Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Keanu Peralta0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views11 pagesThe document summarizes information about two medications - Losartan + HCTZ and Amlodipine. It describes their indications for hypertension, mechanisms of action in lowering blood pressure, potential side effects, and nursing responsibilities related to monitoring, patient education, and addressing any adverse effects.
Original Description:
Original Title
12ed21wds32
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes information about two medications - Losartan + HCTZ and Amlodipine. It describes their indications for hypertension, mechanisms of action in lowering blood pressure, potential side effects, and nursing responsibilities related to monitoring, patient education, and addressing any adverse effects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views11 pagesDrug Study
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Keanu PeraltaThe document summarizes information about two medications - Losartan + HCTZ and Amlodipine. It describes their indications for hypertension, mechanisms of action in lowering blood pressure, potential side effects, and nursing responsibilities related to monitoring, patient education, and addressing any adverse effects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 11
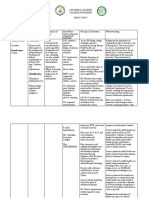
DRUG STUDY
MEDICATION INDICATION MECHANISM OF MECHANISM OF SIDE EFFECTS AND NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
ACTION ACTION IN ADVERSE EFFECTS
RELATION TO
THE PATIENT’S
CASE
LOSARTAN + HCTZ Hypertension Hydrochlorothiazide The drug works Side Effects: BASELINE ASSESSMENT
50/12.5 MG increases renal in high blood dizziness or Obtain B/P, apical pulse
excretion of sodium pressure by lightheadedness as immediately before each
Generic Name: and chloride and relaxing and your body adjusts dose, in addition to regular
Losartan potassium- reduces cardiac widening blood to the medication, monitoring (be alert to
hydrochlorothiazide load. Losartan is an vessels. This stomach pain, fluctuations).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATI
Brand Name: angiotensin II lowers the back pain, tired ON
Hyzaar receptor (type AT1) patient’s blood feeling, skin rash, Maintain hydration (offer
antagonist pressure and runny or stuffy nose, fluids frequently).
antihypertensive makes it easier sore throat, or dry Assess for evidence of
which acts by for the heart to cough. upper respiratory infection,
blocking the pump blood Adverse Side cough.
actions of around your Effects: Monitor B/P, pulse. If
angiotensin II of body. Volume depletion excessive reduction in B/P
renin-angiotensin- and electrolyte occurs, place pt in supine
aldosterone system. imbalance position, feet
The drug and its (especially slightly elevated. Assist with
active metabolite hyperkalaemia); ambulation if dizziness
selectively block dry mouth, thirst; occurs.
the vasoconstrictor lethargy, Monitor daily pattern of
and aldosterone drowsiness; muscle bowel activity, stool
secreting effects of pain and cramps; consistency.
PATIENT/FAMILY
angiotensin II. The rashes, TEACHING
two drugs exert photosensitivity, • Report any sign of
additive effects in thrombocytopenia, infection (sore throat,
hypertension. jaundice, fever), chest pain.
Therapeutic pancreatitis; • Do not take OTC cold
indication: fatigue, weakness; preparations, nasal
Decrease B/P may precipitate an decongestants.
attack of gout; • Do not stop taking
impotence; medication.
hyperglycaemia; • Limit salt intake
anorexia, nausea,
vomiting,
constipation,
diarrhoea;
sialdenitis; raised
urinary calcium
concentration;
headache,
dizziness; back
pain, myalgia; first-
dose hypotension;
angiodema;
neutropenia; GI
disturbances;
transient elevation
of liver enzymes;
taste disturbances,
cough;
exacerbation or
activation of
systemic lupus
erythematous;
palpitations;
xanthopsia;
leucopenia,
agranulocytosis,
aplastic anaemia;
necrotising angiitis;
glucosuria; renal
dysfunction,
interstitial nephritis,
renal failure;
migraine;
hyponatraemia;
UTI; chest pain;
gastritis, wt gain,
dyspepsia,
abdominal pain;
bronchitis, upper
respiratory
infection, nasal
congestion, sinusitis;
rise in cholesterol
and/or
triglycerides.
