Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 viewsDiagnosis Pacemaker Failure To Capture.9
Diagnosis Pacemaker Failure To Capture.9
Uploaded by
Madina KhasanboevaThis document discusses a case of pacemaker failure to capture. It provides the background that pacemakers are used to treat various heart conditions and their use has expanded. The key findings from the 12-lead ECG shown are small pacing spikes that are not consistently associated with the heart rhythm, indicating failure of the pacemaker to stimulate the heart. The cause in this case was found to be a fracture in the pacing wire, as seen on chest x-ray.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- ECG Apib PDFDocument68 pagesECG Apib PDFArthur KakarekoNo ratings yet
- MESOTHERAPYDocument11 pagesMESOTHERAPYimec_coordinator7353100% (3)
- Cardiac Electrical Assistive DevicesDocument14 pagesCardiac Electrical Assistive DevicesaprnworldNo ratings yet
- Case Apsc 2023 - FdaDocument18 pagesCase Apsc 2023 - FdaFariz DwikyNo ratings yet
- Algo Pals TachycardiaDocument1 pageAlgo Pals TachycardiaArdie FratamaNo ratings yet
- Critical: After Cardiopulmonary Bypass: Watching For ComplicationsDocument4 pagesCritical: After Cardiopulmonary Bypass: Watching For ComplicationsLuca Stifmeister CroccoNo ratings yet
- Diapositivas Cardio Compressed 1Document36 pagesDiapositivas Cardio Compressed 1api-667225436No ratings yet
- DysrhythmiasDocument21 pagesDysrhythmiasNestleNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocument9 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Interventio N Rationale Evaluationjosh100% (1)
- NCM 118 - Lesson 11 (Arrhythmia)Document5 pagesNCM 118 - Lesson 11 (Arrhythmia)Bobby Christian DuronNo ratings yet
- Amiodarona y Tiroides - Resumen EvidenciaDocument19 pagesAmiodarona y Tiroides - Resumen EvidenciaFederico WeckesserNo ratings yet
- EJCMPR - Volume 2 - Issue 3 - Pages 165-174Document10 pagesEJCMPR - Volume 2 - Issue 3 - Pages 165-174chairulNo ratings yet
- Overdrive PacingDocument24 pagesOverdrive PacingWilliam Perero RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Circep 118 006934Document9 pagesCircep 118 006934acitri2No ratings yet
- Wa0039. 1 2Document2 pagesWa0039. 1 2IGD RSUD Kota TangerangNo ratings yet
- Wa0039.Document2 pagesWa0039.IGD RSUD Kota TangerangNo ratings yet
- Emboli ParuDocument16 pagesEmboli ParuELF RaniNo ratings yet
- (Clonidine) : Drug Class: Ates Alpha-Adrenoceptors in The Brain Stem. Blood Pressure and Pulse Rate Frequent LyDocument3 pages(Clonidine) : Drug Class: Ates Alpha-Adrenoceptors in The Brain Stem. Blood Pressure and Pulse Rate Frequent LyKrizha Angela NicolasNo ratings yet
- Nababaliw Na Ako Sa Drug StudyDocument52 pagesNababaliw Na Ako Sa Drug StudyKate Husslein ErumNo ratings yet
- Linician Pdate: Catheter Ablation of Ventricular TachycardiaDocument6 pagesLinician Pdate: Catheter Ablation of Ventricular TachycardiaSonia Rahma ANo ratings yet
- ELECTROCARDIOGRAM by Aldrin Jayson AlmadenDocument23 pagesELECTROCARDIOGRAM by Aldrin Jayson AlmadenItsMe AJNo ratings yet
- How To Perform 3 or 5 Lead Monitoring.38Document3 pagesHow To Perform 3 or 5 Lead Monitoring.38robertoNo ratings yet
- Rhythm EKG Rate (BPM) Rhythm EKG InterventionsDocument6 pagesRhythm EKG Rate (BPM) Rhythm EKG InterventionsRawabi rawabi1997No ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanMay Anne ManuzonNo ratings yet
- Standard Treatment: Guidelines 2022Document12 pagesStandard Treatment: Guidelines 2022Dr. Sarthak MishraNo ratings yet
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus Electrocardiogram (ECG)Document10 pagesPatent Ductus Arteriosus Electrocardiogram (ECG)emman_abzNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0736467906006445 PDFDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S0736467906006445 PDFDiego Fernando Escobar GarciaNo ratings yet
- Long-Term Outcome of Neonates and Infants With PJRT 2019Document5 pagesLong-Term Outcome of Neonates and Infants With PJRT 2019Võ Từ NhấtNo ratings yet
- Pals TachycardiaDocument1 pagePals TachycardiadarlingcarvajalduqueNo ratings yet
