Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Plywood
Plywood
Uploaded by
Montasir ShantoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Plywood
Plywood
Uploaded by
Montasir ShantoCopyright:
Available Formats
FES342
Composite materials:
Composites are considered to be compositions of materials (woody or non-wood fibrous
rice or wheat straw, jute, cotton, bamboo etc.)
Constituents retain their entities in the composite in a macro scale
These do not dissolve or merge into each other completely but do act in concert
Materials may be wood or non-wood fibrous (rice or wheat straw, jute, cotton, bamboo
etc.)
Classification:
Fibrous: composed of fibres of wood & non-woody fibrous, like Fibre boards- hard
board, paper board etc.
Lamina: composed of layers of wood (with adhesives), like Plywood, laminated wood
etc.
Particulate: composed of particles of wood & non-woody materials, like Particle or chip
board etc.
Advantages of composites:
Overcomes many weakness of solid wood
Make useful products out of wastes, small piece of wood & inferior species (complete
utilization of raw materials)
Characteristics defects (knots, spiral grain) be eliminated or scattered
Heating, chemical additives etc. carried out to improve physical & mechanical properties
Can be made in large dimensions
Agricultural residues (grass, bamboos, leaves) are manufactured into composite (end-
uses)
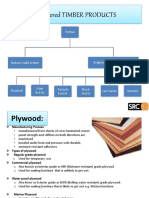
Plywood:
A type of strong thin wooden board consisting of two or more layers glued and pressed together
with the direction of the grain alternating at right angles (90°)
Veneer plywood: all the plies are made of veneers (a thin decorative covering of fine
wood)up to 7 mm thick oriented parallel
Core plywood: having a core (the central or most important part of something)
Wood core plywood: having a core of solid wood or veneers, like Battenboard,
Blockboard, Laminboard.
Cellular plywood: core consists of cellular construction
Composite plywood: core made of materials other than solid wood or veneers.
Advantages:
Dimensional stability (shrinking, swelling & movement)
Strength equalization & enhancement (cross banded nature implies higher strength to
two cross directions)
FES 15th Batch
FES342
Balanced construction (flat plywood panels made with an odd number of plies with
matching plies on each side to balance)
Manufacture of plywood:
Raw materials: veneer (relatively large, thin sheets of wood produced by sawing, slicing or
peeling) & adhesive or glue
Preparation of green veneer:
Log selection and storage:
• Log should be straight, cylindrical & defect free
• Stored in log ponds
• Two-man chain saws used to cut logs then it’s called bolts
Pre-treatments of bolts & flitches:
• Bolts are peeled better when heated, boiling water tanks or steaming chamber
• Brick-cement, concrete or wood tanks equipped with steam coil for heating
• Heating softens texture & makes pliable
• Temperature & time of heating depend on species, diameter & moisture content of bolts
Veneer cutting:
o Rotary-cutting or peeling of veneer
• After pre-treatment bolts are debarked & conveyed to the veneer lathe (a machine for
shaping wood, metal, or other material by means of a rotating drive that turns the piece
being worked on against changeable cutting tools)
• A bolt is centred & dogged between two chucks on the veneer lathe
• For maintaining quality the most important parts are the knife & the nosebar fixed to the
carriage
• The lathe knife extending across the length of the lathe is brought against the bolt
• The nosebar presses against the bolt & compresses the wood just ahead of the knife
• As the bolt revolves veneer is cut by the knife, i.e. peeled off
o Slicing of veneer
• Two types of slicers horizontal & vertical (when logs are smaller) slicers are used
• In the horizontal slicer, the flitch is dogged to the carriage & a heavy knife moves &
slices a thin sheet of veneer
• In the vertical slicer, the knife remains stationary & the flitch is moved downward onto
the knife & a sheet of veneer is sliced
Veneer handling & green clipping
• After rotary-cutting veneer is transported by hand pulling on a table, by reeling or
mechanical tray system
FES 15th Batch
FES342
• The veneer is clipped to size & defects are cut off by veneer clipper, process is called
green clipping
Veneer drying
• Drying of veneer carried out in heated sheds, dry kilns, hot-plate dryers, roller dryers,
vacuum drying etc.
