Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endocrine System
Endocrine System
Uploaded by
Apple AbriamCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Endocrine System
Endocrine System
Uploaded by
Apple AbriamCopyright:
Available Formats
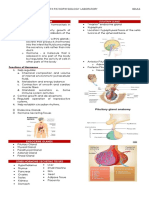
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
- system of different glands in human body
- this is organs
- considered to be glands because it secrete hormones
- liver is responsible for bile
- ductless glands of hormones
- it is for regulation so that the body meet the homeotasis
- it is most related to nervous system
- the hormones are released into the bloodstream and may affect one or several
organs throughout the body
- these hormones regulate the body's growth, the physical and chemical processes of
the body
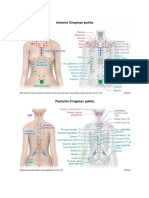
CONNECTION OF CNS AND ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
PITUITARY GLANDS
- wall nut part of brain
- master glands of endorcrine system
- it secrete own hormone
- part of central nervous system
- ability to control other glands
POSTERIOR GLANDS
- home of oxitocin
ANTERIOR PITUITARY
- releasing hormones and regulate AP (adeno hypo physis)
ADRENOCORTICOTROPIC HORMONE (ACTH)
- produced in the anterior, or front, pituitary gland in the brain.
- regulate levels of the steroid hormone cortisol, which released from the adrenal
gland
- adrenocorticotropic hormone.
GLUGOCORTICOIDS
- promotes normal metabolism of all three kinds of food, accelerate catabolism of
fats and proteins.
- accelerate gluconeogenesis
MINERALOCORTICOIDS
- marked accelaration of sodium and water re-absorption, acceleration of potassium
excretion
SEX HORMONES
- small amounts of androgens (for boys) and estrogen (for girls)
FOLLICLE STIMULATING HORMONE (FSH)
- pea-sized gland in the brain that plays an important role in sexual development.
- stimulate the development of eggs in the ovaries and sperm in testes
LUTEINIZING HORMONE (LH)
- helps your reproductive system: specifically, a woman's ovaries and a man's
testes. It's also called lutropin and interstitial cell stimulating hormone, for
men. (ICSH)
- causes ovulation in females and sex hormone secretion in both males and females
GROWTH HORMONE (GH)
- growth hormone
- somatotropin
- It stimulates the growth of essentially all tissues of the body
- dwarfism and gigantism
PROLACTIN
- hormone made by the pituitary gland, a small gland at the base of the brain.
- causes the breasts to grow and make milk during pregnancy and after birth
- Prolactin levels are normally high for pregnant women and new mothers
- Levels are normally low for nonpregnant women and for men
THYROID STIMULATING HORMONES (THS) THYROTROPIN
- stimulate the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones
THYROXINE
- stimulates metabolic rate thus essential for normal, physical and mental
development
THYROCALCITONIN
- decreases blood calcium from blood into bone
TRI-IODOTHYRONINE
- inhibits anterior pituatary secretion of TSH
HYPOTHALAMUS
- part of brain that regulate our emotion, taste, feeding mechanism, balance and
tempereture. This is controlled by hormones
PARATHYROID GLANDS
PARATHORMONE
- increases blood calcium concentration
HYPERSECRETION
- when the amount of hormones that are released is too low.
CALCITONIN
- deacreased loss of calcium from the bone and promotes hypocalimia
HORMONES OF THE ANTERIOR PITUITARY
MEDULA
(Epinephrine)
- increase cardiac output and glucose level
- and Norepinephrine
HORMONES
PROTEIN
- most hormones except those of the adrenal cortex and sex gkands are proteins
STEROIDS
- hormones derived from lipids and produced by the adrenal cortex and sex glands
REGULATION OF HORMONES
NEGATIVE FEEDBACK LOOP
- as the stimuli decreases, hormone secretion gradually decreases. At equilibrium,
hormone release stops
POSITIVE FEEDBACK LOOP
- as the stimuli present, secretion of hormone continues
- presents of secretion is directly proportional to stimuli
- blood sugar keep in liver teporarily (polysaccharide)
HORMONE OF THE POSTERIOR PITUITARY
VASOPRESSIN
- promotes re absorption of water from kidney tubules and thus decreases excretion
of water
THYMUS GLANDS
- has the hormone THYMUSIN
- regulates immunologic process possibly through regulation of the numbers and
types of lymphoid cells
PROLACTINE
- stimulate/produce milk
OXYTOCIN
- ejection of milk
PANCREAS (islets of langerhans)
ALPHA CELLS
- produce glucagon, which increase blood glucoses level when it falls below normal
BETA CELLS
- produce insulin, helps lower blood glucose levels when it is too high.
