Professional Documents
Culture Documents
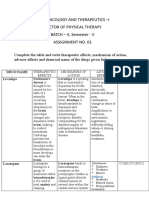
Sedative Hypnotics - RAMELTEON: Not Metabolized by CYP3A4 MOA Pharmacokinetics Indications AE CI Benzodiazepines
Sedative Hypnotics - RAMELTEON: Not Metabolized by CYP3A4 MOA Pharmacokinetics Indications AE CI Benzodiazepines
Uploaded by
JOSLIN ROZ GALILEAOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sedative Hypnotics - RAMELTEON: Not Metabolized by CYP3A4 MOA Pharmacokinetics Indications AE CI Benzodiazepines
Sedative Hypnotics - RAMELTEON: Not Metabolized by CYP3A4 MOA Pharmacokinetics Indications AE CI Benzodiazepines
Uploaded by
JOSLIN ROZ GALILEACopyright:
Available Formats
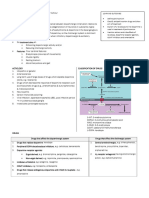
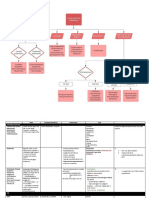
SEDATIVE HYPNOTICS
- RAMELTEON : not metabolized by CYP3A4
- RAMELTEON and BUSPIRONE: active metabolites
MOA PHARMACOKINETICS INDICATIONS AE CI
BENZODIAZEPINES
-Shorter half-lives direct to Phase II (conjugation)
■ Estazolam, Lorazepam, Oxazepam (mnemonic: ELO)
Enhance the inhibitory effects of Sedation Enhance Porphyrin Synthesis
GABA ○ Euphoria
○ Anterograde amnesia
GABAA receptor-chloride ion channel Anesthesia
Major isoform: 2 α1, 2 β2 and 1 γ2 ○ Adjunct in general anesthesia
subunits ○ Rapid tissue redistribution
Muscle Relaxation
GABAA receptor for GABA: a1, b2 ○ Inhibit polysynaptic reflexes and
BZ site: a1, y2 internuncial transmission’
A1 - sedation, amnesia, ataxic effects Anticonvulsant Effect
(zolpidem, zaleplon, eszopiclone) ○ Benzodiazepines: Clonazepam
A2 and a3 - anxiolytic and muscle (absence seizure), Lorazepam,
relaxing actions Diazepam (drug of choice for status
A5 - memory impairment epilepticus)
○ Barbiturates: Phenobarbital,
Metharbital
FLUMAZENIL Benzodiazepine antagonist Abstinence symptoms in
dependent patients
Competitive antagonism at GABAA
receptor
NEW ANXIOLYTICS
BUSPIRONE For relief of anxiety Not for panic states NO marked sedation/euphoria
Partial agonist at 5-HT1A receptor
Facilitate GABA-mediated inhibition at GABAA receptor sites
■ Direct activation
● Inhaled anesthetics, barbiturates, etomidate, propofol
○ Facilitate GABA action:
■ Benzodiazepines, inhaled anesthetics
■ Barbiturates, etomidate, propofol (low concentration)
○ Antagonist at NMDA receptor (glutamate receptor)
■ Ketamine, possibly nitrous oxide
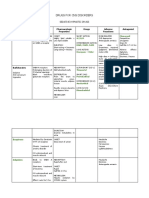
MOA PHARMACOKINETICS INDICATIONS AE CI
GENERAL ANESTHETICS
Synapse as prime focus of anesthetic - Elimination (HESIDN) DESFLURANE: most volatile Nephrotoxicity; enflurane,
effect: :Halothane > enflurane > sevoflurane
○ PRESYNAPTIC - alter release of sevoflurane > isoflurane > Hepatotoxicity: halothane
neurotransmitters desflurane >N2O
○ POSTSYNAPTIC - change frequency
or amplitude of impulses Anesthetics with LOW blood solubility
from the synapse - Desflurane, Nitrous oxide
Anesthetics with MODERATE to HIGH
blood solubility
- Methoxyflurane, halothane
Depress cardiac contractility → ↓
arterial BP
- Halothane and enflurane >
isoflurane, desflurane,
sevoflurane
Peripheral vasodilation and minimal
effect on CO: isoflurane, desflurane,
sevoflurane
Baroreceptor Reflex ( ↓ BP⟶ ↑ HR)
■ Depressed by halothane, enflurane,
sevoflurane
■ Unaffected by isoflurane, and
desflurane
MALIGNANT HYPERTHERMIA