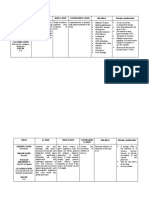
MEDICATION INDICATION MECHANISM OF MECHANISM OF SIDE EFFECTS AND NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
ACTION ACTION IN ADVERSE EFFECTS
RELATION TO THE
PATIENT’S CASE
AMLODIPINE Hypertension Inhibits influx of The drug works in Side Effects: BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Generic Name: extracellular high blood Peripheral Assess baseline
Amlodipine calcium ions, pressure by edema, renal/hepatic function
Brand Name: thereby relaxing and headache, tests, B/P, apical pulse.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATI
Apo-Amlodipine; decreasing widening blood flushing. Dizziness, ON
Norvasc; Katerzia myocardial vessels. This lowers palpitations, Assess B/P (if systolic B/P is
contractility, the patient’s nausea, unusual less than 90 mm Hg,
relaxing coronary blood pressure fatigue or withhold medication,
and vascular and makes it weakness contact physician). Assess
muscles, and easier for the (asthenia). for peripheral edema
decreasing heart to pump Adverse Side behind medial malleolus
peripheral blood around Effects: (sacral area in bedridden
resistance your body. Overdose may pts). Assess skin for flushing.
Therapeutic produce Question for headache,
outcome: excessive asthenia.64 amoxicillin
Decreased B/P peripheral underlined – top
vasodilation, prescribed drug
PATIENT/FAMILY
marked TEACHING
hypotension with • Do not abruptly
reflex discontinue medication.
tachycardia, • Compliance with
syncopy therapy regimen is
essential to control
hypertension.
• Avoid tasks that require
alertness, motor skills until
response to drug is
established.
• Do not ingest grapefruit
products.
• Advise patient to avoid
hazardous activities until
stabilized on product,
dizziness is no longer a
problem
• Instruct patient to avoid
alcohol and OTC products
unless directed by prescriber
• Advise patient to comply in
all areas of medical regimen:
diet, exercise, stress reduction,
smoking cessation, product
therapy; to notify prescriber of
irregular heartbeat, shortness of
breath, swelling of feet, face,
and hands, severe dizziness,
constipation, nausea,
hypotension; use nitroglycerin
when angina is severe
• Teach patient to use as
directed even if feeling better;
may be taken with other
cardiovascular products
(nitrates, b-blockers)
• Advise to avoid large
amounts of grapefruit juice or
alcohol
MEDICATION INDICATION MECHANISM OF MECHANISM OF SIDE EFFECTS AND NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
ACTION ACTION IN ADVERSE EFFECTS
RELATION TO THE
PATIENT’S CASE
TRAMADOL 50 MG Indication: Binds to mu-opioid In the spinal cord, Side Effects: BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Management of receptors, inhibits opioids act on Frequent: Assess onset, type,
Generic Name: moderate to reuptake of specific receptors Dizziness, vertigo, location, duration of pain.
Tramadol moderately norepinephrine, located in pre- nausea, Assess drug history, esp.
Brand Name: severe pain. serotonin, and postsynaptic constipation, carbamazepine,
Ultram, Tramadol Extended- inhibiting synapses in the headache, analgesics, CNS
Hydrochloride ER, Release: Around- ascending and dorsal horn. Pre drowsiness. depressants, MAOIs.
