Professional Documents
Culture Documents
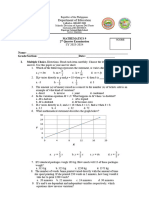
Pre Test TOS Grade 8 Math (2016-17)
Pre Test TOS Grade 8 Math (2016-17)
Uploaded by
Sherelyn Salanda AlcantaraOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
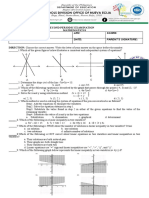
Pre Test TOS Grade 8 Math (2016-17)
Pre Test TOS Grade 8 Math (2016-17)
Uploaded by
Sherelyn Salanda AlcantaraCopyright:
Available Formats
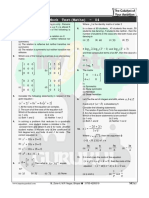
TABLE OF SPECIFICATION
Pretest - Mathematics 8
Item Placement
Understanding
Remembering
No.
Evaluating
Analyzing
Applying
Creating
Learning Competencies of
Item
s
1.factors completely different types of polynomials (polynomials with
common monomial factor, difference of two squares, sum and difference of 1 21
two cubes, perfect square trinomials, and general trinomials).
2. solves problems involving factors of polynomials. 1 31
3. illustrates rational algebraic expressions. 1 1
4. simplifies rational algebraic expressions. 1 41
5. performs operations on rational algebraic expressions. 1 42
6. solves problems involving rational algebraic expressions. 1 32
7. illustrates the rectangular coordinate system and its uses.*** 1 2
8. illustrates linear equations in two variables. 1 11
9. illustrates the slope of a line. 1 12
10. finds the slope of a line given two points, equation, and graph. 1 22
11. writes the linear equation ax + by = c in the form
y = mx + b and vice versa. 1 23
12. graphs a linear equation given (a) any two point ; (b) the x – and
y – intercepts; (c) the slope and a point on the line *** 1 24
13. describe the graph of a linear equation in terms of its intercepts and
slope. *** 1 13
14. find the equation of a line given (a) two points; (b) the slope and point;
(c) the slope and its intercepts. 1 43
15. solves problems involving linear equations in two variables. 1 33
16. illustrates a system of linear equations in two variables. 1 3
17. graph a system of linear equation in two variables. *** 1 44
18. categorized when a given system of linear equations in two variables
has graph that are parallel, intersecting and coinciding. 1 25
19. solves a system of linear equations in two variables by (a) graphing; (b)
substitution; (c) elimination. *** 1 45
20. solves problems involving systems of linear equations in two variables.
1 34
21. illustrates linear inequalities in two variables.
22. differentiates linear inequalities in two variables from linear equations 1 4
in two variables.
23. graphs linear inequalities in two variables. 1 46
24. solves problems involving linear inequalities in two variables. 1 35
25. solves a system of linear inequalities in two variables.*** 1 47
26. solves problems involving systems of linear inequalities in two
variables. 1 36
27. illustrates a relation and a function.
28. verifies if a given relation is a function. 1 5
29. determines dependent and independent variables. 1 26
30. finds the domain and range of a function. 1 14
31. illustrates a linear function.
32. graphs a linear function’s (a) domain; (b) range; (c) table of values; (d) 1 6
intercepts; and (e) slope
33. solves problems involving linear function 1 37
34. determines the relationship between the hypothesis and the conclusion
of an if-then statement. 1 15
35. transforms a statement into an equivalent if-then statement. 1 27
36. determines the inverse, converse, and contrapositive of an if-then
statement. 1 16
37. illustrates the equivalences of: (a) the statement and its contrapositive;
and (b) the converse and inverse of a statement. 1 7
38. uses inductive or deductive reasoning in an argument.
39. writes a proof (both direct and indirect). 1 17
40. describes a mathematical system.
41. illustrates the need for an axiomatic structure of a mathematical system
in general, and in Geometry in particular: (a) defined terms; (b) undefined 1 8
terms; (c) postulates; and (d) theorems.