DANTROLENE DOC Muscle weakness
A spasmolytic Sedation
Interferes with the release of calcium Occasional hepatitis
from the sarcoplasmic reticulum via
ryanodine receptor channel (RyR1)
INTRAVENOUS ANESTHETICS
THIOPENTAL Ultra-short-acting
Taste of garlic evoked just prior to
inducing anesthesia
Methohexital:excitement phenomena
GIVE RECTAL PARA 10 FOLD NG IV
PROPOFOL Rapidly metabolized in Liver, Kidney, Most widely-used IV anesthetic
Lungs ● Rapid induction and awakening
● ↓cerebral blood flow and ICP
X analgesic and amnesic prop
FENTANYL Opioid analgesic:μ receptor agonist High-dose used for cardiovascular
anesthesia
balanced anesthesia
ETOMIDATE Hemodynamic stability Effect Terminated By Redistribution
Cerebral Protection
KETAMINE NMDA receptor antagonism Intracranial effects Catalepsy, sympathetic
○ Blocks membrane effects of the ○ ↑ ↑ ↑: cerebral blood flow, O2 stimulation, profound analgesia
excitatory glutamate consumption, ICP and agitation
● Respiratory effects
○ ↓ respiratory rate
○ Maintains airway muscle tone
○ Usually preserves airway reflexes
S(+) stereoisomer is more potent than
the R(-)
DEXMEDETOMIDI Alpha2 adrenergic agonist Maintains spontaneous respirations
NE ○ Hypnosis/Sedation: Locus
coeruleus in the brain
○ Analgesia: spinal cord
1600-fold greater selectivity for α2
than α1
LOCAL ANESTHETICS
Differential Block:all nerves can be blocked by LAs
○ Desired block: sensory ± motor block
○ Sympathetic NS blockade
■ Hypotension
■ Urinary retention
State-dependent and use-dependent mechanism of LA
■ Sensory fibers: rapid firing and long duration of AP
■ Motor fibers: slow firing and shorter duration of AP
■ A delta and C fibers for pain are rapid firing: blocked earlier
ESTERS
- Prototype: procaine (basta isang i lang)
- Butyrylcholinesterase
- Allergic rxn bc: PABA
- metab : liver and plasma
ARTICAINE Blockade of voltage-gated sodium Persistent paresthesia
channels
BENZOCAINE Atypical kasi walang side chain pota Potential for methemoglobinemia
COCAINE EENT use systemic toxicity
AMIDES
- Prototype: Lidocaine
- Metab: liver only
- Alt for those with PABA allergy
- Rate of metabolism
- ■ Prilocaine (fastest) > lidocaine > mepivacaine > ropivacaine= bupivacaine = levobupivacaine (slowest/long-acting)
BUPIVACAINE Spinal anesthesia Cardiotoxicity
Epidural anesthesia
LEVOBUPIVACAINE S(-) enantiomer of bupivacaine Epidural anesthesia Epidural anesthesia
○ Labor ○ Labor
○ Post-operative pain control ○ Post-operative pain control
○ Caudal block in children ○ Caudal block in children
LIDOCAINE TNS with spinal anesthesia
● Used in arrhythmias
● Used in suppressing responses
to laryngoscopy and extubation
ROPIVACAINE S(-) enantiomer in a homologous Epidural analgesia for labor and
series that include bupivacaine and postoperative pain control
mepivacaine
You might also like
- Psychiatric Nursing Notes PDFDocument12 pagesPsychiatric Nursing Notes PDFClaire Lautner95% (61)
- Psychiatric BankDocument169 pagesPsychiatric BankThatcher M Lima100% (31)
- Mental Health Nursing Practice Test 1Document14 pagesMental Health Nursing Practice Test 1Dr. Jayesh Patidar100% (26)
- Anesthesiology ReviewDocument9 pagesAnesthesiology Reviewrajkumar871992100% (1)