- Hejtmancik Et Al 1959 Technical Errors in ElectrocardiographyDocument4 pagesHejtmancik Et Al 1959 Technical Errors in ElectrocardiographyFernando CarrascoNo ratings yet
- G2015 Adult Tachycardia PDFDocument1 pageG2015 Adult Tachycardia PDFPlabber JuneNo ratings yet
- G2015 Adult Tachycardia PDFDocument1 pageG2015 Adult Tachycardia PDFibbs91No ratings yet
- Cardiac Tamponade: An Educational Review: Massimo Imazio and Gaetano Maria de FerrariDocument9 pagesCardiac Tamponade: An Educational Review: Massimo Imazio and Gaetano Maria de FerrariAngela OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Hs-Ahm-13-Allied Lesson Plan Advanced Cardiovascular Services 2023Document3 pagesHs-Ahm-13-Allied Lesson Plan Advanced Cardiovascular Services 2023api-688305379No ratings yet
- 5 Basic EchoDocument64 pages5 Basic Echoola adelNo ratings yet
- Pvy036 PDFDocument12 pagesPvy036 PDFHimanshu dubeyNo ratings yet
- 12 Lead EKG Interpretation Part 1Document7 pages12 Lead EKG Interpretation Part 1Nuru99100% (1)
- Cardiac Pacing For The SurgeonsDocument46 pagesCardiac Pacing For The SurgeonsRezwanul Hoque BulbulNo ratings yet
- Intern Survival Guide On Cardiology Ward and CCU - R - CardiologyDocument1 pageIntern Survival Guide On Cardiology Ward and CCU - R - Cardiologyhlau2uciNo ratings yet
- WhatsApp Infographic1 PDFDocument1 pageWhatsApp Infographic1 PDFRevanth TNo ratings yet
- 2021 - ECG - Powerpoint - Covid19 - Part 1 - SlidesDocument11 pages2021 - ECG - Powerpoint - Covid19 - Part 1 - SlidesrankotsanalegodiNo ratings yet
- Circulation: Clinical Summaries: Original Research Put Into Perspective For The Practicing ClinicianDocument3 pagesCirculation: Clinical Summaries: Original Research Put Into Perspective For The Practicing ClinicianyanNo ratings yet
- 109 FullDocument8 pages109 FullBinod KumarNo ratings yet
- Rubidium Myocardial Perfusion ScanDocument2 pagesRubidium Myocardial Perfusion ScanRadlinkSingaporeNo ratings yet
- 3 OB Intrapartum Assessment 4in1Document5 pages3 OB Intrapartum Assessment 4in1cruz.cm.sNo ratings yet
- E233078 FullDocument2 pagesE233078 FullRAHUL ROUTNo ratings yet
- Basic 12 Lead ECGDocument36 pagesBasic 12 Lead ECGjonathan69No ratings yet
- NCM 112 MSN Prelim Topic 4 Cardiac Rhythm DisordersDocument5 pagesNCM 112 MSN Prelim Topic 4 Cardiac Rhythm DisordersKim Erida QuezonNo ratings yet
- Right Approach To VTDocument7 pagesRight Approach To VTNicole BabcockNo ratings yet
- SF1-Lecture-03 - Body Fluids and Circulation - NotesDocument7 pagesSF1-Lecture-03 - Body Fluids and Circulation - Notesdisha shuklaNo ratings yet
- Fidelman Et Al 2012 The Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt An UpdateDocument17 pagesFidelman Et Al 2012 The Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt An Updateray liNo ratings yet
- The Case of Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy.6Document2 pagesThe Case of Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy.6Clinica OBNo ratings yet
- Indications and Recommendations For Pacemaker Therapy.Document8 pagesIndications and Recommendations For Pacemaker Therapy.Raul OrtegaNo ratings yet
- AJR Chest Radiography in The ICU Parte II 2012Document10 pagesAJR Chest Radiography in The ICU Parte II 2012wfranelicNo ratings yet
- VAD PercutanDocument1 pageVAD PercutanandreaNo ratings yet
- PacemakerDocument15 pagesPacemakermariet abraham100% (4)
- 273 Full PDFDocument4 pages273 Full PDFSubas SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Neurodevelopment of Empathy in HumanDocument11 pagesThe Neurodevelopment of Empathy in HumanMadina KhasanboevaNo ratings yet
- Essay AssignmentDocument2 pagesEssay AssignmentMadina KhasanboevaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive AutonomyDocument1 pageReproductive AutonomyMadina KhasanboevaNo ratings yet
- IntelligenceDocument34 pagesIntelligenceMadina KhasanboevaNo ratings yet
- Fungal Beta-Glucans As Adjuvants For Treating Cancer Patients - Revisão Sistemática de ECRDocument10 pagesFungal Beta-Glucans As Adjuvants For Treating Cancer Patients - Revisão Sistemática de ECRMaria Vitória Cota de AbreuNo ratings yet
