Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Remark: Rus'an Nasrudin
Remark: Rus'an Nasrudin
Uploaded by
mfajrinurachmanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Remark: Rus'an Nasrudin
Remark: Rus'an Nasrudin
Uploaded by
mfajrinurachmanCopyright:
Available Formats
Remark
Rus’an Nasrudin
December 14, 2021
Rus’an Nasrudin Remark December 14, 2021 1 / 13
Outline
Standard error issues
Make sense your number (estimate)
Cost-effective analysis
Rus’an Nasrudin Remark December 14, 2021 2 / 13
Standard errors and coefficient
In a causal inference work, what matter first is the estimate then the statistical
significance.
Now, let’s talk little bit about the statistical significance and of course the issue of standard
error.
There are two things to remember: when to use robust standard error and the clustered
one.
Rus’an Nasrudin Remark December 14, 2021 3 / 13
Three variance estimators: OLS, robust, and robust cluster
OLS:
1 X 2
VOLS = ( ei ) ∗ (X 0 X)−1
N−k
Robust: X
Vrob = (X 0 X)−1 ∗ [ (ei ∗ xi )0 ] ∗ (ei ∗ xi ) ∗ (X 0 X)−1
Robust cluster X
Vcluster = (X 0 X)−1 ∗ u0j ∗ u j ∗ (X 0 X)−1
j
Rus’an Nasrudin Remark December 14, 2021 4 / 13
Stata implementation
. reg logearn school
Source | SS df MS Number of obs = 2,014
-------------+---------------------------------- F(1, 2012) = 479.25
Model | 259.458632 1 259.458632 Prob > F = 0.0000
Residual | 1089.2706 2,012 .541386978 R-squared = 0.1924
-------------+---------------------------------- Adj R-squared = 0.1920
Total | 1348.72923 2,013 .670009553 Root MSE = .73579
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
logearn | Coef. Std. Err. t P>|t| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
school | .1010255 .0046148 21.89 0.000 .0919752 .1100757
_cons | 4.746692 .0273505 173.55 0.000 4.693054 4.800331
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
.
end of do-file
. hettest
Breusch-Pagan / Cook-Weisberg test for heteroskedasticity
Ho: Constant variance
Variables: fitted values of logearn
chi2(1) = 11.99
Prob > chi2 = 0.0005
Rus’an Nasrudin Remark December 14, 2021 5 / 13
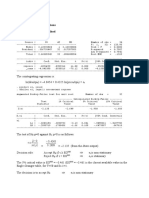
Stata implementation
. reg logearn school, ro
Linear regression Number of obs = 2,014
F(1, 2012) = 521.68
Prob > F = 0.0000
R-squared = 0.1924
Root MSE = .73579
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Robust
logearn | Coef. Std. Err. t P>|t| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
school | .1010255 .0044231 22.84 0.000 .0923511 .1096998
_cons | 4.746692 .0280608 169.16 0.000 4.691661 4.801724
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Rus’an Nasrudin Remark December 14, 2021 6 / 13
Stata implementation
. reg logearn school, vce(cluster school)
Linear regression Number of obs = 2,014
F(1, 19) = 131.06
Prob > F = 0.0000
R-squared = 0.1924
Root MSE = .73579
(Std. Err. adjusted for 20 clusters in school)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Robust
logearn | Coef. Std. Err. t P>|t| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
school | .1010255 .0088246 11.45 0.000 .0825554 .1194956
_cons | 4.746692 .0600509 79.04 0.000 4.621004 4.87238
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Rus’an Nasrudin Remark December 14, 2021 7 / 13
Make sense your number
1 Once you obtain your estimate, critically analyse, compare, and discuss your results
based on direction of bias.
2 Then, always compare your estimates with those from previous published studies to justify
your study’s results, to acknowledge limitations, or conflicts with other studies, if any.
3 Before drawing conclusions, carefully explore step 1 and 2.
Rus’an Nasrudin Remark December 14, 2021 8 / 13
How to use your estimate’s number
Cost-effectiveness analysis: ratio of costs to effect on one outcome.
Cost-benefit analysis: ratio of costs to monetary value of effects on all outcomes.