- Chapters 2-6 in The Hands of Doctors by Paul Stepansky PDFDocument89 pagesChapters 2-6 in The Hands of Doctors by Paul Stepansky PDFJOSLIN ROZ GALILEANo ratings yet
- Psyche AnswersDocument16 pagesPsyche AnswersFreeNursingNotesNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Neuro PharmacologyDocument3 pagesDrugs Used in Neuro PharmacologyNabeel Kouka, MD, DO, MBA, MPH100% (1)
- Adrenergic Agents SeminarDocument48 pagesAdrenergic Agents SeminarTheBoss 20No ratings yet
- Adrenergic Antagonist: PharmacologyDocument3 pagesAdrenergic Antagonist: PharmacologyJB RSNJNNo ratings yet
- Sedative-Hypnotic Drugs Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument2 pagesSedative-Hypnotic Drugs Cheat Sheet: by ViaThư PhạmNo ratings yet
- CNS Pharmacology - 20231120 - 233736 - 0000Document10 pagesCNS Pharmacology - 20231120 - 233736 - 0000Meghana MaddaliNo ratings yet
- 2015 Psych DrugsDocument1 page2015 Psych DrugsmounicapaturuNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic - Antagonists TableDocument3 pagesAdrenergic - Antagonists Tablehovico3936No ratings yet
- Drug ClassificationDocument7 pagesDrug ClassificationDhruv100% (1)
- Mechanism of Action Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effects Contraindication Drug InteractionDocument1 pageMechanism of Action Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effects Contraindication Drug InteractionJubelle SipalayNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On CNSDocument19 pagesDrugs Acting On CNSAditya sagarNo ratings yet
- (Pharma Tables) Reviewers Compiled PDFDocument115 pages(Pharma Tables) Reviewers Compiled PDFMaverick PascualNo ratings yet
- Pharmacodynamics How Drugs WorkDocument21 pagesPharmacodynamics How Drugs WorkWen SilverNo ratings yet
- Philippine College of Health Sciences Pharmacology 1Document5 pagesPhilippine College of Health Sciences Pharmacology 1Ric BarrosNo ratings yet
- DRUG StudyDocument3 pagesDRUG StudyArfe BaquinquitoNo ratings yet
- Opioids PDFDocument2 pagesOpioids PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNo ratings yet
- Toxicology USMLE NotesDocument15 pagesToxicology USMLE NotesDuncan JacksonNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology (1) - 104-122Document19 pagesPharmacology (1) - 104-122Dental LecturesMMQNo ratings yet
- Intravenous AnestheticsDocument10 pagesIntravenous AnestheticsJohn Kevin FelixNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Final Drug TablesDocument388 pagesPharmacology Final Drug TablesTJNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Drugs: Pharmacological Department Medical School - UNPAD Ike HusenDocument33 pagesAdrenergic Drugs: Pharmacological Department Medical School - UNPAD Ike HusenHendra EfendiNo ratings yet
- Sedative HypnoticsDocument39 pagesSedative HypnoticsFatima ShaukatNo ratings yet
- Antiparkinsonian DrugsDocument5 pagesAntiparkinsonian Drugsluq9fifNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Concept MapDocument1 pageHypertension Concept MapmetNo ratings yet
- Veterinary CNS DrugsDocument8 pagesVeterinary CNS DrugsLaureece Salm ApduhanNo ratings yet
- CNS DrugsDocument8 pagesCNS DrugsLaureece Salm ApduhanNo ratings yet
- Pharma PrelimsDocument5 pagesPharma PrelimsRonica PascuaNo ratings yet
- Neurology Pharmacology - 20240517Document9 pagesNeurology Pharmacology - 20240517deidra1120No ratings yet
