Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Properties of Circles (2) : Multiple-Choices Questions
Basic Properties of Circles (2) : Multiple-Choices Questions
Uploaded by
Jimmy LauOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Properties of Circles (2) : Multiple-Choices Questions
Basic Properties of Circles (2) : Multiple-Choices Questions
Uploaded by
Jimmy LauCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 8 Basic Properties of Circles (2) C:\Program Files\HKEP\S_Maths_09\Word\C4 English\Ch8\
Basic Properties of Circles (2)
Multiple-choices Questions
Attempt ALL questions. The full marks of this test are 50.
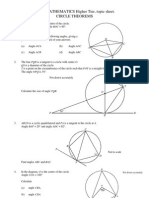
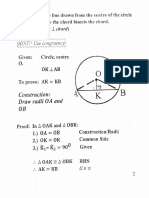
Level 1 3. In the figure, TA is a tangent to the circle.
BC is a diameter. If ABC 25, then
1. In which figure, TA is a tangent to the ATB
circle with centre O?
A. B.
A. 25 o .
B. 35 o .
C. 40 o .
C. D. D. 45 o .
4. In the figure, TA and TB are tangents to
the circle with centre O. Which of the
following may not be true?
2. In the figure, TA is a tangent to the circle
with centre O. OA = AB. Find ATB.
A. AT = BT
A. 30 o
B. OA TA
B. 40 o C. AOT BOT
C. 45 o D. AO = TA
D. 60 o
© Hong Kong Educational Publishing Co. 28
Chapter 8 Basic Properties of Circles (2) C:\Program Files\HKEP\S_Maths_09\Word\C4 English\Ch8\
5. In the figure, TA and TB are tangents to 7. In the figure, BQ is a tangent to the circle.
the circle. AP // BQ and AB = AC. TAB 108.
Find CBQ.
If ACB 110, then ATB
A. 40 o .
A. 32 o
B. 50 o .
B. 36 o
C. 55 o .
o
C. 48 o
D. 70 .
D. 72 o
6. In the figure, PQ is a tangent to the circle.
8. In the figure, a circle is inscribed in
BA is the angle bisector of QAC.
ABCD. AD = h cm and BC = k cm.
AQB 36 and QC PC.
Find the perimeter of ABCD.
Find ACP.
A. 36 o
B. 38 o
A. 2(h + k) cm
C. 42 o
B. hk cm
D. 48 o
C. 4(h + k) cm
D. 2h + k cm
© Hong Kong Educational Publishing Co. 29
Chapter 8 Basic Properties of Circles (2) C:\Program Files\HKEP\S_Maths_09\Word\C4 English\Ch8\
9. In the figure, a circle is inscribed in 12. In the figure, PQ is a tangent to the circle
ABC. AB = 20 cm and AR = 8 cm. with centre O at A.
Find BQ.
Which of the following is false?
A. OAP OAQ
A. 8 cm
B. OAP 90
B. 10 cm
C. OAQ 90
C. 12 cm
D. AP = AQ
D. 14 cm
13. In the figure, PA is a tangent to the circle
10. In the figure, TB is a tangent to the circle.
AB : BC : CA = 4 : 3 : 2. Find CBT.
and O is the centre of the circle.
If BP = 9 cm and OB = 8 cm, find the
A. 40 o length of AP.
B. 60 o A. 15 cm
C. 75 o B. 15.5 cm
D. 80 o C. 16 cm
D. 16.5 cm
11. If a straight line is a tangent to a circle,
how many points of intersection are there
between the straight line and the circle?
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
© Hong Kong Educational Publishing Co. 30
Chapter 8 Basic Properties of Circles (2) C:\Program Files\HKEP\S_Maths_09\Word\C4 English\Ch8\
14. In the figure, PC is a tangent to the circle 16. In the figure, PQ is a tangent to the circle
with centre O. AC is a diameter of the at B and PQ // AC.
circle.
If AOB 80, then BCP = Which of the following angles are the
same as BAC?
A. 30.
I. ABP
B. 40.
II. ABC
C. 50.
III. CBQ
D. 55.
A. I only
B. I and III only
15. In the figure, a circle with radius 5 cm is
C. II and III only
inscribed in ABC. O is the centre of the
D. I, II and III
circle, OB = 13 cm, PC = 10 cm and
AC = 18 cm.
