Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views기말고사 연습용 문제 (1) -1
기말고사 연습용 문제 (1) -1
Uploaded by
sun woongCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Important Questions CSE-stream-All ModulesDocument2 pagesImportant Questions CSE-stream-All Modulesfarhahumera4No ratings yet
- Question BankDocument19 pagesQuestion BankKUNALNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unified PYQDocument29 pagesChemistry Unified PYQoyes2minNo ratings yet
- Fifth Semester Physics Honours - Sample Questions - U - IIIDocument3 pagesFifth Semester Physics Honours - Sample Questions - U - IIIkaushikeesrivastava582No ratings yet
- Chemistry Imp Question BankDocument8 pagesChemistry Imp Question BankLavanya DaniNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument2 pagesChemJathin NakkellaNo ratings yet
- Important Questions Xi 079 PDFDocument3 pagesImportant Questions Xi 079 PDFJessica PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 Yr Important QuestionDocument5 pagesPhysics 2 Yr Important QuestionyashwantNo ratings yet
- SECOND For UkDocument8 pagesSECOND For UkyellaiahNo ratings yet
- Answer Bank ct-1Document9 pagesAnswer Bank ct-1MAHESHWAR M R (RA2111004010136)No ratings yet
- SR Physics Fast LearnerDocument7 pagesSR Physics Fast LearnerShahrukh KhanNo ratings yet
- Mention The Faraday's Laws of Electrolysis.Document2 pagesMention The Faraday's Laws of Electrolysis.BHUMANI MUDULINo ratings yet
- Physics II Year - 121754Document5 pagesPhysics II Year - 121754Quran The MercyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Qualitative Molecular Orbital TheoryDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Qualitative Molecular Orbital TheoryNuansak3No ratings yet
- Xi Chemistry, Comprehensive ChemistryDocument2 pagesXi Chemistry, Comprehensive ChemistrySANGRAM5200% (1)
- 12th PHY ImpDocument6 pages12th PHY ImpmuzaffarusNo ratings yet
- 12th Class Guess Papers 2024 Phy ShortDocument6 pages12th Class Guess Papers 2024 Phy ShortpremiocrownNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For Electricity and MagnetismDocument2 pagesImportant Questions For Electricity and MagnetismYASIR BAIGNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Related Exam Questions and AnswersDocument11 pagesChemistry Related Exam Questions and AnswersJoseph NyabugaNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument9 pagesChemical BondingsaurabhNo ratings yet
- Sample QuestionsDocument5 pagesSample Questionsbhamamanoj02No ratings yet
- Chemistry V SEM P 6Document17 pagesChemistry V SEM P 6sanjay sNo ratings yet
- REVISION Important 5&3 Marks Xii PhysicsDocument2 pagesREVISION Important 5&3 Marks Xii PhysicsGeethika gorakala100% (1)
- Ece II Engineering Physics (10phy 22) AssignmentDocument7 pagesEce II Engineering Physics (10phy 22) AssignmentPrakash ShiggaviNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 Problem Set 2016Document9 pagesTopic 7 Problem Set 2016Paul AmezquitaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument15 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureSoham NagNo ratings yet
- 6 Chapter Chemical Bonding Text Book ExerciseDocument20 pages6 Chapter Chemical Bonding Text Book ExerciseSajid Azeem100% (2)
- Ntroduction To Lectrodynamics Model Questions Short AnswersDocument3 pagesNtroduction To Lectrodynamics Model Questions Short AnswersHasan Babu HNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument13 pagesChemistrynasyieNo ratings yet
- Physics Chemistry 2 MarksDocument5 pagesPhysics Chemistry 2 MarksDeekshitha DanthuluriNo ratings yet
- Question Bank-Virtual Mode Test-Partb I-V 17-01-2021Document7 pagesQuestion Bank-Virtual Mode Test-Partb I-V 17-01-2021Logeshwer SPNo ratings yet
- Questions Bank On ElectrostaticsDocument2 pagesQuestions Bank On Electrostaticsashok Pradhan100% (1)
