Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Composicion Quimica Gtd111: Mater. Process. Technol., Vol. 175, No. 1, Pp. 376-381, 2006
Composicion Quimica Gtd111: Mater. Process. Technol., Vol. 175, No. 1, Pp. 376-381, 2006
Uploaded by
Sebastian AcostaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Composicion Quimica Gtd111: Mater. Process. Technol., Vol. 175, No. 1, Pp. 376-381, 2006
Composicion Quimica Gtd111: Mater. Process. Technol., Vol. 175, No. 1, Pp. 376-381, 2006
Uploaded by
Sebastian AcostaCopyright:
Available Formats
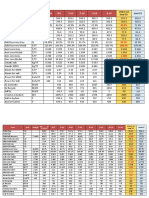
COMPOSICION QUIMICA GTD111
COMPOSICION QUIMICA IN738
Wt% Ni Cr Co Ti W Al Ta Mo Fe C B
GTD111[1] Bal. 13.5 9.5 4.75 3.8 3.3 2.7 1.53 0.23 0.09 0.01
GTD111[2] Bal. 13.5 9.5 4.75 3.8 3.3 2.7 1.53 0.23 0.09 0.01
GTD111[3] Bal. 14 9.5 4.9 4.5 3 2.8 4.5 - 0.1 0.01
GTD111[4] Bal. 13.5 9.5 4.75 3.8 3.3 2.7 1.53 0.23 0.09 0.01
GTD111[5] Bal. 13.5 9.5 4.75 3.8 3.3 2.7 1.53 0.23 0.09 -
GTD111[6] Bal. 14.6 9.48 4.94 3.97 3.01 2.8 1.50 - 0.09
Wt% Ni Cr Co Ti W Al Ta Mo Fe C B Zr
IN-738 [7] BAL. 16.0 8.5 3.40 2.60 - 1.75 1.75 - 0.17 0.01 0.10
IN-738 [8] BAL. 15.7 8.5 3.42 2.51 3.52 1.61 1.88 - 0.11 0.014 0.04
IN-738 [9] BAL. 15.84 8.5 3.47 2.48 3.46 1.69 1.88 0.07 0.11 0.12 0.04
Wt% Ni Cr Co Ti W Al Ta Mo Fe C B
GTD111[1] Bal. 13.5 9.5 4.75 3.8 3.3 2.7 1.53 0.23 0.09 0.01
GTD111[2] Bal. 13.5 9.5 4.75 3.8 3.3 2.7 1.53 0.23 0.09 0.01
GTD111[3] Bal. 14 9.5 4.9 4.5 3 2.8 4.5 - 0.1 0.01
GTD111[4] Bal. 13.5 9.5 4.75 3.8 3.3 2.7 1.53 0.23 0.09 0.01
GTD111[5] Bal. 13.5 9.5 4.75 3.8 3.3 2.7 1.53 0.23 0.09 -
GTD111[6] Bal. 14.6 9.48 4.94 3.97 3.01 2.8 1.50 - 0.09 -
[1] S. A. Sajjadi, S. M. Zebarjad, R. I. L. Guthrie, and M. Isac, “Microstructure evolution of
high-performance Ni-base superalloy GTD-111 with heat treatment parameters,” J.
Mater. Process. Technol., vol. 175, no. 1, pp. 376–381, 2006.
[2] M. Pouranvari, A. Ekrami, and A. H. Kokabi, “Microstructure development during
transient liquid phase bonding of GTD-111 nickel-based superalloy,” J. Alloys Compd.,
vol. 461, no. 1, pp. 641–647, 2008.
[3] Y. Kim, D. K. Lee, I. H. Shin, J. M. Koo, and C. S. Seok, “Microstructural analysis of TMF
failure mechanism of GTD-111 applied to gas turbine blades,” in Procedia Engineering,
2013, vol. 55, pp. 204–209.
[4] P. Wangyao, T. Eiriyakul, S. Polsilapa, P. Srigiofun, and O. Srihakulang, “Effect of Al
Addition in Cast Nickel Base Superalloy, GTD-111 on Microstructures and Oxidation
Behaviors at 900°C and 1000°C,” Appl. Mech. Mater., vol. 548–549, pp. 268–273, 2014.