DELTA CELLS
- produce somatostatin which inhibits secretion of insulin and glucogacon and slows
absoption of nutrients from the Gl
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Musculoskeletal Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument26 pagesMusculoskeletal Anatomy and PhysiologyAmy92% (13)
- Biliran Province State University: Bipsu!Document21 pagesBiliran Province State University: Bipsu!Joy-Rena Sabinay OchondraNo ratings yet
- Melanoma 2016Document413 pagesMelanoma 2016Anca-Raluca Pascu100% (2)
- The Human BodyDocument9 pagesThe Human BodyApple AbriamNo ratings yet
- The Cell and Cellular Metabolism ReproductionDocument4 pagesThe Cell and Cellular Metabolism ReproductionApple AbriamNo ratings yet
- Purc. Reaction PaperDocument1 pagePurc. Reaction PaperApple AbriamNo ratings yet
- Eyes and EarsDocument3 pagesEyes and EarsApple AbriamNo ratings yet
- Taenias IsDocument25 pagesTaenias Iszaid nabeelNo ratings yet
- Pitfalls in Pediatric UltrasoundDocument14 pagesPitfalls in Pediatric UltrasoundDavid Gerry SimatupangNo ratings yet
- World Neurosurgery: X: Teodor Svedung Wettervik, Anders Lew En, Per EnbladDocument13 pagesWorld Neurosurgery: X: Teodor Svedung Wettervik, Anders Lew En, Per EnbladVictor Hugo SilveiraNo ratings yet
- Assessing Fitness To Drive A Guide For Medical ProfessionalsDocument135 pagesAssessing Fitness To Drive A Guide For Medical Professionalsarun kumarNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Eye Disease Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument486 pagesThyroid Eye Disease Diagnosis and TreatmentUnsmil UnguNo ratings yet
- Burn & ScaldDocument35 pagesBurn & ScaldMAHFUZ ISLAMNo ratings yet
- ENT SHORT Cases Checklist OldDocument4 pagesENT SHORT Cases Checklist OldQuranSunnatNo ratings yet
- Oral Surg. Lec.1 (Maxillofacial Trauma)Document39 pagesOral Surg. Lec.1 (Maxillofacial Trauma)ريام الموسويNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System PDFDocument48 pagesFemale Reproductive System PDFTeppy the GreatNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument6 pagesEndocrine System NotesHannah Grace CorveraNo ratings yet
- RBM 2530 - Tutorial 2 - Neuropathology-2011Document6 pagesRBM 2530 - Tutorial 2 - Neuropathology-2011Lina TanNo ratings yet
- Hypothetical IE of Traumatic Brain Injury/TBIDocument10 pagesHypothetical IE of Traumatic Brain Injury/TBIMIKEE MEDRANONo ratings yet
- Handbook of Dental Hygienist (PDFDrive)Document523 pagesHandbook of Dental Hygienist (PDFDrive)neetika guptaNo ratings yet
- тест офтал.Document24 pagesтест офтал.inspire.consultancy00No ratings yet
- A10440681S419Document9 pagesA10440681S419Harshini MNo ratings yet
- Carotid Stenosis (Carotid Artery Disease)Document5 pagesCarotid Stenosis (Carotid Artery Disease)Pieter SteenkampNo ratings yet
- Sense Organs: Structure of Human EyeDocument8 pagesSense Organs: Structure of Human EyeRanveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Tissue: The Living FabricDocument111 pagesTissue: The Living FabricYvez BolinaoNo ratings yet
- BSC Imaging TechnologyDocument74 pagesBSC Imaging Technologyprabakaran0908No ratings yet
- Peripheral Nerves Injury and Management PrinicpleDocument61 pagesPeripheral Nerves Injury and Management PrinicpleMinale MenberuNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing Practice Test Part 1Document57 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Practice Test Part 1Tina Van Winks100% (2)
- Project Proposal CapstonneDocument6 pagesProject Proposal Capstonne44 - 482 - Meher MahbubNo ratings yet
- Principles and Practice of Emergency NeurologyDocument456 pagesPrinciples and Practice of Emergency NeurologyElfan Winoto100% (9)
- Cephalopelvic DisproportionDocument3 pagesCephalopelvic DisproportionAira MiyaNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument10 pagesConcept MapStephen Yor100% (1)
- Neurotransmitters &: Their Mode of ActionDocument45 pagesNeurotransmitters &: Their Mode of ActionAshani AaroraNo ratings yet
- Comlex High YieldDocument4 pagesComlex High Yieldjoey plouffeNo ratings yet