Tramal, Ultram ER the-clock descending pain synaptically, Occasional: Review past medical
management of pathways. opioids decrease Vomiting, pruritus, history, esp. epilepsy,
moderate to Therapeutic Effect: the release of CNS stimulation seizures. Assess renal
moderately Reduces pain. specific pain (e.g., nervousness, function, LFT.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATI
severe pain for neurotransmitters anxiety, agitation, ON
extended period. (i.e. substance P), tremor, euphoria, Monitor pulse, B/P,
while in the mood swings, renal/hepatic function. Dry
postsynaptic hallucinations), crackers, cola may relieve
neuron they asthenia, nausea. Palpate bladder
decrease diaphoresis, for urinary retention.
excitability. Opioid dyspepsia, dry Monitor daily pattern of
receptors produce mouth, diarrhea. bowel activity, stool
their analgesic Rare: Malaise, consistency. Sips of water
effects in the vasodilation, may relieve dry mouth.
spinal cord by anorexia, Assess for clinical
coupling with G- flatulence, rash, improvement, record onset
proteins to both blurred vision, of relief of pain.
PATIENT/FAMILY
alter synaptic urinary retention/ TEACHING
transmission at frequency, • May cause
pain pathways menopausal dependence.
and to decrease symptoms. • Avoid alcohol, OTC
neuronal medications (analgesics,
excitability via the Adverse Side sedatives).
inhibition of cyclic Effects: Seizures • May cause drowsiness,
adenosine reported in pts dizziness, blurred vision.
monophosphate receiving • Avoid tasks requiring
(cAMP). tramadol within alertness, motor skills until
recommended response to drug is
dosage range. established.
May have • Report severe constipation,
prolonged difficulty breathing, excessive
duration of sedation, seizures, muscle
action, weakness, tremors, chest pain,
cumulative effect palpitations.
in pts with
hepatic/renal
impairment,
serotonin
syndrome
(agitation,
hallucinations,
tachycardia,
hyperreflexia).
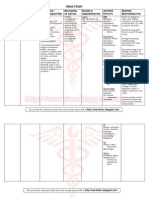
MEDICATION INDICATION MECHANISM OF MECHANISM OF SIDE EFFECTS AND NURSING
ACTION ACTION IN ADVERSE EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITIES
RELATION TO THE
PATIENT’S CASE
CARVEDILOL Hypertension. HF with Block’s stimulation of Carvedilol promotes CNS: dizziness, fatigue, •Monitor BP and pulse
digoxin, diuretics, and beta 1 (myocardial) and neurological function, weakness, anxiety, frequently during dose
Generic Name: ACE inhibitors. Left beta 2 (pulmonary, reduces bone loss and depression, drowsiness, adjustment period and
Carvedilol ventricular dysfunction vascular, and uterine)- attenuates cell damage insomnia, memory loss, periodically during
Brand Name: after MI. adrenergic receptor after acute spinal cord mental status changes, therapy.
Coreg, Coreg CR sites. Also has alpha 1 injury. nervousness, •Assess for orthostatic
blocking activity, which nightmares. EENT: hypotension when
may result in orthostatic blurred vision, dry eyes, assisting
hypotension. intraoperative floppy patient up from supine
Therapeutic Effects: iris syndrome, nasal position.
Decreased heart rate stuffiness. Resp: •Monitor intake and
and BP. Improved bronchospasm, output ratios and daily
cardiac output, slowing wheezing. CV: weight.
of the progression of BRADYCARDIA, HF, •Assess patient
HF and decreased risk PULMONARY routinely for evidence
of death. EDEMA. GI: diarrhea, of fluid overload
constipation, nausea. (peripheral edema,
GU: erectile dyspnea, rales/crackles,
dysfunction, libido. fatigue, weight gain,
jugular venous
distention). Patients
may experience
worsening of symptoms
during initiation of
therapy for HF.
MEDICATION INDICATION MECHANISM OF MECHANISM OF SIDE EFFECTS AND NURSING
ACTION ACTION IN ADVERSE EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITIES
RELATION TO THE
PATIENT’S CASE
TAMSULOSIN Management of outflow Decreases contractions Tamsulosin is used in CNS: dizziness, headache. •Assess patient for
obstruction in male in smooth muscle of men to treat the EENT: rhinitis. CV: symptoms of prostatic
Generic Name: patients with prostatic the prostatic capsule by symptoms of an orthostatic hypotension. hyperplasia (urinary
Carvedilol hyperplasia. preferentially binding enlarged prostate GU: priapism, hesitancy, feeling of
Brand Name: to alpha1-adrenergic (benign prostatic retrograde/diminished incomplete bladder
Flomax receptors. Therapeutic hyperplasia or BPH) ejaculation. emptying, interruption
Effects: Decreased which include of urinary stream,
symptoms of prostatic difficulty urinating. impairment of size and
hyperplasia. force of urinary stream,
terminal urinary
dribbling, straining to
start flow, dysuria,
urgency) before and
periodically during
therapy.