17. In the figure, PQ is a tangent to the circle
with centre O at B. AC is a diameter of
the circle and CQ PQ.
Find the perimeter of ABC.
If BCQ 55, then BOC =
A. 58 cm
A. 35.
B. 60 cm
B. 45.
C. 62 cm
C. 60.
D. 66 cm
D. 70.
© Hong Kong Educational Publishing Co. 31
Chapter 8 Basic Properties of Circles (2) C:\Program Files\HKEP\S_Maths_09\Word\C4 English\Ch8\
18. In the figure, PQ is a tangent to the circle 20. A circle is inscribed in a square with
at A. BA = BC and BAQ 65. Find diagonal 12 cm.
ABC.
Find the radius of the circle.
A. 50 A. 6 cm
B. 55 B. 2 3 cm
C. 60 C. 3 2 cm
D. 65 D. 4 2 cm
19. In the figure, PA and PB are tangents to 21. In the figure, AB and DE are the
the circle. APB 54. Find ACB. diameters of the circle. If ACB 58
and BC is tangent to the circle, then
BED =
A. 54
A. 32.
B. 58
B. 58.
C. 63
C. 62.
D. 64
D. 68.
© Hong Kong Educational Publishing Co. 32
Chapter 8 Basic Properties of Circles (2) C:\Program Files\HKEP\S_Maths_09\Word\C4 English\Ch8\
22. In the figure, AB is a diameter of the 24. In the figure, AC is a tangent to the circle
circle with radius 8 cm. Find AC + BE. and BC is a diameter. OA = 17 cm and
OB = 8 cm. Find AC.
A. 8 cm
B. 1 cm
C. 12 cm A. 12 cm
D. 16 cm B. 14.2 cm
C. 15 cm
23. In the figure, AB is a tangent to the circle. D. 15.5 cm
AO OB, OA = 8 cm and AB = 12 cm.
Find the radius of the circle. (Give the 25. In the figure, TA, TB and PQ are tangents
to the circle. If ATB 40, then
answer correct to 3 significant figures.)
POQ =
A. 40.
A. 4.47 cm B. 65.
B. 5.96 cm C. 70.
C. 6.71 cm D. 75.
D. 7.45 cm
© Hong Kong Educational Publishing Co. 33
Chapter 8 Basic Properties of Circles (2) C:\Program Files\HKEP\S_Maths_09\Word\C4 English\Ch8\
26. In the figure, a circle is inscribed in a 28. In the figure, TA and TB are tangents to
right-angled triangle. AB BC, the circle. If ACB = y, then ATB =
AB = 12 cm and BC = 16 cm. Find AR.
A. 2y 180.
B. 4y 180.
A. 4 cm C. y + 180.
B. 5 cm D. 180 y.
C. 6 cm
D. 8 cm 29. In the figure, DB is a tangent to the circle.
CB = CD and BAC 46. Find ACB.
27. In the figure, TA and TB are tangents to
the circle. ATB 50 and
ABC 55. Find CAB.
A. 92
B. 96
A. 55 C. 98
B. 60 D. 102
C. 65
D. 70
© Hong Kong Educational Publishing Co. 34
Chapter 8 Basic Properties of Circles (2) C:\Program Files\HKEP\S_Maths_09\Word\C4 English\Ch8\
30. In the figure, TA and TB are tangents to 32. In the figure, TB is a tangent to the circle.
the circle. ATB 58 and AB is a diameter. Find BC.
CBT 26. Find CAT.
A. 6 3 cm
B. 7 3 cm
A. 28 C. 4 7 cm
B. 30 D. 6 7 cm
C. 32
D. 35 33. In the figure, a circle is inscribed in
ABCD. PA = 8 cm and QD = 18 cm.
Level 2 AB // DC. Find the radius of the
circle.
31. In the figure, AB is a tangent to the circle.
AC = 12 cm and OC = 18 cm.
Find the area of OAB.
A. 10 cm
B. 12 cm
C. 18 cm
A. 108 cm 2 D. 24 cm
2
B. 144 cm
C. 216 cm 2
D. 270 cm 2
© Hong Kong Educational Publishing Co. 35
Chapter 8 Basic Properties of Circles (2) C:\Program Files\HKEP\S_Maths_09\Word\C4 English\Ch8\
34. In the figure, PQ is a tangent to the circle 36. In the figure, AB passes through the
with centre O. AC is a diameter and centres of both circles. PQ is a tangent to
OQ // AB. Which of the following is/are the smaller circle with radius 5 cm and PQ
true? // AB. If PQ = 24 cm, find the area of the
shaded region.