Rus’an Nasrudin Remark December 14, 2021 9 / 13
Cost-effectiveness analysis 1/3
Rus’an Nasrudin Remark December 14, 2021 10 / 13
Cost-effectiveness analysis 2/3
Rus’an Nasrudin Remark December 14, 2021 11 / 13
Cost-effectiveness analysis 3/3
Rus’an Nasrudin Remark December 14, 2021 12 / 13
Some examples
Rus’an Nasrudin, Budy P. Resosudarmo, Satoshi Yamazaki and Wardis Girsang
Contribution of cash transfers in moderating household food insecurity in small-island
communities: Experimental evidence from Indonesia
Marine Policy. 118 (2020), 104025
Joppe de Ree, Karthik Muralidharan, Menno Pradhan, and Halsey Rogers
Double for Nothing? Experimental Evidence on an Unconditional Teacher Salary Increase
in Indonesia
The Quarterly Journal of Economics 133(2):993–1039
Rus’an Nasrudin Remark December 14, 2021 13 / 13
You might also like
- Cambridge IGCSE Mathematics - Core & Extended, 3rd EditionDocument511 pagesCambridge IGCSE Mathematics - Core & Extended, 3rd EditionAnderson Alfred86% (21)
- The Coefficient Stability TestDocument21 pagesThe Coefficient Stability TestmfajrinurachmanNo ratings yet
- Econometrics by Example Solution PDFDocument122 pagesEconometrics by Example Solution PDFChristian SanguinettiNo ratings yet
- Econometrics Pset #1Document5 pagesEconometrics Pset #1tarun singhNo ratings yet
- Data Interpretation Guide For All Competitive and Admission ExamsFrom EverandData Interpretation Guide For All Competitive and Admission ExamsRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (6)
- A Tour of Scheme in GambitDocument61 pagesA Tour of Scheme in GambitJp JanecekNo ratings yet
- Nu - Edu.kz Econometrics-I Assignment 7 Answer KeyDocument6 pagesNu - Edu.kz Econometrics-I Assignment 7 Answer KeyAidanaNo ratings yet
- MFIN 514 Mod 3Document39 pagesMFIN 514 Mod 3Liam FraleighNo ratings yet
- ECON 301 - Midterm - F2020 Answer Key - pdf-1601016920671Document7 pagesECON 301 - Midterm - F2020 Answer Key - pdf-1601016920671AidanaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document17 pagesLecture 7Adi PravNo ratings yet
- Discrete Choice Modeling: William Greene Stern School of Business New York UniversityDocument58 pagesDiscrete Choice Modeling: William Greene Stern School of Business New York UniversitybluezapperNo ratings yet
- CH 14 HandoutDocument6 pagesCH 14 HandoutJntNo ratings yet
- HeteroskedasticityDocument12 pagesHeteroskedasticityMNo ratings yet
- Department of Economics Problem SetDocument5 pagesDepartment of Economics Problem Setarc08No ratings yet
- QTMS Final Assessment (Spring 2020) PDFDocument6 pagesQTMS Final Assessment (Spring 2020) PDFAbdul RafayNo ratings yet
- B203: Quantitative Methods: y X Z, - Z, XDocument12 pagesB203: Quantitative Methods: y X Z, - Z, Xbereket tesfayeNo ratings yet
- RegressionDocument46 pagesRegressionGiannis GalanakisNo ratings yet
- Nu - Edu.kz Econometrics-I Assignment 4 Answer KeyDocument4 pagesNu - Edu.kz Econometrics-I Assignment 4 Answer KeyAidanaNo ratings yet
- Simple Regression Analysis: April 2011Document10 pagesSimple Regression Analysis: April 2011Arslan TariqNo ratings yet
- Bivariate Regression AnalysisDocument15 pagesBivariate Regression AnalysisCarmichael MarlinNo ratings yet
- Lab Introduction To STATADocument27 pagesLab Introduction To STATAAfifNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Tests of Structural Changes: X y X yDocument8 pages4.2 Tests of Structural Changes: X y X ySaifullahJaspalNo ratings yet
- Solution AssignmentDocument34 pagesSolution AssignmentBizuayehu AyeleNo ratings yet
- Final EM2 2021 Perm 1 VNov22Document14 pagesFinal EM2 2021 Perm 1 VNov22Il MulinaioNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercises AnswerDocument13 pagesLab Exercises Answerarianty83No ratings yet
- Ordinal and Multinomial ModelsDocument58 pagesOrdinal and Multinomial ModelsSuhel Ahmad100% (1)
