Professional Documents
Culture Documents
المحاضرة العاشرة
المحاضرة العاشرة
Uploaded by
sedra toofyOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
المحاضرة العاشرة
المحاضرة العاشرة
Uploaded by
sedra toofyCopyright:
Available Formats
Basrah Engineering Techinical College
Department of Environment and Pollution Industrial Safety
Lecture: 10 Fourth Year,
Definitions:
PEL: This number is the calculated permissible exposure limit for dust to which
the worker may be exposed. It uses the data you supplied and is based on the percent
crystalline silica in the sample. For example: 1.6 mg/m3
TWA: The TWA for the exposure to a chemical can be used when both the
chemical concentration and time for exposure varies over time. It is thus used as the
average exposure to a contaminant to which workers may be exposed without adverse
effect over a period such as in an 8-hour day or 40-hour week (an average work shift).
They are usually expressed in units of ppm (volume/volume) or mg/m3.
Severity: This number is derived by dividing the exposure by the PEL, for
example: 4.8 / 1.6 = 3.0 If the severity number is higher than 1.0 you are above the
limit. If the severity number is less than 1.0 you are below the limit.
Time Weighted Average:
TLV- Threshold Limit Value
Refer to airborne concentrations of substances and represent conditions under which it is
believed that nearly all workers may be repeatedly exposed day after day without adverse
health effects.
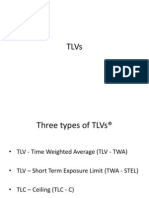
Three types of TLVs ‚
TLV-TWA Threshold Limit Value- Time Weighted Average: is the time weighted
average concentration for an average 8-10 hour day AND 40 hour workweek. ‚
TLV-STEL Threshold Limit Value- Short-Term Exposure Limit : is the concentration to
which workers can be exposed continuously for a short period of time without suffering
from irritation, chronic or irreversible damage, narcosis sufficient to increase likelihood
of injury PROVIDED that the TLV-TWA is not exceeded. It supplements the TLV-TWA
not a separate exposure limit.
TLV-C: ‚ TLV-Ceiling is the concentration that should not be exceeded during any part
of the workday. May be measured instantaneously Direct reading instrument, e.g.,
colorimetric tubes, or more often sampling over a 15 minute period.
Permissible Exposure Limits for Silica:
OSHA regulates silica exposure using the permissible exposure limit (PEL), which is
the maximum amount of airborne dust an employee may be exposed to during a full
work shift.
- % crystalline silica in the air samples (if the laboratory reports the silica
concentrations in units of mass convert the mass to percent - e.g.,
[sample weight (mg) ÷ dust weight (mg) ] × 100% ):
% quartz, % cristobalite, % tridymite
- Total weight of the dust collected in the air samples in milligrams
- Total volume of air sampled for each sample in cubic meters (1000 liters = 1 cubic
meter)
PEL Equations:
1) PEL (respirable fraction) = 10 ÷ [% quartz + (% cristobalite × 2) + (%
tridymite × 2) +2]
2) PEL (total dust) = 30 ÷ [% quartz + (% cristobalite × 2) + (% tridymite × 2) +
2]
Exposure Equation:
Exposure = [(mg/m3(1) × time(1)) + (mg/m3(2) × time(2)) + ... + (mg/m3(n) × time(n))]
÷ 480 minutes
Example:
Two consecutive samples from the same employee taken from a combined exposure
to crystalline silica dusts have the following results:
Example:
Assume that you are an industrial hygienist that has been asked to conduct air
monitoring within a cave at a national part where construction (rock drilling and
cutting)is being done. The cave is mostly granite and quartz and the concern relates to
silica exposure to the construction workers. Being the good IH that you are- you
calibrate your pump at the park office where conditions are NTP. Assume that you
have conducted sampling 1 worker and have been provided the following results from
the lab analysis. Assume that you use a nylon cyclone to collect respirable dust.
Based on the data in the table below, determine whether the worker’s exposure is
above or below the OSHA PEL for silica dust?