[5] M. Pouranvari, “Isothermal solidification during transient liquid-phase bonding of GTD-
111/Ni-Si-B/GTD-111,” Mater. Tehnol., vol. 48, no. 1, pp. 113–118, 2014.
[6] C. Yang et al., “Improvement of stress-rupture life of GTD-111 by second solution heat
treatment,” Mater. Des., vol. 45, pp. 308–315, 2013.
[7] R. A. Stevens and P. E. J. Flewitt, “The effects of ????? precipitate coarsening during
isothermal aging and creep of the nickel-base superalloy IN-738,” Mater. Sci. Eng., vol.
37, no. 3, pp. 237–247, 1979.
[8] K. Banerjee, N. L. Richards, and M. C. Chaturvedi, “Effect of filler alloys on heat-affected
zone cracking in preweld heat-treated IN-738 LC gas-tungsten-arc welds,” Metall.
Mater. Trans. A, vol. 36, no. 7, pp. 1881–1890, 2005.
[9] P. Wangyao, W. Homkrajai, and S. Asavavisithchai, “Effect of postweld heat treatments
on TIG-welded microstructures of superalloy, in - 738,” Chiang Mai J. Sci., vol. 36, no. 3,
pp. 320–330, 2009.
You might also like
- DCC SoloDocument40 pagesDCC SoloDarthFoo67% (3)
- The Technical, Aerodynamic & Performance Aspects of a Helicopter: A Manual for Helicopter Pilots and Engineers Who Want to Know MoreFrom EverandThe Technical, Aerodynamic & Performance Aspects of a Helicopter: A Manual for Helicopter Pilots and Engineers Who Want to Know MoreRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Ara Hunter Trading Ideas Ver 4.0: Wednesday, November 13, 2019Document16 pagesAra Hunter Trading Ideas Ver 4.0: Wednesday, November 13, 2019Bella Nurul IstiqomahNo ratings yet
- Freeletics Rutina 15 SemanasDocument4 pagesFreeletics Rutina 15 SemanasSebastian AcostaNo ratings yet
- 06 - The Modes of Ancient Greece - Elsie HamiltonDocument20 pages06 - The Modes of Ancient Greece - Elsie HamiltonRafa Noguera FernándezNo ratings yet
- No. Sampel: 1 (Selatan) 2 (Utara)Document9 pagesNo. Sampel: 1 (Selatan) 2 (Utara)Andhika NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Pipeng Toolbox - ASME B31.3 Process Piping Thermal Expansion Data ModuleDocument2 pagesPipeng Toolbox - ASME B31.3 Process Piping Thermal Expansion Data ModuleHabib ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- CA Round Swirl DiffuserDocument3 pagesCA Round Swirl DiffuserYapKJNo ratings yet
- Estimating QuickStart 05 2014Document9 pagesEstimating QuickStart 05 2014Avinash PathaniaNo ratings yet
- TM 3206 Metode Pengangkatan Buatan Tugas Desain Gas Lift Prosper Dan PipesimDocument11 pagesTM 3206 Metode Pengangkatan Buatan Tugas Desain Gas Lift Prosper Dan PipesimBabas Samudera HafwandiNo ratings yet
- Tugas / Fungsi Mine Geology & Exploration (MGX) : 1. Mencari Cadangan Bijih NickelDocument15 pagesTugas / Fungsi Mine Geology & Exploration (MGX) : 1. Mencari Cadangan Bijih NickelSyamsuddin mbakrieNo ratings yet
- 2020 Annual Report Printed Version ERRATUM #2Document7 pages2020 Annual Report Printed Version ERRATUM #2JD2750No ratings yet
- RAFTER, COLUMNS-BUILTUP SHIPPING - List (Excel)Document4 pagesRAFTER, COLUMNS-BUILTUP SHIPPING - List (Excel)BUILDSWORTH LEADNo ratings yet
- Book 4Document2 pagesBook 4Marwa AlasheebiNo ratings yet
- Alkynyl-Functionalized Gold NHC Complexes and TheiDocument5 pagesAlkynyl-Functionalized Gold NHC Complexes and TheikarthickrajaNo ratings yet
- RE2 Decline ProblemDocument8 pagesRE2 Decline ProblemTahaNo ratings yet