• In Bangladesh, drying generally done under the sun in open fields
• In commercial purpose sometimes in multi-tier high temperature automatic veneer dryers
(veneer moves continuously on rolls/belts)
Jointing & splicing of dry veneer
• Sliced veneers are glued together along the length to make wider veneers
• Edges are cut straight & parallel by a machine called veneer jointer
• After jointing the veneer is spliced either with a taper or tapeless splicer
Mixing & spreading of adhesive
• While mixing of adhesive instruction of manufacturer should be followed carefully
• A glue spreader is used to apply the prepared adhesive to veneer
• Glue coated veneers are allowed assembly time or period (interval between spreading of
adhesive & the application of pressure)
Pressing of plywood
• Assembled veneers are put under pressure for ensuring proper alignment of component &
intimate contact between the wood & glue
• Pressing at room temperature: cold pressing
• Pressing at elevated temperature : hot pressing
Conditioning & finishing
Conditioning
• Cold pressed plywood are further dried by placing on stickers after these come off the
press & put into a kiln or left at room conditions for final drying
• Hot pressed plywood loose considerable moisture (cause of checking/warping), good to
practice is to add moisture by sprinkling or spraying water immediately
Trimming & sanding
• Trimming done by ripping and cut-off saws
• Trimmed panels are sanded by various types of drum sanders or belt sanders machine
(smoothing surface)
Storage:
• Solid ground
• Solid cover top of each pile protects moisture
FES 15th Batch
You might also like
- Carpentry Canadian 3rd Edition Vogt Solutions Manual DownloadDocument13 pagesCarpentry Canadian 3rd Edition Vogt Solutions Manual DownloadKatherine Joseph100% (22)
- Conquest NUM Inch PostDocument36 pagesConquest NUM Inch PostimanameNo ratings yet
- As 2796.3-1999 Timber - Hardwood - Sawn and Milled Products Timber For Furniture ComponentsDocument7 pagesAs 2796.3-1999 Timber - Hardwood - Sawn and Milled Products Timber For Furniture ComponentsSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- Tle 6 Agri. q1 Module 1Document14 pagesTle 6 Agri. q1 Module 1Arnold A. Baladjay90% (10)
- Plywood Manufacturing ProcessDocument40 pagesPlywood Manufacturing Processanon_61481338767% (3)
- VeneersDocument23 pagesVeneersyashaswini100% (2)
- Fiberboard Manufacture FinalDocument22 pagesFiberboard Manufacture Finalyeng botzNo ratings yet
- Astm A700Document40 pagesAstm A700geav25653855No ratings yet
- Clariant TLP Brosch 2Document22 pagesClariant TLP Brosch 2mutazsalihNo ratings yet
- Particle BoardDocument51 pagesParticle BoardNUR MAZIAH ATIQAH JAININo ratings yet
- Maktab Ahl Al-Bayt Quran English Translation and Brief Commentary (S V Amded Ali) (Z-Library)Document2,160 pagesMaktab Ahl Al-Bayt Quran English Translation and Brief Commentary (S V Amded Ali) (Z-Library)mehdinagem2008No ratings yet
- 21MCA2697 Himanshu Rubrics4Document49 pages21MCA2697 Himanshu Rubrics4HimanshuNo ratings yet
- BNBC LECTURE 13FEB 2022 Geotech 02 FINALDocument40 pagesBNBC LECTURE 13FEB 2022 Geotech 02 FINALEngr. Gazi Golam SarwarNo ratings yet
- Top Universities For Engineering: Yocket Virtual FairDocument20 pagesTop Universities For Engineering: Yocket Virtual Fairruler3382No ratings yet
- UG ProDocument5 pagesUG Prokrish patadiaNo ratings yet
- Sumif, Sumifs, Countif, AverageifDocument9 pagesSumif, Sumifs, Countif, AverageifRaghavendraNo ratings yet
- Events in The Life of Allama Iqbal - CSS ForumsDocument8 pagesEvents in The Life of Allama Iqbal - CSS ForumsJunaid AfzalNo ratings yet
- EPI BangladeshDocument4 pagesEPI BangladeshToufiq Rahman100% (1)
- I Am FatimaDocument59 pagesI Am FatimaHesham Merchant100% (1)