Parameter Value
T & P in cave T= 13 C°, P= 1 atm
Average Flow Rate
Before Sampling 1.72 L/min
After Sampling 1.64 L/min
Sampling Time 405 mins
Lunch & Breaks 65 mins
Filter Weight
Before Sampling 2.315 mg
After Sampling 2.658 mg
8.1% Quartz
Percent Silica 1.2% Tridymite
0.9% Cristobalite
You might also like
- Qatar PrometricDocument38 pagesQatar PrometricWaadAmeer100% (5)
- Nytro® Gemini X: SECTION 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/undertakingDocument20 pagesNytro® Gemini X: SECTION 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/undertakingMambak Udin100% (1)
- Hazardous Substances Continued 2021Document19 pagesHazardous Substances Continued 2021EMMANUEL BOTSHELONo ratings yet
- W4 Industrial Hygiene ULDocument51 pagesW4 Industrial Hygiene ULFakhrulShahrilEzanieNo ratings yet
- Ert 312 - Lecture 5Document43 pagesErt 312 - Lecture 5mabmi17No ratings yet
- W3 Industrial HygieneDocument42 pagesW3 Industrial HygieneThivNo ratings yet
- 0131382268Document21 pages0131382268Soon Yung WangNo ratings yet
- Particulates Not Otherwise Regulated, Total 0500: Definition: Total Aerosol Mass Cas: None Rtecs: NoneDocument6 pagesParticulates Not Otherwise Regulated, Total 0500: Definition: Total Aerosol Mass Cas: None Rtecs: NoneJaydy Carhuamaca BarzolaNo ratings yet
- W4 Industrial HygieneDocument54 pagesW4 Industrial HygieneFakhrulShahrilEzanieNo ratings yet
- 54 Strating NeedleTrapDocument11 pages54 Strating NeedleTrapP SmithNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas Plan PPDocument15 pagesNatural Gas Plan PPbaratniloy1No ratings yet
- 2.3 Workplace Environment Measurement: OSHS Rule 1071 - General ProvisionsDocument8 pages2.3 Workplace Environment Measurement: OSHS Rule 1071 - General ProvisionsMarianne BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Disinfection QuestionsDocument14 pagesDisinfection Questions166069 DavidNo ratings yet
- Results and Discussion: Table 1. Diffusivities at 50 CDocument7 pagesResults and Discussion: Table 1. Diffusivities at 50 CMichelle HutamaresNo ratings yet
- Threshold Limit Values For Chemical Substances: Adopted by ACGIH With Intended ChangesDocument18 pagesThreshold Limit Values For Chemical Substances: Adopted by ACGIH With Intended ChangesrosaNo ratings yet
- CHE135 CH2 Toxicology L2.4 UpdatedDocument28 pagesCHE135 CH2 Toxicology L2.4 UpdatedMuhammad AshmanNo ratings yet
- ELA909 Lecture1 IntroductionandFundamentalsDocument68 pagesELA909 Lecture1 IntroductionandFundamentalsXavier MartinezNo ratings yet
- Pak Waluyo - Standards-and-LimitsDocument37 pagesPak Waluyo - Standards-and-LimitsNdra NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Safety Test 1Document3 pagesSafety Test 1Abdullah AlkalaliNo ratings yet
- Metodo NIOSH 0600 Polvo Respirable PDFDocument6 pagesMetodo NIOSH 0600 Polvo Respirable PDFVane OliveraNo ratings yet
- Radiation MITDocument34 pagesRadiation MITAhmedAmer1No ratings yet
- NIOSH 0600 - Dust RespirableDocument5 pagesNIOSH 0600 - Dust RespirableArief Rachman RamadaniNo ratings yet
- Personnel Monitoring DevicesDocument63 pagesPersonnel Monitoring DevicesPramod Tike100% (1)
- (B) Industrial Hygiene May 2017Document29 pages(B) Industrial Hygiene May 2017scribideNo ratings yet
- Chlorine DeterminationDocument3 pagesChlorine DeterminationKanchanNo ratings yet
- Determination of Water Vapor (Moisture Concentration) in Natural Gas by Tunable Diode Laser Spectroscopy (TDLAS)Document7 pagesDetermination of Water Vapor (Moisture Concentration) in Natural Gas by Tunable Diode Laser Spectroscopy (TDLAS)asmaNo ratings yet
- Especificacion y Manual Equipo HCBT-01 - C-13Document86 pagesEspecificacion y Manual Equipo HCBT-01 - C-13Anthony kalevi MiravalNo ratings yet