- Problem Set 6Document6 pagesProblem Set 6Sila KapsataNo ratings yet
- 2SLS Klein Macro PDFDocument4 pages2SLS Klein Macro PDFNiken DwiNo ratings yet
- QM 10 Instrumental Variables IIDocument27 pagesQM 10 Instrumental Variables IIalmari.muhanadNo ratings yet
- ECON 301 - Midterm - F2023 - Answer KeyDocument4 pagesECON 301 - Midterm - F2023 - Answer KeyAidanaNo ratings yet
- CH 11Document76 pagesCH 11Mhmd AlKhreisatNo ratings yet
- 6013B0519Y T2 Homework Questions 20240424Document7 pages6013B0519Y T2 Homework Questions 20240424Khanh My Ngo TranNo ratings yet
- Grade: A. Great Job! Feel Free To Let Me Know If You Have Any Questions About My CommentsDocument11 pagesGrade: A. Great Job! Feel Free To Let Me Know If You Have Any Questions About My CommentsJeesoo KimNo ratings yet
- Simple Regression & Correlation AnalysisDocument22 pagesSimple Regression & Correlation AnalysisAfaq SanaNo ratings yet
- Interpretation and Statistical Inference With OLS RegressionsDocument17 pagesInterpretation and Statistical Inference With OLS RegressionsXènia Bellet NavarroNo ratings yet
- Reliability Engineering CEO852: Date: March 10, 2022Document5 pagesReliability Engineering CEO852: Date: March 10, 2022jagadish mahataNo ratings yet
- MultipleReg - SchoolData - Stata Annotated Output - UCLADocument6 pagesMultipleReg - SchoolData - Stata Annotated Output - UCLAsd.ashifNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - Slides - Multiple Regression and Effect On Coefficients PDFDocument127 pagesLecture 9 - Slides - Multiple Regression and Effect On Coefficients PDFSyed NoamanNo ratings yet
- hw3s 04Document9 pageshw3s 04Hasan TahsinNo ratings yet
- Homework 5Document5 pagesHomework 5Sam GrantNo ratings yet
- How To Evaluate and Check RegressionDocument4 pagesHow To Evaluate and Check RegressionSuphachai SathiarmanNo ratings yet
- Stata Textbook Examples Introductory Econometrics by Jeffrey PDFDocument104 pagesStata Textbook Examples Introductory Econometrics by Jeffrey PDFNicol Escobar HerreraNo ratings yet
- Regression 1 - Estadistica, Spring 2022 - WebAssignDocument15 pagesRegression 1 - Estadistica, Spring 2022 - WebAssignMarlene Hernández OcadizNo ratings yet
- ECMT1020 - Week 06 WorkshopDocument4 pagesECMT1020 - Week 06 Workshopperthwashington.j9t23No ratings yet
- Example of Detrending RegressionsDocument4 pagesExample of Detrending RegressionsFranco ImperialNo ratings yet
- QM 4 Nonlinear Regression Functions 1Document37 pagesQM 4 Nonlinear Regression Functions 1Darkasy EditsNo ratings yet
- Tatenda Muswere Econometrics AnalyticsDocument11 pagesTatenda Muswere Econometrics AnalyticscultureTeeNo ratings yet
- ch2 WagesDocument5 pagesch2 WagesvghNo ratings yet
- Efectos de InteracciónDocument30 pagesEfectos de InteraccióngamerhobbistaNo ratings yet
- Balanced Incomplete BlockDocument4 pagesBalanced Incomplete BlockItalo GranatoNo ratings yet
- Splines and Generalized Additive Model (Gam) : by Seif AbdulDocument42 pagesSplines and Generalized Additive Model (Gam) : by Seif AbdulseifNo ratings yet
- No Linealidades Stock WatsonDocument59 pagesNo Linealidades Stock WatsonjlcastlemanNo ratings yet
- Financial Econometrics Tutorial Exercise 4 Solutions (A) Engle-Granger MethodDocument5 pagesFinancial Econometrics Tutorial Exercise 4 Solutions (A) Engle-Granger MethodParidhee ToshniwalNo ratings yet
- Dyt A+Bdxt+Cxt-1+Dyt-1+Ut D First Difference Procedure-1Document2 pagesDyt A+Bdxt+Cxt-1+Dyt-1+Ut D First Difference Procedure-1SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Answer Key: Case Exercises Case ExercisesDocument9 pagesChapter 4: Answer Key: Case Exercises Case ExercisesPriyaprasad PandaNo ratings yet
- Im ch01Document11 pagesIm ch01Stefan SvärdNo ratings yet
- Dmba205 - Operations ResearchDocument11 pagesDmba205 - Operations ResearchPriya PriyaNo ratings yet
- Panel Lecture - GujaratiDocument26 pagesPanel Lecture - GujaratiPär Sjölander100% (1)