- Physics 2nd Yr BDocument3 pagesPhysics 2nd Yr BShahrukh KhanNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Question Upto Quantum NumberDocument6 pagesCH 2 Question Upto Quantum NumberibtihazaryanNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 11th Chemistry Question Bank Questions em 216447Document5 pagesNamma Kalvi 11th Chemistry Question Bank Questions em 216447Vaishanavi J.ANo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Molecular and Ionic Compound Structure and PropertiesDocument7 pagesUnit 2: Molecular and Ionic Compound Structure and PropertiesTAHA GABRNo ratings yet
- Sr. PhysicsDocument6 pagesSr. PhysicsMavuluri UmamaheshNo ratings yet
- CBSE Board Class XII Physics - Set 1 Board Paper - 2011 Time: 3 Hours (Total Marks: 70) General Instructions: 1. 2. 3. 4Document6 pagesCBSE Board Class XII Physics - Set 1 Board Paper - 2011 Time: 3 Hours (Total Marks: 70) General Instructions: 1. 2. 3. 4Chandan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Apollo Institute of Engineering & Technology: Question BankDocument1 pageApollo Institute of Engineering & Technology: Question BankNobody cares Nobody caresNo ratings yet
- Bonding in Molecules 2019 2nd Yr Michaelmas TermDocument71 pagesBonding in Molecules 2019 2nd Yr Michaelmas Termtresa.george27No ratings yet
- MaterialmDocument3 pagesMaterialmAbdur RazzakNo ratings yet
- Physics Section Wise Important Questions WMDocument7 pagesPhysics Section Wise Important Questions WMShashank BNo ratings yet
- A2 Physics Unit 4 Definitions and Statements QuestionsDocument1 pageA2 Physics Unit 4 Definitions and Statements QuestionsSomaya AliNo ratings yet
- Aga Khan High School, Kampala Ib2 Physics MCQ On Quantum Mechanics (HL)Document11 pagesAga Khan High School, Kampala Ib2 Physics MCQ On Quantum Mechanics (HL)Abigail NamulondoNo ratings yet
- Essay Type QuestionsDocument5 pagesEssay Type QuestionspoorviNo ratings yet
- B.Sc. VI Semester Physics:: Paper VII Modern Physics:: Question BankDocument3 pagesB.Sc. VI Semester Physics:: Paper VII Modern Physics:: Question BankReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Chem Assingment1 HHWDocument1 pageChem Assingment1 HHWmoksh.meeNo ratings yet
- Physics Question BankDocument15 pagesPhysics Question Bankepicgaming0455No ratings yet
- Chemistry Que Bank CbseDocument3 pagesChemistry Que Bank Cbsepradeep87810No ratings yet
- Questions Bank On ELECTROSTATICSDocument3 pagesQuestions Bank On ELECTROSTATICSAlok ShawNo ratings yet
- Bapatla Engineering College::Bapatla (Autonomous) B.Tech-Short Answer Model Questions Subject: Engineering Physics-II SemesterDocument7 pagesBapatla Engineering College::Bapatla (Autonomous) B.Tech-Short Answer Model Questions Subject: Engineering Physics-II Semesterchanjaneyulu9No ratings yet
- ATOMSDocument10 pagesATOMSschrujhana.jaganNo ratings yet
- Final Exam 2023 PrintDocument21 pagesFinal Exam 2023 PrintMUHAMMAD ZAINNo ratings yet
- II Puc Physics - Assignment (Mid Term 2022) - Gsgp'sDocument20 pagesII Puc Physics - Assignment (Mid Term 2022) - Gsgp'skiranknNo ratings yet
- Xii Pb2 AssignmentDocument2 pagesXii Pb2 Assignmentmehaktyagi422No ratings yet
- EDocument13 pagesESultan Hadi PrabowoNo ratings yet
- Phy SeniorsDocument6 pagesPhy SeniorsRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Che 222 Practice Questions 2020aDocument4 pagesChe 222 Practice Questions 2020adoreenrose739No ratings yet
- Physics (1st Inter)Document1 pagePhysics (1st Inter)rl3559980No ratings yet
- Review Exam1-S23Document43 pagesReview Exam1-S23et268No ratings yet
- Cmap Science9Document17 pagesCmap Science9Michael LopezNo ratings yet
- B.E., Electronics and Communication Engineering: Kumaraguru College of Technology COIMBATORE - 641 049Document81 pagesB.E., Electronics and Communication Engineering: Kumaraguru College of Technology COIMBATORE - 641 049NilT FigNo ratings yet
- (Career Endeavour) IIT JAM CHEMISTRY PDFDocument88 pages(Career Endeavour) IIT JAM CHEMISTRY PDFKiran Mandal100% (1)