- Project Report - Anand AgroDocument7 pagesProject Report - Anand AgrosanskarNo ratings yet
- Schengen Visa Information2020Document9 pagesSchengen Visa Information2020MUSSIE MIHRETABNo ratings yet
- Quran Yasin in Rohingya Language Translation.Document15 pagesQuran Yasin in Rohingya Language Translation.Mohammed Siddique BasuNo ratings yet
- Isbo Terms and Conditions enDocument8 pagesIsbo Terms and Conditions encharan saiNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Glycolysis and Krebs CycleDocument10 pagesDifference Between Glycolysis and Krebs CycleKuresh RabidNo ratings yet
- Pipe Fittings PDFDocument204 pagesPipe Fittings PDFrezandriansyahNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Treatment Planning - Removable Partial Denture Part-1Document38 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment Planning - Removable Partial Denture Part-1Ahmed AliNo ratings yet
- Mahdi S Advent End of DarknessDocument24 pagesMahdi S Advent End of Darknesswww.alhassanain.org.englishNo ratings yet
- 2019 RCGP CurricullumDocument101 pages2019 RCGP CurricullumKiran ShahNo ratings yet
- 3DSEJ Progress Map 20211211Document1 page3DSEJ Progress Map 20211211Mega SaraswatiNo ratings yet
- Translated To English By: Alal TaniDocument344 pagesTranslated To English By: Alal TaniAlmeida EderNo ratings yet
- False Story About Prophet Muhammad SAWDocument35 pagesFalse Story About Prophet Muhammad SAWNabeelNo ratings yet
- Growth & DevelopmentDocument74 pagesGrowth & DevelopmentSubhashini RajshekarNo ratings yet
- บันทึกหลักสูตรปลูกป่าประณีตDocument81 pagesบันทึกหลักสูตรปลูกป่าประณีตpim ppNo ratings yet
- The Hidden Words of Baha'u'llah - ArabicDocument10 pagesThe Hidden Words of Baha'u'llah - ArabicBahaIQ Search EngineNo ratings yet
- 1.2 StressDocument8 pages1.2 Stresskeihoina keihoinaNo ratings yet
- Disadvantages of WPC BoardDocument32 pagesDisadvantages of WPC BoardvidhiNo ratings yet
- Nur Isfarina Binti Ismail Muhamad Basri Bin MD Daud Mohd Fazli Bin Abu Hasan Sadam Bin Kahar Muhamad Hafiz Bin MD SaadDocument24 pagesNur Isfarina Binti Ismail Muhamad Basri Bin MD Daud Mohd Fazli Bin Abu Hasan Sadam Bin Kahar Muhamad Hafiz Bin MD Saadjassi nishadNo ratings yet
- 873 - 52 - 473 - Module 1 Wood SubstitutesDocument18 pages873 - 52 - 473 - Module 1 Wood SubstitutesAlexNo ratings yet
- Engineered TIMBER PRODUCTSDocument9 pagesEngineered TIMBER PRODUCTSAr Ayoushika Abrol0% (1)
- Plywood TechnologyDocument37 pagesPlywood TechnologyDr.E.Sreenivasan83% (6)
- What Is VeneerDocument45 pagesWhat Is Veneeraliyah khalidNo ratings yet
- Special Woods and Wood AlternativesDocument61 pagesSpecial Woods and Wood AlternativesnadiajmiNo ratings yet
- Timber Product Stage 1Document68 pagesTimber Product Stage 1Ayush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lec-6 Building Materials - TimberDocument25 pagesLec-6 Building Materials - TimberMr. Shahriar MahmudNo ratings yet
- Wood Finishes Final 24-08Document40 pagesWood Finishes Final 24-08Sanal SamsonNo ratings yet
- Wood PresentationDocument32 pagesWood PresentationSuBchooNo ratings yet
- Carpentry and MasonryDocument81 pagesCarpentry and MasonryCassandra Noreen Pacayra SantosNo ratings yet
- Building Materials2Document51 pagesBuilding Materials2jeo TinioNo ratings yet
- Advance Construction and MaterialsDocument23 pagesAdvance Construction and MaterialsSaki Saki SakiNo ratings yet
- The Manufacturing of PlywoodDocument12 pagesThe Manufacturing of PlywoodLogarithemNo ratings yet
- Wood Substitutes - Industrial Products As Substitutes ForDocument18 pagesWood Substitutes - Industrial Products As Substitutes ForashimaNo ratings yet
- Plywood ReportDocument13 pagesPlywood ReportJonas Nathan CadatalNo ratings yet
- Woodworking 150606073133 Lva1 App6892Document84 pagesWoodworking 150606073133 Lva1 App6892bereket gNo ratings yet