- Clinical Guidelines in PediatricsDocument267 pagesClinical Guidelines in PediatricsDrshaukat N PanjawaniNo ratings yet
- Vitamins (Kuposhana Janya Vyadhi) FinalDocument74 pagesVitamins (Kuposhana Janya Vyadhi) FinalGuna Soundari100% (1)
- Exams MedsurgDocument29 pagesExams MedsurgUy Jezrielle MicahNo ratings yet
- AIIMS Dental PG November 2009 Solved Question Paper PDFDocument16 pagesAIIMS Dental PG November 2009 Solved Question Paper PDFDr-Amit PandeyaNo ratings yet
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Karnataka, Bangalore Proforma For Registration of Subjects For DissertationDocument9 pagesRajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Karnataka, Bangalore Proforma For Registration of Subjects For DissertationTiara Febriani NurantiNo ratings yet
- Gordons Functional Health Patterns Assessment 1Document11 pagesGordons Functional Health Patterns Assessment 1Katherine Lizell Lopez100% (1)
- 8th Seminar-Diseases of PulpDocument81 pages8th Seminar-Diseases of PulpSriya Saatwika ReddyNo ratings yet
- Under Five Clinic Visit (1) For Non CHN StudentDocument7 pagesUnder Five Clinic Visit (1) For Non CHN Studentnathsujitkr1980No ratings yet
- Cology: NCLEX® Examination Review QuestionsDocument1 pageCology: NCLEX® Examination Review QuestionsYehimyNo ratings yet
- 06 Why Did You Decide To Be A DentistDocument10 pages06 Why Did You Decide To Be A Dentistangi paola puicon ruizNo ratings yet
- A Review On Nanoparticle Based Herbal Remedies For The Management of AlopeciaDocument17 pagesA Review On Nanoparticle Based Herbal Remedies For The Management of AlopeciaVikas JhawatNo ratings yet
- Arnica ReviewDocument18 pagesArnica ReviewArunNo ratings yet
- Medical ReimbursementDocument7 pagesMedical ReimbursementHayderi GMNo ratings yet
- TT Test LabDocument2 pagesTT Test LabSamantha ReynoldsNo ratings yet
- Punjab Nursing Council GNM Record BookDocument32 pagesPunjab Nursing Council GNM Record BookMES Sanmati Group Adv. Vaishali Jain EducationNo ratings yet
- WBC DisordersDocument32 pagesWBC Disordersbpt295% (19)
- Organs of The Immune SystemDocument19 pagesOrgans of The Immune SystemprabuNo ratings yet
- PMLS Nature of Clinical Laboratory TransDocument4 pagesPMLS Nature of Clinical Laboratory TransJEUEL DYLAN DINSAYNo ratings yet
- Bipolar DisorderDocument4 pagesBipolar DisorderDeepak BamNo ratings yet
- Byu Covid Masks AbbottDocument11 pagesByu Covid Masks AbbottAlyssa RobertsNo ratings yet
- The Role of Occupational Therapy in Cardiac RehabilitationDocument35 pagesThe Role of Occupational Therapy in Cardiac Rehabilitationsdsd100% (1)
- ET Health Page-4Document1 pageET Health Page-4Kdmfuffad liNo ratings yet
- Eb Hiv March-Aidsreg2017Document6 pagesEb Hiv March-Aidsreg2017Omar Khalif Amad PendatunNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis: Bonoan, Camille Grace Chua, ManilynDocument29 pagesCholecystitis: Bonoan, Camille Grace Chua, ManilynCams BonoanNo ratings yet
- Final 2016 ResumeDocument4 pagesFinal 2016 Resumeapi-311457885No ratings yet
- Pain - SkillsDocument67 pagesPain - SkillsKim RamosNo ratings yet
- Narrative Pathophysiology of PregnancyDocument2 pagesNarrative Pathophysiology of PregnancyMarvin ChulyaoNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing Module 17Document31 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Module 17weissNo ratings yet
Diagnosis Pacemaker Failure To Capture.9
Diagnosis Pacemaker Failure To Capture.9
Uploaded by
Madina Khasanboeva0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageThis document discusses a case of pacemaker failure to capture. It provides the background that pacemakers are used to treat various heart conditions and their use has expanded. The key findings from the 12-lead ECG shown are small pacing spikes that are not consistently associated with the heart rhythm, indicating failure of the pacemaker to stimulate the heart. The cause in this case was found to be a fracture in the pacing wire, as seen on chest x-ray.