- Chapter 2 The Chemical Basis of Life: Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece Et Al.)Document14 pagesChapter 2 The Chemical Basis of Life: Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece Et Al.)Yazmin QuevedoNo ratings yet
- CHM 102-Dr AzeezDocument24 pagesCHM 102-Dr Azeezbalikisolayemi2005No ratings yet
- Chemistry ConceptsDocument60 pagesChemistry ConceptsElla Jean LanoteNo ratings yet
- Perez Benito2003Document8 pagesPerez Benito2003Brent WoottonNo ratings yet
- Concept Review With Key TermsDocument4 pagesConcept Review With Key TermsWaqar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Polar Covalent Bonds - Acids and BasesDocument53 pagesChapter 2 - Polar Covalent Bonds - Acids and BasesWALTEVAN BEZERRA DOS SANTOS100% (1)
- 4.1.1 Protic Vs Aprotic SolventDocument36 pages4.1.1 Protic Vs Aprotic SolventDawit BirhanuNo ratings yet
- Susan Maraj Ionic and Covalent BondingDocument14 pagesSusan Maraj Ionic and Covalent BondingKelseyNo ratings yet
- ACT BIOLOGY HighlightsDocument157 pagesACT BIOLOGY HighlightsOmar SedkeyNo ratings yet
- 2019 Johor Chemistry K2 Set 2 JawapanDocument10 pages2019 Johor Chemistry K2 Set 2 JawapanchaNo ratings yet
- TRB Chemistry Syllabus-2023Document3 pagesTRB Chemistry Syllabus-2023dreamletNo ratings yet
- Detailed Notes Topic 2 Bonding and Structure Edexcel Chemistry A LevelDocument17 pagesDetailed Notes Topic 2 Bonding and Structure Edexcel Chemistry A LevelttjjjNo ratings yet
- Chemistry BookDocument145 pagesChemistry BookFatima Viterbo MontalvoNo ratings yet
- Carbon Compounds: Grade 9Document21 pagesCarbon Compounds: Grade 9Rosalyn RayosNo ratings yet
- Molecular Geometry and CrystallineDocument102 pagesMolecular Geometry and CrystallineRenNo ratings yet
- Probing The Fluxional Bonding Nature of Rapid Cope Rearrangements in Bullvalene C10H10 and Its Analogs C8H8, C9H10, and C8BH9Document8 pagesProbing The Fluxional Bonding Nature of Rapid Cope Rearrangements in Bullvalene C10H10 and Its Analogs C8H8, C9H10, and C8BH9PeterNo ratings yet
- CHE434 Lesson Plan2014Document6 pagesCHE434 Lesson Plan2014Nurtasha AtikahNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document39 pagesCH 10Chala1989No ratings yet
- Dr. A. A. Akinsiku: Selected Topics in Chemistry For Chemical Engineering 1 BYDocument63 pagesDr. A. A. Akinsiku: Selected Topics in Chemistry For Chemical Engineering 1 BYIfiok UsoroNo ratings yet
- Ionic Vs Covalent Compounds - Volatility, Conductivity and Solubility - WorksheetDocument4 pagesIonic Vs Covalent Compounds - Volatility, Conductivity and Solubility - WorksheetKaren OrlanskiNo ratings yet
- Carbocation StabilityDocument2 pagesCarbocation StabilityRoaring LionNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Chemistry 112 October 7, 2013Document5 pagesExam 1 Chemistry 112 October 7, 2013Karren Ferrer-Mora HandayanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Microproject 1Document12 pagesChemistry Microproject 1Aachal GulhaneNo ratings yet
- Reacciones de Los Halogenuros de AlquiloDocument6 pagesReacciones de Los Halogenuros de AlquiloMaria Jesus TorresNo ratings yet
- 2013 H2 Chem JC Papers PDFDocument1,601 pages2013 H2 Chem JC Papers PDFShu Qing NgNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Organic Chemistry Mechanistic Patterns 1st Edition by OgilvieDocument25 pagesTest Bank For Organic Chemistry Mechanistic Patterns 1st Edition by Ogilviecruralmorphonv9rp2100% (44)
기말고사 연습용 문제 (1) -1
기말고사 연습용 문제 (1) -1
Uploaded by
sun woong0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views8 pagesOriginal Title
기말고사 연습용 문제 (1)-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views8 pages기말고사 연습용 문제 (1) -1
기말고사 연습용 문제 (1) -1
Uploaded by
sun woongCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 8
현대물리 기말고사 연습용 문제
1. Convert Schrödinger's equation to a spherical
coordinate system and explain what advantages it has.