•Assess patient for first-
dose orthostatic
hypotension and
syncope. Incidence may
be dose related.
Observe patient closely
during this period and
take precautions to
prevent injury.
•Monitor intake and
output ratios and daily
weight, and assess for
edema daily, especially
at beginning of therapy.
Report weight gain or
edema.
MEDICATION INDICATION MECHANISM OF MECHANISM OF SIDE EFFECTS AND ADVERSE NURSING
ACTION ACTION IN EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITIES
RELATION TO
THE PATIENT’S
CASE
PREGABALIN Neuropathic pain Binds to calcium Pregabalin is an CNS: SUICIDAL THOUGHTS, •Monitor closely for
associated with channels in CNS anticonvulsant drug dizziness, drowsiness, impaired notable changes in
Generic Name: diabetic peripheral tissues which regulate used to treat attention/concentration/thinking. CV: behavior that could
Pregabalin neuropathy. neurotransmitter neuropathic pain edema. EENT: blurred vision. GI: dry indicate the
Brand Name: Postherpetic release. Does not bind conditions and mouth, abdominal pain, constipation emergence or
Lyrica neuralgia. to opioid receptors. fibromyalgia worsening of suicidal
Fibromyalgia. Therapeutic Effects: thoughts or behavior
Neuropathic pain Decreased or depression.
associated with neuropathic or post- •Seizures: Assess
spinal cord injury. herpetic pain. location, duration,
Adjunctive therapy Decreased partial- and characteristics of
of partial-onset onset seizures. seizure activity.
seizures in adults. •Caution patient to
avoid driving or
activities requiring
alertness until
response to
medication is known.
You might also like
- National Geographic December 2015Document170 pagesNational Geographic December 2015AnaAna100% (3)
- Journal # 1 of Module 2 (Sandiwa) : Your Presence Gives Justice!Document1 pageJournal # 1 of Module 2 (Sandiwa) : Your Presence Gives Justice!Keanu PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Neuropathic Pain SlidesDocument28 pagesNeuropathic Pain SlidesAndrias Oz100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyKeanu PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Indications Actions Side Effects / Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Patient TeachingDocument10 pagesDrugs Indications Actions Side Effects / Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Patient TeachingTyrone IglesiasNo ratings yet
- HF and CAD Case ScenarioDocument17 pagesHF and CAD Case ScenarioElla Neiza AngelesNo ratings yet
- NCP DS NCM114 RleDocument12 pagesNCP DS NCM114 RleAllysa Kyle AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- TAMBALDocument4 pagesTAMBALVianca Kate MarquezNo ratings yet
- Ate Mitch HN DRUG STUDYDocument23 pagesAte Mitch HN DRUG STUDYMarice VenNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-CardioDocument7 pagesDrug Study-CardioCharmaine ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Categorize The Treatment Options For Patients With Existing Medical ConditionDocument3 pagesCategorize The Treatment Options For Patients With Existing Medical ConditionMicah LatosaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyJenniferValmocenaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study D InsipidusDocument7 pagesDrug Study D InsipidusAisha MarieNo ratings yet
- Drug Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Considerations Generic Name: Brand NameDocument8 pagesDrug Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Considerations Generic Name: Brand Namekuu faalNo ratings yet
- (Per System Preferably) : AntihypertensiveDocument4 pages(Per System Preferably) : AntihypertensiveGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Enalapril, Metropolol, Aspirin, CiticolineDocument8 pagesEnalapril, Metropolol, Aspirin, CiticolineGabriel MatibagNo ratings yet