- Extract of Circular Appended in The EndDocument33 pagesExtract of Circular Appended in The EnddaneshwerNo ratings yet
- 60 - Sensor TriggerDocument9 pages60 - Sensor TriggerP SmithNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Industrial Hygiene - FinalDocument41 pagesChapter 3 - Industrial Hygiene - FinalSatvik SaxenaNo ratings yet
- TOLUENE (Diffusive Sampler) 4000: C H CH MW: 92.14 CAS: 108-88-3 RTECS: XS5250000Document4 pagesTOLUENE (Diffusive Sampler) 4000: C H CH MW: 92.14 CAS: 108-88-3 RTECS: XS5250000VaninaNo ratings yet
- IMPCA MethanolDocument13 pagesIMPCA MethanolHito Jimenez SalinasNo ratings yet
- Exposure LimitsDocument34 pagesExposure Limitsedry_pg100% (3)
- LAB-X5000: LAB-X5000 For Analysis of Sulfur in Fuels and Petroleum ProductsDocument2 pagesLAB-X5000: LAB-X5000 For Analysis of Sulfur in Fuels and Petroleum ProductsSarbast H. SaeedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Occupational Health StandardDocument41 pagesLecture 4 Occupational Health Standardsiti zubaidahNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Monitoring Laboratory Schulte UNLDocument11 pagesAir Pollution Monitoring Laboratory Schulte UNLMira FazziraNo ratings yet
- CPE615-Lecture 8 Industrial HygieneDocument17 pagesCPE615-Lecture 8 Industrial HygieneNaufal Rafif LupikoNo ratings yet
- RSE Study Guide 2015Document41 pagesRSE Study Guide 2015phanthanhhungNo ratings yet
- Rescocast 17 MSDSDocument3 pagesRescocast 17 MSDSgroovercm15No ratings yet
- A Project Report O1Document65 pagesA Project Report O1Pratik PacharneNo ratings yet
- I Am Sharing 'Industrial Hygiene 1' With YouDocument27 pagesI Am Sharing 'Industrial Hygiene 1' With YouFAISAL DESHPANDENo ratings yet
- 835 2310Document21 pages835 2310Addin AkbarNo ratings yet
- I-131 InorganicDocument2 pagesI-131 InorganicCrizzz001No ratings yet
- TL VsDocument16 pagesTL VsSohil BakshiNo ratings yet
- Iodine 131Document5 pagesIodine 131Crizzz001No ratings yet
- Health and Safety HazardsDocument4 pagesHealth and Safety HazardsAbdullah IshaqNo ratings yet
- 01 - Process Description & Sequence of OperationDocument33 pages01 - Process Description & Sequence of OperationSayed Abo ElkhairNo ratings yet
- Appendix7 I-131Document4 pagesAppendix7 I-131Crizzz001No ratings yet
- Definitions: Parts Per Million Gases Particulates Dust Smoke Mist Molecular WeightDocument1 pageDefinitions: Parts Per Million Gases Particulates Dust Smoke Mist Molecular WeightBhuvan Ur FrndNo ratings yet
- Calculation, Discussion, Appendices, ReferencesDocument5 pagesCalculation, Discussion, Appendices, Referencespowershif solarNo ratings yet
- K2SO4 (Eng)Document8 pagesK2SO4 (Eng)Purnama HadiNo ratings yet
- Compressed Air ValidationDocument11 pagesCompressed Air Validationamit guptaNo ratings yet
- HalflivesDocument18 pagesHalflivesapi-252814424No ratings yet
- Exposure To Graphene in A Pilot Production PlantDocument8 pagesExposure To Graphene in A Pilot Production PlantDR. JunioNo ratings yet
- Taxanol PDFDocument47 pagesTaxanol PDFsriatul2006No ratings yet
- Radiello d1 d6Document6 pagesRadiello d1 d6opethmmadNo ratings yet
- Cet Aprs STP CBRN 0310 508Document13 pagesCet Aprs STP CBRN 0310 508Omar Marghani SalmaNo ratings yet
- W3 - Air Pollutants Emission MeasurementDocument35 pagesW3 - Air Pollutants Emission Measurementevolution95No ratings yet
- ENZYME ENGG: Assay of Alcohol Dehydrogenase (ADH)Document10 pagesENZYME ENGG: Assay of Alcohol Dehydrogenase (ADH)utk335No ratings yet
- ESM Andersen BrochureDocument12 pagesESM Andersen BrochureGezgin BiriNo ratings yet