4. 왜 orbital quantum number 이라고 이름이
붙혀졌는가? 또한 orbital quantum number 의 물리적인
의미는 무엇인가?
5. Why can't we know the orientation of angular
momentum?
2. With the results derived from the above problem,
derive a second new quantum number and a third
new quantum number.
6. In addition to the above problem, explain what the
magnetic quantum number means.
3. 기존 보어모델과 슈뢰딩거 적용 모델과 비교해보아라 7. Explain the role of n, l, m l by drawing a graph
based on the Ψ(r, θ, Φ) function.
8. Based on the angular momentum, derive the
formula for the magnetic moment of the electron.
11. What does the following picture mean?
9. Looking at the following figure, find the magnetic
potential energy (Um) of an electron.
12. What does the above phenomenon have to do
with the Zeeman effect?
13. What are the experiments to observe the above
phenomena, and how did they proceed?
10. If l=1 in the Zeeman Effect, why do electrons emit
only 3 spectrums?
14. What can we learn from the above experiment?
19. What is the Hund's rule?
20. Why do subshells (degenerated) of the same shell
have different energies?
15. Explain the Pauli Exclusion Principle.
21. What is the meaning of 'Transition metal'?
16. Suppose the electrons are particles that do not
overlap and are not distinct. Is the Wave function
Symmetric or Antisymmetric?
22. Compare the atomic radius and ionization energy
of Na and Mg.
23. Compare the atomic radius and ionization energy
of Ar and K.
17. fermion 과 boson 을 비교 설명하시오
24. Using the following periodic table, explain the
tendency of the atomic radius and ionization energy.
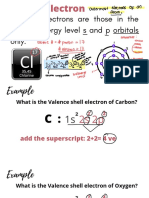
18. Explain Shell, Subshell, Orbital by drawing.
28. Draw the V-r graph of H2+ and describe how
covalent bonds can be formed.
25. What does the following picture mean?
29. Explain the process of bonding electrons using the
Symmetric/Antisymmetric wave function. So what
contradictions arise?
26. Explain the ionic bond using Cl and Na as an
example.
27. What is the difference between covalent and ionic
bonds?
30. In the following graph, explain why two hydrogen
atoms cannot be completely overlapped to become
helium atoms.
33. Explain the Sigma bond and the Pi bond.
34. What happens when the energy of the s orbital
and the p orbital overlap?
35. What do LUMO and HOMO mean?
31. How can we explain the contradiction identified in
question 29?
36. How is the formula for the number of particles
present in that energy expressed?
37. 3 가지 통계처리법을 비교허시오
32. The following table shows the electronegativity of
C, O, and H.
Explain the difference between CO 2 and H2O based on
this.
38. What does the following graph mean?
39. What are the representative values of n(v)? 42. B-E distribution 의 의미는 무엇인가?
40. What can be inferred by looking at the following
graph?
43. F-D distribution 의 의미는 무엇인가?
44. Fermi level 의 진짜 의미는 무엇인가?
41. What does the M-B distribution do not match with
quantum mechanics, and what are the solutions to it?
45. Explain the characteristics of the following graph.
48. Explain why the following values are different in
terms of bonding.
Al ionization energy: 5.986eV
Al work function: 4.3eV
46. The following figure shows the lattice structure of
Na+ and Cl-, and Ucoulomb of this lattice structure is 49. Why only consider the valence electron of the
negative. As the distance between Na and Cl gets atom?
closer, it will stabilize and become infinitely close, but
it is not. Why?
50. Mg should be an insulator in terms of molecular
orbital analysis. But this is a conductor in reality. Why?
47. Describe Van der Waals Bonding.
51. Like question 50, C is a conductor in terms of
molecular orbitals. But this is an insulator in reality.
