Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Multiple Choice Questions - NETWORKS
Multiple Choice Questions - NETWORKS
Uploaded by
renji rajOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Multiple Choice Questions - NETWORKS
Multiple Choice Questions - NETWORKS
Uploaded by
renji rajCopyright:
Available Formats
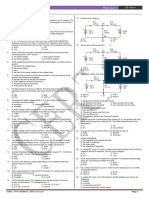
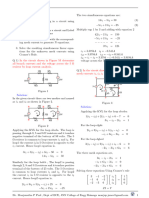
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS C.
equal to load resistance
D. none of these
5. Efficiency of power transfer when
1. The equivalent resistance between maximum transfer of power occurs is
point A to B in the following Fig. Na-I is
approximately given by A.50% B. 75% C. 100% D. None of these
A. 4𝛺 B. 1𝛺 C.8𝛺 D.𝛺
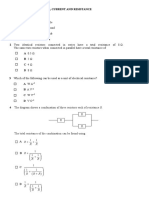
6. If the energy is supplied from a source
whose resistance is 20 K𝛺 to a load of
100𝛺, The source will be
2. The Thevenin’s equivalent between
point A & B for the network shown in
Fig. NA- 2 is given by A. a current source
B. a voltage source
C. both of these
7. The resistance across AB in the adjacent
figure ( Fig. NA-4)will be
A. 0 V,10𝛺 B. 10 V, 10𝛺
C. 10 V, 𝛺 D. 10 V, 0𝛺
3. For the network shown below (Fig. NA
-3 ) the steady state voltage between
point A and B is given by A. 15 B. 3.33 𝛺 C.30𝛺 D.20𝛺
8. Two resistance R1 and R2 are
connected in the circuit such that R1+
1 1 1
R2 = 25, + = . The values of
R1 R2 6
R1and R2 are
A. +75 V B. +25 V C. 0 V D. ∞
A. 9 𝛺 and 16 𝛺
4. For high efficiency of transfer of power, B. 20 𝛺 and 5 𝛺
the internal resistance of the source C. 10 𝛺 and 15 𝛺
should be D. 10 𝛺 and 15 𝛺 or 15 𝛺 and 10 𝛺
A. More than load resistance
B. less than load resistance
9. An ideal voltage source
A. has terminal voltage in proportion to
current
B. has terminal voltage in proportion to
load A. 100 μC B. 50 μC C. 40 μC D. 20 μC
C. has zero internal resistance
D. has open circuit voltage nearly equal 14. In a series parallel circuit with 6
to the voltage on full load resistances, if there are there in one
parallel bank, these three resistances
10. Which of the following is the passive must have
element ?
A. the same current as in the voltage
A. ideal current source source
b. ideal voltage source B. the same current
C. capacitance C. the same IR drop
D. all of the above D. an IR drop equal to the applied
11. Two 500 ohm 1 watt resistors are voltage.
connected in parallel. Their combined
resistance and wattage rating is 15. A voltage source having a high input
A. 5000 ohms, 1 watt impedance and a very low load
B. 250 ohms, 2 watts impedance may be treated as a
C. 1000 ohms, 2 watts A. constant voltage sources
D. 500 ohms 2 watts B. constant power source
12. In the circuit given in Fig. NA -5 , the C. constant current source
ammeter reads 1 ampere and voltmeter D. none of the above
10 volts . What is the value of R ?