I. BD = DC
II. APB~ BPC
III. A, O, D and B are concyclic.
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only A. 128 cm 2
D. I, II and III B. 132 cm 2
C. 140 cm 2
35. In the figure, PA is a tangent to the circle. D. 144 cm 2
PA = 12 cm and PC = 8 cm.
Find the ratio of the area of APC to 37. In the figure, PA is a tangent to the circle
the area of BPA. with centre O. BC = CD and
DAP 42.
A. 2:3
B. 3:4
C. 4:9
D. 4 : 15
Find ADC.
A. 94
B. 112
C. 114
D. 118
© Hong Kong Educational Publishing Co. 36
Chapter 8 Basic Properties of Circles (2) C:\Program Files\HKEP\S_Maths_09\Word\C4 English\Ch8\
38. In the figure, PQ is a common tangent to 40. In which of the following figures is TA a
the circles. The radii of the two circles are tangent to the circle with centre O?
8 cm and 6 cm respectively. Find the A.
length of AB.
B.
A. 7 3 cm
B. 8 3 cm
C. 9 2 cm
C.
D. 9 3 cm
39. In the figure, TA is a tangent to the circle.
Which of the following must be true?
D.
I. TAC ~ TBA
II. ACT ~ ABC
III. BAC ACT
A. I only
B. III only
C. I and II only
D. II and III only
© Hong Kong Educational Publishing Co. 37
Chapter 8 Basic Properties of Circles (2) C:\Program Files\HKEP\S_Maths_09\Word\C4 English\Ch8\
41. In the figure, TA and TC are tangents to 43. In the figure, a circle is inscribed in ABC.
the circle. AB is a diameter of the circle. If AB = 18 cm, BQ = 8 cm and
BCD 26, then ATD = CR = 6 cm. Find the perimeter of the
triangle.
A. 52.
B. 54. A. 46 cm
C. 58. B. 48 cm
D. 62. C. 50 cm
D. 52 cm
42. In the figure, TC is a tangent to the circle.
44. In the figure, PQ is a tangent to the circle.
OA // CB and BAQ 38. Find OCB.
Which of the following is true.
A. BC 2 AC TC
B. TA2 TC AC
C. TC 2 BA TB
D. TC 2 TA TB A. 38
B. 52
C. 76
D. 78
© Hong Kong Educational Publishing Co. 38
Chapter 8 Basic Properties of Circles (2) C:\Program Files\HKEP\S_Maths_09\Word\C4 English\Ch8\
45. In the figure, PA is a tangent to the circle 47. In the figure, PA is a tangent to the circle.
and PA // QB. If CAP 25 and AQ = 12 cm, CQ = 6 cm, DQ = 8 cm and
BAC 80, then QBC = PA 84 cm. Find the length of PD.
A. 25. A. 3.5 cm
B. 35. B. 4 cm
C. 40. C. 4.5 cm
D. 50. D. 4.8 cm
46. In the figure, a circle is inscribed in ABC. 48. In the figure, TC and TD are tangents to
QPR 58 and OCB 34. Find the circles. CTD is a right-angled
BAC. triangle. If TC = x and TD = y, then the
radius of the circle is
A. 52
B. 54 x y
A. .
C. 58 2
D. 62 x y
B. .
xy
xy
C. .
x y
1 2
D. x y2 .
2
© Hong Kong Educational Publishing Co. 39
Chapter 8 Basic Properties of Circles (2) C:\Program Files\HKEP\S_Maths_09\Word\C4 English\Ch8\
49. In the figure, PA is a tangent to the circle.
Which of the following must be true?
I. APD ~ CPA
II. ABC ~ ADP
III. ACD ~ ADP
A. I only
B. II only
C. I and III only
D. I, II and III
50. In the figure, TA and TB are tangents to
the circle such that TA TB and
AD BC.
Which of the following must be true?