- LC DX StudyDocument2 pagesLC DX StudyJhexy Rhay BayagenNo ratings yet
- Johnlevy, ENDODocument3 pagesJohnlevy, ENDOAERONH JOHN PURIFICANDONo ratings yet
- LosartanDocument2 pagesLosartanAngeliqueNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyLester Paul SivilaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Omeprazole & LosartanDocument4 pagesDrug Study - Omeprazole & LosartanCarla Tongson MaravillaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyPauline AñesNo ratings yet
- DRUGSTUDY Update (Table 3)Document5 pagesDRUGSTUDY Update (Table 3)SONY MANDAPNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs: Drug Action Indications Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Management Atropine SulfateDocument15 pagesEmergency Drugs: Drug Action Indications Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Management Atropine Sulfate092109No ratings yet
- ER BatMC 2 Drug StudyDocument4 pagesER BatMC 2 Drug StudyFalqueza JanelleNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Losartan)Document1 pageDrug Study (Losartan)Baji ۦۦNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Cva Drug StudyDocument5 pagesCva Drug Studykristine86badgirlNo ratings yet
- Atropine Sulfate Indications: Adverse Effects: CNS: Headache, Ataxia, Contraindication: Assessment & Drug EffectsDocument4 pagesAtropine Sulfate Indications: Adverse Effects: CNS: Headache, Ataxia, Contraindication: Assessment & Drug EffectsMarie Kris Chua AbelleraNo ratings yet
- Drug LordsDocument25 pagesDrug LordsGlen DaleNo ratings yet
- ParaDocument2 pagesParaMary Kate ClarosNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of FurosemideDocument5 pagesDrug Study of FurosemideAntonette Lei100% (1)
- EnalaprilDocument4 pagesEnalaprilGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NamehahahaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudySocial BaeNo ratings yet
- Sweet Glomerulus: A Case of Diabetic NephropathyDocument9 pagesSweet Glomerulus: A Case of Diabetic NephropathyRon OpulenciaNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Dopamine Indications Contraindications Mechanism of Action Common Side-Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument4 pagesDrug Name Dopamine Indications Contraindications Mechanism of Action Common Side-Effects Nursing ConsiderationsPRINCESS LARA CASILAONo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument21 pagesDrug StudyRhuby Pascual AbenojaNo ratings yet
- Final Drug StudyDocument14 pagesFinal Drug StudyStephany Rae MamauagNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage, Frequency, Route, Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument13 pagesName of Drug Dosage, Frequency, Route, Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilitieskev mondaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Captopril)Document1 pageDrug Study (Captopril)Baji ۦۦNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - IbuprofenDocument2 pagesDrug Study - Ibuprofenanon-326479No ratings yet
- Escaran - Drug Study - Set ADocument4 pagesEscaran - Drug Study - Set AFrancis Alfred EscaranNo ratings yet
- CaptoprilDocument2 pagesCaptoprilVina Jane P Laurel100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyAnne Marie BuenvenidaNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Action Indication Contraindicat Ions Side Effects Nursing Considerations GenericDocument3 pagesDrug Name Action Indication Contraindicat Ions Side Effects Nursing Considerations GenericGenevang SeaweedsNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument28 pagesDrug Studyginosan100% (1)
