Milton's "Lycidas"Document3 pagesHyacinth Blooms in Milton's "Lycidas"Alex ENo ratings yet
- CloudEngine 6863 Data Center Switch DatasheetDocument13 pagesCloudEngine 6863 Data Center Switch DatasheetRiqo SetyoNo ratings yet
- UOP DTS Fastfeed A4 V3Document2 pagesUOP DTS Fastfeed A4 V3higgsboson83No ratings yet
- Kantar Worldpanel 5 Key FMCG Trends in Vietnam 2023 ENDocument25 pagesKantar Worldpanel 5 Key FMCG Trends in Vietnam 2023 ENbrianNo ratings yet
- Viscosity-1 Viscometer-2 Relation Between Viscosity &temperature-3 Vogel Equation-4 Programming ofDocument71 pagesViscosity-1 Viscometer-2 Relation Between Viscosity &temperature-3 Vogel Equation-4 Programming ofDr_M_SolimanNo ratings yet
- Aic1084-33ce Regulador 3.3Document7 pagesAic1084-33ce Regulador 3.3VictorManuelBernalBlancoNo ratings yet
- Structural Theory 1 (Double Integration Method)Document22 pagesStructural Theory 1 (Double Integration Method)acurvz2005No ratings yet