Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mind Map - Nor Aliya Aunie Binti Mohd Noor - Ba1182a - 2021105053
Mind Map - Nor Aliya Aunie Binti Mohd Noor - Ba1182a - 2021105053
Uploaded by
Mrs AliyaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mind Map - Nor Aliya Aunie Binti Mohd Noor - Ba1182a - 2021105053
Mind Map - Nor Aliya Aunie Binti Mohd Noor - Ba1182a - 2021105053
Uploaded by
Mrs AliyaCopyright:
Available Formats
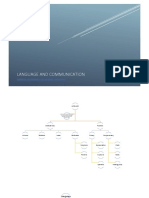
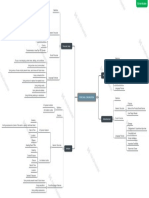
Medium through which messages
M I N D M A P bridge, always takes place over two or
more channels simultaneously
SIGNAL TO RECEIVER
There are gatekeepers, that allow some
May be auditory
messages to get from sender to receiver
communication that
impacts and defines Obstruction – one or more channels is
(hearing), visual
physiologically damaged (seeing), tactile
distorts THE message
the relationship.
takes place between
(touching), olfactory
Physical Noise
people who are in a (smelling) and gustatory
Physiological Noise
Channel (tasting)
some way “connected”, Psychological noise Messages
and interdependent Semantic noise
NATURE
–
NOISE
ELEMENTS Encoding: Refers to
Encoding
the act of producing
Decoding
messages: e.g.
verbal and nonverbal
CONTEXT
Source – Speaking or writing
Decoding: Reverse
interaction between two Receiver
(or sometimes more than
CHAPTER 1: Physical Dimension
and refers to the act
of understanding the
Temporal Dimension
message
two) interdependent Socio-Psychological
FOUNDATIONS OF INTERPERSONAL
Dimension
people.
Involves at least two
Cultural Dimension
persons
COMMUNICATION
Source: Formulates and
send message
RECEIVER
Role vs. personal
information TO LEARN
CHARACTERISTIC
DISTINGUISH
Societal vs.
AXIOMS/
IMPERSONAL TO RELATE
personal rules
PRINCIPLES
& PERSONAL
TO HELP
Predictive vs. TO INFLUENCE
Social vs.
explanatory data TO PLAY
personal messages NAMA: NOR ALIYA AUNIE BINTI MOHD NOOR
NO. MATRIK: 2021105053
KELAS: D1BA1182A
HIGH AND LOW CONTEXT CULTURES
INDIVIDUALIST AND COLLECTIVIST
1. High context cultures
ORIENTATIONS
Much of the information in communication is in the context or in the person
ENCULTURATION ETHNIC IDENTITY 1. Individualist
for e.g., information that was shared through previous communication and
Members are responsible for
shared experience.
themselves and perhaps their
cultures spend lots of time getting to know one another interpersonally and
immediate family.
ACCULTURATION socially
2. Collectivist
2. Low context cultures
Members are responsible for the
Most of the information is explicitly stated in the verbal messages.
entire group.
Culture consist of values, Individualist culture as it place less emphasis on personal information and
beliefs, artifacts, and language; more emphasis on verbalized, explicit explanation and on written contract in
ways of behaving and ways of CULTURE business transactions.
thinking; arts, laws, religion, POWER DISTANCES
styles, attitudes. 1. High Power Distance
Rely more on symbols of power.
2. Low Power Distance
Less on symbols of power, and less of a
problem is crated if you fail to use a
CHAPTER 2 respectful title.
The Relevance of Culture
CULTURAL HOW CULTURES
1. Demographic Changes
MASCULINE AND FEMININE CULTURES
2. Sensitivity to Cultural Differences BELIEFS AND CULTURE AND INTERPERSONAL
DIFFERS 1. Masculine Cultures
3. Economic and Political Interdependence
4. Spread of Technology
VALUES COMMUNICATION
Men are viewed as assertive, oriented to
material success and strong.
5. Culture specific Nature of Interpersonal
More likely to confront conflicts directly and
communication
to competitively fight out any differences.
2. Feminine Cultures
Women are viewed as modest, focused on
THE AIM OF A the quality of life and tender.