16. The circuit whose properties are same
in either direction is known as
A. irreversible circuit
B. reversible circuit
C. unilateral circuit
A. 11 ohms B. 12 ohms D. bilateral circuit.
C. 10 ohms D. none of the above.
17. The ohm’s law states that
13. The accumulate charge on 0.8 μF A. V is proportional to I
capacitor (Fig. NA-6) is B. I is proportional to V
C. V is proportional to IR
D. V is proportional to R.
18. The Kirchhoffs laws fail in
A. lumped parameters circuit
B. distributed parameters circuit D. node.
24. If a network contains B branches, an N
C. non-linear circuits nodes, then the number of mesh
D. bilateral circuits. current equations would
A. B –(N -1) B. N –(B -1)
19. An ideal current source has zero C. B –N – 1 D. (B +N) -1
25. Assuming V = 5 volt, find the value of
A. internal conductance
V s in the network shown in Fig. NA – 7 :
B. internal resistance
C. voltage on no load
D. ripple.
20. A practical voltage source consists of
A. 50 V B. 80 V C. 85 V D. 100 V
A. an ideal voltage source in series with
26. In the given (Fig . NA – 8 ) circuit I 0 = 5
an internal resistance
A, The current I is given by
B. an ideal voltage source in parallel
A. – 5A B. 0 A C. 2 A D. 5 A
with an internal resistance
C. both A and B are correct
D. none of the above.
21. A practical current source consists of
A. an ideal current source in series with
an impedance
B. an ideal current source in parallel 27. The charging discharging characteristics
series with an impedance of a capacitor is shown in Fig. NA-9 .
What is the current drawn by the
C. both are correct capacitance at the end of first half
D. none of the above. second ?
22. Which of the following is an active
element of circuit ?
A. resistance
B. inductance
C. capacitance
D. ideal current source.
23. A terminal where three or more A. 10 A B. 8 A C. 0 A D. ∞ A
branches meet is known as
A. combination 28. The current drawn by the capacitance
B. terminus eat the end of one second will be
C. anode A . 10 A B. 0 A C. -10 A D. 1 A
29. Kirchoff’s law is applicable to 34. In the adjoining circuit (Fig. NA- 11) I 0 is
A. Passive networks only
B. a.c. circuits only
C. d.c. circuits only
D. both a.c as well d.c. circuits
30. Kirchoff’s law is not applicable to A. 6 A B. 4 A C. 3 A D. 2 A
circuits with
A. lumped parameters 35. The number of independent equations
B. passive elements to solve a network in graph theory is
C. distributed parameters equal to
D. non- linear resistances. A. the number of chords
B. the number of branches
31. Kirchoff’s voltage law can be applied to C. sum of the number of branches and
circuits with chords
A. non-linear elements only D. sum of number of branches , chords
B. linear elements only and nodes.
C. linear , non-linear, active and passive
elements 36. In the circuit in Fig. NA – 12, V s is given
D. linear, non-linear , active, passive, by
time varying as well as time in variant
elements.
32. The internal resistance of the circuit
looking from x-y is
A. 2 V B. 4 V C. 6 V D. 12 V
37. What is the value of R¿ in the circuit as
shown in Fig. NA- 13 ?
A. 5 𝛺 B. 10 Ω C.0 D. 20 𝛺
33. In the adjoining circuit (Fig. NA- 10), V 0
is
A. less than 100 𝛺
B. less than 2 𝛺
C. less than 1 𝛺
A. 8 V B. 10 V C. 12 V D. 2 V. D. less than 10 𝛺
38. In the adjacent (Fig. NA-14) of a cube
AG will be
A. 1 A B. 2 A C. 1.5 A D. 2.5 A .
A. R ohm B. 2R 𝛺 43. Current through R2 in the same figure
1 1 is
C. R ohm D. R ohm.
2 12
39. AC will be
A. 2.5 A B. 3 A C. 1.5 A D. 1 A
3 5
A. R ohm B. R ohm 44. Voltage across cell E1 in the same
6 6
figure is
A. 2.25 V B. 3.25 V C. 1.25 V D. 3 V
1 1
C. R𝛺 D. R ohm. 45. In the following Fig. NA- 17 the
6 12
resistance across AB is,
40. AD in the same cube will be 1 10
A. 2 𝛺 B. 3 C. D. 𝛺 ohm
3 3
3 5 46. If the following (Fig. NA -18 (a) exhibits
A. . R ohm B. . R ohm the current waveform in an inductor ( 1
4 6
H) for 0 – 8 secs, which of the other
7 5 figures (Fig. NA – 18 (b) – (e) does
C. . R ohm D. . R ohm exhibit the corresponding voltage
12 12
waveform ?