Original Description:
Original Title
Diagnosis Pacemaker Failure to Capture.9
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses a case of pacemaker failure to capture. It provides the background that pacemakers are used to treat various heart conditions and their use has expanded. The key findings from the 12-lead ECG shown are small pacing spikes that are not consistently associated with the heart rhythm, indicating failure of the pacemaker to stimulate the heart. The cause in this case was found to be a fracture in the pacing wire, as seen on chest x-ray.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageDiagnosis Pacemaker Failure To Capture.9
Diagnosis Pacemaker Failure To Capture.9
Uploaded by
Madina KhasanboevaThis document discusses a case of pacemaker failure to capture. It provides the background that pacemakers are used to treat various heart conditions and their use has expanded. The key findings from the 12-lead ECG shown are small pacing spikes that are not consistently associated with the heart rhythm, indicating failure of the pacemaker to stimulate the heart. The cause in this case was found to be a fracture in the pacing wire, as seen on chest x-ray.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
January 2007 ■ EMN 11
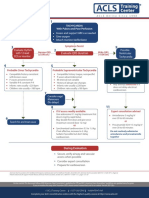
Cases in Diagnosis: Pacemaker Failure to Capture
Electrocardiography
Continued from p. 8
By Theodore Chan, MD,
William Brady, MD, &
Richard Harrigan, MD
T he 12-lead ECG demonstrates atrial
fibrillation with a narrow QRS com-
plex rhythm at a rate of 55 beats/minute
with intermittent irregularity. More
importantly, there are small pacer spikes
seen throughout the 12-lead ECG that
have no clear or consistent association
with the QRS complexes. (Fig. 2: circles.)
This finding, along with the fact that her
rate is bradycardic and below most pro-
grammed pacing thresholds is consistent
with pacemaker failure to capture.
Implantable cardiac pacemakers
were first used to prevent Adams-Stokes Figure 2. Initial 12-lead ECG. Note the low amplitude pacing spikes (circles) with no consistent capture or association with
Downloaded from http://journals.lww.com/em-news by BhDMf5ePHKav1zEoum1tQfN4a+kJLhEZgbsIHo4XMi0hCywCX1AWnYQp/IlQrHD3i3D0OdRyi7TvSFl4Cf3VC1y0abggQZXdgGj2MwlZLeI= on 12/22/2021
attacks. Since then, indications for pace- ventricular activity.
makers have grown remarkably and now
include atrioventricular (AV) node and to slow the rate with carotid massage or
sinus node dysfunction, hypersensitive adenosine can be helpful, but should be
carotid sinus syndrome and neurally- performed with extreme caution in the
mediated syncope (vasovagal syncope), pacemaker patient. Finally, if routine
prevention of tachycardia with long QT evaluation yields no abnormalities, the
syndrome, hypertrophic cardiomyopa- pacemaker should be interrogated.
