Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gove Operations Process Flow Single Page
Gove Operations Process Flow Single Page
Uploaded by
Mayke Cezar WippelOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gove Operations Process Flow Single Page
Gove Operations Process Flow Single Page
Uploaded by
Mayke Cezar WippelCopyright:
Available Formats
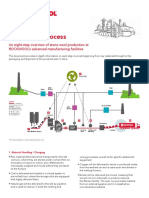
Mining Operations
Gove Operations bauxite mine and alumina refinery is located on the Gove Peninsula in the east Arnhem Land region of
Australia’s Northern Territory. From this remote location Gove operations supplies alumina for the international
aluminium industry.
1. Tree Clearing 2. Overburden
Timber clearing is carried out two to five years prior to mining. This The bauxite deposit is overlain by less than one metre of overburden
allows all the understorey plant species to propagate within the and topsoil. The overburden and topsoil is returned directly to mined
topsoil. It also helps the various bacteria in the topsoil to flourish areas as part of the rehabilitation process. A twin engine scraper
creating a healthy and viable topsoil. The redistribution of the topsoil removes approximately 50 per cent of the overburden. The remaining
on mined areas is a key part of our rehabilitation process overburden is removed by the truck and loader fleet.
3. Rehabilitation 4. Mining
As part of the rehabilitation program, seeds and plant species from
the area to be mined are collected, with the assistance of local The bauxite ore is mined using track bulldozers which rip the bauxite
indigenous people, carefully catalogued and stored. The topsoil is re- and push it into stockpiles. Front-end loaders then load the ore into
laid over the prepared areas and area is ‘deep-ripped’ to promote trucks which transport the ore to the crusher. Prior to mining, grade
drainage, aeration and root penetration. This step, which is the control drilling is undertaken to establish the grade of ore in each
nucleus of the regeneration program, preserves the soil biota and area of the mine. The mined ore from various areas of the mine is
encourages plant regeneration. The area is then planted and blended to ensure the ore meets the specifications required in the
fertilised immediately before the commencement of the wet season. refinery.
5. Crushing and Screening 6. Bauxite Stockpiles
The haul trucks dump the bauxite into a hopper at the crusher. It then The crushed bauxite is stacked at the refinery on stockpiles. It is
passes through a primary crusher, screening plant and secondary laid down on the stockpiles by a stacker that constantly passes up
crusher to produce material that is less than 25mm in size. The ore is and down the stack being built to ensure a uniform grade of bauxite.
held in 1700 tonne surge bins before being transported to the refinery There are four 100,000 tonne stockpiles and crushed bauxite is
on the 18.7 kilometre overland conveyor. reclaimed from the stockpiles by either a barrel reclaimer or a
bucket reclaimer.
Refinery
Operations
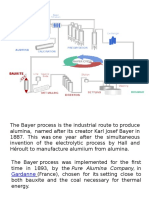
Gove Operations uses the Bayer alumina
production process developed by Austrian 1. Grinding
chemist Karl Joseph Bayer in 1888. The Bauxite ore is ground to a fine powder in three grinding mills before
being mixed with caustic soda to form a slurry.
main stages in the refining process are as
follows:
4. Security Filtration 5. Mud Washing
Bauxite residue is washed to recover as much caustic as possible
Liquor is pumped to security filtration where Kelly and Gaudfrin filters
prior to the mud being pumped to the Residue Disposal Area. The
remove fine bauxite residue particles from the turbid liquor that is not
caustic is washed from the bauxite residue using recycled
settled in ferrosilt.
condensate in a counter-current washing process. Recovered caustic
is recycled from mud washing.
8. Precipitation 9. Hydrate Classification
With the sand and mud removed, the solution is filtered and cooled Hydro-cyclones in classification separate the slurry into three sizes;
before being ‘seeded’ with crystals of alumina tri-hydrate, causing the product, fine seed and coarse seed.
alumina trihydrate in the solution to deposit in solid form around the
seed crystals.
12. Silos 13. Port
The alumina is stored in concrete silos until it is conveyed via the Situated in Melville Bay, the port facility is connected to the refinery
export conveyor to waiting bulk carriers. by a 3 kilometre conveyor loading up to 2,000 tonnes of alumina per
hour. The port has two tugs named Baru and Guya, which in Yolgnu
Matha, the local language, mean crocodile and fish.