41. For the circuit shown in Fig. NA- 15, the
equivalent resistance between A and B
is
A. 4 𝛺 B. 2 𝛺 C. 6 𝛺 D. 3
42. Current through R1 in the adjoining
(Fig. NA- 16 ) is
49. Current through R in the following (Fig.
NA- 20 ) network is given by
A. figure b
B. figure c
A. 2.22 A B. 2 A C. 10 A D. 11 A
C. figure d
D. figure e
50. In the adjoining Fig. NA- 21, V L = 2
47. In the above case which figure volts . Find I 0
represents the instantaneous power ?
A. figure b
B. figure c
C. figure d
D. figure e.
A. 5 A B. 10 A C. 8 A D. 11 A.
48. The impedance matrix R and input
voltage vector V for the adjacent Fig.
NA -19 circuit are
R V
3−7 2
A. [−2 1 ] [ −1 ]
7−2 −07
B. [−21 ][ 5 ]
C. [ 3−2
–27 ] [ 7
−2 ]
2−7
D. [−22 ] [−72]
You might also like
- 1-Fundamentals of Power Semiconductors For Automotive ApplicationsDocument316 pages1-Fundamentals of Power Semiconductors For Automotive ApplicationsHind EL HAFIDINo ratings yet
- DC-1Document4 pagesDC-1jj012586100% (1)
- Digital Control in Power ElectronicsDocument159 pagesDigital Control in Power Electronicsthietdaucong100% (2)
- Mock Up ExamDocument4 pagesMock Up Examsolomonlemma14No ratings yet
- MCQsDocument9 pagesMCQsAlbert AlemaniaNo ratings yet
- MR Logbo - Grade 10 Physics 2ND MP Exam 22 - 23Document4 pagesMR Logbo - Grade 10 Physics 2ND MP Exam 22 - 23Joel LogboNo ratings yet
- Objective Questions Set 01Document19 pagesObjective Questions Set 01GAURAV GUPTANo ratings yet
- AC and DC CircuitsDocument3 pagesAC and DC CircuitsEugene Embalzado Jr.No ratings yet
- Ot 2Document9 pagesOt 2Eugene MartinNo ratings yet
- EEP1 Sample2 QPDocument10 pagesEEP1 Sample2 QPSaiful IslamNo ratings yet
- Ee Terms 3Document6 pagesEe Terms 3Lester James SaingNo ratings yet
- Yaun MCQ Ac CircuitsDocument5 pagesYaun MCQ Ac CircuitsYaun, Aslie Jane S.No ratings yet
- CPP 2 Current Electricity Part 1Document8 pagesCPP 2 Current Electricity Part 1ullas agrawalNo ratings yet
- QUIZ#2Document6 pagesQUIZ#2FrancesNo ratings yet
- Visit: St. Louis Review Center, Inc Davao Tel. No. (082) 224-2515 or 222-8732 18Document6 pagesVisit: St. Louis Review Center, Inc Davao Tel. No. (082) 224-2515 or 222-8732 18Marjorie MalalayNo ratings yet
- Electronics - Master Book MCQs - Insight MDCATDocument10 pagesElectronics - Master Book MCQs - Insight MDCATwbk22222No ratings yet
- Weekly Exam 1 - DC & Ac CircuitsDocument5 pagesWeekly Exam 1 - DC & Ac CircuitsHary KrizNo ratings yet
- Electricity MCQDocument14 pagesElectricity MCQPraphul MalolNo ratings yet
- Electrical CircuitDocument14 pagesElectrical CircuitDaisy BeñasNo ratings yet
- Ica Engineering Academy - Calicut - Kochi - Malappuram - TrivandrumDocument12 pagesIca Engineering Academy - Calicut - Kochi - Malappuram - TrivandrumNidhiNo ratings yet
- 3rd Grading Gen Physics 2 2019-2020Document2 pages3rd Grading Gen Physics 2 2019-2020Mariel VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Physics Electro PaperDocument8 pagesPhysics Electro Paperabhijeet singhNo ratings yet
- Csec Electrical and Electronic Technolohy PDF FreeDocument9 pagesCsec Electrical and Electronic Technolohy PDF FreeNadia PowellNo ratings yet
- Encircle or Write Down The Letter of Correct Answer For Each Statement (1 Point Each)Document4 pagesEncircle or Write Down The Letter of Correct Answer For Each Statement (1 Point Each)Sonic HedgehogNo ratings yet