It is necessary to understand culture as it influences if Emphasize compromise and negotiation in
you’re to understand how communication works and CULTURAL resolving conflicts.
master its skills. INDULGENCE AND RESTRAINT LONG AND SHORT TERM
It influences what you say to yourself and how you talk
PERSPECTIVE 1. Indulgence ORIENTATION
HIGH AMBIGUITY TOLERANT AND LOW AMBIGUITY
with friends, lovers, and family. focus on having fun and enjoying life. 1. Short term orientation
TOLERANT CULTURES
It influences how you interact in a group. 2. Restraint These cultures look more to the past and
1. High Ambiguity Tolerant Cultures
It influences the topics you talk about and the strategies Members are more cynical, pessimistic and the present and members of this culture
People in these cultures readily tolerate
you use in communicating information or persuading. are less likely to remember positive spend their resources for the present and
individuals who don’t follow the same rules as
Success in interpersonal communication at your job and in emotions. want quick results from their effort.
the cultural majority and may even encourage
your social and personal life will depend on your 2. Long term orientation
different approaches and perspectives.
understanding & your ability to communicate effectively Organization in short term orientation
NAMA: NOR ALIYA AUNIE BINTI MOHD NOOR 2. Low Ambiguity Tolerant Cultures
with person who are culturally different. look to more immediate rewards.
NO. MATRIK:2021105053
They see uncertainty as threatening and as
something that must be counteracted.
KELAS:D1BA1182A
NOR ALIYA AUNIE BINTI MOHD NOOR
2021105053
BA1182A Self-fulfilling Prophecy
Implicit Personality Theory Impression formation (person perception)
Perceptual accentuation consists of a variety of processes that you go INTERPERSONAL
Primacy-recency through in forming an impression of another PERCEPTION STAGES
Consistency person
Attribution of control STAGE ONE: STIMULATION
Selective exposure: You expose yourself to
people or messages that will confirm your
existing beliefs, contribute to your
IMPRESSION
FORMATION
objectives, or prove satisfying in some way
PROCESS
STAGE TWO: ORGANIZATION
1. Organization by Rules
Another rule is similarity things that are
SELF CONCEPT physically similar (they look a like) are
Other's image perceived as belonging together and forming
Social Comprisons a unit
SELF ESTEEM 2. Organization by Schemata
Attack Self-Destructive Beliefs
Cultural teaching
Self-Evaluation CHAPTER 3 Is a mental template that help you organize
the millions of items of information you come
Seek Out Nourishing People
PERCEPTION AND THE into contact with every day
Work on Projects That Will result in 3. Organization by Scripts
Success An organized body of information about some
Remind Yourself of Your Success
Secure Affirmation
SELF IN INTERPERSONAL action, event, or procedure
THE SELF STAGE THREE: INTERPRETATION-EVALUATION
COMMUNICATION Greatly influenced by your experiences,
needs, wants, values, etc.
Will be influenced by your rules, schemata,
scripts and even gender.
SELF AWARENESS STAGE FOUR: MEMORY
The Open Self All the perceptions and interpretation-
GROWING
Ask yourself about yourself
The Blind Self evaluation are put into memory
The Hidden Self PERCEPTION
Listen to others
Actively seek information
The Unknown Self STAGE FIVE: RECALL
about yourself Involves accessing the information you have
See your different selves
Is the process by which you become aware of
objects, events and especially people through
stored in memory
Increase your open self your sense sight, smell, taste, touch and hearing
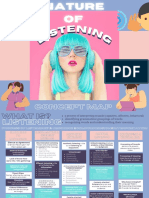
EMPHATIC AND OBJECTIVE LISTENING
STAGE ONE: Receiving Emphatic listening is understanding
Begins with hearing, the TO RELATE TO INFLUENCE TO PLAY what a person means and what a
process of receiving the person us felling, you need to listen.
messages the speaker sends. (POV).
Objective listening is go beyond
empathy and measure meanings and
feelings against some objective
TO LEARN TO HELP reality.
STAGE TWO: Understanding
Is the stage at which you learn
what the speaker means
NONJUDGMENTAL AND CRITICAL
LISTENING
STAGE THREE: Remembering THE PURPOSE AND BENEFITS OF LISTENING Nonjudgmental listening is listen with
What you remember is not an open mind with a view toward
what was said but what you understanding.
remember said. Critical listening is listen critically
with a view toward making some kind
of evaluation or judgment.
CHAPTER4:
THE PROCESS OF LISTENING
LISTENING IN INTERPERSONAL
STYLE OF LISTENING
COMMUNICATION
STAGE FOUR: Evaluating SURFACE AND DEPTH LISTENING
Consists of judging the message Listening is the absorption of the meanings of Surface listening is a literal reading
words and sentences by the brain.
in some away. Listening leads to the understanding of facts and of the words and sentences.
ideas. Depth listening is listening dimension
It requires concentration.
involves the extent to which you
focus to the ideas or infromation.