2. Digestion 3. Ferrosilt
The slurry is heated to 145°C in low temperature digestion and 220°C After cooling, the slurry is pumped into large tanks where bauxite
in high temperature digestion. The combination of caustic soda and residue is separated, washed and pumped to a residue disposal
heat dissolves the aluminium oxide out of the bauxite. Following area. Bauxite residue is separated from alumina rich caustic slurry in
digestion, the slurry passes though a series of flash vessels which large tanks called high rate decanters. Polymer is added to assist in
reduce the pressure and allow the steam to flash off. the settling of bauxite residue.
6. Geho Pumps 7. Evaporation
Large positive displacement Geho pumps are used to deliver high The evaporation plant removes water from spent caustic liquor to
density bauxite residue waste to the Residue Disposal Area. enable the liquor to be recycled to the digestion area. The water
evaporated from the liquor is condensed and recycled in the mud
washing process.
10. Hydrate Filtration 11. Calcination
The slurry is filtered through disc filters to remove liquor which is then After being washed and filtered, the alumina trihydrate is heated to
returned to evaporation. The product from the pan filters is conveyed 1,100°C in large kilns to dry it and drive off the chemically bound
to calcination, and the hydrate from the disc filters is recycled back to water molecules, transforming it from alumina tri-hydrate to alumina,
precipitation as a seed. a fine white powder. Gove has four rotary kilns and three fluid bed
calciners.
14. Lime Kiln 15. Residue Disposal
The lime kiln is heated by fuel oil. The limestone is burnt in the kiln, Bauxite residue from the refining process is drystacked at the
transformed into burnt lime and then slaked with water to produce Residue Disposal Area. Dry stacking is an efficient disposal method
milk of lime which is pumped to Redside (used for filter aid which provides environmental benefits including the need for less
preparation and impurities control). area and improved rehabilitation.
Refinery Process Flow
www.pacificaluminium.com.au
You might also like
- Djj10022 Fitting ReportDocument7 pagesDjj10022 Fitting ReportTamil passang songNo ratings yet
- Coal Processing MethodsDocument3 pagesCoal Processing MethodsMael MohammedNo ratings yet
- Methods, Processes, and Equipment Involved in Manufacturing CementDocument22 pagesMethods, Processes, and Equipment Involved in Manufacturing Cementanon_497391427No ratings yet
- Alumina RefiningDocument9 pagesAlumina RefiningAtik Faysal AyonNo ratings yet
- The Bayer Process Was Invented and Patented in 1887 by Austrian Scientist Karl Josef BayerDocument3 pagesThe Bayer Process Was Invented and Patented in 1887 by Austrian Scientist Karl Josef Bayeracanis1016No ratings yet
- Alumina ProcessDocument16 pagesAlumina Processashwini_kumar1984No ratings yet
- Sugar Industry EvaporatorDocument17 pagesSugar Industry EvaporatorScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Carmen Copper CorporationDocument9 pagesCarmen Copper CorporationMariel Mae A. MaculbeNo ratings yet
- Notes On Production of Beer: 1.1.1. Raw Material Handling and StorageDocument10 pagesNotes On Production of Beer: 1.1.1. Raw Material Handling and Storagetap isko006No ratings yet
- 1Document12 pages1PRAVEEN KUMARNo ratings yet
- AppendixT NitrocelluloseManufacturingProcessDocument8 pagesAppendixT NitrocelluloseManufacturingProcesswahnobeldfNo ratings yet
- Cement ProcessDocument14 pagesCement ProcessChristian RuedaNo ratings yet
- KMML 2013Document13 pagesKMML 2013KuttikuttanNo ratings yet
- Part B GBDDocument15 pagesPart B GBDP.Prithivi RajNo ratings yet
- Educational Trip To Sasini Coffee FactoryDocument5 pagesEducational Trip To Sasini Coffee Factoryjobkazi9725No ratings yet
- Cleaner Production Assessment in CementDocument5 pagesCleaner Production Assessment in CementMadanKarkiNo ratings yet