Compare and explain this with Si and Ge atoms.
52. Explain the Kronig-Penney Model.
You might also like
- Important Questions CSE-stream-All ModulesDocument2 pagesImportant Questions CSE-stream-All Modulesfarhahumera4No ratings yet
- Question BankDocument19 pagesQuestion BankKUNALNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unified PYQDocument29 pagesChemistry Unified PYQoyes2minNo ratings yet
- Fifth Semester Physics Honours - Sample Questions - U - IIIDocument3 pagesFifth Semester Physics Honours - Sample Questions - U - IIIkaushikeesrivastava582No ratings yet
- Chemistry Imp Question BankDocument8 pagesChemistry Imp Question BankLavanya DaniNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument2 pagesChemJathin NakkellaNo ratings yet
- Important Questions Xi 079 PDFDocument3 pagesImportant Questions Xi 079 PDFJessica PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 Yr Important QuestionDocument5 pagesPhysics 2 Yr Important QuestionyashwantNo ratings yet
- SECOND For UkDocument8 pagesSECOND For UkyellaiahNo ratings yet
- Answer Bank ct-1Document9 pagesAnswer Bank ct-1MAHESHWAR M R (RA2111004010136)No ratings yet
- SR Physics Fast LearnerDocument7 pagesSR Physics Fast LearnerShahrukh KhanNo ratings yet
- Mention The Faraday's Laws of Electrolysis.Document2 pagesMention The Faraday's Laws of Electrolysis.BHUMANI MUDULINo ratings yet
- Physics II Year - 121754Document5 pagesPhysics II Year - 121754Quran The MercyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Qualitative Molecular Orbital TheoryDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Qualitative Molecular Orbital TheoryNuansak3No ratings yet
- Xi Chemistry, Comprehensive ChemistryDocument2 pagesXi Chemistry, Comprehensive ChemistrySANGRAM5200% (1)
- 12th PHY ImpDocument6 pages12th PHY ImpmuzaffarusNo ratings yet
- 12th Class Guess Papers 2024 Phy ShortDocument6 pages12th Class Guess Papers 2024 Phy ShortpremiocrownNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For Electricity and MagnetismDocument2 pagesImportant Questions For Electricity and MagnetismYASIR BAIGNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Related Exam Questions and AnswersDocument11 pagesChemistry Related Exam Questions and AnswersJoseph NyabugaNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument9 pagesChemical BondingsaurabhNo ratings yet
- Sample QuestionsDocument5 pagesSample Questionsbhamamanoj02No ratings yet
- Chemistry V SEM P 6Document17 pagesChemistry V SEM P 6sanjay sNo ratings yet
- REVISION Important 5&3 Marks Xii PhysicsDocument2 pagesREVISION Important 5&3 Marks Xii PhysicsGeethika gorakala100% (1)
- Ece II Engineering Physics (10phy 22) AssignmentDocument7 pagesEce II Engineering Physics (10phy 22) AssignmentPrakash ShiggaviNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 Problem Set 2016Document9 pagesTopic 7 Problem Set 2016Paul AmezquitaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument15 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureSoham NagNo ratings yet
- 6 Chapter Chemical Bonding Text Book ExerciseDocument20 pages6 Chapter Chemical Bonding Text Book ExerciseSajid Azeem100% (2)
- Ntroduction To Lectrodynamics Model Questions Short AnswersDocument3 pagesNtroduction To Lectrodynamics Model Questions Short AnswersHasan Babu HNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument13 pagesChemistrynasyieNo ratings yet
- Physics Chemistry 2 MarksDocument5 pagesPhysics Chemistry 2 MarksDeekshitha DanthuluriNo ratings yet
- Question Bank-Virtual Mode Test-Partb I-V 17-01-2021Document7 pagesQuestion Bank-Virtual Mode Test-Partb I-V 17-01-2021Logeshwer SPNo ratings yet
- Questions Bank On ElectrostaticsDocument2 pagesQuestions Bank On Electrostaticsashok Pradhan100% (1)