- Statistical LearningDocument92 pagesStatistical LearningIgnasi AymerichNo ratings yet
- PS3 StataDocument3 pagesPS3 StataToulouse18No ratings yet
- Regression Analysis - Stata Annotated Output: Use Https://stats - Idre.ucla - Edu/stat/stata/notes/hsb2Document6 pagesRegression Analysis - Stata Annotated Output: Use Https://stats - Idre.ucla - Edu/stat/stata/notes/hsb2Yusra Rehman KhanNo ratings yet
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Difference-In-Difference: Rus'an NasrudinDocument38 pagesDifference-In-Difference: Rus'an NasrudinmfajrinurachmanNo ratings yet
- Regression Discontinuity Design (RDD) : Rus'an NasrudinDocument27 pagesRegression Discontinuity Design (RDD) : Rus'an NasrudinmfajrinurachmanNo ratings yet
- Medicaid: Classification: PublicDocument5 pagesMedicaid: Classification: PublicmfajrinurachmanNo ratings yet
- Instrumental Variable: Rus'an NasrudinDocument29 pagesInstrumental Variable: Rus'an NasrudinmfajrinurachmanNo ratings yet
- Forest Cover of TunisiaDocument14 pagesForest Cover of TunisiaArif PasaditaNo ratings yet
- Physics Report Simple PendulumDocument3 pagesPhysics Report Simple PendulumGracey- Ann Johnson100% (3)
- Data Base Management System Lab ManualDocument34 pagesData Base Management System Lab ManualMohiuddin BabanbhaiNo ratings yet
- Math XI QBDocument93 pagesMath XI QBTejas SalviNo ratings yet
- STLDocument6 pagesSTLlop mkNo ratings yet
- 1mathematics SM025 (Integration) by Azmil Hafez (Student)Document32 pages1mathematics SM025 (Integration) by Azmil Hafez (Student)muhd zulkifliNo ratings yet
- Abinitio QuestionsDocument33 pagesAbinitio Questionsadityak780% (1)
- Discrete Mathematics - Chapter 7 Posets Lattices & Boolean AlgeDocument82 pagesDiscrete Mathematics - Chapter 7 Posets Lattices & Boolean AlgeBeautiful-Pretty Happy-WealthyNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper / Model Test Paper CBSE SA - 2 (II) 2012 Subject - Mathematics Section-ADocument4 pagesSample Paper / Model Test Paper CBSE SA - 2 (II) 2012 Subject - Mathematics Section-ARakesh DwivediNo ratings yet
- TEST-4: JEE MainDocument20 pagesTEST-4: JEE MainRishabh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document20 pagesChapter 1RXDoomNo ratings yet
- Learnxinyminutes PDFDocument671 pagesLearnxinyminutes PDFAnand PanchalNo ratings yet
- New NetSwitchTeam PDFDocument4 pagesNew NetSwitchTeam PDFJoséMiguelLeonisioTorrejónNo ratings yet
- Model Reduction in Chemical EngineeringDocument312 pagesModel Reduction in Chemical EngineeringAdilson J. de AssisNo ratings yet
- Lab 0. Preliminary: 1 InstructionsDocument2 pagesLab 0. Preliminary: 1 InstructionsKevin MoralesNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For BSNL JTODocument10 pagesSyllabus For BSNL JTOSriramamurthy GurugubelliNo ratings yet
- Rouse Ball and Coxeter Mathematical Recreations (1949)Document434 pagesRouse Ball and Coxeter Mathematical Recreations (1949)Anonymous 4yWrEQjUNo ratings yet
- ADLC JobDocument2 pagesADLC JobClarence YeungNo ratings yet
- ExampleDocument8 pagesExamplesalehnaib0% (1)
- History of BinaryDocument231 pagesHistory of BinarygrandpafranckNo ratings yet
- INFOSYS Puzzles Part2Document20 pagesINFOSYS Puzzles Part2Kaushal KumarNo ratings yet
- UCK351E Fall2012 M1QsDocument2 pagesUCK351E Fall2012 M1QsEser GülNo ratings yet
- Midterm NotesDocument4 pagesMidterm NotesmelNo ratings yet
- Matrix Analysis of Heat Transfer Problems: e (X, T) I (X, T)Document12 pagesMatrix Analysis of Heat Transfer Problems: e (X, T) I (X, T)Anders AguilarNo ratings yet
- 2.0 - P34x - EN - MD - J76Document184 pages2.0 - P34x - EN - MD - J76Diana Vanessa VelCruzNo ratings yet
- Mining Class ComparisonsDocument4 pagesMining Class Comparisonsmurali_20c100% (1)
- 4 - HYPERBOLIC and Circular FunctionsDocument4 pages4 - HYPERBOLIC and Circular Functionsdfgb fbnNo ratings yet