thy, certain cases of congestive heart fail- The cause of this patient’s pacemaker
ure, and prevention of atrial fibrillation. malfunction and failure to capture were
(Circulation 1998;97:1325.) Advances in seen on the chest radiograph, which
technology, expanding indications, and demonstrated a fracture in the pacing
the aging population ensure that EPs will wire. (Fig. 3: circle.) This wire fracture not
encounter more patients with cardiac only caused the failure to capture, but also
pacemakers on a regular basis. failure to sense native ventricular activity
A five-position code has been devel- as well as some aspect of failure to pace
oped to describe pacemakers. (Pacing with low amplitude pacer spikes. The
Clin Electrophysiol 1993;16:1776.) Posi- patient was admitted to the electrophysi-
tion I indicates the chambers being ology service, at which time the fractured
paced, atrium (A), ventricle (V), both (D, right ventricular pacing lead as well as
Figure 3. Chest radiograph demonstrating implantable pacemaker with fractured
dual), or none (0). Position II gives the pacemaker generator were replaced. After
lead (circle).
location where the pacemaker senses
native cardiac electrical activity (A, V, D, left ventricle, resulting in a right
or O). Position III indicates the pacemak- bundle branch block pattern).
er’s response to sensing: triggering (T), (Emerg Med Clinics NA
inhibition (I), both (D), or none (O). Posi- 2006;24[1]:179.) Because of the
tion IV indicates the programmability of abnormal ventricular depolariza-
the pacemaker and the capability to adap- tion seen in paced rhythms,
tively control rate; position V identifies repolarization also occurs abnor-
the presence of antitachydysrhythmia mally, and ST segments and T
functions. Pacemakers are commonly waves should typically be discor-
classified to the first three position codes. dant with the QRS complex.
Most patients will have a card in their (Acad Emerg Med 1998;5:52.)
wallet identifying the make and model of Pacemaker malfunction
pacemaker. Manufacturers also place an includes failure to pace, failure
identification number in the generator to capture, undersensing, and Figure 4. Repeat 12-lead ECG after replacement of fractured pacing wire and generator. Note
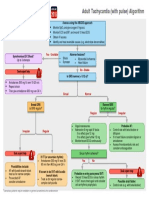
that is sometimes visible on chest x-ray. pacemaker-mediated dysrhyth- the higher amplitude ventricular pacing spikes. There is sensing of native ventricular activity
The most commonly encountered mias. Failure to pace occurs (thin arrow), as well as normal pacing with good ventricular capture (wide arrow).
pacer is the DDD pacemaker, where when the pacemaker does not
both the atria and the ventricles are fire when pacing should occur. On the a pacemaker fails to sense or detect native the procedure, the patient’s symptoms
sensed and either paced or inhibited ECG, there are no visible pacing spikes cardiac activity. Pacing spikes will be seen resolved. A follow-up12-lead ECG demon-
depending on the native cardiac activity where they should have occurred. Caus- when none should occur. strates normal ventricular pacing. (Fig. 4.)
sensed. VVI pacing is useful in those es include oversensing, pacing lead Patients with pacemaker malfunction
with chronically ineffective atria, such problems (dislodgement or fracture), often have vague and nonspecific symp- Dr. Chan is a professor of clinical med-
as chronic atrial fibrillation or atrial flut- battery or component failure, and elec- toms. Beyond the 12-lead ECG, cautious icine and the medical director of emer-
ter. In this mode, the ventricle is sensed tromagnetic interference. use of a magnet can assist in evaluating gency medicine at the University of
and paced. If the native ventricular activ- Failure to capture occurs when a pac- pacer function. For example, if there is California, San Diego School of Medi-
ity is sensed, then pacing is inhibited. ing stimulus is generated, but fails to trig- no pacemaker activity on the ECG, plac- cine. Dr. Harrigan is an associate pro-
Because the ventricular pacing lead is ger myocardial depolarization. On the ing a magnet over the pacer will switch fessor of emergency medicine at Temple
placed in the right ventricle, the ventricles ECG, failure to capture is identified by the the pacemaker to asynchronous pacing University School of Medicine in
depolarize from right to left rather than by presence of pacing spikes without associ- and allow for assessment of capture. Philadelphia. Dr. Brady is a professor
the regular conduction system, producing ated myocardial depolarization. Causes Appropriate experience with this diag- of emergency medicine and internal
an overall QRS morphology similar to a left include pacing lead problems, battery or nostic approach is urged prior to its use, medicine and the vice chairman of
bundle branch block with QRS interval component failure, low pacing voltage or however. Similarly, if the patient’s native emergency medicine at the University
prolongation (occasionally, intracardiac elevated myocardial pacing thresholds, cardiac rhythm is above the lower rate of Virginia School of Medicine in
pacemaker leads may be placed over the and exit block. Undersensing occurs when threshold for pacing, cautious attempts Charlottesville.