- Ans NursingDocument15 pagesAns Nursingwww.nikhilbabu123No ratings yet
- Pharmacology - Drugs For CNS DisordersDocument4 pagesPharmacology - Drugs For CNS DisordersJireh MejinoNo ratings yet
- Nitrous Oxide Isoflurane Halothane Enflurane Sevoflurane DesfluraneDocument3 pagesNitrous Oxide Isoflurane Halothane Enflurane Sevoflurane DesfluraneNariska CooperNo ratings yet
- Antiemetic DrugsDocument2 pagesAntiemetic DrugsAch Ri Fa INo ratings yet
- Adrenergic DrugsDocument3 pagesAdrenergic Drugsdlneisha61100% (1)
- Drugs For Anxiety P Colg RP 3Document48 pagesDrugs For Anxiety P Colg RP 3Theola FrancescaNo ratings yet
- ParkinsonDocument13 pagesParkinsonKirti SinghNo ratings yet
- Short Notes On Sedatives and HypnoticsDocument15 pagesShort Notes On Sedatives and HypnoticsPratham KhairnarNo ratings yet
- Pharma Downloads Pharma Downloads: 1-Clinodin 2-Guanbenz 3-GuanfacineDocument5 pagesPharma Downloads Pharma Downloads: 1-Clinodin 2-Guanbenz 3-GuanfacineSrihari Divya100% (1)
- Movement Disorder TreatmentsDocument3 pagesMovement Disorder TreatmentsJustin HulinNo ratings yet
- PHARMA SupertableDocument2 pagesPHARMA SupertablelpanatalioNo ratings yet
- 03 Sympathomimetics-And-Blockers NCM206Document9 pages03 Sympathomimetics-And-Blockers NCM206julinka beyla yansonNo ratings yet
- ANS2Document16 pagesANS2yaya mohaNo ratings yet
- Case 8-13Document24 pagesCase 8-13Trizian ManaliliNo ratings yet
- Unit 7. Sympathomimetics and SympatholyticsDocument44 pagesUnit 7. Sympathomimetics and SympatholyticsApril Mergelle Lapuz100% (2)
- CAS 3 Drug ChartDocument20 pagesCAS 3 Drug Chartnaazaninrahat76No ratings yet
- Generic Name Brand Name Mechanism of ActionDocument10 pagesGeneric Name Brand Name Mechanism of ActionRosario VicencioNo ratings yet
- Year 2 Drug ListDocument8 pagesYear 2 Drug ListRay100% (1)
- CNS Drugs-2Document34 pagesCNS Drugs-2semessor021245No ratings yet
- Antipsychotic AgentsDocument18 pagesAntipsychotic AgentsmengakuNo ratings yet
- The Hitchhiker's Guide To Clinical Pharmacology: Pharmacodynamics: How Drugs WorkDocument23 pagesThe Hitchhiker's Guide To Clinical Pharmacology: Pharmacodynamics: How Drugs WorkMylz MendozaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology SummaryDocument14 pagesPharmacology SummaryteddyjolinNo ratings yet
- Antiadrenergic Drugs (Adrenergic Receptor Antagonist)Document2 pagesAntiadrenergic Drugs (Adrenergic Receptor Antagonist)Eftakharul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Anestesi UmumDocument42 pagesAnestesi UmumBryan HoriandoNo ratings yet
- Obat2 Yang Bekerja Pada Ganguan Kesadaran: Elly Usman Bagian Farmakologi Dan Terapi, Fakultas Kedokteran, UnandDocument29 pagesObat2 Yang Bekerja Pada Ganguan Kesadaran: Elly Usman Bagian Farmakologi Dan Terapi, Fakultas Kedokteran, UnandKhairani HakimNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitter Function Receptor Action Related Drugs/Illnesses Nicotinic Ach-R Curare (N1), Hexamethonium (N2) Atropine (M)Document2 pagesNeurotransmitter Function Receptor Action Related Drugs/Illnesses Nicotinic Ach-R Curare (N1), Hexamethonium (N2) Atropine (M)Yob Ynnos100% (1)
- Benzo ChartDocument1 pageBenzo Chartnateman216No ratings yet
- PHARMACOLOGY Assisgnment 01Document5 pagesPHARMACOLOGY Assisgnment 01muhammadhamza muhammadiqbalNo ratings yet