- Air Quality ManagementFrom EverandAir Quality ManagementSuresh T. NesaratnamNo ratings yet
- ME Sci 11 - 12 Q3 0402 SGDocument13 pagesME Sci 11 - 12 Q3 0402 SGRonnaDhel RaraNo ratings yet
- De SizingDocument11 pagesDe SizingarafathosainNo ratings yet
- Uses of Clarified Lemon Juice As An AcidulantDocument36 pagesUses of Clarified Lemon Juice As An AcidulantAlfonso MenaNo ratings yet
- WI-TU-001 Fire Fighting and Protection SystemDocument12 pagesWI-TU-001 Fire Fighting and Protection SystemIrfan FauziNo ratings yet
- 17 Reactionsofaromaticcompounds Wade7th 140409022156 Phpapp01Document70 pages17 Reactionsofaromaticcompounds Wade7th 140409022156 Phpapp01trangNo ratings yet
- Kar 2018Document7 pagesKar 2018andrianexcelNo ratings yet
- PH of Soil Solution in Water and KCLDocument16 pagesPH of Soil Solution in Water and KCLJia Hui100% (1)
- Investigations Into Compost Tea For The Control of Plant Pathogenic FungiDocument12 pagesInvestigations Into Compost Tea For The Control of Plant Pathogenic FungiPennsylvania Association for Sustainable Agriculture100% (1)
- Air Microbiology 2018 - IswDocument26 pagesAir Microbiology 2018 - IswOktalia Suci AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- Design, Analysis and Comparison of Underground Rectangular Water Tank by Using STAAD Provi8 SoftwareDocument6 pagesDesign, Analysis and Comparison of Underground Rectangular Water Tank by Using STAAD Provi8 SoftwareNitin shepurNo ratings yet
- Box Jellyfish: Tarlac Christian CollegeDocument7 pagesBox Jellyfish: Tarlac Christian CollegeNaddie DeoreNo ratings yet
- Cos Modul 3 Engine RepairDocument22 pagesCos Modul 3 Engine RepairYUGENDRANNo ratings yet
- Three Mile Island AccidentDocument18 pagesThree Mile Island Accidentsoha89No ratings yet
- IB Physics HL - 2025 Questionbank - Thermal Energy TransfersDocument35 pagesIB Physics HL - 2025 Questionbank - Thermal Energy TransfersRahul Sharma100% (1)
- Philosophy 103Document8 pagesPhilosophy 103GS DmpsNo ratings yet
- T 53 G O 0001 00 A2 Sparing Standby PhilosophyDocument12 pagesT 53 G O 0001 00 A2 Sparing Standby PhilosophyThirukkumaranBalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- BP-HF301 Datasheet: High-Flow Back Pressure RegulatorDocument4 pagesBP-HF301 Datasheet: High-Flow Back Pressure RegulatorIdehen KelvinNo ratings yet
- Why Is The Human Visual System Sensitive 760 To 380nmDocument6 pagesWhy Is The Human Visual System Sensitive 760 To 380nmlaura nataly sierra caicedoNo ratings yet
- An Experimental Study On The Effectiveness of SodaDocument6 pagesAn Experimental Study On The Effectiveness of Sodaraye annNo ratings yet
- Dayton Close Coupled Centrifugal Pumps OIPM PDFDocument48 pagesDayton Close Coupled Centrifugal Pumps OIPM PDFstepa79No ratings yet
- 0273e Fatty Alcohol EsterDocument6 pages0273e Fatty Alcohol Esterhada33100% (1)
- Astm D5462 - 13Document6 pagesAstm D5462 - 13Ali Saleh Saad AL-isawi100% (1)
- Traditional Butter and Ghee Production, Processing and Handling in Ethiopia: A ReviewDocument11 pagesTraditional Butter and Ghee Production, Processing and Handling in Ethiopia: A ReviewAlexandra CîrsteaNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument55 pagesFinalEl Magnifico X-8No ratings yet
- Tbutyl Report PDFDocument20 pagesTbutyl Report PDFEhsan RahmanNo ratings yet
- Capillary Tube For Refrigeration and Air Conditioning SystemsDocument3 pagesCapillary Tube For Refrigeration and Air Conditioning SystemsIjazzzAliNo ratings yet
- Products Catalogue: Elastomers-NBRDocument5 pagesProducts Catalogue: Elastomers-NBRharsharanmannNo ratings yet
- Balston Nitrogen GeneratorDocument10 pagesBalston Nitrogen GeneratorNguyễn NgọcNo ratings yet