- Staad Result NMMCDocument185 pagesStaad Result NMMCKIM BIGZNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of The Elements (Chemistry) PDFDocument2 pagesPeriodic Table of The Elements (Chemistry) PDFWilliam CarverNo ratings yet
- Ulllted States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,136,672 B2Document11 pagesUlllted States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,136,672 B2pamururamuNo ratings yet
- Data WH Unit General Oct16Document6 pagesData WH Unit General Oct16Ayu Kusuma HastutiNo ratings yet
- Nexen Group, IncDocument1 pageNexen Group, IncJulio C. SalinasNo ratings yet
- Budget Statistics 2005 - 2011: Ministry of Finance Republic of IndonesiaDocument16 pagesBudget Statistics 2005 - 2011: Ministry of Finance Republic of IndonesiaSurjadiNo ratings yet
- Fuel+Table+ +excavatorsDocument4 pagesFuel+Table+ +excavatorsHopper GrassNo ratings yet
- Parameters Well 3/9 A2 FIT15 Reservoir ParametersDocument3 pagesParameters Well 3/9 A2 FIT15 Reservoir ParametersKone YacouNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.471,082 B2Document10 pagesUnited States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.471,082 B2Hazeq AzaharNo ratings yet
- Hasil Pengecekan TeraDocument2 pagesHasil Pengecekan TeraRizal KhoirulNo ratings yet
- Appendix E Soil Thermal Resistivity TestingDocument14 pagesAppendix E Soil Thermal Resistivity TestingroylesterlaraNo ratings yet
- Excavation QuantityDocument1 pageExcavation QuantityTaslim_ANo ratings yet
- Database Hematite Alpha Fe2o3Document3 pagesDatabase Hematite Alpha Fe2o3Erina Rizki NugrahaniNo ratings yet
- Embankment Quality TestsDocument10 pagesEmbankment Quality TestsMansoor AliNo ratings yet
- Welding Consumable Calculation (WCC) : Doc. No P.O No Rev. No Project Details Technical Requirement ConsumablesDocument10 pagesWelding Consumable Calculation (WCC) : Doc. No P.O No Rev. No Project Details Technical Requirement ConsumablesAhmad KamilNo ratings yet
- Plate Load Test ReportDocument9 pagesPlate Load Test ReportAtul Kumar Engineer100% (8)
- A Procedure For Calculating The Equilibrium Distribution of Trace Elements Among The Minerals of Cumulate Rocks, and The Concentration of Trace Elements in The Coexisting Liquids IDocument11 pagesA Procedure For Calculating The Equilibrium Distribution of Trace Elements Among The Minerals of Cumulate Rocks, and The Concentration of Trace Elements in The Coexisting Liquids IfredyzNo ratings yet
- 6.4.4.4 Short Circuit ReportDocument580 pages6.4.4.4 Short Circuit ReportMohamed FaroukNo ratings yet
- Daftar Tagihan Tanah Urug Pt. DPS: NO Tanggal Volume/M3 KETDocument24 pagesDaftar Tagihan Tanah Urug Pt. DPS: NO Tanggal Volume/M3 KETdhe la kemenNo ratings yet
- Welding Consumable Calculation (WCC) : Doc. No Project Client Project Details Technical Requirement ConsumablesDocument8 pagesWelding Consumable Calculation (WCC) : Doc. No Project Client Project Details Technical Requirement Consumableskeymal9195No ratings yet
- ValidationDocument4 pagesValidationurbanphantomguyNo ratings yet
- Financial Profile OkeDocument84 pagesFinancial Profile Okeapi-19931483No ratings yet
- 2.5 Coal Resources and ReservesDocument17 pages2.5 Coal Resources and ReservesGbenga AdewumiNo ratings yet
- 001.instrumentation 20120911Document11 pages001.instrumentation 20120911Marisa HuangNo ratings yet
- Table H1 Total Final Energy Consumption in Australia, by Fuel, Energy Units ADocument5 pagesTable H1 Total Final Energy Consumption in Australia, by Fuel, Energy Units AChunwai LiongNo ratings yet