- Physics 2nd Yr BDocument3 pagesPhysics 2nd Yr BShahrukh KhanNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Question Upto Quantum NumberDocument6 pagesCH 2 Question Upto Quantum NumberibtihazaryanNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 11th Chemistry Question Bank Questions em 216447Document5 pagesNamma Kalvi 11th Chemistry Question Bank Questions em 216447Vaishanavi J.ANo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Molecular and Ionic Compound Structure and PropertiesDocument7 pagesUnit 2: Molecular and Ionic Compound Structure and PropertiesTAHA GABRNo ratings yet
- Sr. PhysicsDocument6 pagesSr. PhysicsMavuluri UmamaheshNo ratings yet
- CBSE Board Class XII Physics - Set 1 Board Paper - 2011 Time: 3 Hours (Total Marks: 70) General Instructions: 1. 2. 3. 4Document6 pagesCBSE Board Class XII Physics - Set 1 Board Paper - 2011 Time: 3 Hours (Total Marks: 70) General Instructions: 1. 2. 3. 4Chandan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Apollo Institute of Engineering & Technology: Question BankDocument1 pageApollo Institute of Engineering & Technology: Question BankNobody cares Nobody caresNo ratings yet
- Bonding in Molecules 2019 2nd Yr Michaelmas TermDocument71 pagesBonding in Molecules 2019 2nd Yr Michaelmas Termtresa.george27No ratings yet
- MaterialmDocument3 pagesMaterialmAbdur RazzakNo ratings yet
- Physics Section Wise Important Questions WMDocument7 pagesPhysics Section Wise Important Questions WMShashank BNo ratings yet
- A2 Physics Unit 4 Definitions and Statements QuestionsDocument1 pageA2 Physics Unit 4 Definitions and Statements QuestionsSomaya AliNo ratings yet
- Aga Khan High School, Kampala Ib2 Physics MCQ On Quantum Mechanics (HL)Document11 pagesAga Khan High School, Kampala Ib2 Physics MCQ On Quantum Mechanics (HL)Abigail NamulondoNo ratings yet
- Essay Type QuestionsDocument5 pagesEssay Type QuestionspoorviNo ratings yet
- B.Sc. VI Semester Physics:: Paper VII Modern Physics:: Question BankDocument3 pagesB.Sc. VI Semester Physics:: Paper VII Modern Physics:: Question BankReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Chem Assingment1 HHWDocument1 pageChem Assingment1 HHWmoksh.meeNo ratings yet
- Physics Question BankDocument15 pagesPhysics Question Bankepicgaming0455No ratings yet
- Chemistry Que Bank CbseDocument3 pagesChemistry Que Bank Cbsepradeep87810No ratings yet
- Questions Bank On ELECTROSTATICSDocument3 pagesQuestions Bank On ELECTROSTATICSAlok ShawNo ratings yet
- Bapatla Engineering College::Bapatla (Autonomous) B.Tech-Short Answer Model Questions Subject: Engineering Physics-II SemesterDocument7 pagesBapatla Engineering College::Bapatla (Autonomous) B.Tech-Short Answer Model Questions Subject: Engineering Physics-II Semesterchanjaneyulu9No ratings yet
- ATOMSDocument10 pagesATOMSschrujhana.jaganNo ratings yet
- Final Exam 2023 PrintDocument21 pagesFinal Exam 2023 PrintMUHAMMAD ZAINNo ratings yet
- II Puc Physics - Assignment (Mid Term 2022) - Gsgp'sDocument20 pagesII Puc Physics - Assignment (Mid Term 2022) - Gsgp'skiranknNo ratings yet
- Xii Pb2 AssignmentDocument2 pagesXii Pb2 Assignmentmehaktyagi422No ratings yet
- EDocument13 pagesESultan Hadi PrabowoNo ratings yet
- Phy SeniorsDocument6 pagesPhy SeniorsRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Che 222 Practice Questions 2020aDocument4 pagesChe 222 Practice Questions 2020adoreenrose739No ratings yet
- Physics (1st Inter)Document1 pagePhysics (1st Inter)rl3559980No ratings yet
- Review Exam1-S23Document43 pagesReview Exam1-S23et268No ratings yet
- Cmap Science9Document17 pagesCmap Science9Michael LopezNo ratings yet