- Pharma Notes MarianoDocument6 pagesPharma Notes MarianoJayson Mherl GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Cough and Cold PrepDocument3 pagesCough and Cold PrepJOSLIN ROZ GALILEANo ratings yet
- Cough and Cold PrepDocument3 pagesCough and Cold PrepJOSLIN ROZ GALILEANo ratings yet
- Group No. 6: Case 6Document12 pagesGroup No. 6: Case 6JOSLIN ROZ GALILEANo ratings yet
- Trans - PDR - Moy 2Document1 pageTrans - PDR - Moy 2JOSLIN ROZ GALILEANo ratings yet
- Psychiatry Sample Osce Exam eDocument4 pagesPsychiatry Sample Osce Exam ePNo ratings yet
- Baby Katzung Second Shifting Reviewer PDFDocument13 pagesBaby Katzung Second Shifting Reviewer PDFJoanne Aluzan100% (1)
- C 315Document54 pagesC 315Rumana AliNo ratings yet
- Anti Anxiety DrugsDocument26 pagesAnti Anxiety DrugsSANJIV KUMAR YADAV100% (1)
- Topnotch Mnemonics - March 2019Document9 pagesTopnotch Mnemonics - March 2019euphrosyne92100% (1)
- Reporting On IV AnestheticsDocument88 pagesReporting On IV AnestheticsPaul Rizel LedesmaNo ratings yet
- Seizure DrugsDocument3 pagesSeizure DrugsBwatNo ratings yet
- Clinical AssignmentDocument22 pagesClinical AssignmentKeziah GillNo ratings yet
- 11Document8 pages11Tyson Easo JonesNo ratings yet
- Status EpilepticusDocument3 pagesStatus Epilepticusapi-534699819No ratings yet
- Pocket Reference For ICU Staff Critical Care Medicine ServicesDocument63 pagesPocket Reference For ICU Staff Critical Care Medicine ServicesOrion John100% (4)
- Benzodiazepines ToxicityDocument19 pagesBenzodiazepines ToxicityNagendra NayakNo ratings yet
- Glasgow Modified Alcohol Withdrawal ScaleDocument5 pagesGlasgow Modified Alcohol Withdrawal ScaleRichard SymondsNo ratings yet
- Part XVIDocument17 pagesPart XVIphp_czarina04421No ratings yet
- Drugs:: Side Effects of Psychotropic MedicationsDocument32 pagesDrugs:: Side Effects of Psychotropic MedicationsMARIE ROSE L. FUNTANARNo ratings yet
- The History of Benzodiazepines: in PracticeDocument10 pagesThe History of Benzodiazepines: in PracticeKairo AlbernazNo ratings yet
- Status EpilepticusDocument70 pagesStatus Epilepticusfloppyfishh100% (1)
- ICU Pharmacology: Sedatives Analgesics Paralytics PressorsDocument51 pagesICU Pharmacology: Sedatives Analgesics Paralytics Pressorsdevi trismiaNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Exam SmpleDocument18 pagesPsychiatric Exam SmpleAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- TCP AlcoholicDocument13 pagesTCP AlcoholicTracey MarieNo ratings yet
- REVISED Medicines For Nausea and Vomiting 201602v2 PDFDocument3 pagesREVISED Medicines For Nausea and Vomiting 201602v2 PDFKlausNo ratings yet
- Sedative Hypnotics PDFDocument8 pagesSedative Hypnotics PDFMae DoctoleroNo ratings yet
- Social Benefits of SmokingDocument7 pagesSocial Benefits of SmokingToseef AhmadNo ratings yet
- Feed Your Brain FirstDocument60 pagesFeed Your Brain FirstHarry Truman100% (4)
- Agitation and Delirium at The End of Life: "We Couldn't Manage Him"Document15 pagesAgitation and Delirium at The End of Life: "We Couldn't Manage Him"Ivonne Soledad Che PiñeiroNo ratings yet
- Postreading Self Assessment and CME Test Preferred.28Document22 pagesPostreading Self Assessment and CME Test Preferred.28مجاهد إسماعيل حسن حسينNo ratings yet