You might also like
- ECG Apib PDFDocument68 pagesECG Apib PDFArthur KakarekoNo ratings yet
- MESOTHERAPYDocument11 pagesMESOTHERAPYimec_coordinator7353100% (3)
- Cardiac Electrical Assistive DevicesDocument14 pagesCardiac Electrical Assistive DevicesaprnworldNo ratings yet
- Case Apsc 2023 - FdaDocument18 pagesCase Apsc 2023 - FdaFariz DwikyNo ratings yet
- Algo Pals TachycardiaDocument1 pageAlgo Pals TachycardiaArdie FratamaNo ratings yet
- Critical: After Cardiopulmonary Bypass: Watching For ComplicationsDocument4 pagesCritical: After Cardiopulmonary Bypass: Watching For ComplicationsLuca Stifmeister CroccoNo ratings yet
- Diapositivas Cardio Compressed 1Document36 pagesDiapositivas Cardio Compressed 1api-667225436No ratings yet
- DysrhythmiasDocument21 pagesDysrhythmiasNestleNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocument9 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Interventio N Rationale Evaluationjosh100% (1)
- NCM 118 - Lesson 11 (Arrhythmia)Document5 pagesNCM 118 - Lesson 11 (Arrhythmia)Bobby Christian DuronNo ratings yet
- Amiodarona y Tiroides - Resumen EvidenciaDocument19 pagesAmiodarona y Tiroides - Resumen EvidenciaFederico WeckesserNo ratings yet
- EJCMPR - Volume 2 - Issue 3 - Pages 165-174Document10 pagesEJCMPR - Volume 2 - Issue 3 - Pages 165-174chairulNo ratings yet
- Overdrive PacingDocument24 pagesOverdrive PacingWilliam Perero RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Circep 118 006934Document9 pagesCircep 118 006934acitri2No ratings yet
- Wa0039. 1 2Document2 pagesWa0039. 1 2IGD RSUD Kota TangerangNo ratings yet
- Wa0039.Document2 pagesWa0039.IGD RSUD Kota TangerangNo ratings yet
- Emboli ParuDocument16 pagesEmboli ParuELF RaniNo ratings yet
- (Clonidine) : Drug Class: Ates Alpha-Adrenoceptors in The Brain Stem. Blood Pressure and Pulse Rate Frequent LyDocument3 pages(Clonidine) : Drug Class: Ates Alpha-Adrenoceptors in The Brain Stem. Blood Pressure and Pulse Rate Frequent LyKrizha Angela NicolasNo ratings yet
- Nababaliw Na Ako Sa Drug StudyDocument52 pagesNababaliw Na Ako Sa Drug StudyKate Husslein ErumNo ratings yet
- Linician Pdate: Catheter Ablation of Ventricular TachycardiaDocument6 pagesLinician Pdate: Catheter Ablation of Ventricular TachycardiaSonia Rahma ANo ratings yet
- ELECTROCARDIOGRAM by Aldrin Jayson AlmadenDocument23 pagesELECTROCARDIOGRAM by Aldrin Jayson AlmadenItsMe AJNo ratings yet
- How To Perform 3 or 5 Lead Monitoring.38Document3 pagesHow To Perform 3 or 5 Lead Monitoring.38robertoNo ratings yet
- Rhythm EKG Rate (BPM) Rhythm EKG InterventionsDocument6 pagesRhythm EKG Rate (BPM) Rhythm EKG InterventionsRawabi rawabi1997No ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanMay Anne ManuzonNo ratings yet
- Standard Treatment: Guidelines 2022Document12 pagesStandard Treatment: Guidelines 2022Dr. Sarthak MishraNo ratings yet
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus Electrocardiogram (ECG)Document10 pagesPatent Ductus Arteriosus Electrocardiogram (ECG)emman_abzNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0736467906006445 PDFDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S0736467906006445 PDFDiego Fernando Escobar GarciaNo ratings yet
- Long-Term Outcome of Neonates and Infants With PJRT 2019Document5 pagesLong-Term Outcome of Neonates and Infants With PJRT 2019Võ Từ NhấtNo ratings yet
- Pals TachycardiaDocument1 pagePals TachycardiadarlingcarvajalduqueNo ratings yet
- Hejtmancik Et Al 1959 Technical Errors in ElectrocardiographyDocument4 pagesHejtmancik Et Al 1959 Technical Errors in ElectrocardiographyFernando CarrascoNo ratings yet