STAGE FIVE: Responding
Responses you make while the
is talking ( back-channeling
cues) ACTIVE AND INACTIVE LISTENING
Responses you make after the PET ( Parent Effectinveness Training)
speaker has stopped talking technique; it is a process of sending back
(expressing empathy) NAMA: NOR ALIYA AUNIE BINTI MOHD NOOR to the speaker what you as a listener
think the speaker meant-both in content
NO.MATRIK: 2021105053
and in feelings.
KELAS: BA1182A
You might also like
- Understanding The Filipino Values: Professor Felipe M. de Leon, JRDocument22 pagesUnderstanding The Filipino Values: Professor Felipe M. de Leon, JRJohn Carlo SacramentoNo ratings yet
- Lion Bold Records - Cue SheetDocument3 pagesLion Bold Records - Cue SheetAndyNSNo ratings yet
- ZOOLOGY - PDF - Google DriveDocument1 pageZOOLOGY - PDF - Google Drivekushbansal.inNo ratings yet
- Deaf Space - ResearchDocument2 pagesDeaf Space - Researcharmein 007No ratings yet
- Diagrama en BlancoDocument1 pageDiagrama en BlancoAle PinedaNo ratings yet
- AML TB3 CH12 HighlightedDocument9 pagesAML TB3 CH12 HighlightedAdityavk GshanbhagNo ratings yet
- HciDocument25 pagesHcibeleharshwardhanNo ratings yet
- DSP Lecture-1Document3 pagesDSP Lecture-1Puneet TyagiNo ratings yet
- Programs Script Visual Require Ment Audio Require Ment Time Allot Ment Assigne D EditorDocument10 pagesPrograms Script Visual Require Ment Audio Require Ment Time Allot Ment Assigne D EditorGemmy Ronald TevesNo ratings yet
- Language and Communication: Daniela Alejandra Villalobos GuarachiDocument4 pagesLanguage and Communication: Daniela Alejandra Villalobos GuarachiDaniela VillalobosNo ratings yet
- Effective Business Communication 1-3Document2 pagesEffective Business Communication 1-3sikandar khanNo ratings yet
- 2 AES ImmersiveDocument5 pages2 AES ImmersiveDavid BonillaNo ratings yet
- No:-I - I CR - 1: Sri Lanka Institute of Information TechnologyDocument8 pagesNo:-I - I CR - 1: Sri Lanka Institute of Information TechnologyAyola JayamahaNo ratings yet
- Choral Skills and Dispositions 2019Document1 pageChoral Skills and Dispositions 2019lhercule071No ratings yet
- Sound Scape 1Document14 pagesSound Scape 1Haidy AshrafNo ratings yet
- First and Second Language AcquisitionDocument1 pageFirst and Second Language AcquisitionGatika JessiNo ratings yet
- Acoustic Brochure UK 1019 - WEBDocument16 pagesAcoustic Brochure UK 1019 - WEBAntonioPalloneNo ratings yet
- Model 7Document1 pageModel 7Angel NasayaoNo ratings yet
- Ionescu: AndraDocument14 pagesIonescu: AndraCutest PowNo ratings yet
- READING TOEFL STRATEGY (Fix)Document7 pagesREADING TOEFL STRATEGY (Fix)Saefull OhNo ratings yet
- APGA Presentation 2019Document20 pagesAPGA Presentation 2019Stephan FreychetNo ratings yet
- Oboes - Extended TechniquesDocument2 pagesOboes - Extended TechniquesManuel BrásioNo ratings yet
- Understand Face-To-Face Conversation With Little Difficulty, But May Be Unable To Comprehend Discussion If Many Are Speaking at OnceDocument2 pagesUnderstand Face-To-Face Conversation With Little Difficulty, But May Be Unable To Comprehend Discussion If Many Are Speaking at OnceMadge MajnanNo ratings yet
- Mini HI-FI Component System: MHC-EC98Pi/EC78Pi/ EC68PiDocument2 pagesMini HI-FI Component System: MHC-EC98Pi/EC78Pi/ EC68PisanjitNo ratings yet
- PeltoriDocument1 pagePeltoriCășeriu BiancaNo ratings yet
- Groundhog Day Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesGroundhog Day Lesson Planapi-709040597No ratings yet
- Making Sound Accessible The Labelling ofDocument20 pagesMaking Sound Accessible The Labelling ofJorge VeraNo ratings yet
- Audio Visual CommunicationDocument7 pagesAudio Visual CommunicationMugaahed AlfutaahyNo ratings yet