- Pictorial Diagram of The Bayer Process 2Document6 pagesPictorial Diagram of The Bayer Process 2natsmdNo ratings yet
- iCON SB150 Professional Plant PDFDocument18 pagesiCON SB150 Professional Plant PDFmurci2929No ratings yet
- Mumias Sugar Company ReportDocument49 pagesMumias Sugar Company Reportstephenbwogora50% (4)
- Grain Distillery ProcessDocument7 pagesGrain Distillery Processkem_engr7682No ratings yet
- The Use of Heavy-Medium Separation in The Processing of Iron OresDocument4 pagesThe Use of Heavy-Medium Separation in The Processing of Iron OresaghilifNo ratings yet
- Viscose RayonDocument30 pagesViscose Rayonnaimur.7566No ratings yet
- A Case Study in Lime Production: No.2. Improved Techniques at Chenkumbi, MalawiDocument6 pagesA Case Study in Lime Production: No.2. Improved Techniques at Chenkumbi, MalawiMilian Asha Bio MuradNo ratings yet
- My RecordsDocument16 pagesMy RecordsKolawole KehindeNo ratings yet
- Savaksha Distallery DetailDocument30 pagesSavaksha Distallery DetailRakesh GairolaNo ratings yet
- Energy Technology: Processing of Solid FuelsDocument30 pagesEnergy Technology: Processing of Solid FuelsParth PatelNo ratings yet
- Bisleri InternshipDocument14 pagesBisleri Internshipvishnu kpNo ratings yet
- GLT 3137C Albion FS Copper Concentrates ENG 07-SRDocument14 pagesGLT 3137C Albion FS Copper Concentrates ENG 07-SRGERMAN YENKA RAMOS OXANo ratings yet
- PPoMP 2017 53 2 893 907Document10 pagesPPoMP 2017 53 2 893 907Eduardo CandelaNo ratings yet
- Introduction - History of The Organization - Special FeaturesDocument24 pagesIntroduction - History of The Organization - Special Featuressrinibashb5546No ratings yet
- Caustic Soda ManufactureDocument14 pagesCaustic Soda Manufacturenikhilchhatre100% (1)
- Industry Sectors - CementDocument16 pagesIndustry Sectors - CementCrestian Nebreja MortaNo ratings yet
- Principles of MillingDocument5 pagesPrinciples of MillingjasmenenojasNo ratings yet
- Us4994244 PDFDocument11 pagesUs4994244 PDFSyifaNo ratings yet
- Cooling Water Male Up Pump HouseDocument1 pageCooling Water Male Up Pump HouseAngel Tania BasuNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Location and Size of The PlantDocument21 pages2.1 Location and Size of The PlantRizelle VinaraoNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Presentation at UNITED BREWERIES LTD. LUDHIANADocument21 pagesSummer Training Presentation at UNITED BREWERIES LTD. LUDHIANAketan171092No ratings yet
- Implementation of Mathematical Equation For Calculating Alumina Extraction From Bauxite Tailing ExtractionDocument6 pagesImplementation of Mathematical Equation For Calculating Alumina Extraction From Bauxite Tailing ExtractionSyifaNo ratings yet
- Portland Cement ManufacturingDocument7 pagesPortland Cement ManufacturingCynric Leonardo100% (2)
- AGRO-industrial Attachment - II (AIA 414)Document26 pagesAGRO-industrial Attachment - II (AIA 414)love singhNo ratings yet
- Overall Increase in Efficiency in Raw MeDocument6 pagesOverall Increase in Efficiency in Raw MeMadanKarkiNo ratings yet
- FI-465 Potash Ore ProcessingDocument7 pagesFI-465 Potash Ore ProcessingtrinhtrungNo ratings yet
- Submitted To: Tewodros Ali Submitted Date:mar15/2021Document13 pagesSubmitted To: Tewodros Ali Submitted Date:mar15/2021LamiNo ratings yet
- Ash Handling System For Utility BoilersDocument15 pagesAsh Handling System For Utility BoilersSulakshana Muramalla100% (4)
- Merrill-Crowe Precipitate Acid Treatment Optimization ProposalDocument5 pagesMerrill-Crowe Precipitate Acid Treatment Optimization ProposalruelonepieceNo ratings yet
- Pasar PDFDocument70 pagesPasar PDFRalph Carlo EvidenteNo ratings yet
- A. Indira National Power Training InstituteDocument80 pagesA. Indira National Power Training InstituteAyan MajiNo ratings yet
- RefineryDocument14 pagesRefinerykrishna sharmaNo ratings yet
- Ash Handling SystemDocument19 pagesAsh Handling Systemrach1t.s1n9hNo ratings yet
- Rockwool Stone Wool Manufacturing Production Process Fact SheetDocument2 pagesRockwool Stone Wool Manufacturing Production Process Fact Sheetprashant_salima6377No ratings yet