- Drug Study CardioDocument7 pagesDrug Study CardioCharmaine ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive - ABCDDocument5 pagesAntihypertensive - ABCDTingCheung100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY-1st BatchDocument27 pagesDRUG STUDY-1st BatchCanny CańasNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic Class: Therapeutic Class: Atypical: Dibenzothiazepine Derivative AntipsychoticDocument2 pagesPharmacologic Class: Therapeutic Class: Atypical: Dibenzothiazepine Derivative AntipsychoticBianca Nicole Gacad Fernandez100% (1)
- Med LopressorDocument2 pagesMed LopressorDeanna Lang ThibodauxNo ratings yet
- Tolvaptan-Drug StudyDocument1 pageTolvaptan-Drug Studykaycelyn jimenez100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyArnel MacabalitaoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - LosartanDocument2 pagesDrug Study - LosartanCath Bril50% (2)
- A.2 Category B and e Pharma ActDocument7 pagesA.2 Category B and e Pharma ActMichael Angelo CarballoNo ratings yet
- 13 Med MNGTDocument19 pages13 Med MNGTKate ChavezNo ratings yet
- Antidepressants, Antihistamines, General Anesthetics, MAO Inhibitors, OpioidsDocument3 pagesAntidepressants, Antihistamines, General Anesthetics, MAO Inhibitors, Opioidskaycelyn jimenezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 4C Case 2 Final PDFDocument18 pagesDrug Study 4C Case 2 Final PDFRegine Kate JuntoNo ratings yet
- Captopril Is An ACE Inhibitor and Works by Relaxing Blood Vessels So That Blood Can Flow More EasilyDocument4 pagesCaptopril Is An ACE Inhibitor and Works by Relaxing Blood Vessels So That Blood Can Flow More EasilyKsksksksNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- TeenPreg Juvenile Seminar (Edited)Document2 pagesTeenPreg Juvenile Seminar (Edited)Keanu PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Simple and Compound InterestDocument17 pagesSimple and Compound InterestKeanu PeraltaNo ratings yet
- BLOGDocument1 pageBLOGKeanu PeraltaNo ratings yet
- CL Final ExamDocument2 pagesCL Final ExamKeanu PeraltaNo ratings yet
- EAPP ReviewerDocument12 pagesEAPP ReviewerKeanu PeraltaNo ratings yet
- OCIC ReviewerDocument3 pagesOCIC ReviewerKeanu PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Neuro Curse HeroDocument10 pagesNeuro Curse HeroKeanu PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Into-Philo ReviewerDocument1 pageInto-Philo ReviewerKeanu PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Journal #5 (Sambuhay) : Your Presence Proclaims The Grandeur of God's CreationDocument2 pagesJournal #5 (Sambuhay) : Your Presence Proclaims The Grandeur of God's CreationKeanu PeraltaNo ratings yet
- 23 Eqed 23Document10 pages23 Eqed 23Keanu PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Journal #5 (Sambuhay) : Your Presence Proclaims The Grandeur of God's CreationDocument2 pagesJournal #5 (Sambuhay) : Your Presence Proclaims The Grandeur of God's CreationKeanu PeraltaNo ratings yet
- The Philippine Indigenous Peoples: Keanu Gybs C. Peralta BSN 3 - CFE 5106 CDocument8 pagesThe Philippine Indigenous Peoples: Keanu Gybs C. Peralta BSN 3 - CFE 5106 CKeanu PeraltaNo ratings yet
- The Philippine Indigenous Peoples: Keanu Gybs C. Peralta BSN 3 - CFE 5106 CDocument27 pagesThe Philippine Indigenous Peoples: Keanu Gybs C. Peralta BSN 3 - CFE 5106 CKeanu PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Journal #4 (Sambuhay) : "Come and Celebrate With The Joy of Your Master."Document2 pagesJournal #4 (Sambuhay) : "Come and Celebrate With The Joy of Your Master."Keanu PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Week 6-February 27Document2 pagesWeek 6-February 27Keanu PeraltaNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument20 pagesDrugsLee Won100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument16 pagesDrug StudypamelaideaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology. Sedative HypnoticDocument16 pagesPharmacology. Sedative HypnoticJean FlorencondiaNo ratings yet