- Sonido Espacial para Una Inmersión Audiovisual de Alto RealismoDocument13 pagesSonido Espacial para Una Inmersión Audiovisual de Alto RealismoKaren NataliaNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument2 pagesConcept MapGeraldine FloresNo ratings yet
- Object Purpose and NecessityDocument5 pagesObject Purpose and NecessityQueen BeeNo ratings yet
- Quantifying Sound Quality in Loudspeaker Reproduction: MSC Computer Science Game & Media TechnologyDocument14 pagesQuantifying Sound Quality in Loudspeaker Reproduction: MSC Computer Science Game & Media TechnologyZaini AascNo ratings yet
- Legend:: Christelle Jan Montejo Christelle Jan MontejoDocument1 pageLegend:: Christelle Jan Montejo Christelle Jan MontejoLester John PrecillasNo ratings yet
- Nouns Verbs Adjectives - Cheat SheetDocument1 pageNouns Verbs Adjectives - Cheat SheetMissia H. SabtalNo ratings yet
- Oral PhysioDocument1 pageOral PhysioDegoma, Mary NoelynNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - Sibayan, Winson Oliver Bsba 1aDocument2 pagesActivity 1 - Sibayan, Winson Oliver Bsba 1aSIBAYAN, WINSON OLIVERNo ratings yet
- Ec Pekalongan Item Matrix TableDocument4 pagesEc Pekalongan Item Matrix TableYoutube MeNo ratings yet
- Notturno E Passacaglia From Ennio MorriconeDocument1 pageNotturno E Passacaglia From Ennio MorriconeGiuseppe GalliNo ratings yet
- Rundown Malam Sabtu....Document2 pagesRundown Malam Sabtu....Rizky JPNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument121 pagesUntitledValerioNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Jun 02, 2023Document8 pagesAdobe Scan Jun 02, 2023mustafaNo ratings yet
- PCVE StratCom Monitoring Tool FormatDocument5 pagesPCVE StratCom Monitoring Tool FormatSolano DJNo ratings yet
- EG Seq2seqDocument13 pagesEG Seq2seqEmna BouhajebNo ratings yet
- Acoustics Is ArtDocument3 pagesAcoustics Is Artapi-354935013No ratings yet
- Linking Words DisplayDocument2 pagesLinking Words DisplayAlyonaNo ratings yet
- MinmapDocument1 pageMinmap20 18100% (1)
- Personal ComunicationDocument1 pagePersonal ComunicationadiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document68 pagesUnit 1Aaditya AttigeriNo ratings yet
- TikFinity (LIVE) (6 Viewers)Document1 pageTikFinity (LIVE) (6 Viewers)ale.root04No ratings yet
- Tooth SpeakerDocument3 pagesTooth SpeakerJack LawnerNo ratings yet
- The Wacky World of Acoustics - Decibel "Funny" Math and Human Hearing - SiemeDocument15 pagesThe Wacky World of Acoustics - Decibel "Funny" Math and Human Hearing - SiemeManel MontesinosNo ratings yet
- Total Score: Egra Scoring Template SY 2014-2015Document3 pagesTotal Score: Egra Scoring Template SY 2014-2015Lea Iglesias100% (1)
- WhisperX ModelDocument6 pagesWhisperX ModelyerashithiNo ratings yet
- Zero-G Nostalgia (MT34)Document1 pageZero-G Nostalgia (MT34)agapocorpNo ratings yet
- IB English Paper 1Document1 pageIB English Paper 1spam mailNo ratings yet
- CAV2083 Chapter 2-Overview of The Audio Technology (Part 1)Document13 pagesCAV2083 Chapter 2-Overview of The Audio Technology (Part 1)Zhoheer Kazuma DesyoNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis: Mycobacterium BacilliDocument1 pageTuberculosis: Mycobacterium BacilliDeni Marie GomonidNo ratings yet
- Excess: Honky Boomy Sibilant Harsh MuddyDocument1 pageExcess: Honky Boomy Sibilant Harsh MuddyMaria Camila InfanteNo ratings yet
- Product Information Sheet - Envisioning A Culture For QualityDocument1 pageProduct Information Sheet - Envisioning A Culture For QualityMarcel NitanNo ratings yet