- G2015 Adult Tachycardia PDFDocument1 pageG2015 Adult Tachycardia PDFPlabber JuneNo ratings yet
- G2015 Adult Tachycardia PDFDocument1 pageG2015 Adult Tachycardia PDFibbs91No ratings yet
- Cardiac Tamponade: An Educational Review: Massimo Imazio and Gaetano Maria de FerrariDocument9 pagesCardiac Tamponade: An Educational Review: Massimo Imazio and Gaetano Maria de FerrariAngela OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Hs-Ahm-13-Allied Lesson Plan Advanced Cardiovascular Services 2023Document3 pagesHs-Ahm-13-Allied Lesson Plan Advanced Cardiovascular Services 2023api-688305379No ratings yet
- 5 Basic EchoDocument64 pages5 Basic Echoola adelNo ratings yet
- Pvy036 PDFDocument12 pagesPvy036 PDFHimanshu dubeyNo ratings yet
- 12 Lead EKG Interpretation Part 1Document7 pages12 Lead EKG Interpretation Part 1Nuru99100% (1)
- Cardiac Pacing For The SurgeonsDocument46 pagesCardiac Pacing For The SurgeonsRezwanul Hoque BulbulNo ratings yet
- Intern Survival Guide On Cardiology Ward and CCU - R - CardiologyDocument1 pageIntern Survival Guide On Cardiology Ward and CCU - R - Cardiologyhlau2uciNo ratings yet
- WhatsApp Infographic1 PDFDocument1 pageWhatsApp Infographic1 PDFRevanth TNo ratings yet
- 2021 - ECG - Powerpoint - Covid19 - Part 1 - SlidesDocument11 pages2021 - ECG - Powerpoint - Covid19 - Part 1 - SlidesrankotsanalegodiNo ratings yet
- Circulation: Clinical Summaries: Original Research Put Into Perspective For The Practicing ClinicianDocument3 pagesCirculation: Clinical Summaries: Original Research Put Into Perspective For The Practicing ClinicianyanNo ratings yet
- 109 FullDocument8 pages109 FullBinod KumarNo ratings yet
- Rubidium Myocardial Perfusion ScanDocument2 pagesRubidium Myocardial Perfusion ScanRadlinkSingaporeNo ratings yet
- 3 OB Intrapartum Assessment 4in1Document5 pages3 OB Intrapartum Assessment 4in1cruz.cm.sNo ratings yet
- E233078 FullDocument2 pagesE233078 FullRAHUL ROUTNo ratings yet
- Basic 12 Lead ECGDocument36 pagesBasic 12 Lead ECGjonathan69No ratings yet
- NCM 112 MSN Prelim Topic 4 Cardiac Rhythm DisordersDocument5 pagesNCM 112 MSN Prelim Topic 4 Cardiac Rhythm DisordersKim Erida QuezonNo ratings yet
- Right Approach To VTDocument7 pagesRight Approach To VTNicole BabcockNo ratings yet
- SF1-Lecture-03 - Body Fluids and Circulation - NotesDocument7 pagesSF1-Lecture-03 - Body Fluids and Circulation - Notesdisha shuklaNo ratings yet
- Fidelman Et Al 2012 The Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt An UpdateDocument17 pagesFidelman Et Al 2012 The Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt An Updateray liNo ratings yet
- The Case of Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy.6Document2 pagesThe Case of Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy.6Clinica OBNo ratings yet
- Indications and Recommendations For Pacemaker Therapy.Document8 pagesIndications and Recommendations For Pacemaker Therapy.Raul OrtegaNo ratings yet
- AJR Chest Radiography in The ICU Parte II 2012Document10 pagesAJR Chest Radiography in The ICU Parte II 2012wfranelicNo ratings yet
- VAD PercutanDocument1 pageVAD PercutanandreaNo ratings yet
- PacemakerDocument15 pagesPacemakermariet abraham100% (4)
- 273 Full PDFDocument4 pages273 Full PDFSubas SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Neurodevelopment of Empathy in HumanDocument11 pagesThe Neurodevelopment of Empathy in HumanMadina KhasanboevaNo ratings yet
- Essay AssignmentDocument2 pagesEssay AssignmentMadina KhasanboevaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive AutonomyDocument1 pageReproductive AutonomyMadina KhasanboevaNo ratings yet