- B.E., Electronics and Communication Engineering: Kumaraguru College of Technology COIMBATORE - 641 049Document81 pagesB.E., Electronics and Communication Engineering: Kumaraguru College of Technology COIMBATORE - 641 049NilT FigNo ratings yet
- (Career Endeavour) IIT JAM CHEMISTRY PDFDocument88 pages(Career Endeavour) IIT JAM CHEMISTRY PDFKiran Mandal100% (1)
- Chapter 2 The Chemical Basis of Life: Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece Et Al.)Document14 pagesChapter 2 The Chemical Basis of Life: Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece Et Al.)Yazmin QuevedoNo ratings yet
- CHM 102-Dr AzeezDocument24 pagesCHM 102-Dr Azeezbalikisolayemi2005No ratings yet
- Chemistry ConceptsDocument60 pagesChemistry ConceptsElla Jean LanoteNo ratings yet
- Perez Benito2003Document8 pagesPerez Benito2003Brent WoottonNo ratings yet
- Concept Review With Key TermsDocument4 pagesConcept Review With Key TermsWaqar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Polar Covalent Bonds - Acids and BasesDocument53 pagesChapter 2 - Polar Covalent Bonds - Acids and BasesWALTEVAN BEZERRA DOS SANTOS100% (1)
- 4.1.1 Protic Vs Aprotic SolventDocument36 pages4.1.1 Protic Vs Aprotic SolventDawit BirhanuNo ratings yet
- Susan Maraj Ionic and Covalent BondingDocument14 pagesSusan Maraj Ionic and Covalent BondingKelseyNo ratings yet
- ACT BIOLOGY HighlightsDocument157 pagesACT BIOLOGY HighlightsOmar SedkeyNo ratings yet
- 2019 Johor Chemistry K2 Set 2 JawapanDocument10 pages2019 Johor Chemistry K2 Set 2 JawapanchaNo ratings yet
- TRB Chemistry Syllabus-2023Document3 pagesTRB Chemistry Syllabus-2023dreamletNo ratings yet
- Detailed Notes Topic 2 Bonding and Structure Edexcel Chemistry A LevelDocument17 pagesDetailed Notes Topic 2 Bonding and Structure Edexcel Chemistry A LevelttjjjNo ratings yet
- Chemistry BookDocument145 pagesChemistry BookFatima Viterbo MontalvoNo ratings yet
- Carbon Compounds: Grade 9Document21 pagesCarbon Compounds: Grade 9Rosalyn RayosNo ratings yet
- Molecular Geometry and CrystallineDocument102 pagesMolecular Geometry and CrystallineRenNo ratings yet
- Probing The Fluxional Bonding Nature of Rapid Cope Rearrangements in Bullvalene C10H10 and Its Analogs C8H8, C9H10, and C8BH9Document8 pagesProbing The Fluxional Bonding Nature of Rapid Cope Rearrangements in Bullvalene C10H10 and Its Analogs C8H8, C9H10, and C8BH9PeterNo ratings yet
- CHE434 Lesson Plan2014Document6 pagesCHE434 Lesson Plan2014Nurtasha AtikahNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document39 pagesCH 10Chala1989No ratings yet
- Dr. A. A. Akinsiku: Selected Topics in Chemistry For Chemical Engineering 1 BYDocument63 pagesDr. A. A. Akinsiku: Selected Topics in Chemistry For Chemical Engineering 1 BYIfiok UsoroNo ratings yet
- Ionic Vs Covalent Compounds - Volatility, Conductivity and Solubility - WorksheetDocument4 pagesIonic Vs Covalent Compounds - Volatility, Conductivity and Solubility - WorksheetKaren OrlanskiNo ratings yet
- Carbocation StabilityDocument2 pagesCarbocation StabilityRoaring LionNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Chemistry 112 October 7, 2013Document5 pagesExam 1 Chemistry 112 October 7, 2013Karren Ferrer-Mora HandayanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Microproject 1Document12 pagesChemistry Microproject 1Aachal GulhaneNo ratings yet
- Reacciones de Los Halogenuros de AlquiloDocument6 pagesReacciones de Los Halogenuros de AlquiloMaria Jesus TorresNo ratings yet
- 2013 H2 Chem JC Papers PDFDocument1,601 pages2013 H2 Chem JC Papers PDFShu Qing NgNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Organic Chemistry Mechanistic Patterns 1st Edition by OgilvieDocument25 pagesTest Bank For Organic Chemistry Mechanistic Patterns 1st Edition by Ogilviecruralmorphonv9rp2100% (44)