- A.C Fundamentals, Circuits and Circuit TheoryDocument12 pagesA.C Fundamentals, Circuits and Circuit TheoryMD.RAKIBUL HASASNNo ratings yet
- Currentelec BKLTDocument3 pagesCurrentelec BKLTSabyasachi RayNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity - D C PandeyDocument34 pagesCurrent Electricity - D C Pandeydevshah7707No ratings yet
- RHM Elex 1Document21 pagesRHM Elex 1kdNo ratings yet
- Apllied Electric Circuit Objective Question and AnswerDocument42 pagesApllied Electric Circuit Objective Question and AnswerGanesan KandasamyNo ratings yet
- Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering Paper-IDocument12 pagesElectronics and Telecommunication Engineering Paper-Ipranavsid09100% (1)
- Holistic ExamDocument108 pagesHolistic Examwilliam100% (2)
- Current Electricity Exercise.2Document2 pagesCurrent Electricity Exercise.2Chaitanya JoshiNo ratings yet
- Elec Devices Nci RcsDocument36 pagesElec Devices Nci RcsJoyce MillanNo ratings yet
- Circuitry AssignmentDocument19 pagesCircuitry AssignmentGhazi DallyNo ratings yet
- Invalidate Your Answer.: Name: SectionDocument5 pagesInvalidate Your Answer.: Name: SectionreynanNo ratings yet
- SR Physics PH V Pet-6 (Adv) QP DT 05.07.21Document18 pagesSR Physics PH V Pet-6 (Adv) QP DT 05.07.21kumarNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity 1Document3 pagesCurrent Electricity 1NK NikhilNo ratings yet
- Epektus 1Document5 pagesEpektus 1Laxus DreyarNo ratings yet
- BJT Frequency ResponseDocument19 pagesBJT Frequency ResponsechristopherNo ratings yet
- 2024 01 02 0.8285244275971122Document26 pages2024 01 02 0.8285244275971122legendpranat4132No ratings yet
- AC CircuitDocument4 pagesAC CircuitsanjayNo ratings yet
- DC 1 2022Document4 pagesDC 1 2022Gabriel Gei Francisco RocaNo ratings yet
- Power Elec SDocument12 pagesPower Elec SJoyce MillanNo ratings yet
- CE EeDocument4 pagesCE Eejj012586No ratings yet
- Electricity Test 2010Document8 pagesElectricity Test 2010holaNo ratings yet
- ES Quiz 2Document4 pagesES Quiz 2arnavgupta1175No ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions / Practice Test Electrical Circuits - Set 3Document8 pagesMultiple Choice Questions / Practice Test Electrical Circuits - Set 3reniel fabroNo ratings yet
- GibiliscoDocument30 pagesGibiliscoRaine LopezNo ratings yet
- INDIABIX PART 3 ELEX MCQs 080918 PDFDocument41 pagesINDIABIX PART 3 ELEX MCQs 080918 PDFJehuNo ratings yet
- EEP1 Sample3 QPDocument8 pagesEEP1 Sample3 QPSaiful IslamNo ratings yet
- Take Home - Basic ElectronicsDocument2 pagesTake Home - Basic ElectronicsDarwin TacubanzaNo ratings yet
- Basic-Model For Communication StreamDocument19 pagesBasic-Model For Communication StreamERMIAS AmanuelNo ratings yet
- Power Elex Finals PDFDocument5 pagesPower Elex Finals PDFDanilo PerezNo ratings yet
- Ch-03 Current Electricity: Daily Practice Problem 04Document3 pagesCh-03 Current Electricity: Daily Practice Problem 04AlokNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits S1 S8Document24 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits S1 S8Zyrah ManaloNo ratings yet
- AC CircuitsEE 03 01 To EE 03 04 QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesAC CircuitsEE 03 01 To EE 03 04 QuestionnaireCelina RoxasNo ratings yet
- Physics TestDocument6 pagesPhysics TestSABARI SRINIVAS ANo ratings yet