I. TAB is an isosceles triangle.
II. BCD is an isosceles triangle.
III. ABC is a right-angled triangle.
A. I only
B. II only
C. I and III only
D. I, II and III
END OF TEST
© Hong Kong Educational Publishing Co. 40
You might also like
- GCE O-Level Mathematics Syllabus 'D' May/June 2016 Paper 2Document20 pagesGCE O-Level Mathematics Syllabus 'D' May/June 2016 Paper 2huudaaNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Applied GeostatisticsDocument92 pagesAn Introduction To Applied GeostatisticsAllan ErlikhmanNo ratings yet
- Basic Properties of Circles (1) : Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocument12 pagesBasic Properties of Circles (1) : Multiple-Choice QuestionsJimmy LauNo ratings yet
- CirclesDocument2 pagesCirclesMeenakshiSundareshNo ratings yet
- 17 Geometry (Circle) (MC)Document30 pages17 Geometry (Circle) (MC)Raistlin Chan Ching KitNo ratings yet
- 2023 12 09 173243M9 - Circles - TS2Document2 pages2023 12 09 173243M9 - Circles - TS2AnanyaNo ratings yet
- Basic Properties of Circles II (Q)Document34 pagesBasic Properties of Circles II (Q)Hoi Yee Karis LauNo ratings yet
- M9 Circles WS2 1702119819934 b5PUMDocument2 pagesM9 Circles WS2 1702119819934 b5PUMAnanyaNo ratings yet
- f4 General Mathematics Quiz 20090326 CircleDocument7 pagesf4 General Mathematics Quiz 20090326 Circlehjteoh2No ratings yet
- M10 Circles WS2 1667050036134 OteASDocument1 pageM10 Circles WS2 1667050036134 OteASMeeraaj RajeshNo ratings yet
- 35 - 02 - Geometry (Tangents To A Circle)Document13 pages35 - 02 - Geometry (Tangents To A Circle)Zhu JiankunNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - CirclesDocument24 pagesModule 2 - CirclesjeanNo ratings yet
- CirclesDocument6 pagesCircleskumarm78No ratings yet
- Sohcahtoa Worksheet 1Document6 pagesSohcahtoa Worksheet 1Daffa Guevara RaushanfikriNo ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4B12 12c lv2 E-1Document4 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4B12 12c lv2 E-1林俊佑No ratings yet
- Cbjemaco 10Document11 pagesCbjemaco 10Fawaz ZaheerNo ratings yet
- Secondary 5 Mathematics: 〔Whole Syllabus〕Document9 pagesSecondary 5 Mathematics: 〔Whole Syllabus〕CHIU KEUNG OFFICIAL PRONo ratings yet
- 1701832667764.QP PS CB IX Math CirclesDocument7 pages1701832667764.QP PS CB IX Math Circleskabbur.anushkaNo ratings yet
- Basic Properties of CirclesDocument70 pagesBasic Properties of Circleswww.ieo20040814No ratings yet
- Trigonometry Assignment5Document12 pagesTrigonometry Assignment5ayekyawtkyawtnyeinNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 10 New WorksheetDocument3 pagesChapter - 10 New Worksheetjayrawat1504No ratings yet
- Geometry Homework5Document4 pagesGeometry Homework5yitsongtang6334No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4B12 12f lv1 E-1Document2 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4B12 12f lv1 E-1林俊佑No ratings yet
- SSLC Mathematics Important Questions Chap 2 EM CIRCLESDocument11 pagesSSLC Mathematics Important Questions Chap 2 EM CIRCLESviruthaivikas matric schoolNo ratings yet
- 1701151029942.PS QP CB IX Math CirclesDocument5 pages1701151029942.PS QP CB IX Math Circlesaditya.shelar3179No ratings yet
- Ch. 11 Properties of Circles AnsDocument16 pagesCh. 11 Properties of Circles AnsSzeman YipNo ratings yet
- Circles WorksheetDocument4 pagesCircles Worksheetbdmmyytx99No ratings yet
- TT Math TangentUnit Sec2Document4 pagesTT Math TangentUnit Sec2haraaakNo ratings yet
- Angle Properties of Circles QDocument7 pagesAngle Properties of Circles Qjulius muiruriNo ratings yet
- Circle Notes - w1Document5 pagesCircle Notes - w1satya.ibsNo ratings yet