- Outline For Calcium Carbonate ProcessDocument9 pagesOutline For Calcium Carbonate ProcessRobert DsouzaNo ratings yet
- The Oil Sands ProcessDocument2 pagesThe Oil Sands Processdaffodils2No ratings yet
- Limestone FinesDocument9 pagesLimestone FinesgrestemNo ratings yet
- Extraction & Characterization of Silica From Rice HuskDocument16 pagesExtraction & Characterization of Silica From Rice HuskShreyanshu Agrawal100% (1)
- Draft: Is No. TitleDocument8 pagesDraft: Is No. TitleRajeshkumar ElangoNo ratings yet
- KelvinoDocument21 pagesKelvinoalefiya razeeNo ratings yet
- Wissington FactoryDocument3 pagesWissington Factoryjgascoine011No ratings yet
- CIE 316 LimeDocument6 pagesCIE 316 LimeinnocentNo ratings yet
- AbebeDocument19 pagesAbebesofi dollaNo ratings yet
- Lignin Process Kraft 42400 - v1 - 17Document27 pagesLignin Process Kraft 42400 - v1 - 17V U P RaoNo ratings yet
- 10.5 Extraction of MetalsDocument19 pages10.5 Extraction of MetalsUmida ZaylobiddinovaNo ratings yet
- Amasuomo E and Baird J. 2016. The Concept of Waste and Waste Management. J. Manage. Sustain. 6 (4) :88-96Document4 pagesAmasuomo E and Baird J. 2016. The Concept of Waste and Waste Management. J. Manage. Sustain. 6 (4) :88-96Kedamawi RecordsNo ratings yet
- Welding DefectsDocument15 pagesWelding DefectsMohamed Al-OdatNo ratings yet
- Cobra ShakersDocument2 pagesCobra ShakersAku NoshNo ratings yet
- HDPE Manufacturer RecommendationDocument3 pagesHDPE Manufacturer Recommendation721917114 47100% (1)
- Zintek® 300 HP + Techseal® Glossy Black SLDocument9 pagesZintek® 300 HP + Techseal® Glossy Black SLSyedMazharAliShahNo ratings yet
- Production ESE GATE 2020Document500 pagesProduction ESE GATE 2020NAMAN GARG CO18139No ratings yet
- Brother EF4 B956CDocument31 pagesBrother EF4 B956CMartin JauckNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Advanced Plasma Processing Techniques Book ReviewDocument1 pageHandbook of Advanced Plasma Processing Techniques Book Reviewmustafa alasadyNo ratings yet
- 20CHT394-Advanced Wastewater Treatment TechniquesDocument6 pages20CHT394-Advanced Wastewater Treatment TechniquesULLAS KRISHNAN J NNo ratings yet
- Kiompl SFQP Mech-R1Document21 pagesKiompl SFQP Mech-R1mukherjeemohul25No ratings yet
- Quiz and Answers - Group 2Document6 pagesQuiz and Answers - Group 2Paul Christian PerezNo ratings yet
- Rotary Tool KitDocument13 pagesRotary Tool KitjorgeNo ratings yet
- Aisi H10Document6 pagesAisi H10Diego ParedesNo ratings yet
- KMBD Mech BoostersDocument2 pagesKMBD Mech BoostersMark V FarrellNo ratings yet
- Process CostingDocument12 pagesProcess CostingKylie Luigi Leynes BagonNo ratings yet
- Densit WearCast 2000 11-17 1515493405Document2 pagesDensit WearCast 2000 11-17 1515493405Cioz NguyenNo ratings yet
- TD DuroglossDocument2 pagesTD DuroglossSigit Adhy PratamaNo ratings yet
- Structured Method Statement For Concrete Repair - 1Document15 pagesStructured Method Statement For Concrete Repair - 1m.umar100% (1)
- Forklift ZoomlionDocument2 pagesForklift ZoomlionWarishNo ratings yet
- Steel Grades en 10028 AstmDocument24 pagesSteel Grades en 10028 AstmYahya AljarokNo ratings yet
- Lec Solid Waste ManagementDocument31 pagesLec Solid Waste Managementkhloud rafatNo ratings yet
- Reduccion Concentrica 6 X 4 SCH 40 X SCH 40 16814Document1 pageReduccion Concentrica 6 X 4 SCH 40 X SCH 40 16814antoniosofwareNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Lean Supply Chain ManagementDocument76 pagesChapter 16 Lean Supply Chain ManagementAnh NguyenNo ratings yet
- PG-21-Series 1-1 PH-63 Rev. Dec. 2022Document2 pagesPG-21-Series 1-1 PH-63 Rev. Dec. 2022Francisco Rodríguez100% (1)
- VeneersDocument8 pagesVeneersBob CalebNo ratings yet
- How To Measure Roller UnoutDocument6 pagesHow To Measure Roller UnoutMakrem CherifNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Uni L SNB 36Document4 pagesDatasheet Uni L SNB 36Bluemonday BluemondayNo ratings yet