- Cross Cultural Leadership & Gender Based Leadership: Presented By, Kopika Raj Preetha BDocument9 pagesCross Cultural Leadership & Gender Based Leadership: Presented By, Kopika Raj Preetha BHarleen queenzelNo ratings yet
- Discovering Your Authentic LeadershipDocument25 pagesDiscovering Your Authentic LeadershipAwais Ahmad100% (3)
- Cipd l5 DVP Wk2 Lol v1.2Document22 pagesCipd l5 DVP Wk2 Lol v1.2JulianNo ratings yet
- Elc 121 Intro To LiraDocument9 pagesElc 121 Intro To LirafifoNo ratings yet
- Ob QBDocument20 pagesOb QBSelva KumarNo ratings yet
- Dalal Social PsychologyDocument26 pagesDalal Social PsychologyAnant_Jadhav_6188No ratings yet
- Dissertation On Intimate RelationshipsDocument6 pagesDissertation On Intimate RelationshipsWebsiteThatWillWriteAPaperForYouOmaha100% (1)
- (LEA's Communication Series) Greene, John O - Handbook of Communication and Social Interaction Skills (2009, Routledge) - Libgen - lc-6Document6 pages(LEA's Communication Series) Greene, John O - Handbook of Communication and Social Interaction Skills (2009, Routledge) - Libgen - lc-6Henrique FreitasNo ratings yet
- Student Council Charter 23-24Document9 pagesStudent Council Charter 23-24RishikaNo ratings yet
- Interpersonal Media in The Age of Social MediaDocument5 pagesInterpersonal Media in The Age of Social MediaFabyan fNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Introduction To Social PsychologyDocument5 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To Social PsychologyAayushNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2. Theory and Practice of Counseling and Psychotherapy (Corey)Document5 pagesChapter 2. Theory and Practice of Counseling and Psychotherapy (Corey)Angela Angela100% (1)
- Intercultural CommunicationDocument21 pagesIntercultural Communicationapi-262786958100% (1)
- Gender-Based Violence in Conflict ZoneDocument3 pagesGender-Based Violence in Conflict ZoneYu Myat SoeNo ratings yet
- Family Deficit ModelDocument11 pagesFamily Deficit ModelApril Joy Andres MadriagaNo ratings yet
- AdolescenceDocument21 pagesAdolescenceVani Jain100% (1)
- Nola Pender 1Document18 pagesNola Pender 1Hyacinth Gillian TongNo ratings yet
- MAED - Educational Leadership Report - HernandezSicangcoDocument23 pagesMAED - Educational Leadership Report - HernandezSicangcoJelly Flores SicangcoNo ratings yet
- Trairchic Psychopathy Measure Validity in Relation To Normal Range TraitsDocument12 pagesTrairchic Psychopathy Measure Validity in Relation To Normal Range TraitsMaría González MartínNo ratings yet
- The Self ConceptDocument37 pagesThe Self ConceptSabahat Tanoli100% (1)
- Forming Impressions of PersonalityDocument31 pagesForming Impressions of PersonalityFurther InstructionsNo ratings yet
- This Content Downloaded From 196.43.178.1 On Mon, 20 Feb 2023 11:00:34 UTCDocument6 pagesThis Content Downloaded From 196.43.178.1 On Mon, 20 Feb 2023 11:00:34 UTCmax3katsNo ratings yet
- Eye of Beholder AnalysisDocument2 pagesEye of Beholder AnalysisAyushRajNo ratings yet
- Self Efficacy TheoryDocument14 pagesSelf Efficacy TheoryN-Dean Cabalfin100% (1)
- 11Th Grade-Personal Development Journal: Lindsay Sibayan St. CatherineDocument11 pages11Th Grade-Personal Development Journal: Lindsay Sibayan St. CatherineLindsay SibayanNo ratings yet
- "Who Am I?" The Cultural Psychology of The Conceptual Self (Kanagawa, Cross + Markus, 2001)Document14 pages"Who Am I?" The Cultural Psychology of The Conceptual Self (Kanagawa, Cross + Markus, 2001)Alene SauryNo ratings yet
- Sample Critical AnalysisDocument2 pagesSample Critical AnalysisZabdiel B. BatoyNo ratings yet
- Effective Business Communication SkillsDocument22 pagesEffective Business Communication SkillsMahmudur RahmanNo ratings yet