- Medium Density Fibrerboard: Mohammed Sharafulla 140909830Document26 pagesMedium Density Fibrerboard: Mohammed Sharafulla 140909830rayiz shameerNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint of Plywood ManufacturingDocument33 pagesPowerpoint of Plywood Manufacturingmikogonzalve100% (4)
- Wood Substitutes - Industrial Products As Substitutes ForDocument19 pagesWood Substitutes - Industrial Products As Substitutes ForkunjuvavuNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 TimberDocument72 pagesUnit 6 TimberJeewan KunwarNo ratings yet
- CarpentryDocument15 pagesCarpentryay mieNo ratings yet
- Market Sorvey On PlywoodDocument19 pagesMarket Sorvey On PlywoodEduardo MafraNo ratings yet
- Veneers and LaminatesDocument31 pagesVeneers and LaminatesVijaya Ratna MNo ratings yet
- WOOD PRODUCTS (Compatibility Mode)Document29 pagesWOOD PRODUCTS (Compatibility Mode)BackupFilesNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Process of Veneer WoodDocument2 pagesManufacturing Process of Veneer WoodSachin HarriramNo ratings yet
- Tle NotesDocument49 pagesTle NotesFerlynNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TO INDUSTRIAL ARTS PART 2 Information Sheet 1.3Document5 pagesINTRODUCTION TO INDUSTRIAL ARTS PART 2 Information Sheet 1.3Merry Cris PadoNo ratings yet
- Carpentry Fo Group StudyDocument137 pagesCarpentry Fo Group StudyKristian ReignNo ratings yet
- TimberDocument83 pagesTimbergjcdesignskochiNo ratings yet
- Ozturk, 2020Document4 pagesOzturk, 2020RafaelNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Waste Paper Recycling MachineDocument20 pagesDesign and Analysis of Waste Paper Recycling MachineMelaku AssefaNo ratings yet
- Jatoba TREE ORIGINALLYDocument3 pagesJatoba TREE ORIGINALLYHeaven2012No ratings yet
- Jigs and XyxwDocument247 pagesJigs and XyxwThe ash Designe GalaryNo ratings yet
- Wood Magazine - Issue 259 - March 2019 - FullDocument69 pagesWood Magazine - Issue 259 - March 2019 - FullKen Lock100% (2)
- PublicationDocument167 pagesPublicationavicohvacrNo ratings yet
- Wood Magazine 140 2002Document70 pagesWood Magazine 140 2002cgsharp100% (1)
- Machine Tool Shanks (Tapers)Document22 pagesMachine Tool Shanks (Tapers)michaelguzziNo ratings yet
- Inglés 3 CuadernilloDocument140 pagesInglés 3 CuadernillogabysoteloNo ratings yet
- Timber 1Document36 pagesTimber 1CHIRAG SNo ratings yet
- Company Profile PT. MAP Eksportir ArangDocument10 pagesCompany Profile PT. MAP Eksportir ArangAnwar mBatuNo ratings yet
- Top 20 Woodworking TipsDocument24 pagesTop 20 Woodworking TipsGrafo Bogdanov Novi SadNo ratings yet
- A Feasibility Study of A Shredded Mixture of Cassava Stalks and Corn Cobs in The Production of Lantay Particle BoardDocument67 pagesA Feasibility Study of A Shredded Mixture of Cassava Stalks and Corn Cobs in The Production of Lantay Particle BoardJohn Paulo GregorioNo ratings yet
- WOOD As A BUILDING MATERIAL 2Document9 pagesWOOD As A BUILDING MATERIAL 2Jays Tioxon IIINo ratings yet
- Sample Capstone PDFDocument17 pagesSample Capstone PDFMark Julius FulgencioNo ratings yet
- Kfri rr281Document131 pagesKfri rr281Pixel monsterNo ratings yet
- JKReportDocument16 pagesJKReportKavya SindalNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 PDFDocument14 pagesUnit 2 PDFPremchand BoddapatiNo ratings yet
- Timber Rivet ConnectionsDocument25 pagesTimber Rivet ConnectionsJoe HowardNo ratings yet
- Teak Tissue CultureDocument19 pagesTeak Tissue CultureNAVNEET BAGGANo ratings yet
- Animal Glues: Their Manufacture, Testing, and PreparationDocument14 pagesAnimal Glues: Their Manufacture, Testing, and PreparationNihad NagiNo ratings yet
- Cellon BruagDocument2 pagesCellon BruagRoxana StanNo ratings yet
- Woodworking Workbench PlansDocument1 pageWoodworking Workbench PlansArmando PlancarteNo ratings yet