42. illustrates triangle congruence.. 1 9
43. illustrates the SAS, ASA and SSS congruence postulates.*** 1 18
44. solves corresponding parts of congruent triangles 1 48
45. proves two triangles are congruent. 1 28
46. proves statements on triangle congruence.
47. applies triangle congruence to construct perpendicular lines and angle 1 38
bisectors.
48. illustrates theorems on triangle inequalities (Exterior Angle Inequality
Theorem, Triangle Inequality Theorem, Hinge Theorem).*** 1 19
49. applies theorems on triangle inequalities. 1 39
50. proves inequalities in a triangle. 1 49
51. proves properties of parallel lines cut by a transversal.***
52. determines the conditions under which lines and segments are parallel 1 29
or perpendicular.
53. illustrates an experiment, outcome, sample space and event.*** 1 10
54. counts the number of occurrences of an outcome in an experiment: (a)
table; (b) tree diagram; (c) systematic listing; and (d) fundamental counting 1 50
principle.***
55. finds the probability of a simple event. 1 30
56. illustrates an experimental probability and a theoretical probability.
1 20
Ccc 57. solves problems involving probabilities of simple events. 1 40
TOTAL 50 10 10 10 10 10
Prepared by:
ISABELO P. CUARTO
Grade 8 Teacher
You might also like
- 2ND Quarter 1ST Summative Test Math8Document2 pages2ND Quarter 1ST Summative Test Math8Lady-Ann LugoNo ratings yet
- DLL (1) JaysonDocument2 pagesDLL (1) JaysonBenying Gianan100% (1)
- Basic Geometric Ideas Lesson Plan (Extended)Document3 pagesBasic Geometric Ideas Lesson Plan (Extended)api-25394254950% (6)
- MATH-8-TOS 2nd QuarterDocument3 pagesMATH-8-TOS 2nd QuarterAries C. FigueroaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Exam 9 - 2023-2024Document5 pages2nd Quarter Exam 9 - 2023-2024vergel itimNo ratings yet
- Math 8 TosDocument2 pagesMath 8 TosJay Ariel D. Alegato II100% (1)
- X BX+C 0: Quarter 1: SUMMATIVE TEST #1 (Quadratic Equation and Quadratic Inequality) Mathematics 9Document3 pagesX BX+C 0: Quarter 1: SUMMATIVE TEST #1 (Quadratic Equation and Quadratic Inequality) Mathematics 9Guada LupeNo ratings yet
- Our Lady of Guadalupe Minor Seminary Area A Table of Specification 1 Quarter Mathematics 8 School Year: 2020-2021Document1 pageOur Lady of Guadalupe Minor Seminary Area A Table of Specification 1 Quarter Mathematics 8 School Year: 2020-2021Bernadette Remigio - JovellanosNo ratings yet
- Math 9 1st Summative TestDocument4 pagesMath 9 1st Summative TestMariel PastoleroNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Del Rosario Integrated SchoolDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Del Rosario Integrated SchoolJudith CuevaNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in Mathematics 8Document4 pagesSummative Test in Mathematics 8Garry D. DivinagraciaNo ratings yet
- Life Is The Most Difficult Exam. Many People Fail Because They Try To Copy Others, Not Realizing That Everyone Has A Different Question Paper.Document3 pagesLife Is The Most Difficult Exam. Many People Fail Because They Try To Copy Others, Not Realizing That Everyone Has A Different Question Paper.Agyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- 2021 10 12Document2 pages2021 10 12Ludwig Van BeethovenNo ratings yet
- 2nd QuarterDocument4 pages2nd QuarterCarlo Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Name: LRN: Score: Grade & Section: Date: Parent'S SignatureDocument7 pagesName: LRN: Score: Grade & Section: Date: Parent'S SignatureAries C. FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in Mathematics 8: Quarter 1Document3 pagesSummative Test in Mathematics 8: Quarter 1zaldy mendozaNo ratings yet