- F5C3 Electricity Part 2Document44 pagesF5C3 Electricity Part 2DOROTHY LING YU CHANG MoeNo ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Vtu NotesDocument91 pagesVtu NotesSanthosh Chandu CNo ratings yet
- Ktu SyllabusDocument87 pagesKtu SyllabusPratheesh BoseNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 DC CircuitsDocument44 pagesUnit-1 DC CircuitsLatha BarlaNo ratings yet
- I2C Serial InterfaceDocument11 pagesI2C Serial InterfaceBobyNo ratings yet
- Thevenin Nortons TheoremDocument36 pagesThevenin Nortons TheoremVaneeza EemanNo ratings yet
- 11.Zero-Crossing Detector For AcDocument6 pages11.Zero-Crossing Detector For AcSourabh kulkarniNo ratings yet
- LS7183 / LS7184: Encoder To Counter Interface ChipsDocument3 pagesLS7183 / LS7184: Encoder To Counter Interface ChipsAgim ZilkicNo ratings yet
- RF Design With Aplac Aaltonen1997Document6 pagesRF Design With Aplac Aaltonen1997benitogaldos19gmail.comNo ratings yet
- (ELECS2) Exp6 - Differential Amplifier Circuits - The GWAPINGSDocument21 pages(ELECS2) Exp6 - Differential Amplifier Circuits - The GWAPINGSFrodolfre Reginald LazoNo ratings yet
- Depletion MOSFETsDocument10 pagesDepletion MOSFETsXavier Pacheco PaulinoNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between VSI and CSI Fed Induction Motor Drives in MATLAB Environment Based On THD PerformanceDocument71 pagesComparison Between VSI and CSI Fed Induction Motor Drives in MATLAB Environment Based On THD Performancethegopal100% (2)
- Understanding CMRRDocument36 pagesUnderstanding CMRRilet09No ratings yet
- Ic Lab AllDocument45 pagesIc Lab AllRaghu KasulaNo ratings yet
- BRWinter 18 DACDocument5 pagesBRWinter 18 DACSuyog DhakneNo ratings yet
- Discrete BJT Amplifier ProjectDocument10 pagesDiscrete BJT Amplifier ProjectRoland VladutescuNo ratings yet
- ProblemsDocument42 pagesProblemsAlison ValbüenaNo ratings yet
- Mesh Node AnalysisDocument35 pagesMesh Node AnalysisjashmithajanuNo ratings yet
- Preventive Maintenance SOP: GTP™ - Good Titration Practice™Document14 pagesPreventive Maintenance SOP: GTP™ - Good Titration Practice™Fernando Chacmana LinaresNo ratings yet
- MOSFET Current Mirror PDFDocument27 pagesMOSFET Current Mirror PDFaliNo ratings yet
- Manual Circuit 4Document36 pagesManual Circuit 4Gustavo YerenaNo ratings yet
- JZJSJZJSKDocument86 pagesJZJSJZJSKMarvin SinuesNo ratings yet
- General Amplifier Concepts: Engr. Jomer V. Catipon 0928 6654227Document68 pagesGeneral Amplifier Concepts: Engr. Jomer V. Catipon 0928 6654227Jacklyn Kate Caballero GarduqueNo ratings yet
- CH 4 - Second PartDocument34 pagesCH 4 - Second PartNasser AlmofariNo ratings yet
- Simple Circuit Design Tutorial For PoE ApplicationsDocument10 pagesSimple Circuit Design Tutorial For PoE ApplicationsTayyeb AliNo ratings yet
- Ee1010 Electric Circuit LaboratoryDocument81 pagesEe1010 Electric Circuit LaboratoryNaveen Reddy100% (1)
- Audible Milliohm Meter Parts List: Collection and Sharing Out by Pravin MevadaDocument4 pagesAudible Milliohm Meter Parts List: Collection and Sharing Out by Pravin MevadaakashNo ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis Midterm Exam PDFDocument5 pagesCircuit Analysis Midterm Exam PDFJuanito CayNo ratings yet
- Electrical CircuitDocument81 pagesElectrical CircuitBharat Chandra SahuNo ratings yet