- File Jee Arcs and Subtended Angles Solved Practice Questions PDF 1582281787Document32 pagesFile Jee Arcs and Subtended Angles Solved Practice Questions PDF 1582281787Lisa BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Circles AssignmentDocument2 pagesCircles AssignmentpiyushNo ratings yet
- Circle TheoremsDocument3 pagesCircle Theoremstaliahspence123No ratings yet
- Topic No 11 Properties of CircleDocument14 pagesTopic No 11 Properties of CircleKhizar SaysNo ratings yet
- Circular Measure With TrigonometryDocument2 pagesCircular Measure With TrigonometryabdullahNo ratings yet
- Finding Tangents and Secants Measurement PDFDocument5 pagesFinding Tangents and Secants Measurement PDFJeff AragonNo ratings yet
- Arc Length W (Slash) Radians (A-Level Only)Document31 pagesArc Length W (Slash) Radians (A-Level Only)/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- Practice Questions S4Document2 pagesPractice Questions S4rick.arinaitweNo ratings yet
- Geometry Circle (Part-1 To 08) 20230922061125Document16 pagesGeometry Circle (Part-1 To 08) 20230922061125Rishabh KumarNo ratings yet
- 1 1 Cicles and Areas Question Bank 2010-1Document74 pages1 1 Cicles and Areas Question Bank 2010-1Балауса ЖандарбекNo ratings yet
- Circle TheoremsDocument3 pagesCircle TheoremsAmir Mohd100% (1)
- LQ Unit 10 Geometry II - Circles PDFDocument10 pagesLQ Unit 10 Geometry II - Circles PDFSamson YauNo ratings yet
- Ying Wa Girls' School Mathematics Test 3 Secondary 4 MathematicsDocument10 pagesYing Wa Girls' School Mathematics Test 3 Secondary 4 MathematicsShelbyNo ratings yet
- Topic 13-Symmetric Properties of TangentsDocument15 pagesTopic 13-Symmetric Properties of TangentsIndah KartikasariNo ratings yet
- Arc and Area of SectorDocument5 pagesArc and Area of Sectorleena_louisNo ratings yet
- Geom Proofs Theorem 1 2 and 3Document3 pagesGeom Proofs Theorem 1 2 and 3Priyanka KanaNo ratings yet
- Circle TheoremDocument2 pagesCircle TheoremCarole ThamiNo ratings yet
- Circles Worksheet-AnswersDocument12 pagesCircles Worksheet-AnswersSanjay SridharNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Maths Cbse Circles NotesDocument11 pagesClass 9 Maths Cbse Circles Notesdinesh_kp7647No ratings yet
- Geometry II AssignmentDocument102 pagesGeometry II Assignmentkoushik reddyNo ratings yet
- The Circle + Circles & Central Angles HWDocument1 pageThe Circle + Circles & Central Angles HWsa saNo ratings yet
- Tangent To A CircleDocument2 pagesTangent To A CircleYashh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Circle Geometry Part-2 Abhay Mahajan - 230806 - 170926Document13 pagesLecture 4 Circle Geometry Part-2 Abhay Mahajan - 230806 - 170926Nihal NihalNo ratings yet
- Circles - Practice Sheet PDFDocument6 pagesCircles - Practice Sheet PDFUtkarsh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Subject: Math's B (May) Topic: Test - 4Document2 pagesSubject: Math's B (May) Topic: Test - 4TanzimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - Circle Exercise Ex. 17 (A)Document21 pagesChapter 17 - Circle Exercise Ex. 17 (A)Fahad pathanNo ratings yet
- CirclesDocument9 pagesCirclessknkamalaNo ratings yet
- Inbound 3884587476884818562Document5 pagesInbound 3884587476884818562Anniezel Mae NillasNo ratings yet
- Form4 Chap8Document3 pagesForm4 Chap8PREBASUBAH A/P RAMALINGGAM MoeNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Ch3-Forces DynamicsDocument42 pagesCh3-Forces DynamicsJimmy LauNo ratings yet
- Basic Properties of Circles (1) : Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocument12 pagesBasic Properties of Circles (1) : Multiple-Choice QuestionsJimmy LauNo ratings yet
- Circular and Curvilinear MotionsDocument26 pagesCircular and Curvilinear MotionsJimmy LauNo ratings yet
- Ch1-Units Dimensional AnalysisDocument10 pagesCh1-Units Dimensional AnalysisJimmy LauNo ratings yet