- IntelligenceDocument34 pagesIntelligenceMadina KhasanboevaNo ratings yet
- Fungal Beta-Glucans As Adjuvants For Treating Cancer Patients - Revisão Sistemática de ECRDocument10 pagesFungal Beta-Glucans As Adjuvants For Treating Cancer Patients - Revisão Sistemática de ECRMaria Vitória Cota de AbreuNo ratings yet
- Clinical Guidelines in PediatricsDocument267 pagesClinical Guidelines in PediatricsDrshaukat N PanjawaniNo ratings yet
- Vitamins (Kuposhana Janya Vyadhi) FinalDocument74 pagesVitamins (Kuposhana Janya Vyadhi) FinalGuna Soundari100% (1)
- Exams MedsurgDocument29 pagesExams MedsurgUy Jezrielle MicahNo ratings yet
- AIIMS Dental PG November 2009 Solved Question Paper PDFDocument16 pagesAIIMS Dental PG November 2009 Solved Question Paper PDFDr-Amit PandeyaNo ratings yet
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Karnataka, Bangalore Proforma For Registration of Subjects For DissertationDocument9 pagesRajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Karnataka, Bangalore Proforma For Registration of Subjects For DissertationTiara Febriani NurantiNo ratings yet
- Gordons Functional Health Patterns Assessment 1Document11 pagesGordons Functional Health Patterns Assessment 1Katherine Lizell Lopez100% (1)
- 8th Seminar-Diseases of PulpDocument81 pages8th Seminar-Diseases of PulpSriya Saatwika ReddyNo ratings yet
- Under Five Clinic Visit (1) For Non CHN StudentDocument7 pagesUnder Five Clinic Visit (1) For Non CHN Studentnathsujitkr1980No ratings yet
- Cology: NCLEX® Examination Review QuestionsDocument1 pageCology: NCLEX® Examination Review QuestionsYehimyNo ratings yet
- 06 Why Did You Decide To Be A DentistDocument10 pages06 Why Did You Decide To Be A Dentistangi paola puicon ruizNo ratings yet
- A Review On Nanoparticle Based Herbal Remedies For The Management of AlopeciaDocument17 pagesA Review On Nanoparticle Based Herbal Remedies For The Management of AlopeciaVikas JhawatNo ratings yet
- Arnica ReviewDocument18 pagesArnica ReviewArunNo ratings yet
- Medical ReimbursementDocument7 pagesMedical ReimbursementHayderi GMNo ratings yet
- TT Test LabDocument2 pagesTT Test LabSamantha ReynoldsNo ratings yet
- Punjab Nursing Council GNM Record BookDocument32 pagesPunjab Nursing Council GNM Record BookMES Sanmati Group Adv. Vaishali Jain EducationNo ratings yet
- WBC DisordersDocument32 pagesWBC Disordersbpt295% (19)
- Organs of The Immune SystemDocument19 pagesOrgans of The Immune SystemprabuNo ratings yet
- PMLS Nature of Clinical Laboratory TransDocument4 pagesPMLS Nature of Clinical Laboratory TransJEUEL DYLAN DINSAYNo ratings yet
- Bipolar DisorderDocument4 pagesBipolar DisorderDeepak BamNo ratings yet
- Byu Covid Masks AbbottDocument11 pagesByu Covid Masks AbbottAlyssa RobertsNo ratings yet
- The Role of Occupational Therapy in Cardiac RehabilitationDocument35 pagesThe Role of Occupational Therapy in Cardiac Rehabilitationsdsd100% (1)
- ET Health Page-4Document1 pageET Health Page-4Kdmfuffad liNo ratings yet
- Eb Hiv March-Aidsreg2017Document6 pagesEb Hiv March-Aidsreg2017Omar Khalif Amad PendatunNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis: Bonoan, Camille Grace Chua, ManilynDocument29 pagesCholecystitis: Bonoan, Camille Grace Chua, ManilynCams BonoanNo ratings yet
- Final 2016 ResumeDocument4 pagesFinal 2016 Resumeapi-311457885No ratings yet
- Pain - SkillsDocument67 pagesPain - SkillsKim RamosNo ratings yet
- Narrative Pathophysiology of PregnancyDocument2 pagesNarrative Pathophysiology of PregnancyMarvin ChulyaoNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing Module 17Document31 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Module 17weissNo ratings yet