- WCC.11031MM (Rolled Pipe)Document7 pagesWCC.11031MM (Rolled Pipe)keymal9195No ratings yet
- Pharma Sector Quantitative Analysis (As On 12 Nov, 2010)Document4 pagesPharma Sector Quantitative Analysis (As On 12 Nov, 2010)trade-rajNo ratings yet
- Trending Value Portfolio Implementation-GoodDocument260 pagesTrending Value Portfolio Implementation-Gooddheeraj nautiyalNo ratings yet
- Lampiran C Waktu Edar Alat Muat Backhoe Caterpillar 330 BLDocument3 pagesLampiran C Waktu Edar Alat Muat Backhoe Caterpillar 330 BLRoby RahmatNo ratings yet
- Lifting ShacklesDocument8 pagesLifting Shacklesgechaves1No ratings yet
- Crime StatsDocument2 pagesCrime StatsbklocalNo ratings yet
- Item Unit Budget W1 1-Jul 2-Jul 3-Jul 4-Jul: June'21 UTD 1-13 June'21Document4 pagesItem Unit Budget W1 1-Jul 2-Jul 3-Jul 4-Jul: June'21 UTD 1-13 June'21Adhi TriadiNo ratings yet
- Gaskets938gDocument3 pagesGaskets938gikperha jomafuvweNo ratings yet
- 52402-BDK-PIP-CS-010 Pipe Wall Thickness Rev 0Document3 pages52402-BDK-PIP-CS-010 Pipe Wall Thickness Rev 0sudjonoNo ratings yet
- DSSCsDocument3 pagesDSSCsAndrea CabreraNo ratings yet
- jnc15713 Sup 0001 SupinfoDocument20 pagesjnc15713 Sup 0001 SupinfoDevonNo ratings yet
- Welding Consumable Calculation (WCC) : Doc. No Project Client Project Details Technical Requirement ConsumablesDocument7 pagesWelding Consumable Calculation (WCC) : Doc. No Project Client Project Details Technical Requirement Consumableskeymal9195No ratings yet
- Welding Consumable Calculation (WCC) : Doc. No Project Client Project Details Technical Requirement ConsumablesDocument8 pagesWelding Consumable Calculation (WCC) : Doc. No Project Client Project Details Technical Requirement Consumableskeymal9195No ratings yet
- Appendix 1. Helicopter Data: 1. INTRODUCTION. This Appendix Contains 2. VERIFICATION. The Published InformationDocument20 pagesAppendix 1. Helicopter Data: 1. INTRODUCTION. This Appendix Contains 2. VERIFICATION. The Published Informationsamirsamira928No ratings yet
- United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,076,507 B2Document12 pagesUnited States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,076,507 B2Manuel Gonzalez GalvezNo ratings yet
- Charsle ColDesDocument23 pagesCharsle ColDesokechukwu1benjaminNo ratings yet
- SITRA Energy AuditDocument14 pagesSITRA Energy Auditkshahulhameed0% (1)
- Structure1 AnlDocument116 pagesStructure1 Anlsinu_emailNo ratings yet
- MiCOM IDMT Caculation ToolDocument6 pagesMiCOM IDMT Caculation ToolVũDuyTânNo ratings yet
- Screw A (In 2) M (K-In) R (FT) R (In) R 2 (In 2) M R QMDocument19 pagesScrew A (In 2) M (K-In) R (FT) R (In) R 2 (In 2) M R QMjoelNo ratings yet
- W01-V03 Change View OptionsDocument107 pagesW01-V03 Change View Optionspritish chadhaNo ratings yet
- Boehler CN 13 4-MC - SWDocument1 pageBoehler CN 13 4-MC - SWSebastian AcostaNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Rating Plate: GAP 3501 DC and GAP 3501 DC USA: IdentificationDocument6 pages3.1 Rating Plate: GAP 3501 DC and GAP 3501 DC USA: IdentificationSebastian AcostaNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument169 pagesPDFSebastian AcostaNo ratings yet
- Yellow Submarine (The Beatles) Imagine (John Lenon)Document2 pagesYellow Submarine (The Beatles) Imagine (John Lenon)Sebastian AcostaNo ratings yet
- Ansi Asa S3.1 1999 R2008Document27 pagesAnsi Asa S3.1 1999 R2008fco2312100% (1)