- Kinematics: Motion of A Particle in One and Two DimensionsDocument23 pagesKinematics: Motion of A Particle in One and Two DimensionsJimmy LauNo ratings yet
- Koopa Ming Pao Mock 2021 Paper 2 EngDocument16 pagesKoopa Ming Pao Mock 2021 Paper 2 EngJimmy LauNo ratings yet
- Time Series Documentation - MathematicaDocument214 pagesTime Series Documentation - MathematicaTraderCat Solaris100% (2)
- Gram Schmidt OrthogonalizationDocument5 pagesGram Schmidt OrthogonalizationlordhokNo ratings yet
- Bluman 5th Chapter 4 HW SolnDocument3 pagesBluman 5th Chapter 4 HW SolnFrancis Philippe Cruzana CariñoNo ratings yet
- Statistics 427-SP 2011 Midterm II - Solution: Question 1 (6x2.5 Points)Document7 pagesStatistics 427-SP 2011 Midterm II - Solution: Question 1 (6x2.5 Points)Shahin AgahzadehNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2Document4 pagesProblem Set 2bijan shresthaNo ratings yet
- Relativistic Calogero-Moser Model As Gauged WZW TheoryDocument23 pagesRelativistic Calogero-Moser Model As Gauged WZW TheorytareghNo ratings yet
- Multiple Regression - EstimationDocument18 pagesMultiple Regression - EstimationSakshi VashishthaNo ratings yet
- Mat303 Stony BrookDocument17 pagesMat303 Stony BrooksakuruvrNo ratings yet
- Name Date Class: Color 1 Color 1 Color 1 Color 1Document2 pagesName Date Class: Color 1 Color 1 Color 1 Color 1Leigh YahNo ratings yet
- SLIM Sparse Linear Methods For Top-N Recommender SystemsDocument10 pagesSLIM Sparse Linear Methods For Top-N Recommender SystemsfcrkudxujdemptrdapNo ratings yet
- t2 M 4664-3-4 and 8 Christmas Multiplication Mosaic Activity SheetsDocument8 pagest2 M 4664-3-4 and 8 Christmas Multiplication Mosaic Activity SheetsivyNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Holidays HomeworkDocument5 pagesMathematics Holidays Homeworkccg jjNo ratings yet
- Greene ErrataDocument25 pagesGreene Erratar0arkNo ratings yet
- Questions & Answers On Genetic AlgorithmDocument15 pagesQuestions & Answers On Genetic AlgorithmPragya JainNo ratings yet
- Pre Board CBRC Region 7 200 ItemsDocument215 pagesPre Board CBRC Region 7 200 ItemsMichelle Chale LumabaoNo ratings yet
- 10th CBSE (SA - 1) Revision 3 (Maths) - 1Document23 pages10th CBSE (SA - 1) Revision 3 (Maths) - 1Mohd Sohail AhmedNo ratings yet
- Discrete Structures: Prof. Dipanwita RoychowdhuryDocument536 pagesDiscrete Structures: Prof. Dipanwita RoychowdhurySiddesh JadhavNo ratings yet
- Area and PerimeterDocument3 pagesArea and Perimeterapi-313703851No ratings yet
- Microscope LabDocument16 pagesMicroscope LabNelson AbdulNo ratings yet
- Basic Queuing Theory Formulas: P (X = k - T = t) = (λt) k! e, k = 0, 1, 2, - .Document2 pagesBasic Queuing Theory Formulas: P (X = k - T = t) = (λt) k! e, k = 0, 1, 2, - .Efe FelixNo ratings yet
- Haros Graphs: An Exotic Representation of Real NumbersDocument39 pagesHaros Graphs: An Exotic Representation of Real NumbersJohnNo ratings yet
- EE31Document176 pagesEE31Rhean Rheign VergaraNo ratings yet
- Uncertainty Quantifi Cation and Predictive Computational ScienceDocument349 pagesUncertainty Quantifi Cation and Predictive Computational SciencePedro AquinoNo ratings yet
- Psychology Strategy ConflictDocument27 pagesPsychology Strategy ConflictIulia PopoviciNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Equations, Inequalities and Absolute ValuesDocument31 pagesChapter 2: Equations, Inequalities and Absolute Valuesjokydin92No ratings yet
- Module 1.1: Operations Research Introduction To Operations ResearchDocument7 pagesModule 1.1: Operations Research Introduction To Operations ResearchchinnavenkateswarluNo ratings yet
- Gambler's RuinDocument7 pagesGambler's RuinTimNo ratings yet
- Direct Stiffness Method ThermalDocument17 pagesDirect Stiffness Method ThermalFrance Mico SobrevegaNo ratings yet