- Math 8 First Quarterly Exam 2022 2023Document6 pagesMath 8 First Quarterly Exam 2022 2023Carmina Cunanan100% (2)
- 3rd Periodical Test 2015Document6 pages3rd Periodical Test 2015Danilo de Mesa100% (1)
- Briz District, Tagum City: Liceo de DavaoDocument4 pagesBriz District, Tagum City: Liceo de DavaoAnnie Rose Ansale100% (2)
- Grade 8 - 1st Periodical Examination-BloomsDocument3 pagesGrade 8 - 1st Periodical Examination-BloomsDAHLIA CONTAOI100% (2)
- G8 2ndquarterDocument3 pagesG8 2ndquarterVirginia QueroNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter Exam Mathematics 7Document3 pagesSecond Quarter Exam Mathematics 7angelen buhawe0% (1)
- Math 9 TOS Q3Document4 pagesMath 9 TOS Q3Amelita TupazNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1578879127577Document4 pagesOrca Share Media1578879127577Klay Stephen JuarezNo ratings yet
- DLL Math 8 Quarter 2 Week 4Document6 pagesDLL Math 8 Quarter 2 Week 4Jay Paul T. BadenasNo ratings yet
- First Quarterly Exam in Math 8 - Junior High School Table of SpecificationDocument1 pageFirst Quarterly Exam in Math 8 - Junior High School Table of SpecificationAnderson Marantan100% (1)
- G-8 3rd Summative TestDocument2 pagesG-8 3rd Summative TestJulius Agacid BangeroNo ratings yet
- X X X X: Triala National High SchoolDocument4 pagesX X X X: Triala National High SchoolApple Gacutan Olayra50% (2)
- First Quarter Exam in Grade 9 MathematicsDocument1 pageFirst Quarter Exam in Grade 9 MathematicsRoyce Dunhill Fortes DomondonNo ratings yet
- EsP - Second Periodical Test Grade 9Document5 pagesEsP - Second Periodical Test Grade 9Camz DelnaNo ratings yet
- Table of Specifications Mathematics 8 1 Quarter: M8AL-Ia-b-1Document2 pagesTable of Specifications Mathematics 8 1 Quarter: M8AL-Ia-b-1Joseph S. Palileo Jr.No ratings yet
- Summative Test in Special ProductsDocument3 pagesSummative Test in Special ProductsNeil JoNo ratings yet
- Final QuestionnaireDocument5 pagesFinal QuestionnaireCharlene FiguracionNo ratings yet
- Math 7 1stDocument13 pagesMath 7 1stWerty Gigz Durendez100% (1)
- Summative Test in Mathematics 10Document3 pagesSummative Test in Mathematics 10Alfred QuintoNo ratings yet
- A. B. C. D.: First Quarter Unit TestDocument3 pagesA. B. C. D.: First Quarter Unit TestAhron RivasNo ratings yet
- TOS Math 8 2ndQDocument2 pagesTOS Math 8 2ndQReina Chenna Sergantes SaulongNo ratings yet
- Math 8 - First Quarter First Long TestDocument12 pagesMath 8 - First Quarter First Long TestJon Jon D. MarcosNo ratings yet
- Q1.Math9.Summative Test 1Document2 pagesQ1.Math9.Summative Test 1CLARICE VENTURANo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Q2 - Summative Assessment Weeks 1 & 2Document4 pagesGrade 8 Q2 - Summative Assessment Weeks 1 & 2Zahjid Callang100% (1)
- Second Periodical Examination in Mathematics 9Document4 pagesSecond Periodical Examination in Mathematics 9Jhim Corpuz100% (2)
- Math 9 1st Summative Test FinalDocument5 pagesMath 9 1st Summative Test FinalMariel PastoleroNo ratings yet
- Math 7-1st Quarter Final Exam With TOS and Answer KeyDocument3 pagesMath 7-1st Quarter Final Exam With TOS and Answer KeyJingle Pagas CelestianNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodical Math 8Document3 pages1st Periodical Math 8Cjay ManingasNo ratings yet
- 4th SUMMATIVE TEST IN MATH 7 QUARTER 1Document1 page4th SUMMATIVE TEST IN MATH 7 QUARTER 1Jaylor Garido0% (2)