- Ccs Assignment 2Document7 pagesCcs Assignment 2VINIKSHA SHREE A CSE studentNo ratings yet
- Science Subject For Middle School - 7th Grade - DNA in Biology by SlidesgoDocument55 pagesScience Subject For Middle School - 7th Grade - DNA in Biology by SlidesgoJenniferNo ratings yet
- BBI2421 SCL WORKSHEET 1 (WEEK 2-3) - SENTENCE STRUCTURE, SENTENCE ERRORS & TENSES SEM 2 2017-18-1Document12 pagesBBI2421 SCL WORKSHEET 1 (WEEK 2-3) - SENTENCE STRUCTURE, SENTENCE ERRORS & TENSES SEM 2 2017-18-1Aina NadhirahNo ratings yet
- Marketing Communications in The Digital AgeDocument49 pagesMarketing Communications in The Digital Age2m shoppingNo ratings yet
- SH Walkthrough iNTRODUCTION TO PHILOSOPHY COREDocument10 pagesSH Walkthrough iNTRODUCTION TO PHILOSOPHY COREMaricris Galman SalamatNo ratings yet
- PDFViewer PDFDocument376 pagesPDFViewer PDFRaveendran Sukumaran PareshnathNo ratings yet
- Documents - Pub Sharir Kriya Ayurvedic Physiology InstrumentsDocument137 pagesDocuments - Pub Sharir Kriya Ayurvedic Physiology InstrumentsRAMESH SANAPNo ratings yet
- Crossing The Jordan River 08-06-20Document37 pagesCrossing The Jordan River 08-06-20elmerdlpNo ratings yet
- Iot Security FrameworkDocument14 pagesIot Security Frameworkboka987No ratings yet
- Microwave Oven: User'S ManualDocument20 pagesMicrowave Oven: User'S ManualRuiPereiraNo ratings yet
- Full Chapter Advances in Manufacturing Processes Select Proceedings of Ram 2020 Harshit K Dave PDFDocument53 pagesFull Chapter Advances in Manufacturing Processes Select Proceedings of Ram 2020 Harshit K Dave PDFelizabeth.mccleese721100% (4)
- S. No Y: PSG College of Technology: Coimbatore - 641004Document2 pagesS. No Y: PSG College of Technology: Coimbatore - 641004HariharanNo ratings yet
- MAN Diesel: Tools For Reconditioning 52001-02Document4 pagesMAN Diesel: Tools For Reconditioning 52001-02manuel canas nunezNo ratings yet
- Sark Prime 4 BrochureDocument8 pagesSark Prime 4 BrochureHar DonNo ratings yet
- Weight and Mass SEDocument5 pagesWeight and Mass SEGabriel LouimaNo ratings yet
- The Union of Concerned ScientistsDocument13 pagesThe Union of Concerned ScientistsIlser ReineNo ratings yet
- Pile Load Test MethodologyDocument4 pagesPile Load Test MethodologyAkhilesh Dwivedi100% (1)
- Metercat 6.1.1.0 Release NotesDocument7 pagesMetercat 6.1.1.0 Release NotesCarlos Guzman BonifacioNo ratings yet
- MPI GTU Study Material E-Notes Introduction-To-Microprocessor 13052022114954AMDocument4 pagesMPI GTU Study Material E-Notes Introduction-To-Microprocessor 13052022114954AMKartik RamchandaniNo ratings yet
- Free Flow Air GaugeDocument11 pagesFree Flow Air GaugeKARAN KHANNANo ratings yet
- Prashant Pandey Roll No 57 FinalDocument87 pagesPrashant Pandey Roll No 57 FinalSMF022VANSH JAINNo ratings yet
- Price List Djuragan FrozenDocument34 pagesPrice List Djuragan FrozenIsrainiNo ratings yet
- SWE2007 - Fundamentals of Operating SystemsDocument6 pagesSWE2007 - Fundamentals of Operating SystemsmaneeshmogallpuNo ratings yet
- Ponce Final Paper - Luis Ramirez-With-Cover-Page-V2Document27 pagesPonce Final Paper - Luis Ramirez-With-Cover-Page-V2Roswitha Klassen0% (1)
- RegressionDocument5 pagesRegressionharpreet kaurNo ratings yet
- Smart Technology in Smart CityDocument37 pagesSmart Technology in Smart CityAnaTasya Dian Jr.100% (1)
- Untitled: Pandas PD OsDocument55 pagesUntitled: Pandas PD OsGustavo Cano GallegosNo ratings yet