- DPS 2011 2 6 127 131Document5 pagesDPS 2011 2 6 127 131anuradha.d.bhat9860No ratings yet
- Treatment of Diabetic Neuropathy - UpToDateDocument20 pagesTreatment of Diabetic Neuropathy - UpToDateKarina MilaréNo ratings yet
- MetanxDocument18 pagesMetanxDougNo ratings yet
- Adjuvants DrugsDocument38 pagesAdjuvants DrugsIppank F SjNo ratings yet
- Pregabalin Sciecure 25 MG, 50 MG, 75 MG, 100 MG, 150 MG, 200 MG, 225 MG, 300 MG Hard CapsulesDocument8 pagesPregabalin Sciecure 25 MG, 50 MG, 75 MG, 100 MG, 150 MG, 200 MG, 225 MG, 300 MG Hard CapsulesA-OUafi SeDDikiNo ratings yet
- PAMI Pain Mangement and Dosing Guide 02282017Document2 pagesPAMI Pain Mangement and Dosing Guide 02282017Hawsin100% (1)
- Comparative Role of Pregabalin and Carbamazepine Regarding Efficacy in Painful Diabetic NeuropathyDocument4 pagesComparative Role of Pregabalin and Carbamazepine Regarding Efficacy in Painful Diabetic NeuropathyNur AyuNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyMa R DyNo ratings yet
- Pre Gabal in Drug StudyDocument1 pagePre Gabal in Drug StudyHailMarieSBarcenasNo ratings yet
- Pregabalin, Celecoxib, and Their Combination For Treatment of Chronic Low-Back PainDocument7 pagesPregabalin, Celecoxib, and Their Combination For Treatment of Chronic Low-Back Painskola onlajnNo ratings yet
- Pregabalin An Anticonvulsant DrugDocument2 pagesPregabalin An Anticonvulsant DrugmeimeiliuNo ratings yet
- PAMI Dosing Guide Nov.2.2020Document2 pagesPAMI Dosing Guide Nov.2.2020Rafael RiveraNo ratings yet
- Effects of Preoperative Pregabalin On Outcome of Spinal Anaesthesia For Patients Undergoing Open MyomectomyDocument8 pagesEffects of Preoperative Pregabalin On Outcome of Spinal Anaesthesia For Patients Undergoing Open Myomectomyema moralesNo ratings yet
- UKMi QA Brand-Name Prescribing Update Nov2017 PDFDocument9 pagesUKMi QA Brand-Name Prescribing Update Nov2017 PDFMarcelitaTaliaDuwiriNo ratings yet
- The Biopharmaceutical Classification System (BCS) : DR Mohammad IssaDocument24 pagesThe Biopharmaceutical Classification System (BCS) : DR Mohammad IssaDevi IndrianiNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic DrugsDocument65 pagesAntiepileptic DrugsZarish IftikharNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Pregabalin With PramipexoleDocument49 pagesComparison of Pregabalin With PramipexoleFrans JobethNo ratings yet
- Ogrania: Pregabalin 75 MG CapsulesDocument9 pagesOgrania: Pregabalin 75 MG Capsulesمصطفى الجبوريNo ratings yet
- Adjuvant AnalgesicsDocument44 pagesAdjuvant AnalgesicsZulfan EfendiNo ratings yet
- Art of Drug SynthesisDocument6 pagesArt of Drug SynthesisAlok Kumar Sharma0% (1)
- Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of Pregabalin Treatment For Paintful Diabetic Peripheral NeurophatyDocument7 pagesEfficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of Pregabalin Treatment For Paintful Diabetic Peripheral NeurophatyadityaNo ratings yet
- Fibromyalgia: by Tara E. Dymon, Pharm.D., BCACPDocument14 pagesFibromyalgia: by Tara E. Dymon, Pharm.D., BCACPAnggi CalapiNo ratings yet
- Meganeuron OD Plus Capsule - View Uses, Side Effects, Price and Substitutes - 1mgDocument4 pagesMeganeuron OD Plus Capsule - View Uses, Side Effects, Price and Substitutes - 1mgAMITAVA RAYNo ratings yet
- Formulary - 2014Document20 pagesFormulary - 2014vijay kumarNo ratings yet
- Fibromyalgia Pathogenesis and Treatment Options Update (2016) PDFDocument10 pagesFibromyalgia Pathogenesis and Treatment Options Update (2016) PDFBecados PsiquiatriaNo ratings yet