- Summative Test For Quadratic Equations2Document2 pagesSummative Test For Quadratic Equations2AsmiraMangontra0% (1)
- FIRST QUARTER EXAM IN MATH 9 ... EditedDocument2 pagesFIRST QUARTER EXAM IN MATH 9 ... EditedNORMAN BARDELAS100% (1)
- Summative Test Math Grade 8Document2 pagesSummative Test Math Grade 8Armilyn Macasero Lubuguin100% (1)
- Q2 Curriculum Map - Mathematics 10Document5 pagesQ2 Curriculum Map - Mathematics 10Manilyn BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Math 9 AWS Week-1Document2 pagesMath 9 AWS Week-1Edmundo Garcia Bukas Jr.No ratings yet
- TOS Math7Document5 pagesTOS Math7Dawn RazonableNo ratings yet
- 1st COT Math 8 PresentationDocument29 pages1st COT Math 8 PresentationEL Filibusterisimo Paul CatayloNo ratings yet
- DLL Math 8Document21 pagesDLL Math 8Jeferson Eborda Rosel100% (2)
- Summative 8 4THDocument2 pagesSummative 8 4THMaria Carmela Oriel MaligayaNo ratings yet
- Math 8 Summative Test: - Encircle The Letter of The Correct Answer RDocument5 pagesMath 8 Summative Test: - Encircle The Letter of The Correct Answer Retheljoy agpaoaNo ratings yet
- Summative Test Math 7 2nd QuarterDocument4 pagesSummative Test Math 7 2nd QuarterRaign Yuan Baguio100% (1)
- DLL 1st Week For Math 8Document6 pagesDLL 1st Week For Math 8Melba RamosNo ratings yet
- First Periodic Test: RD RDDocument13 pagesFirst Periodic Test: RD RDJUVELYN BELLITANo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 Unit Topic 1: Factoring PolynomialsDocument2 pagesQuarter 1 Unit Topic 1: Factoring PolynomialsHyacinth De LeonNo ratings yet
- Budget of WorkDocument7 pagesBudget of WorkPatrick Dag-um MacalolotNo ratings yet
- BOW in MATH 8Document3 pagesBOW in MATH 8Eric ManotaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 10 Quarter 4 Week 3: Interpreting Measure of PositionDocument37 pagesMathematics 10 Quarter 4 Week 3: Interpreting Measure of PositionSherelyn Salanda Alcantara0% (1)
- Assessment Math10 - SY 18-19Document80 pagesAssessment Math10 - SY 18-19Sherelyn Salanda AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter Test RadicalDocument2 pagesChapter Test RadicalSherelyn Salanda AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Law of Cosines SEPDocument2 pagesLaw of Cosines SEPSherelyn Salanda AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- PreTEST Question GR.7 (2016-17)Document3 pagesPreTEST Question GR.7 (2016-17)Sherelyn Salanda AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Permutations and CombinationsDocument1 pagePermutations and CombinationsSherelyn Salanda AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- DiagnosticNUMERACY TEST Grade 9 (2016-17)Document2 pagesDiagnosticNUMERACY TEST Grade 9 (2016-17)Sherelyn Salanda AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- To Graph A Circle in A Coordinate Plane Given Its Equation: To Graph A Circle in A Coordinate Plane Given Its EquationDocument7 pagesTo Graph A Circle in A Coordinate Plane Given Its Equation: To Graph A Circle in A Coordinate Plane Given Its EquationSherelyn Salanda AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Dasig Alcantara EM203 Written ReportDocument16 pagesDasig Alcantara EM203 Written ReportSherelyn Salanda AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Rational ExponentsDocument1 pageRational ExponentsSherelyn Salanda AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- SYLLABUS of SOLID GEOMETRYDocument3 pagesSYLLABUS of SOLID GEOMETRYJenny Lyne Sangalang LisayenNo ratings yet
- GEOMETRY - Postulates, Theorems, and DefinitionsDocument6 pagesGEOMETRY - Postulates, Theorems, and DefinitionsClarisse AnnNo ratings yet
- Circles 4Document6 pagesCircles 4babufatafatiNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD CommandsDocument3 pagesAutoCAD CommandsAtika AlamNo ratings yet
- Third Quarter Week 3Document3 pagesThird Quarter Week 3edelmar benosaNo ratings yet
- Math8 3rd ExamDocument6 pagesMath8 3rd ExamSuzy Jean Geverola-Dagani MalaqueNo ratings yet
- Teaching StrategyDocument28 pagesTeaching StrategyDj22 JakeNo ratings yet
- 4.5 Proving Quadrilateral PropertiesDocument27 pages4.5 Proving Quadrilateral PropertiesHazel Clemente CarreonNo ratings yet
- Junior Certificate Maths SyllabusDocument100 pagesJunior Certificate Maths Syllabusapi-214726372No ratings yet
- Vectors: DefinitionsDocument25 pagesVectors: DefinitionssonalisabirNo ratings yet
- 中三 三角形的特殊線和中心 (Special Lines and Centres in a Triangle) - V3 - Final - GDocument61 pages中三 三角形的特殊線和中心 (Special Lines and Centres in a Triangle) - V3 - Final - G丛头越No ratings yet
- Teacher S Copy. Geometry Unit 5. Circles With and Without Coordinates. Eureka Math. Eureka MathDocument289 pagesTeacher S Copy. Geometry Unit 5. Circles With and Without Coordinates. Eureka Math. Eureka MathryuNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form 2 2017Document14 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form 2 2017Hazrin HazreynaldoNo ratings yet
- TG GeometryDocument135 pagesTG GeometryVivekRajuNo ratings yet
- Attempt This Question.: Geometrical Reasoning ADocument5 pagesAttempt This Question.: Geometrical Reasoning AFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- 2019 MA Maxima and Minima Worksheet HSC Questions W SolutionsDocument24 pages2019 MA Maxima and Minima Worksheet HSC Questions W SolutionsEm GibsonNo ratings yet
- Math Project CabriDocument7 pagesMath Project Cabriapi-282226781No ratings yet
- Syllabus: Cambridge IGCSE International MathematicsDocument29 pagesSyllabus: Cambridge IGCSE International Mathematicsmichelangelo mellingNo ratings yet
- مساحة كوت٩٨٨٦٥Document11 pagesمساحة كوت٩٨٨٦٥NadirNo ratings yet
- Digital Unit Plan Template Unit Title: Triangles Name: Mackenzie Sheppard Content Area: Math - Geometry Grade Level: 9 & 10Document2 pagesDigital Unit Plan Template Unit Title: Triangles Name: Mackenzie Sheppard Content Area: Math - Geometry Grade Level: 9 & 10api-403395161No ratings yet
- BTech Chemical Engineering Syllabus 2015 16 PDFDocument112 pagesBTech Chemical Engineering Syllabus 2015 16 PDFShaviz SoudagarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics - 25 Questions Bank: ScaleDocument4 pagesEngineering Graphics - 25 Questions Bank: ScaleWarren RiveraNo ratings yet
- 10.1 Tangents To CirclesDocument32 pages10.1 Tangents To CirclesArnab Biswas100% (1)
- IOE Nepal BCT Year 1 Part 1 SyllabusDocument19 pagesIOE Nepal BCT Year 1 Part 1 SyllabusBulmi HilmeNo ratings yet
- Basic Geometry GlossaryDocument46 pagesBasic Geometry GlossarydocdocdeeNo ratings yet
- 024e5840b21e1-Mock Test (Maths) - 04Document11 pages024e5840b21e1-Mock Test (Maths) - 04Aman GoelNo ratings yet
- Ellipse-01 - TheoryDocument13 pagesEllipse-01 - TheoryRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Math 4 Compleza, Andrea Gael P.Document7 pagesMath 4 Compleza, Andrea Gael P.AG Pendon ComplezaNo ratings yet
- Construct A Fold Cross-Section Using The Arc (Busk) MethodDocument14 pagesConstruct A Fold Cross-Section Using The Arc (Busk) MethodMuhsan Iskandar Juarsa100% (1)